The Complete Guide to Caffeine Supplements
☕ Caffeine: A Comprehensive Scientific Guide to Caffeine Supplements – Roles, Sources, Benefits, and Usage in Bodybuilding and Health
✅ Did you know that a small caffeine capsule can boost your energy, focus, and workout performance more effectively than any energy drink? Caffeine isn’t just a simple stimulant—it’s one of the few supplements officially approved by the ISSN and IOC, and hundreds of scientific studies have confirmed its effects on strength, fat-burning, and endurance.
✔️ But here’s the important part:
Caffeine in supplement form works very differently from the caffeine in coffee or tea.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll cover everything—from the exact dosage and best timing to side effects, real benefits, and evidence-based research—so you can decide whether this supplement is right for you.
Caffeine Supplement
Pelank Supplement ©
✅ Introduction and Overview
✔️ Caffeine is one of the most well-known natural stimulants in the world, naturally found in coffee beans, tea leaves, cocoa, and certain energizing plants. But caffeine supplements offer a purer, more precise, and more controlled form of this compound, typically produced as tablets, capsules, powders, or anhydrous caffeine.
✅ At specific doses, this supplement can significantly boost your energy levels, focus, fat-burning, and athletic performance—without needing to consume large amounts of coffee or energy drinks.

✅ Why is it one of the most popular sports supplements in the world?
🔰 Caffeine has been at the top of the list of the most popular sports supplements for years—but its popularity isn’t just about “more energy.”
🟢 The main reasons behind its worldwide popularity include:
1️⃣ Increased power and energy before workouts
2️⃣ Reduced fatigue and improved training endurance
3️⃣ Enhanced fat-burning and metabolism
4️⃣ Better focus and neuromuscular reaction
5️⃣ Fast, predictable effects
6️⃣ Low cost and easy accessibility
✅ The massive amount of scientific evidence (hundreds of studies) has also made caffeine one of the most trusted and reliable sports supplements—not just another “marketing hype” product.
✅ Its Position Among Ergogenic Aids
Ergogenic Supplements
🔰 Ergogenic aids are supplements that directly enhance athletic performance.
💠 Two major global organizations:
✔️ ISSN – International Society of Sports Nutrition
✔️ IOC – International Olympic Committee
🟢 Both classify caffeine as an approved ergogenic supplement.
🔹 This means:
✔️ Its effectiveness has been proven across numerous studies
✔️ It is safe and reliable for athletes
✔️ It enhances performance in endurance running, HIIT, weightlifting, team sports, and strength training
✔️ It is permitted in official competitions (unlike ephedrine and stronger stimulants)
✅ Caffeine has long been one of the top recommendations by sports nutrition experts for performance enhancement.
✅ The Difference Between Supplemental Caffeine and Natural Caffeine
🔰 Although both come from the same compound, there are important differences between the caffeine found in coffee/tea and supplemental caffeine:
1️⃣ Precise, controllable dosage
🔹 Coffee can contain anywhere from 30 to 250 mg of caffeine.
🔹 Supplements, however, typically deliver a precise 100–200 mg per serving.
2️⃣ Faster and stronger effect
Anhydrous caffeine is absorbed more quickly and produces a more potent effect.
3️⃣ No interfering compounds
💠 Coffee contains:
🔹 Acids
🔹 Antioxidants
🔹 Bitter compounds
✔️ But caffeine supplements are pure and free from additional compounds that may affect absorption or tolerance.
4️⃣ Ideal for professional athletes
🔹 In competitive sports, precise and consistent dosing matters.
That’s why caffeine supplements are a top choice for athletes, cyclists, bodybuilders, and runners.
What is a caffeine supplement?
Supplement Overview
✅ Scientific Definition
🟢 A caffeine supplement is a pure, precise, and standardized form of caffeine, most commonly produced as caffeine anhydrous.
💠 Compared to the natural caffeine found in coffee or tea, this form:
1️⃣ Has a stronger potency
2️⃣ Is absorbed more quickly
3️⃣ Provides a fully accurate and controlled dosage
✅ For these reasons, professional athletes, bodybuilders, active individuals, and anyone seeking steady energy and focus typically prefer caffeine supplements over caffeinated beverages.
✔️ Caffeine anhydrous is produced through a specialized extraction and drying process that removes nearly all moisture, resulting in a highly stable, potent, and measurable compound.

✅ Available Forms of Caffeine Supplements on the Market
🟢 Caffeine supplements come in various forms depending on the desired absorption speed and training goals:
1️⃣ Pills
✔️ The most common and precise form
✔️ Typically available in 100, 150, 200, and 300 mg doses
✔️ Steady absorption with predictable effects
2️⃣ Capsules
✔️ Similar to pills but often absorbed faster
✔️ Ideal for pre-workout
✔️ Popular among bodybuilders
3️⃣ Anhydrous Caffeine Powder
✔️ The purest and most potent form of caffeine
✔️ Must be measured with a milligram-scale
✔️ Commonly used in pre-workout formulas
✔️ Suitable for professional athletes or those needing custom dosages
4️⃣ Liquid Caffeine
✔️ Ultra-fast absorption
✔️ Great for those who want to feel the effects 15–20 minutes before training
✔️ Found in energy shots and performance ampoules
5️⃣ Caffeine Gels & Gum
✔️ Absorbed through the mouth (buccal absorption)
✔️ Ideal for endurance athletes like runners and cyclists
✔️ Very fast-acting, perfect for competitions
💠 Each form has its own absorption rate and advantages, and the best choice depends on your training goals, activity intensity, and individual sensitivity.
✅ Production Standards, Purity, and Laboratory Testing
🟢 To guarantee purity, quality, and safety, reputable caffeine supplements must carry globally recognized certifications. The most important ones include:
1️⃣ NSF Certified for Sport
🔰 This certification ensures that the product:
✔️ Contains no banned substances
✔️ Delivers an accurate and truthful caffeine dose
✔️ Has been tested in accredited laboratories
✔️ Is essential for professional and competitive athletes
2️⃣ Informed Sport
🔰 One of the world’s most trusted standards for sports supplements. In this program:
✔️ Every batch is tested
✔️ No prohibited substances are present
✔️ The product is safe for use in international competitions
3️⃣ Purity Standards & GMP (Good Manufacturing Practice)
✔️ Ensures production-line quality
✔️ Prevents cross-contamination
✔️ Guarantees consistent dosage in every pill or capsule
✔️ Uses validated and controlled raw materials
4️⃣ Reputable Independent Laboratories
🔰 Many professional manufacturers rely on independent testing labs such as:
✔️ Labdoor
✔️ Eurofins
✔️ BSCG
✔️ USP Verified
✅ These certifications significantly increase user and athlete confidence in the product’s true dosage and purity.
✅ Short Summary
🟢 A caffeine supplement is a pure, controlled, and highly potent form of caffeine available in various formats such as pills, capsules, powders, and liquids.
🟢 When sourced from reputable brands with certifications like NSF and Informed Sport, it becomes one of the safest and most effective supplements for boosting energy, strength, focus, and athletic performance.
Types of Caffeine Supplements
🔰 Caffeine supplements come in several different forms, each with its own absorption speed, effectiveness, and specific use. Choosing the right form can significantly enhance the impact of caffeine.
🔹 Below, we’ll examine each form individually:
✅ Caffeine Anhydrous | The Most Potent Form of Caffeine
👑 Caffeine anhydrous is the purest, most stable, and most potent form of caffeine.
🟢 This is the form used in pills, capsules, and most pre-workout formulas.
🔰 Absorption Speed
✔️ Very fast; effects begin within 20–30 minutes
🔰 Peak Effect:
45–60 minutes
🔰 Performance Difference
✔️ Stronger stimulant effect compared to coffee
✔️ Fully precise and predictable dosage
✔️ The best option for intense training sessions
🔰 Advantages
✔️ High purity
✔️ Fast-acting
✔️ Ideal for professional athletes
✔️ Precise dosage control
🔰 Disadvantages
❌ May cause anxiety in sensitive individuals
❌ Requires careful dosing

✅ Caffeine Capsules
🟢 Capsules are one of the most popular forms of caffeine supplements.
🔰 Absorption Speed
✔️ Fast (especially if the capsule is gelatin-based)
🔰 Onset of Effect:
✔️ 20–35 minutes
🔰 Effectiveness
✔️ Consistent and stable
✔️ Ideal for pre-workout use
🔰 Advantages
✔️ Easy to swallow
✔️ Accurate dosage (100–200 mg)
✔️ Affordable
🔰 Disadvantages
❌ May absorb slightly slower in individuals with digestive issues
✅ Caffeine Powder
🟢 This form is usually pure caffeine anhydrous.
🔰 Absorption Speed
✔️ The fastest form after liquid caffeine
🔰 Peak Effect:
✔️ 20–30 minutes
🔰 Effectiveness
✔️ Allows full control over custom dosing
✔️ Excellent for making homemade pre-workout blends
🔰 Advantages
✔️ High purity
✔️ Very cost-effective
✔️ Suitable for professional athletes
🔰 Disadvantages
❌ High risk of incorrect dosing
❌ Requires a milligram-scale
❌ Improper use can be dangerous
✅ Liquid Caffeine / Energy Shots
🟢 This form is sold in energy shots or small liquid vials.
