The Comprehensive Guide to Ashwagandha Supplement
🌿 Ashwagandha: The Most Complete Scientific Guide to Benefits, Dosage, Sources, and Best Fish Oil Supplements
✅ Ashwagandha has become one of the best-selling and most-searched supplements in America these days; but why has a traditional Indian herb managed to conquer the world?
🔥 Can it truly reduce stress, improve sleep, and boost daily energy?
💪 How is it possible for a plant root to affect body strength, testosterone, and even mental focus?
🧠 Are these benefits scientifically backed, or is it just a hype wave?
📈 Why are millions of Americans, professional athletes, and even complementary medicine specialists using it?
✨ In this comprehensive Pelank guide, backed by scientific studies and a detailed examination of its mechanisms, you will understand exactly what Ashwagandha is, how it works, and why it has become one of the most powerful supplements in the world.
👇 If you want to know whether this herb is truly worth taking or not, you just need to read this page to the end. The answers to all your questions are right here.
Ashwagandha Smart Questionnaire 🧠🌿
This tool is for educational purposes only and is not a substitute for medical advice.
Recommendations apply to healthy adults 18+ and do not replace professional medical care.
Introduction to the Ashwagandha Supplement
Pelank Supplement ©
🌿 Ashwagandha is a potent medicinal herb from the Solanaceae family, whose scientific name is Withania somnifera. This plant is also known in scientific texts by other names such as Indian Ginseng and Winter Cherry, but the most authoritative and correct name is Ashwagandha.
📜 The history of this herb dates back over 3,000 years to Ayurvedic medicine, where it was used to boost vital energy (Prana), strengthen the mind, reduce stress, and improve sleep. In Ayurveda, Ashwagandha is considered one of the “Rasayanas”—compounds that help restore youth and increase longevity.
⚡ Ashwagandha is a true Adaptogen; meaning it can make the body more resilient against physical, mental, and environmental stresses. Adaptogens are substances that help bring the function of the nervous, hormonal, and immune systems closer to a state of balance (Homeostasis).
🌍 The reasons for Ashwagandha’s global popularity in the last decade are very extensive:
🧪 Strong scientific backing in reducing cortisol and managing stress
😴 Improved sleep and relaxation
🧠 Boosting focus, memory, and cognitive function
💪 Increased strength, muscle, and improved athletic performance
🔝 Explosive growth in the U.S. supplement market due to increased societal need for calm, quality sleep, and sustained energy
✨ Today, Ashwagandha is recognized not only in Europe and America but across the globe as one of the most researched and popular supplements. A compound that targets the balance of mind and body.

Botanical Characteristics
Botanical Profile
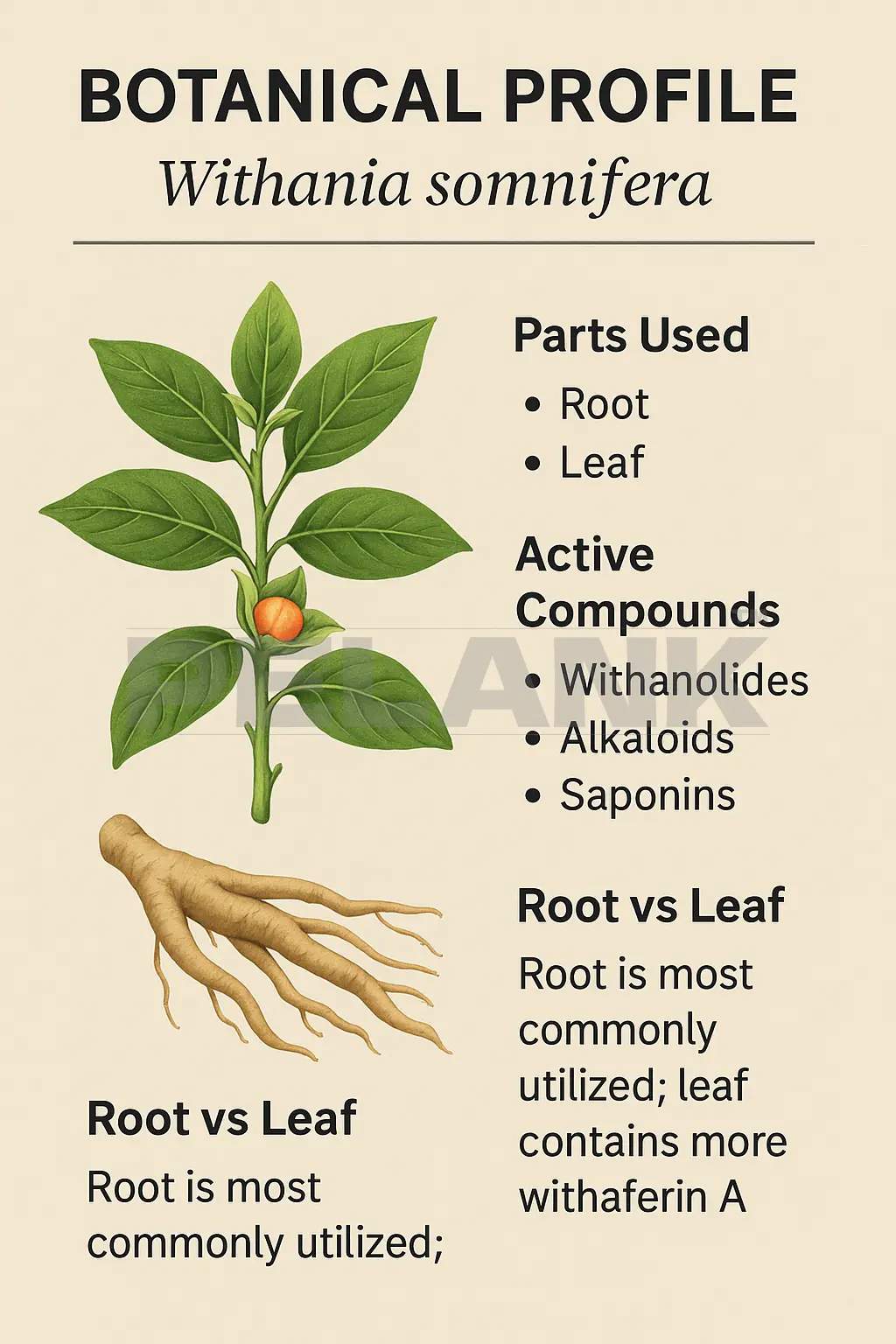
🌱 Ashwagandha, scientifically named Withania somnifera, is a medicinal plant belonging to the Solanaceae family; the same family that includes potatoes, tomatoes, and eggplant. This plant is native to the dry regions of India, Nepal, Pakistan, and parts of the Middle East, and thrives well in warm, poor soils.
🌿 The plant structure is short and woody, typically reaching a height of 30 to 60 centimeters. The leaves are oval and velvety, and its fruit is a small, orange-red seed similar to physalis berries.
🪵 The most important part of this plant used is its root; this is where the highest concentration of active compounds (Withanolides) is located. However, the leaves also contain beneficial alkaloids and saponins, but the world’s most standardized commercial extracts (like KSM-66) are specifically derived from the pure root.
⚗️ Main Active Compounds of Ashwagandha
⚗️ The main active compounds of Ashwagandha include the following:
🔸 Withanolides – The most important class of compounds with anti-inflammatory, anti-stress, and adaptogenic effects
🔸 Alkaloids – Affective on the nervous system and relaxation
🔸 Saponins – Immune response boosters and antioxidants
🔸 Withaferin A – The most potent biological compound, with potential anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer effects
🌾 Difference in Function Between Root and Leaf
🟤 Root → Contains stable and balanced amount of Withanolides, suitable for reducing stress, improving sleep, and enhancing athletic performance.
🟢 Leaf → Richer in Withaferin A; a compound that has stronger effects but is not suitable for long-term consumption and is generally less used in standardized supplements.
✨ This is why virtually all reputable brands worldwide—KSM-66, Sensoril, and Shoden—use root extract to ensure both consistent efficacy and greater safety for long-term consumption.