🔰 Absorption Speed
✔️ Extremely fast (15–20 minutes)
✔️ Ideal when you have very little time before your workout
🔰 Effectiveness
✔️ The best option for an instant pre-workout boost
✔️ Suitable for competitions
🔰 Advantages
✔️ Ultra-fast absorption
✔️ Portable and easy to use
🔰 Disadvantages
❌ More expensive
❌ Some products contain sugar or additives
✅ Caffeine in Pre-Workout Supplements
🟢 Most professional pre-workout formulas contain between 150 and 350 mg of caffeine.
🔰 Absorption Speed
✔️ Fast, due to being combined with other stimulants
🔰 Effectiveness
✔️ Provides the strongest boost in energy and focus
✔️ Ideal for high-intensity strength training
🔰 Advantages
✔️ Synergistic effects (bicarbonate, beta-alanine, L-tyrosine, etc.)
✔️ Increases strength, pump, focus, and endurance
🔰 Disadvantages
❌ Possible post-workout “energy crash”
❌ May be too strong for beginners
✅ Chewable Forms: Chewables / Gum / Strips
🟢 This form is designed for endurance athletes.
🔰 Absorption Speed
✔️ The fastest absorption among all forms
✔️ Absorbed through the mouth’s mucosal membrane (buccal absorption)
🔰 Onset of Effect:
✔️ 5–10 minutes
🔰 Effectiveness
✔️ Excellent for races and situations where an immediate effect is needed
🔰 Advantages
✔️ Extremely fast absorption
✔️ Lightweight, compact, and easy to carry during running/cycling
✔️ No need for water or swallowing
🔰 Disadvantages
❌ Lower dosage
❌ Shorter duration of effect compared to pills and powders
✅ Final Comparison of Different Caffeine Forms
Form | Absorption Speed | Effect Strength | Best For | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Anhydrous | Fast | Very strong | Bodybuilding, HIIT | Accurate and standardized | Sensitivity in certain individuals |
Capsule | Fast | Strong | General athletes | Easy, accurate | Slight delay in some individuals |
Powder | Very fast | Very strong | Professionals | Cheap, pure | Risk of incorrect dosing |
Liquid | Very fast | Moderate–strong | Instant pre-workout | Fast-acting | More expensive |
Pre-workout | Fast | Very strong | Heavy training | Synergistic effect | Possible crash |
Gum / Strips | Ultra-fast | Moderate | Endurance competitions | Immediate effect | Short duration |
Mechanism of Action of Caffeine Supplements
🔰 Caffeine supplements act through several physiological and neuromuscular pathways. These combined effects significantly enhance athletic performance, anaerobic power, focus, and fat-burning.
🔹 Below, we’ll examine the most important mechanisms in a precise and scientific way:
✅ Effect on Adenosine Receptors
Adenosine Receptor Antagonism
🟢 Caffeine is a competitive antagonist of the adenosine A1 and A2A receptors.
🟩 What does adenosine do?
1️⃣ Reduces neuronal activity
2️⃣ Creates the feeling of fatigue
3️⃣ Lowers motivation and focus
4️⃣ Decreases muscular excitability
🟩 What does caffeine do?
✔️ Binds to adenosine receptors in place of adenosine
✔️ Blocks adenosine from attaching
✔️ Prevents the brain from receiving “fatigue signals”
🟩 Result:
✔️ Reduced perception of fatigue
✔️ Increased focus
✔️ Greater motivation
✔️ Longer and more intense training sessions
✅ This mechanism is the fundamental basis of caffeine’s stimulant effect.
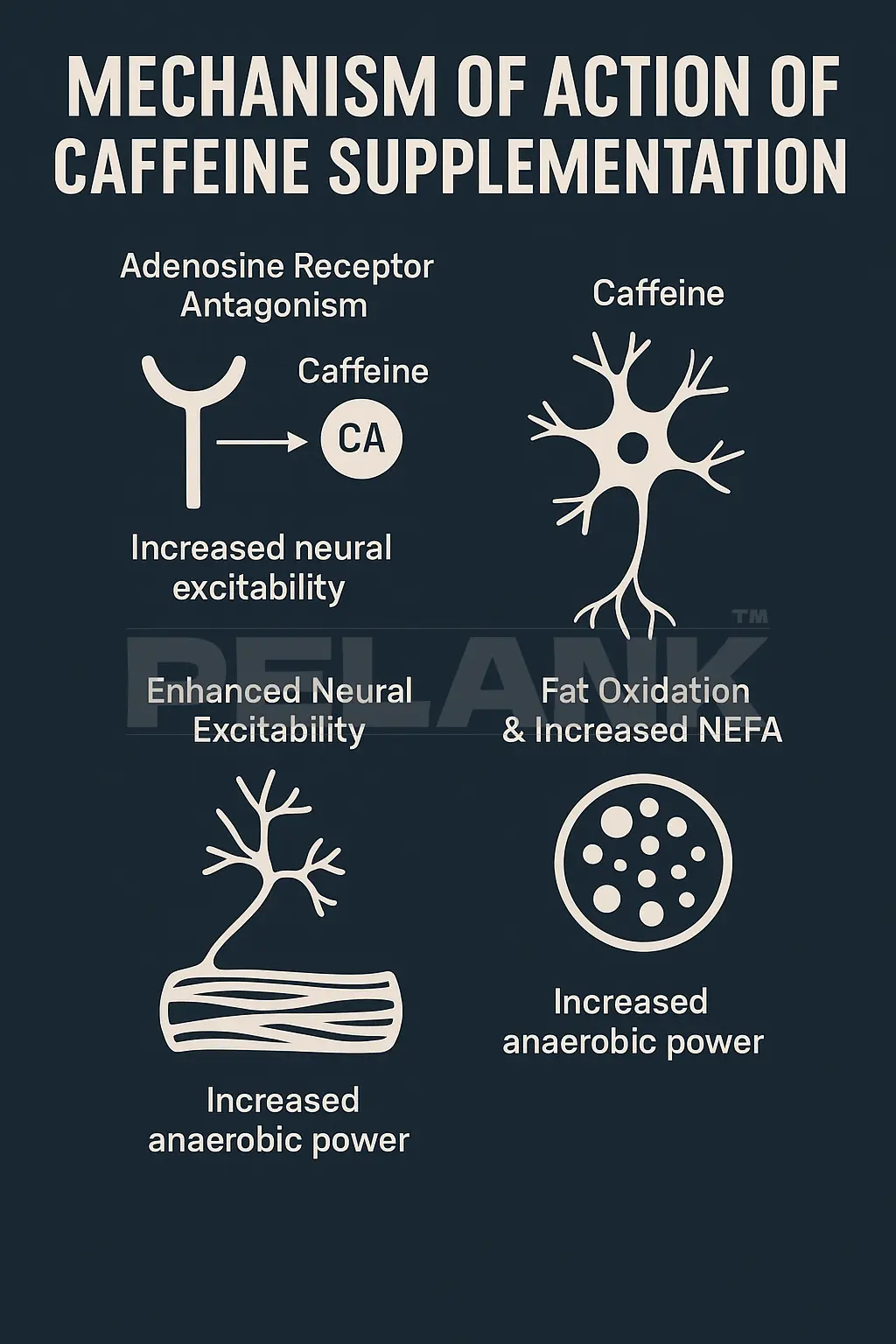
✅ Increased Neural Excitability
🟢 When adenosine receptors are blocked, the central nervous system (CNS) shifts into a state of heightened alertness.
🟩 Effects on the nervous system:
✔️ Increased dopamine release
✔️ Increased norepinephrine
✔️ Greater activation in the motor cortex
✔️ Faster neuronal firing rates toward muscles
🟩 Result:
✔️ Faster reaction time
✔️ Improved focus during training
✔️ Enhanced neuromuscular coordination
✔️ Increased instantaneous power output (neuromuscular power)
✅ This is exactly what athletes feel at the start of a workout or during a heavy set.
✅ Effect on the muscles
Calcium Release / EC Coupling
🟢 Caffeine acts directly on the muscle itself—not just the brain.
🟩 How?
🔰 Caffeine affects the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR), causing:
✔️ Increased release of calcium ions (Ca²⁺)
✔️ From the SR reservoir into the muscle fiber
🟩 Why is this important?
✔️ Muscle contraction occurs only when calcium is released.
🟩 So increased calcium release means:
✔️ Stronger contractions
✔️ Greater power
✔️ Faster force production
✔️ Improved excitation–contraction coupling
✅ This is the direct effect of caffeine on strength and anaerobic power.
✅ Effect on Fat Oxidation and NEFA Release
🟢 Caffeine enhances fat-burning by activating the sympathetic system and increasing catecholamines.
🟩 Main effects:
✔️ Increased epinephrine and norepinephrine
✔️ Increased lipolysis
✔️ Increased release of free fatty acids (NEFA) from adipose tissue
✔️ Increased fat oxidation in the mitochondria
🟩 Result:
✔️ More fat enters the bloodstream
✔️ The body burns more fat during exercise
✔️ Especially effective in aerobic training, HIIT, and fasted training
✅ This is why caffeine is considered one of the best fat oxidation enhancers in sports supplements.
✅ Increased anaerobic power
Anaerobic Power Boost
🟢 In addition to its effects on the CNS and muscles, caffeine also enhances anaerobic energy systems.
🟩 How?
✔️ Increases ATP turnover
✔️ Increases activation of fast-twitch motor units (Type II fibers)
✔️ Reduces RPE (perceived exertion)
✔️ Increases instantaneous power output
🟩 Result:
✔️ Stronger jumps
✔️ Faster sprints
✔️ Heavier reps in weightlifting
✔️ Better performance in anaerobic movements
🟩 This effect is especially noticeable in:
✔️ HIIT, CrossFit, sprinting, and strength bodybuilding.
🎯 Scientific summary of the mechanisms
✅ Caffeine supplements act through four simultaneous pathways:
✔️ Brain → Adenosine blockade → Reduced fatigue
✔️ CNS → Increased excitability → Greater focus and strength
✔️ Muscle → Increased calcium release → Stronger contractions
✔️ Metabolism → Increased NEFA → Higher fat oxidation
✔️ Anaerobic power → Increased power output
✅ This is why it is one of the most powerful ergogenic supplements in the world.
Benefits of Caffeine Supplements for Sports
Performance Benefits
🔰 Caffeine is one of the few supplements whose effects are validated by the ISSN, IOC, ACSM, and WADA. More than 300 studies show that caffeine can significantly enhance athletic performance across all domains—from endurance to strength and fat-burning.
🔹 Below, we’ll break down each benefit individually and scientifically:
✅ Endurance Performance
🔰 Caffeine is one of the most effective supplements for aerobic and long-duration activities.
⚡ Blocking adenosine receptors reduces central fatigue.
🔹 It increases VO₂max, improves running economy, and boosts TTE (time to exhaustion).
🟢 Enhanced fat oxidation helps spare glycogen, allowing you to maintain activity for longer.
🔍 Studies consistently show a 2–4% improvement in endurance performance.

✅ Increased muscle strength
🔰 Caffeine increases strength through both central nervous system stimulation and direct effects on muscle fibers.
💥 Increased neural drive to the muscles → faster and stronger neuronal firing to motor units.
🟩 Increased calcium release from the SR → stronger and more efficient contractions.
🔰 Its effect on Type II (fast-twitch) fibers enhances maximal power movements.
🔍 On average, studies show a 3–5% increase in 1RM strength.
✅ Increased anaerobic power
Sprint / HIIT
🔰 Caffeine has exceptionally strong effects on short-duration, high-intensity activities.
⚡ Increases peak power and mean power in anaerobic tests like the Wingate.
🚀 More effective activation of fast-twitch motor units → ideal for sprints, jumps, and HIIT.
🟢 Reduces fatigue during explosive sets.
🔍 Studies show a 6–12% increase in anaerobic power output.
✅ Increased focus and reduced mental fatigue
🔰 Caffeine directly affects the cerebral cortex.
🧠 Blocking adenosine in the CNS increases alertness, attention, and focus.
⚡ Improves reaction time in speed-based sports and activities requiring quick decision-making.
🔹 Reduces mental fatigue during long sessions such as cycling and distance running.
✔️ Result: better training quality, faster decision-making, and higher precision in movements.
✅ Improved performance in heavy training sessions
High-Intensity Training
🔰 Caffeine is one of the few supplements that helps maintain performance even in the final sets.
💥 Increases force production in strength movements.
🟢 Reduces performance drop-off between sets in intense training.
🔹 Increases the number of reps and overall training quality.
✔️ Result: high-intensity training with less fatigue and better quality.
✅ Increased fat burning
Fat Oxidation
🔰 Caffeine is a strong stimulant for the lipolysis process.
🔥 Increases the release of catecholamines (epinephrine and norepinephrine).
🟩 Increases NEFA (free fatty acids) in the bloodstream.
🔰 Increases fat oxidation, especially during aerobic and fasted training.
⚡ Raises resting metabolic rate (RMR).
🔍 Studies show a 10–29% increase in fat oxidation.
✅ Reduced RPE
Perceived difficulty of exercise
🔰 One of the most interesting benefits of caffeine is its ability to reduce RPE.
🟢 The perceived difficulty of exercise decreases without any reduction in actual performance capacity.
⚡ This allows the individual to maintain higher intensity for a longer duration.
💪 Result: longer activity, greater intensity, and better output in each set.
🔍 This effect is directly linked to adenosine blockade and increased neural excitability.
🎯 Final summary of benefits
🟢 Increased endurance and aerobic capacity
💥 Enhanced muscle strength
🚀 Increased anaerobic power
🧠 Greater focus and reduced mental fatigue
🏋️ Better performance in heavy training
🔥 Increased fat burning and lipolysis
⚡ Lower RPE (less perceived effort)
✅ This is why caffeine is listed among the most powerful approved ergogenic aids.
The best scientifically proven caffeine dosages
Scientifically Optimal Dosages
🔰 The appropriate caffeine dosage depends on body weight, training goals, experience level, gender, form of intake, and timing.
🔬 The ISSN and hundreds of reputable PubMed studies have outlined the following precise protocols.
✅ ISSN athletic protocol
Global standard dosage
🧪 ISSN (International Society of Sports Nutrition) provides the best and most reliable dosing protocol:
✔️ Standard dose: 3–6 mg/kg
✔️ Meaning: 3 to 6 mg of caffeine per kilogram of body weight
✔️ Timing: 60 to 30 minutes before training
🕒 This timing aligns perfectly with caffeine’s absorption peak (45–60 minutes).

✅ Low doses and their applications
Low Doses: 1–2 mg/kg
🔰 This dosage is suitable for beginners or individuals who are sensitive to caffeine.
🟢 Benefits:
✔️ Reduced jitteriness, anxiety, and elevated heart rate
✔️ Suitable for light, endurance, or long-duration workouts
✔️ Appropriate for evening use without disrupting sleep
🔥 Quick applications: aerobic training, brisk walking, light cycling, fasted training.
✅ High doses and their risks
High Doses: 9 mg/kg
🔰 A dose of 9 mg/kg is one of the highest levels ever recorded in research.
⚠️ Warning: This dose is used only in laboratory settings and only for professional athletes.
❌ Possible side effects:
🔹 Increased heart rate
🔹 Tremors
🔹 Anxiety
🔹 Severe insomnia
🔹 Digestive issues
🔹 Nausea
⚠️ Performance can actually decrease due to excessive stimulation.
🔴 This dosage is absolutely not recommended for general use.
✅ Body weight based dosage chart
Dose by Weight Table
✅ Below are the 3, 4, 5, and 6 mg/kg dosages calculated for all common body weights.
🟦 Dosage table (mg) based on body weight according to the ISSN protocol
🟢 Practical note:
Most caffeine pills on the market are 200 mg or 300 mg → meaning that for most people weighing 60 to 90 kg, a single 200–300 mg pill covers the standard dose.
Body weight (kg) | Dose 3 mg/kg | Dose 4 mg/kg | Dose 5 mg/kg | Dose 6 mg/kg |
|---|---|---|---|---|
50 kg | 150 mg | 200 mg | 250 mg | 300 mg |
55 kg | 165 mg | 220 mg | 275 mg | 330 mg |
60 kg | 180 mg | 240 mg | 300 mg | 360 mg |
65 kg | 195 mg | 260 mg | 325 mg | 390 mg |
70 kg | 210 mg | 280 mg | 350 mg | 420 mg |
75 kg | 225 mg | 300 mg | 375 mg | 450 mg |
80 kg | 240 mg | 320 mg | 400 mg | 480 mg |
85 kg | 255 mg | 340 mg | 425 mg | 510 mg |
90 kg | 270 mg | 360 mg | 450 mg | 540 mg |
100 kg | 300 mg | 400 mg | 500 mg | 600 mg |
110 kg | 330 mg | 440 mg | 550 mg | 660 mg |
✅ Caffeine dosage for women based on the hormonal cycle
🟢 Estrogen and progesterone influence the rate of caffeine metabolism.
🔹 Follicular phase (early cycle to ovulation):
🟢 Faster metabolism → higher caffeine tolerance
✔️ Recommended dose: 3–5 mg/kg
🔹 Luteal phase (post-ovulation to period):
🔰 Slower metabolism
🔴 Greater sensitivity to caffeine
✔️ Recommended dose: 1–3 mg/kg
🔹 Pregnancy & breastfeeding:
⚠️ Only very low doses (maximum 200 mg per day) and strictly with medical approval.
✅ Dosage for teenagers and young athletes
🔰 Teenagers’ bodies are more sensitive to stimulants.
🟨 Recommended dose for ages 12–18:
✔️ 1–3 mg/kg
❌ Higher doses are not recommended under any circumstances.
⚠️ Especially for high-intensity sports, use should be supervised by a professional coach.
✅ Best timing for each form
Timing by Supplement Form
🔰 Each form of caffeine has a different absorption speed:
✔️ Pill / Capsule
🕒 Onset: 30–45 minutes
🔹 Best timing: 45 minutes before training
✔️ Anhydrous Powder
🕒 Fast absorption
🔹 Best timing: 20–30 minutes before
✔️ Liquid / Energy Shot
⚡ Immediate effect
🔹 Best timing: 10–15 minutes before
✔️ Gum and Strips
🚀 Very fast buccal absorption
🔹 Best timing: 5–10 minutes before
🔰 The best option for running competitions and team sports requiring instant effect.