Biopharmacology and Absorption
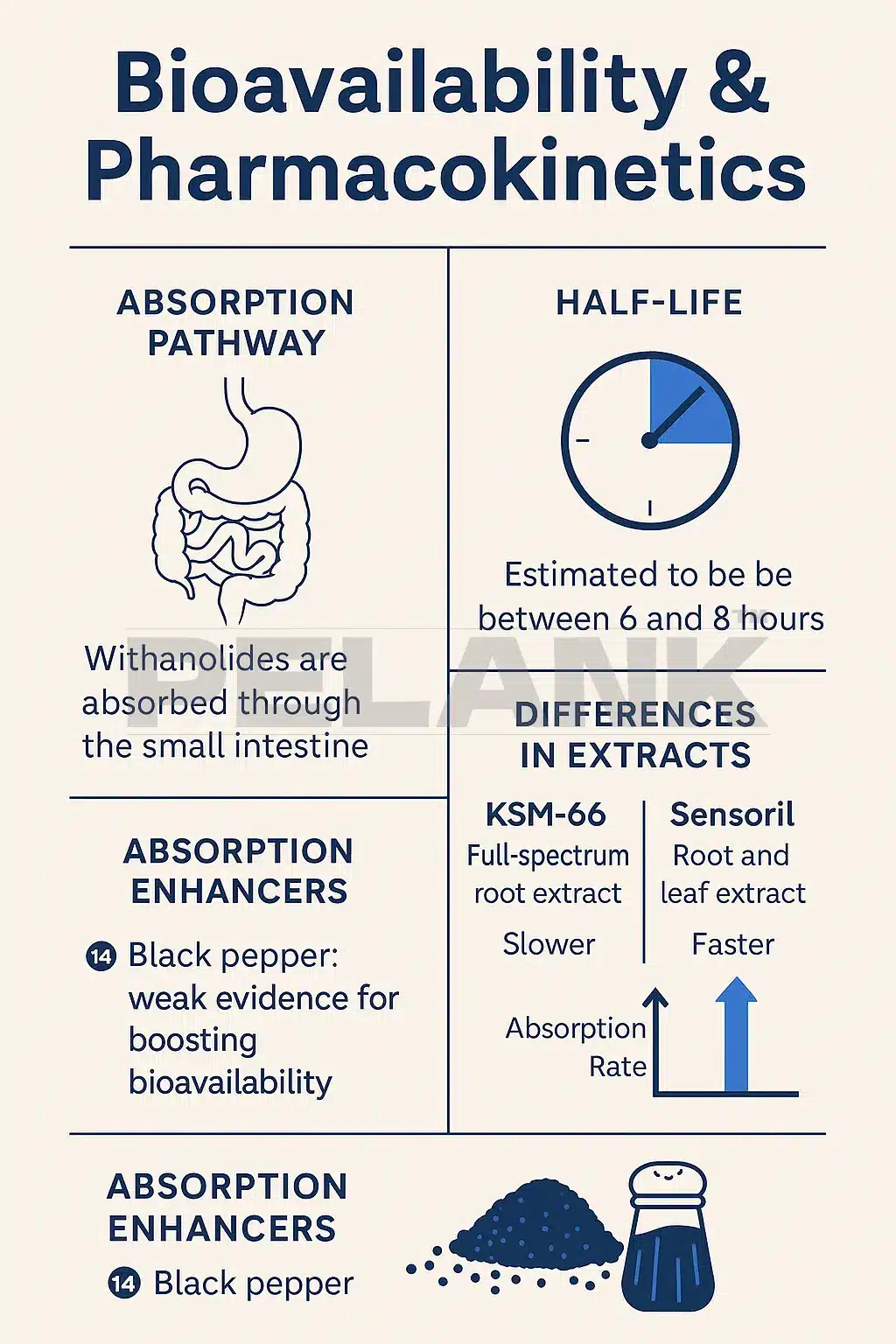
🧬 After oral consumption, Ashwagandha is absorbed through the small intestine, and its active compounds—especially the Withanolides—enter the bloodstream via lipophilic pathways. Due to the fat-loving nature of these compounds, their absorption is slightly enhanced in the presence of healthy fatty foods.
⏱️ The half-life of Ashwagandha’s active compounds is estimated to be between 6 and 8 hours; for this reason, many experts suggest taking one to two doses per day to maintain relatively stable blood levels. For athletic use (pre-workout), the effects of stress reduction and strength improvement peak 3–4 hours after consumption.
⚗️ Differences in Absorption and Efficacy of Extracts
⚗️ The difference in absorption and efficacy among extracts is very important, and this is the main reason for the differences between various brands. For example:
🌿 KSM-66 → A full-spectrum extract from the root; a perfect balance of Withanolides, with slower but more stable absorption.
🌱 Sensoril → A standardized and stronger extract from the root + leaf; faster absorption but sometimes with a greater sedative effect.
🍃 Shoden → Contains highly concentrated Withanolides; the highest bioavailability at low doses.
📈 Studies show that standardized extracts (such as KSM-66 and Sensoril) have up to 3 times higher bioavailability compared to regular powdered extracts. This means that a smaller amount of the supplement yields greater effects.
🧪 Absorption Enhancers
Unlike many medicinal herbs, there is insufficient evidence for the effect of black pepper (piperine) on increasing the absorption of Ashwagandha. Most studies show that piperine affects compounds like curcumin, but its effect on Withanolides is minimal or unclear. Therefore, adding piperine to the formula is more of a marketing move than a scientific one.
🔬 Why do KSM-66 and Sensoril have different absorption profiles?
The main reasons for the difference in absorption between these two extracts can be summarized as follows:
🧬 Different withanolide structures → Sensoril contains a higher amount of Withaferin A.
🪵 Plant part used → KSM-66 uses only the root; Sensoril uses both root + leaf.
⚗️ Extraction method → KSM-66 uses a “Green Extraction” technique without alcohol, preserving the natural balance of compounds.
💧 Solvents and separation processes → These affect particle size, solubility, and absorption rate.
✨ Conclusion:
KSM-66 → Stable absorption, suitable for long-term use, with mild and balanced effects.
Sensoril → Faster absorption, stronger calming and anti-stress effects, suitable for shorter-term use.
Mechanism of Action of Ashwagandha
Mechanisms of Action
🧠 HPA Axis Modulation
Ashwagandha influences the Hypothalamus–Pituitary–Adrenal (HPA) axis, the body’s primary stress-management system, helping regulate hormonal balance. This mechanism reduces the body’s reactivity to stress and promotes a faster return to a state of calm.

⬇️ Cortisol Reduction
One of the most important effects of ashwagandha is a significant reduction in cortisol levels. Studies have shown that standardized ashwagandha extracts can reduce cortisol by up to 30%, leading to reduced anxiety, improved sleep quality, sustained energy levels, and prevention of muscle breakdown.
🔥 Anti-inflammatory and Antioxidant Effects
Withanolides exhibit strong anti-inflammatory activity. These compounds help reduce systemic inflammation, improve recovery, and protect cells by lowering inflammatory cytokines and increasing the body’s natural antioxidants (such as SOD and catalase).
🧬 Effects on the GABA and Serotonin Systems
Evidence suggests that ashwagandha may increase GABA receptor activity and enhance serotonin synthesis or pathway sensitivity. These mechanisms support its calming, anti-anxiety, and mood-enhancing effects—without causing dependence.
💆 Improved Stress Response
Ashwagandha’s active compounds increase stress resilience, meaning the body’s ability to cope with and recover from physical and psychological stress. This effect is especially noticeable in athletes, busy individuals, and those experiencing inadequate sleep.
🦋 Effects on Thyroid Function
Thyroid Function Support
Limited studies suggest that ashwagandha may cause a mild increase in T3 and T4 levels and a reduction in TSH—particularly in individuals with mild (subclinical) hypothyroidism.
✔ However, this effect is not beneficial for everyone and is not recommended for individuals with overt hyperthyroidism.
Scientifically Proven Benefits of Ashwagandha
Evidence-Based Benefits
1️⃣ Reduce stress and anxiety
🧾 Study Summary: [1]
🌿 Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial in individuals with chronic stress.
👥 Study population: 64 highly stressed adults; study duration: 60 days.
💊 Dosage: 300 mg of ashwagandha root extract (KSM-66) taken twice daily.
🎯 Results:
✔️ Significant reduction in perceived stress scores (PSS)
✔️ 27–30% reduction in serum cortisol compared to placebo
✔️ Improved overall well-being and quality of life
🧾 Systematic Review and Meta-analysis (2024): [2]
👥 9 clinical trials, 558 participants.
🎯 Results: Compared to placebo, ashwagandha significantly reduces stress, anxiety, and cortisol levels.
2️⃣ Sleep Improvement
🧾 Study Summary (Insomnia): [3]
👥 150 individuals with sleep disorders; randomized, double-blind trial lasting 6–8 weeks.
💊 Dosage: 120 to 300 mg of standardized root extract, taken once or twice daily.
🎯 Results:
✔️ Significant improvement in sleep quality (Insomnia Severity Index, Sleep Quality)
✔️ Reduced sleep latency (time to fall asleep)
✔️ Increased total effective sleep duration
✔️ Good tolerability with no serious adverse effects reported
🧾 Study in college students (30 days): [4]
👥 60 university students, 700 mg of full-spectrum root extract per day.
🎯 Results: Reduced stress, improved sleep quality, and decreased food cravings.
3️⃣ Cognitive Enhancement and Focus
🧾 Study Summary (Ashwagandha SR): [5]
👥 135 healthy individuals with stress and mild concentration issues; 90-day trial.
💊 Dosage: One sustained-release ashwagandha capsule per day (standardized root extract).
🎯 Results:
✔️ Significant improvements in memory and focus on standardized cognitive tests
✔️ Reduced stress and improved sleep
✔️ No serious adverse effects reported
4️⃣ Mood and Mental Health Improvement
🧾 Study Summary (Mood & Stress): [6]
👥 60 adults with mild to moderate stress and anxiety; 60 days of ashwagandha vs placebo.