🎯 Final scientific summary of caffeine dosing
🟢 Standard ISSN dose → 3–6 mg/kg
⚡ Best timing → 30–60 minutes before training
🟡 Low doses → suitable for sensitive individuals
🔴 High doses → high risk, not recommended
🟣 Women → dosage varies by cycle phase
🟢 Teenagers → only 1–3 mg/kg
🚀 Best instant form → gum / strips
🔵 Best steady form → pills, capsules
Absorption Speed and Differences Between Caffeine Forms
🟢 The absorption speed and intensity of caffeine’s effects depend on the supplement form, purity level, digestive conditions, and timing. Different forms of caffeine show clear differences in bioavailability, onset of action, and plasma concentration peak.
✅ Why is anhydrous caffeine faster and stronger?
Caffeine Anhydrous
🔰 Anhydrous caffeine is the purest form of caffeine—free of moisture, plant fibers, and the additional compounds found in coffee.
⚡ This purity leads to:
🟢 Faster absorption in the small intestine
💥 A more rapid spike in blood concentration
🔰 A shorter, stronger peak effect
⚡ A more intense stimulant impact on the CNS
🔍 Research shows that caffeine anhydrous produces 25–30% stronger neural stimulation compared to the caffeine found in coffee.

✅ Pills vs Powder vs Liquid
Complete comparison of the forms
⭐ Comparison table of different caffeine forms
Caffeine form | Onset of action | Peak effect | Intensity of effect | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Caffeine Anhydrous – Pills/Capsules | ⏱ 30–45 minutes | ⏫ 45–60 minutes | 💥 Strong | Precise dosage, stable effect, strong neural stimulation |
Powder (Anhydrous Powder) | ⏱ 20–30 minutes | ⏫ 40–50 minutes | ⚡ Very strong | Faster absorption due to better solubility |
Liquid / Energy Shot | ⚡ 10–15 minutes | 🔺 25–35 minutes | 🔥 Moderate–strong | Great for immediate pre-workout; fast absorption |
Gum / Strips | 🚀 5–10 minutes | ⏫ 20–30 minutes | ⚡ Immediate | Buccal absorption through the mouth; best for competition |
Natural coffee | ⏱ 30–60 minutes | 🔺 60–90 minutes | 🟡 Moderate | Slower absorption due to the presence of other plant compounds |
✅ Bioavailability
✅ Bioavailability refers to how much of the consumed caffeine actually enters the bloodstream.
🟢 Caffeine has very high bioavailability, around 99–100%.
🔰 However, the speed of entry varies by form:
💥 Anhydrous → fastest
⚡ Liquid → moderate with immediate onset
🟡 Coffee/Cocoa → slower due to plant compounds
🚀 Gum → direct entry through the mouth → fast but shorter-lasting
✅ Peak Concentration
🔰 Peak effect is the time when caffeine concentration in the blood reaches its maximum.
⚡ Caffeine Anhydrous → 45–60 minutes
🚀 Gum / Strips → 20–30 minutes
🔺 Liquid → 25–35 minutes
🟡 Coffee → 60–90 minutes
✔️ The faster the peak, the faster the surge in energy and focus.
✅ Difference in absorption on an empty stomach vs. a full stomach
🍽 1️⃣ Taken on an empty stomach
⚡ Faster onset (10–20 minutes earlier)
💥 Stronger peak effect
🔰 Ideal for pre-workout
❌ But in sensitive individuals, may cause nausea or heart palpitations.
🍔 2️⃣ Taken after a meal / full stomach
🟡 Slower onset
🔹 Milder peak effect
✔ Suitable for people prone to anxiety or jitters
🔵 Good for evening training to reduce the risk of a crash
🎯 Summary
🟢 Caffeine Anhydrous → fastest, strongest, most predictable
🚀 Gum → fastest onset
⚡ Liquid → instant-option
🟡 Coffee → slower but steadier
🍽 Empty stomach → faster effect
🍔 Full stomach → milder effect
Effects of Caffeine Supplements on Fat Burning
🔰 Caffeine is one of the few supplements approved by both the ISSN and the IOC for fat burning. Its effect is not just about increasing energy; it directly activates the metabolic pathways involved in fat breakdown.
✅ Lipolysis Mechanism
Caffeine increases fat burning through three primary mechanisms:
1️⃣ Adenosine receptor inhibition → increased norepinephrine
🔹 This stimulates the sympathetic nervous system.
🔹 Result: initiation of lipolysis in fat cells.
2️⃣ Activation of HSL (Hormone-Sensitive Lipase)
🔥 This enzyme is the key factor responsible for releasing fatty acids (FFA/NEFA) from fat cells.
Caffeine → norepinephrine ↑ → HSL ↑ → fat breakdown increases.
3️⃣ Increased thermogenesis
Caffeine raises the body’s heat production:
🟠 Thermogenesis ↑ → higher energy expenditure → increased fat burning.
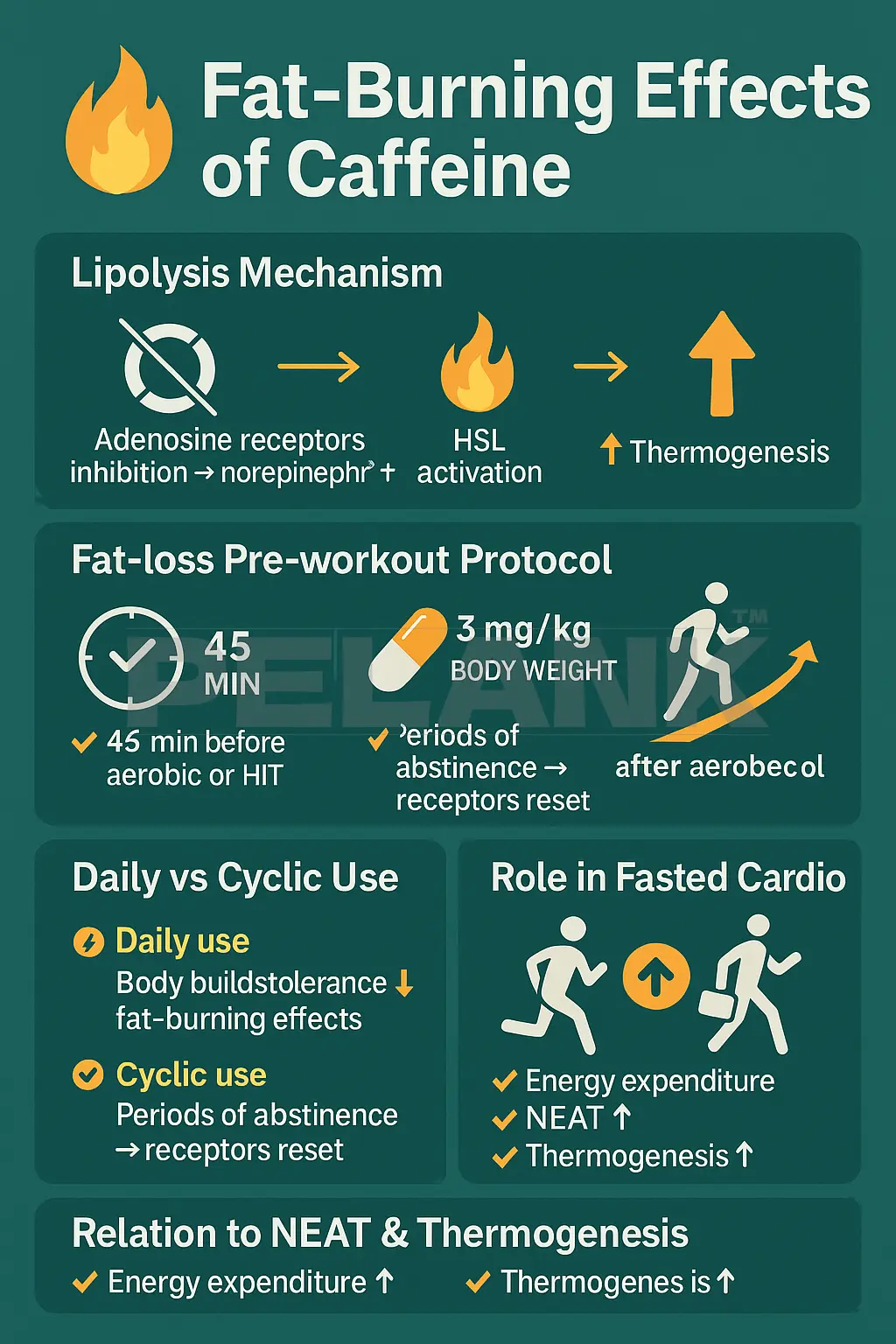
✅ Pre-workout fat-burning protocol
The best pre-workout fat-burning protocol according to PubMed:
🟢 3 mg/kg body weight
🕒 45 minutes before training
🏃 Preferably aerobic exercise or HIIT
✔️ This dose increases NEFA, enhances fat oxidation, and reduces RPE.
✅ Difference between daily use and cyclical use
Daily vs Cyclic Use
⚡ Daily use
🟡 The body develops tolerance within 10–14 days.
This means adenosine receptors become less sensitive → fat-burning effects decrease.
🔥 Cyclic use
The best method for consistent fat loss:
2–4 weeks of use
1 week off
Repeat
🔵 This pattern allows the receptors to reset and restores the fat-burning effect.
✅ The role of caffeine in fasted cardio
Fasted Cardio
Fasted training with caffeine is one of the most powerful fat-burning protocols.
✔️ Empty stomach → low insulin
✔️ Low insulin → greater release of fatty acids
✔️ Caffeine → stimulates HSL and increases norepinephrine
✔️ Result:
🔥 At least a 28–30% increase in fat oxidation compared to the fed state
(this number is based on multiple reputable studies)
🔺 Warning: may cause elevated heart rate or nausea in sensitive individuals.
✅ Relationship with NEAT and thermogenesis
NEAT = calories burned from non-exercise daily movements (walking, fidgeting, etc.)
🎯 Caffeine increases NEAT because:
Energy and alertness ↑
Daily activity ↑
Lethargy ↓
According to research:
🟢 Caffeine can increase NEAT by about 10–15%.
🔥 Fat-burning summary
✔️ Caffeine directly activates lipolysis
✔️ Best fat-burning dose: 3 mg/kg before training
✔️ Cyclic use delivers the best results
✔️ Highly effective during fasted cardio
✔️ Increases thermogenesis and NEAT
✔️ One of the strongest natural fat burners in the world
Side Effects of Caffeine Supplements
🔰 Caffeine is one of the safest and most well-studied supplements, but dosage, timing, and individual sensitivity play major roles in the likelihood of side effects. In general, caffeine’s side effects are dose-dependent—meaning the higher the dose, the greater the chance of experiencing them.
✅ Dose-Dependent Effects
🟢 1–3 mg/kg:
Minimal side effects → suitable for sensitive individuals and evening training.
🟠 3–6 mg/kg:
Standard athletic dose → mild anxiety or elevated heart rate may occur in sensitive people.
🔴 6–9 mg/kg:
High likelihood of moderate to severe side effects → generally not recommended.

✅ Anxiety and restlessness
🔰 Caffeine increases sympathetic nervous system activity:
⚡ Norepinephrine ↑
⚡ Adrenaline ↑
🟩 For this reason, some individuals may experience:
🔝 Anxiety
🔝 Restlessness
🔝 Nervous heart palpitations
🔝 Sensory sensitivity
These effects are more common at doses above 3–4 mg/kg.
✅ Increased heart rate
Tachycardia
🔰 Caffeine increases heart rate by stimulating the beta-adrenergic receptors.
✔️ Healthy individuals → generally no significant issues
⚠️ People with heart conditions → should only use it under medical supervision
✅ Insomnia or reduced sleep quality
🟩 Caffeine has a relatively long half-life:
⏱ 5 to 7 hours (half-life)
⚠️ This means if you take 200 mg at 5 PM, around 100 mg is still active in your system by 10 PM.
❌ Consuming it after 3–4 PM lowers sleep quality for most people.
✅ Tremors
🔰 At higher doses, increased stimulation of the nervous system can cause:
🔹 Hand tremors
🔹 Muscle restlessness
🔹 A feeling of being “overstimulated”
🔺 More common in individuals who are lightweight or sensitive to stimulants.
✅ Dehydration
🔰 Caffeine has a mild diuretic effect.
✔️ Its impact is much lower than what was previously believed.
❗ However, at high doses + intense training, you should definitely increase your water intake.
✅ Dependence, tolerance, and habituation
Tolerance
🔰 Tolerance:
🟩 After 10–14 days of continuous use, the body reduces the sensitivity of adenosine receptors.
🔵 Result:
🔸 Reduced effect
🔸 Less energy
🔸 Need for a higher dose
🔵 Psychological dependence:
🔸 Due to its mild dopamine-enhancing effect, some people develop a daily craving for it.
🔵 Solutions:
🔸 Cyclical use (2–4 weeks on / 1 week off)
🔸 Gradual dose reduction
✅ Caffeine toxicity
🟢 Caffeine toxicity is very rare, but at extremely high doses, it can be dangerous.
⚠️ Symptoms of caffeine toxicity:
🔴 Nausea and vomiting
🔴 Severe restlessness
🔴 Irregular heartbeat
🔴 Intense anxiety
🔴 Elevated blood pressure
🔴 Uncontrolled tremors
🔴 Several hours of insomnia
🔴 In severe cases: seizures
⚠️ Toxic and lethal doses (LD50):
🔰 LD50 in humans:
🔻 Approximately 150–200 mg/kg
(For example, for a 70 kg person → around 12,000–14,000 mg)
⚠️ However, actual death can occur at lower doses if the individual has underlying health conditions.
⛔ Extremely dangerous doses:
⚠️ More than 10 mg/kg → severe side effects
⚠️ 40 mg/kg or higher → hospitalization likely
⚠️ 100+ mg/kg → potentially fatal
✅ Treatment of caffeine toxicity:
🏥 In hospital care:
✅ Gastric lavage (stomach wash)
✅ Activated charcoal
✅ Intravenous fluids
✅ Heart rhythm monitoring
✅ Benzodiazepines to control seizures
✅ Continuous 24-hour medical supervision
🎯 Summary of side effects
🔹 Caffeine side effects depend on dose and individual sensitivity
🔹 Standard doses are generally safe
🔹 Insomnia, tremors, anxiety, and tachycardia are the most common side effects
🔹 Tolerance develops with long-term use
🔹 Caffeine toxicity is rare but serious, especially at doses above 10 mg/kg
🔹 Conscious consumption and proper timing → a very safe and effective supplement
Who should not take caffeine supplements ?
🔰 Although caffeine is safe for most people, certain medical conditions or medications can make its use dangerous or prohibited. In these individuals, even standard doses can cause severe side effects.
✅ Patients with heart disease or irregular heart rhythm
Arrhythmia / Heart Disease
❌ Caffeine increases heart rate and blood pressure.
🔸 Arrhythmia
🔸 Tachycardia
🔸 PVC and PAC
🔸 Heart failure
These conditions can worsen with caffeine consumption.
🔴 Recommendation: only use with a cardiologist’s approval.

✅ Individuals with chronic anxiety or panic attacks
Anxiety / Panic Disorder
⚠️ Caffeine activates the sympathetic nervous system and can cause:
🔸 Increased anxiety
🔸 Restlessness
🔸 Panic attacks
🔸 Nervous palpitations
🔴 Individuals with GAD, Panic Disorder, or OCD → should use very low doses or avoid it entirely.
✅ Pregnant and breastfeeding women
⛔ Caffeine crosses the placenta and affects the fetus.
🔸 Low birth weight
🔸 Increased risk of miscarriage
🔸 Elevated fetal heart rate
🔺 Global recommended limits:
✔️ Pregnant women: less than 200 mg per day
✔️ Breastfeeding: up to 200 mg, spaced appropriately from feeding
❌ High-dose supplements (300–400 mg) are not recommended.
✅ Individuals with sleep disorders
Insomnia / Poor Sleep Quality
⏳ Caffeine has a half-life of 5–7 hours.
For these individuals, it can worsen:
🔸 Light sleep
🔸 Nighttime awakenings
🔸 Increased cortisol
🔸 Chronic sleep deprivation
🔴 Recommendation: consume before noon or avoid high-dose supplements.
✅ Individuals with high blood pressure
Hypertension
⚠️ Caffeine temporarily increases:
🔝 Systolic blood pressure
🔝 Diastolic blood pressure
🔝 Heart rate
🔺 Individuals with Stage 1 and Stage 2 hypertension should be cautious.
❗ In some patients, an increase of 8–10 mmHg has been reported.
✅ Dangerous drug interactions
🔰 Caffeine has serious interactions with certain medications and can unexpectedly increase the levels of either the drug or caffeine in the blood.
🔸 Drugs that interact with caffeine:
1️⃣ SSRIs (antidepressants)
Examples:
🔹 Fluoxetine
🔹 Sertraline
🔹 Paroxetine
🟡 Can increase caffeine levels in the blood.
2️⃣ MAOIs (older and very dangerous)
Examples: Phenelzine, Tranylcypromine
🔴 Can cause severe increases in blood pressure.
3️⃣ Anxiolytics / sedatives
Examples:
🔹 Benzodiazepines
🔹 Zolpidem
❗ Caffeine can counteract the calming effects of these drugs.
4️⃣ Certain antibiotics (Ciprofloxacin / Norfloxacin)
🚫 These drugs inhibit liver enzymes that break down caffeine → caffeine becomes 2–4 times stronger.
5️⃣ Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs)
💥 Can increase heart rate, anxiety, and blood pressure.
6️⃣ Theophylline and asthma medications
Caffeine is structurally similar to theophylline → strong interaction → increased heart rate and nausea.
🎯 Definitive summary of this section
The following individuals should avoid caffeine or only use it under medical supervision:
❌ Patients with heart disease
❌ Individuals with anxiety or panic disorders
❌ Pregnant and breastfeeding women
❌ People with sleep disorders
❌ Individuals with high blood pressure
❌ People taking medications such as MAOIs, SSRIs, antibiotics, antidepressants, or asthma medications
Adaptation and tolerance of the body to caffeine
🟢 One of the most important limitations of caffeine is that the body develops tolerance over time.
This means that with the same previous dose, the effects become weaker:
⚡ Less energy
⚡ Reduced focus
⚡ Lower fat-burning effects
⚡ Need for a higher dose
Caffeine tolerance is a neuro-receptor phenomenon and is fully reversible.
✅ Why do the effects of caffeine decrease over time?
Mechanism of Tolerance
1️⃣ Upregulation of Adenosine Receptors (A1 & A2A)
When caffeine is consumed continuously, the body compensates for adenosine blockade by:
🔹 Increasing the number of adenosine receptors.
This means:
✔ Less effect from caffeine
✔ More sleepiness
✔ Lower baseline energy
2️⃣ Reduced Neural Sensitivity
Caffeine constantly activates the sympathetic nervous system.
To maintain balance, the body:
⚠ Reduces neural sensitivity → caffeine efficiency ↓
3️⃣ Reduced Response to Norepinephrine and Dopamine
Chronic caffeine use can:
🔸 Decrease β-adrenergic response
🔸 Decrease dopaminergic response
This means the “energy + focus” effects diminish over time.
4️⃣ Increased Caffeine Metabolism (CYP1A2 Enzyme Activity)
With daily use, the liver becomes more efficient at breaking down caffeine.
Result:
⏱ Shorter duration of effect
💥 Lower intensity of effect
Conclusion:
The body fully learns how to counteract caffeine’s effects. But…
Good news:
🔵 Caffeine tolerance is fully reversible and can be reset using scientific protocols.

✅ Best method to reduce tolerance
Caffeine Reset
✅ 7-Day Caffeine Reset Protocol
Suitable for: individuals with moderate tolerance
Days 1–2:
🟡 Reduce intake to 50% of usual amount
Example: from 300 mg → 150 mg
Days 3–5:
⚪ Only 50–100 mg if really needed
Days 6–7:
🔵 Complete caffeine abstinence (no coffee or energy drinks)
✔ Result:
Most adenosine receptors reset, and caffeine’s effects return to baseline.
✅ 14-Day Full Tolerance Reset Protocol
Suitable for: individuals consuming 300–600 mg daily or long-term users
Days 1–2:
⬇️ Reduce to 1–2 mg/kg
Days 3–7:
⬇️ Reduce to 50 mg or less
Days 8–14:
❌ Complete abstinence
🔥 Best protocol for fully restoring neurological and metabolic effects of caffeine.
✅ Microcycling (3–4 Day Cycles)
🔰 A favorite strategy among professional athletes to prevent tolerance.
🟩 Pattern:
🟢 2–3 days of use → 1–2 days off
🟢 Or: 5 days of use → 2 days off (e.g., Saturday–Thursday use, Friday–Saturday off)
✔ The body never has a chance to upregulate adenosine receptors.
✔ Caffeine effects remain strong and consistent.
🎯 Recommended Protocol for Pelank Athletes
🟢 If your goal is fat burning, focus, and high performance:
🔥 5 days of use + 2 days off
(The most globally recommended pattern)
Or
🔥 Caffeine Reset every 6–8 weeks → 7 days
These two methods ensure that caffeine’s effects never weaken.
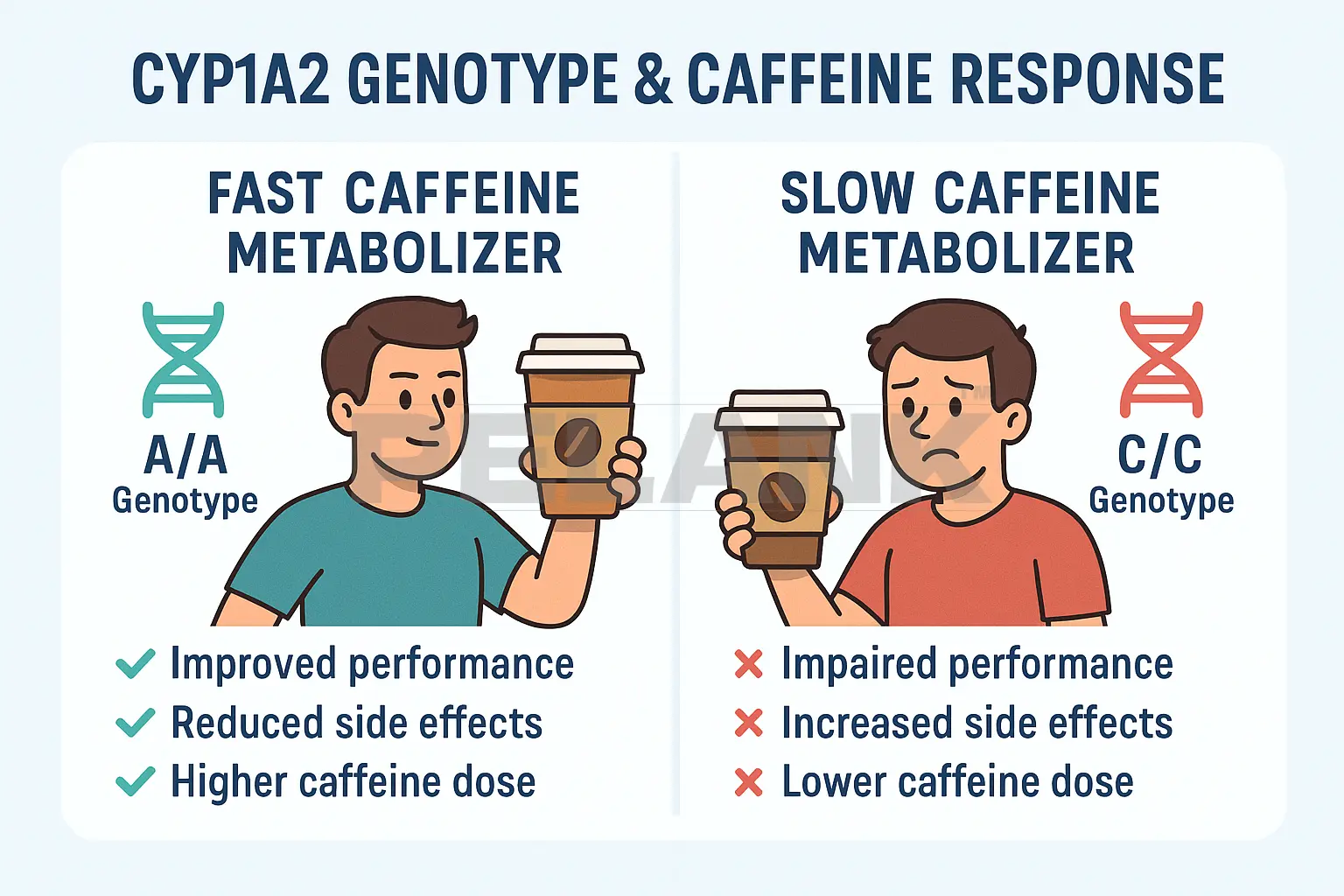
Caffeine and Genetics
CYP1A2 Genotype & Caffeine Response
🔰 The body’s response to caffeine depends not only on dose and timing but also on the CYP1A2 gene, which governs caffeine metabolism in the liver. This determines who responds better or worse to caffeine.
✔️ This factor has become highly relevant in sports science and is even considered in the US Olympic Committee and Elite Athletes Genomic Profiles.
✅ Fast vs. Slow Metabolizers
Fast Metabolizer vs Slow Metabolizer
🟢 The CYP1A2 gene has three main patterns:
1️⃣ Fast Metabolizer — those who metabolize caffeine quickly (A/A Genotype)
🔹 Caffeine is metabolized rapidly
🔹 Shorter but stronger peak effects
🔹 Fewer side effects (anxiety, increased heart rate, insomnia)
🔹 Caffeine tolerance develops more slowly
🔴 These individuals perform better in sports with caffeine.
📌 Research shows:
A/A individuals consuming 3–6 mg/kg in endurance sports improved performance by 5–8%.
2️⃣ Slow Metabolizer — those who metabolize caffeine slowly (C/C Genotype)
🔹 Caffeine is metabolized slowly
🔹 Longer-lasting effects (sometimes up to 8 hours)
🔹 Higher likelihood of side effects
🔹 Common issues: insomnia, anxiety, tachycardia
🔹 Caffeine tolerance develops faster
🔴 These individuals may experience worse performance with caffeine.
📌 According to Guest et al., 2018:
C/C individuals consuming 3–4 mg/kg had decreased performance and excessively high heart rates.
3️⃣ Intermediate Metabolizer — moderate group (A/C Genotype)
🔹 Intermediate response
🔹 Effects are neither too fast nor too slow
🔹 Sports performance improves with moderate doses
Recommendation: consuming 2–3 mg/kg is optimal.
✅ Individuals who perform better with caffeine
✔️ Athletes with A/A genotype (Fast metabolizers)
✔️ Those engaging in aerobic and HIIT activities
✔️ Individuals with low sensitivity to stimulants
🔹 These individuals benefit the most from doses of 3–6 mg/kg.
✅ Individuals whose performance worsens with caffeine
❌ Individuals with C/C genotype (Slow metabolizers)
❌ Those experiencing anxiety, tachycardia, or insomnia
❌ Individuals sensitive to stimulants
🔰 In this group:
🔸 Excessive heart rate
🔸 Anxiety
🔸 Reduced endurance
🔸 Decreased performance after peak effect
All are likely.
✅ Should caffeine dosage be adjusted based on genetics?
Yes, absolutely
🔰 This is what professional sports call Precision Nutrition.
🔵 Genetics-based dosing recommendations:
🟢 A/A — Fast metabolizer
✔️ Optimal dose: 3–6 mg/kg
✔️ Even 7–8 mg/kg is well tolerated in some professional athletes
🟡 A/C — Intermediate
✔️ Optimal dose: 2–3 mg/kg
✔️ Higher doses → possible anxiety + reduced focus
🔴 C/C — Slow metabolizer
✔️ Optimal dose: 1–2 mg/kg
✔️ Higher doses → decreased performance
✔️ Gum form is more suitable (fast effect + short duration)
🎯 Summary of the Genetics (CYP1A2) Section
✅ The CYP1A2 gene determines how quickly caffeine is metabolized
✅ A/A = excellent response to caffeine
✅ C/C = higher risk of poor performance and side effects
✅ Dosage should be adjusted based on genetics
✅ Professional sports (CrossFit, Endurance, HIIT) use this data
Comparison of Caffeine with Other Supplement Stimulants
🔰 Stimulants each have different mechanisms, effect intensities, and side effect profiles. In this section, we compare caffeine with the most popular and well-established stimulants on the market.
✅ Caffeine — The Gold Standard of Stimulants
🟩 Effect intensity: Moderate – strong
🟩 Duration: 3–5 hours
🟩 Mechanism: Adenosine blockade, increased norepinephrine and dopamine
🟩 Benefits: Most extensively researched / ISSN and IOC approved
🟩 Side effects: Insomnia, increased heart rate, tolerance
✔️ The safest and most well-studied stimulant in the world
✔️ The best choice for endurance, strength, and focus

✅ Yohimbine HCL
🟨 Effect intensity: Moderate
🟨 Duration: 1–2 hours
🟨 Mechanism: α2 receptor antagonist → increases lipolysis
🔹 Best performance for targeted (interstitial) fat loss
🔹 More effective when taken on an empty stomach
🔹 High-dose side effects: anxiety, tremors, tachycardia
❌ Not suitable for beginners or individuals with anxiety
❌ Dangerous at high doses
✔️ A very effective supplement, but only for professional fat-loss protocols
✅ Synephrine / Bitter Orange Extract
🟦 Effect intensity: Mild – moderate
🟦 Duration: 2–4 hours
🟦 Mechanism: β3 receptor stimulation → increases thermogenesis
✔️ Relatively safer than ephedrine
✔️ Supports fat-burning
✔️ Commonly used in many pre-workout supplements
❗ However, its effect is not as strong as caffeine or yohimbine.
✅ Ephedrine — Banned by WADA
🟥 Effect intensity: Very strong
🟥 Duration: 4–6 hours
🟥 Mechanism: Increases norepinephrine release + CNS stimulation
✔️ Very strong effects on focus, energy, and fat-burning
✔️ Previously used in the ECA Stack (Ephedrine + Caffeine + Aspirin)
❌ Banned by WADA (World Anti-Doping Agency)
❌ High risks: severe increases in heart rate, blood pressure, arrhythmia
❌ Many countries have restricted OTC sales
For these reasons, caffeine is considered a legal and safe alternative to ephedrine.
✅ Guarana — A naturally weakened form of caffeine
🟫 Effect intensity: Mild
🟫 Duration: Longer than regular caffeine
🟫 Mechanism: Caffeine + Theobromine + Theophylline
Why it’s weaker:
🔸 Slow release rate
🔸 Actual caffeine content uncertain
🔸 Lower peak effect
✔️ Suitable for mild, sustained energy
❌ Not suitable for intense training
✅ Green Tea and EGCG
🟩 Effect intensity: Very mild
🟩 Duration: Short
🟩 Mechanism: Antioxidant + mild metabolism boost
EGCG is not a stimulant on its own, but:
✔️ Slightly increases thermogenesis
✔️ Synergizes with caffeine
✔️ Suitable for those who cannot tolerate strong stimulants
❌ Almost never a substitute for caffeine in performance.
✅ Final Summary: Effect Intensity – Duration – Side Effects
🟩 Effect Strength
1️⃣ Ephedrine (very strong – banned)
2️⃣ Caffeine
3️⃣ Yohimbine
4️⃣ Synephrine
5️⃣ Guarana / EGCG
🟦 Duration
1️⃣ Caffeine
2️⃣ Ephedrine
3️⃣ Guarana
4️⃣ Synephrine
5️⃣ Yohimbine
🟥 Side Effects
(from high → low)
1️⃣ Ephedrine
2️⃣ Yohimbine
3️⃣ Caffeine
4️⃣ Synephrine
5️⃣ Guarana / EGCG
🎯 Final Conclusion:
✔️ Caffeine has the best “effect → safety” ratio
✔️ The only stimulant with strong support from sports research
✔️ Suitable for all goals: strength, endurance, focus, fat-burning
✔️ The best legal and safe alternative to ephedrine
Quality and Standards for Choosing a Caffeine Supplement
🔰 When choosing a professional caffeine supplement, three critical criteria should be considered:
1️⃣ Actual caffeine purity
2️⃣ Safety and anti-doping standards
3️⃣ Country and manufacturer of production
✅ Global Quality Standards
🟢 NSF Certified for Sport®
The world’s #1 standard for professional sports supplements.
✔️ Tests for contamination with banned stimulants
✔️ WADA banned substance testing
✔️ Heavy metals testing (lead, arsenic, mercury)
✔️ Purity and actual dose verification
If an athlete wants to compete officially, NSF is the best choice.
🟦 Informed Sport / Informed Choice
A highly reputable anti-doping system used in Europe and the USA.
✔️ Guarantees no contamination with banned substances
✔️ Batch testing for every production run
✔️ Suitable for Olympic-level athletes
Any supplement with the Informed Sport logo means:
“This product is safe for professional athletes.”
🟡 USP Verified (less common for caffeine but reliable)
✔️ Verifies actual dose
✔️ Stability testing
✔️ Purity testing of anhydrous form
✔️ GMP protocols

✅ Purity Testing and Its Importance
✅ Caffeine should be in Caffeine Anhydrous ≥ 99% form.
The best global brands use the following tests:
✔️ HPLC (High-Performance Liquid Chromatography)
➖ The most accurate method for measuring purity
➖ Detects chemical impurities
➖ Confirms the actual dose (e.g., 200 or 300 mg)
✔️ GC-MS
➖ For precise detection of contamination with prohibited stimulants
✔️ Heavy Metals Test
➖ To prevent contamination with heavy metals
✅ Preventing Contamination with Banned Substances
WADA Compliant
🔰 The biggest risk in the supplement market:
Accidental contamination with WADA banned stimulants
For example:
❌ DMAA
❌ DMHA
❌ Methylsynephrine
❌ Ephedrine
❌ SARMs
❌ Yohimbine in some countries
Contamination may be accidental, but it can lead to disqualification in competitions.
🔸 Best ways to prevent it:
✔️ Purchase supplements with NSF certification
✔️ Or Informed Sport certification
✔️ Or brands that publish Batch Numbers and COAs
✅ Best Countries to Buy Caffeine Supplements
Based on quality, purity, and regulation control
🇺🇸 United States (US FDA + NSF) — The best global choice
✔️ Strictest regulations
✔️ Best pre-workout and caffeine pill brands
✔️ Most extensive testing
🇬🇧 United Kingdom (Informed Sport Hub)
✔️ Very low contamination
✔️ Trusted sports products for Olympic teams
✔️ Consistent quality
🇨🇦 Canada
✔️ Strict Health Canada regulations
✔️ High purity
✔️ Transparent brands
🇩🇪 Germany / 🇳🇱 Netherlands / 🇩🇰 Denmark (Europe)
✔️ EFSA standards
✔️ Strict control over raw materials
✔️ Excellent reputation in pharm-grade supplements
🇯🇵 Japan (Pharmaceutical Grade)
✔️ Highest purity
✔️ Slightly more expensive
✔️ Exceptional quality
✅ Countries Where Caution Is Needed for Caffeine and Stimulants
🔴 China (many factories are reputable, but some lack independent testing)
🔴 India (huge variation between factories)
🔴 Countries without GMP or HACCP standards
(Not always bad, but the absence of COA and Batch Testing is risky.)
✅ Final Criteria for Choosing the Best Caffeine Supplement
Pelank Checklist for Selecting the Best Product:
✔️ Valid Certification:
NSF / Informed Sport / COA / GMP
✔️ Purity:
Caffeine Anhydrous ≥ 99%
✔️ Transparency:
Certificate of Analysis available
(downloadable from the brand’s website)
✔️ Accurate Dose:
200–300 mg actual, not less or more
✔️ No Dangerous Additives:
❌ DMAA
❌ DMHA
❌ High Synephrine
❌ Unknown stimulants
✔️ Country of Production:
USA / UK / Germany / Canada / Japan
Best Caffeine Consumption Methods for Different Goals
Complete Protocol + Timing
🟢 Caffeine’s effects vary depending on your athletic goal, timing, training intensity, and nutritional status. In this section, we provide a precise, tested, and practical protocol for each goal.
✅ Muscle Building
Muscle Building / Strength Hypertrophy
🟩 Goal: Increase strength, high-quality sets, and lower RPE
🕒 Timing: 30–45 minutes before training
💊 Dose: 3–4 mg/kg
Full Protocol:
✔ 3–4 mg/kg as Caffeine Anhydrous
✔ For heavy leg or upper-body sessions → 4–5 mg/kg
✔ For explosive power training: Gum form 5–10 minutes before training works best
Result:
🔥 Maximum strength increase
🔥 Greater output in heavy sets
🔥 Lower RPE (perceived exertion)

✅ Fat Burning
Fat Loss / Cutting
🟧 Goal: Increase lipolysis, thermogenesis, and NEAT
🕒 Timing:
45 minutes before training
Or in the morning on an empty stomach for fasted cardio
💊 Dose: 3 mg/kg
Full Protocol:
✔ 3 mg/kg before aerobic or HIIT sessions
✔ If fasted → effects increase by 20–30%
✔ On rest days → 100 mg is sufficient to boost metabolism
Result:
🔥 Increased lipolysis
🔥 Elevated NEFA
🔥 Continuous fat burning
✅ Intense Training
Heavy Lifting / Powerlifting
🟥 Goal: Increase neural drive and CNS stimulation
🕒 Timing: 20–30 minutes before training
💊 Dose: 4–5 mg/kg
Full Protocol:
✔ Use Anhydrous form for the fastest CNS effect
✔ For Deadlift / Squat / Bench PR → 5 mg/kg
✔ For moderate compound exercises → 3–4 mg/kg
Result:
⚡ Enhanced explosive strength
⚡ Improved neural focus
⚡ Reduced neural fatigue
✅ Competition
Competition / Race Day Protocol
🟦 Goal: Peak Performance
🕒 Timing:
Strength competitions: 30 minutes before
Endurance competitions: 45–60 minutes before
💊 Dose: 3–6 mg/kg
Full Competition Protocol:
✔ Beginner or sensitive athlete → 3 mg/kg
✔ Professional athlete → 4–6 mg/kg
✔ Long-duration events → Split Dose
Split Dose (for long competitions):
4 mg/kg → 45 minutes before start
1–2 mg/kg → mid-event (gel or gum)
Result:
🔥 Maintained power
🔥 High focus
🔥 Prevents energy drop
✅ HIIT and Sprint Training
🟪 Goal: Increase anaerobic and explosive power
🕒 Timing: 20 minutes before training
💊 Dose: 3–4 mg/kg
⚡ Best Form: Caffeine Gum
Full Protocol:
✔ 3–4 mg/kg
✔ 1–2 pieces of Gum → 10 minutes before training (ultra-fast peak)
✔ If on an empty stomach → reduce dose by 10–15%
Result:
🔥 Faster sprints
🔥 Increased anaerobic power
🔥 Lower RPE
✅ Long-Distance Running
Endurance / Marathon / Cycling
🟩 Goal: Increase endurance, enhance fat utilization, conserve glycogen
🕒 Timing: 45–60 minutes before running
💊 Dose: 3 mg/kg
Full Protocol:
✔ 3 mg/kg before running
✔ For runs over 90 minutes: 1–2 mg/kg mid-run (gel or drink)
Result:
🔥 5–8% performance improvement
🔥 Greater reliance on fat
🔥 Delayed onset of fatigue
✅ Focus for Work and Study
Cognitive Enhancement
🟦 Goal: Enhance focus, alertness, and reduce mental fatigue
🕒 Timing: Any time except afternoon
💊 Dose: 1–2 mg/kg
⚡ Best Form: Coffee or low-dose caffeine
Full Protocol:
✔ 50–150 mg for focus
✔ Use a Micro-dose Protocol: 50 mg every 3–4 hours
✔ Combine with L-Theanine (100–200 mg) → focus without stress
Result:
🧠 Improved mental clarity
📚 Longer concentration
⌛ Reduced mental fatigue
✅ Final Summary Table of Caffeine Protocols
Goal | Dose (mg/kg) | Timing | Best Form |
|---|---|---|---|
Muscle Building | 3–4 | 30–45 min before | Tablet / Powder |
Fat Burning | 3 | 45 min before / fasted | Tablet |
Intense Training | 4–5 | 20–30 min before | Anhydrous |
Competition | 3–6 | 30–45 min before | Tablet + Gel |
HIIT / Sprint | 3–4 | 20 min before | Gum |
Long-Distance Running | 3 | 45–60 min before | Tablet + Extra Gel |
Work / Study Focus | 1–2 | Any time + before noon | Coffee / Low-dose |
Frequently Asked Questions
FAQ
✔ Answer: Yes, indirectly. Consuming 3–6 mg/kg before training increases strength and power, which in turn supports muscle growth…
✔ Usually 30–60 minutes before training. Forms like gum 10–20 minutes before are also effective…
✔ Not necessarily. Pre-workouts contain more stimulants but also have a higher risk of side effects…
✔ Scientific evidence rejects a direct link to hair loss…
✔ 3–4 times before training is optimal. To avoid tolerance, daily use is not recommended…
✔ Yes, it increases lipolysis and thermogenesis…
✔ Not in usual doses. But hydration is important during intense training…
✔ Yes, a significant effect remains…
✔ Yes. It has a long half-life (5–7 hours)…
✔ Only in very low doses and under professional guidance…
✔ Yes, temporarily; people with high blood pressure should be cautious…
✔ Yes. Liquid and gum act faster than pills…
✔ For endurance competitions, yes, but not recommended on regular days…
✔ Usually not. If used, the dose should be very low…
✔ Yes, but up to 200 mg per day max…
✔ Hair loss: no; acne may increase only with stress + poor sleep…
✔ Depends on the goal; gum acts fastest…
✔ Yes, it increases focus and reduces anxiety…
✔ No; it’s a supplement, not a replacement for sleep, nutrition, or training program…
✔ Usually no; to avoid tolerance, it’s better not to take it on off days…
✔ For healthy individuals, yes, but side effects are more likely…
✔ They may increase heart-related side effects and anxiety…
✔ Yes; older adults are more sensitive…
✔ Possible at high doses…
✔ At least 6 hours before sleep…
✔ Yes, for focus and alertness…
✔ Yes, non-responders exist, but they are very few…
✔ Yes, especially during training…
✔ Food slows absorption; if taken before training, take it slightly earlier…
✔ Yes, as long as it doesn’t exceed the prohibited limit; caffeine is legal…
Is caffeine supplementation worth taking?
Summary
✔️ Is caffeine supplementation worth taking?
✅ Yes — According to dozens of reputable studies from ISSN, ACSM, IOC, WADA, and Cochrane, caffeine is one of the most powerful, safe, and effective sports supplements in the world. Among all ergogenic aids, caffeine is classified as one of the 5 “truly effective” supplements.
🟢 Scientifically proven effects:
✔️ Increased endurance
✔️ Enhanced anaerobic power
✔️ Increased strength
✔️ Improved focus, alertness, and reduced mental fatigue
✔️ Increased fat burning during exercise
➖ In fact, no other supplement has as much strong scientific evidence as caffeine.
🟩 Who benefits most from caffeine?
🔰 Groups with the highest benefit:
1️⃣ Endurance athletes (running, cycling, CrossFit)
2️⃣ Strength athletes in heavy training
3️⃣ Individuals requiring high focus (students, precision work)
4️⃣ Those who train in the morning
5️⃣ Individuals with adequate sleep
6️⃣ Fast metabolizers (CYP1A2 AA genotype)
🟨 Groups with moderate benefit:
1️⃣ People who drink a lot of coffee daily (due to tolerance)
2️⃣ Those who do light workouts
🟥 Groups with low or potentially negative benefit:
➖ Slow metabolizers
➖ Individuals with anxiety
➖ Stimulant-sensitive people
➖ Those with poor sleep
🔰 Scientific evidence at a glance:
📌 1. Effect on athletic performance:
Over 250 high-quality studies show:
↗️ 2–6% increase in strength
↗️ 4–12% increase in endurance
↗️ 5–10% increase in anaerobic power
↘️ 5–30% reduction in RPE (perceived exertion)
These results are also confirmed in 2024 meta-analyses.
📌 2. Effect on fat loss:
Studies indicate:
↗️ Increased NEFA (non-esterified fatty acids)
↗️ Increased thermogenesis
↗️ Higher metabolic rate (7–13%)
↗️ Increased lipolysis during fasted cardio
↗️ Increased NEAT (non-exercise activity thermogenesis) throughout the day
However, caffeine alone is not fat-burning; it is only supportive.
📌 3. Safety and risk:
➖ In standard doses (3–6 mg/kg), it is completely safe for healthy individuals.
Higher doses (9 mg/kg or more) carry a risk of side effects and toxicity.
Pregnant women, heart patients, and anxious individuals should limit intake.
✅ Final verdict:
If you exercise, get enough sleep, and are not sensitive to stimulants, caffeine is one of the best and most “valuable” supplements you can take.
✔ Safe
✔ Cost-effective
✔ Scientific
✔ Effective across all sports
✔ Supports fat loss and focus
And this is why caffeine, after protein and creatine, is the third best-selling supplement in the world.

Scientific sources and references
✔️ International Organizational / Governmental Sources
✔️ Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review Studies (2010–2025)
✔️ Sources Related to Mechanism of Action (Neuro, Muscle, Metabolism)
✔️ Sources on Sleep, Anxiety, and Side Effects
✔️ Safety, Toxicity, and Lethal Dose
Pelank Life | Body Health Assessment
The Best Body Health Calculators Using Scientific Methods
Developed by Pelank Life ©

Mohsen Taheri
November 28, 2025