💊 Dosage: 250–300 mg of root extract twice daily.
🎯 Results:
✔️ Reduced anxiety and stress on DASS and HAM-A scales
✔️ Improved mood and sense of well-being
✔️ Reduced fatigue and increased vigor
5️⃣ Increased Testosterone in Men
🧾 Study Summary (Overweight Men): [7]
👥 57 men aged 40–70 with moderate overweight; 16-week study.
💊 Dosage: 600 mg of ashwagandha root extract per day.
🎯 Results:
✔️ 14–15% increase in testosterone compared to placebo
✔️ 18% increase in DHEA-S
✔️ Modest improvements in fatigue and sexual health (no significant change in cortisol)
🧾 More recent study on the Asvaman® formula (2025): [8]
👥 Men with low–normal testosterone; 42-day intervention.
🎯 Results: A significant increase in serum testosterone in the ashwagandha group compared to placebo.
6️⃣ Improved Fertility and Sexual Health
🧾 Study Summary (Male Sexual Health): [9]
👥 64 men with reduced sexual function; randomized, double-blind study.
💊 Dosage: Standardized ashwagandha root extract, approximately 600 mg per day for 8 weeks.
🎯 Results:
✔️ Significant improvements in libido, erectile function, and sexual satisfaction
✔️ Increased testosterone levels and improved semen quality in a subset of participants
7️⃣ Increased Muscle Mass, Strength, and Athletic Performance
🧾 Classic Study Summary (2015): [10]
👥 57 young men following an 8-week resistance training program.
💊 Dosage: 300 mg of ashwagandha root extract taken twice daily.
🎯 Results:
✔️ Greater increases in arm and chest muscle size compared to placebo
✔️ Significant increases in 1RM strength for the bench press and deadlift
✔️ Greater reductions in muscle damage (lower CK levels) and body fat
🧾 New 2024 Study (Men and Women): [11]
👥 Trained men and women; 8 weeks of resistance training plus ashwagandha.
💊 Dosage: Standardized root extract (AG), 600–700 mg per day.
🎯 Results:
Increased strength, muscle mass, and muscular endurance in both sexes
Improved cardiorespiratory endurance indices
No significant adverse effects reported
🧾 Systematic Review and Meta-analysis on Athletic Performance (2020–2021): [12]
🎯 Results: Ashwagandha can significantly improve VO₂max, strength, and muscular power in athletes and physically active individuals.
8️⃣ Reduced Inflammation and Improved Recovery
🧾 Study Summary (Inflammatory Markers & Performance): [13]
👥 Healthy, physically active volunteers; randomized, double-blind 8-week trial.
💊 Dosage: Daily ashwagandha root extract.
🎯 Results:
✔️ Reduction in certain inflammatory markers (such as CRP and IL-6)
✔️ Improved athletic performance and perceived recovery
✔️ Good tolerability with no serious adverse effects
9️⃣ Effects on Metabolism (Blood Sugar, Lipids) and Overall Health
🧾 NIH Review and Human Studies: [14]
🎯 Findings:
✔️ In some small studies, ashwagandha has shown modest improvements in fasting blood glucose and lipid profiles, particularly in stressed or overweight individuals.
✔️ However, the evidence remains limited and it should not be considered a substitute for diabetes or lipid-lowering medications.
🧾 Multiple studies on quality of life: [15]
🎯 Overall conclusion:
✔️ Improvements in overall health, sleep quality, daily energy, and psychological well-being
✔️ Side effects are generally mild (such as gastrointestinal discomfort and drowsiness) and dose-dependent.
✅ The strongest evidence supports:
✔️ Reduced stress and anxiety
✔️ Improved sleep
✔️ Enhanced cognition and mood
✔️ Increased strength and muscle gains alongside training
✔️ Mild increases in testosterone in stressed or overweight men
⚠️ Evidence regarding metabolic effects (blood sugar/lipids) and long-term outcomes is still limited and evolving, so ashwagandha should not replace primary medical treatments.
Potential and Emerging Benefits
1️⃣ Potential Anti-Cancer Effects
🧪 What do we know?
🧬 In in vitro (cell-based laboratory) studies and in vivo animal studies, compounds such as Withaferin A and Withanolide D have shown the ability to:
✔️ Halt the cell cycle of cancer cells
✔️ Trigger apoptosis (programmed cancer cell death)
✔️ Reduce tumor spread and metastasis
🔗 Examples of laboratory references:
Study on Withaferin A and inhibition of NF-κB and STAT3 pathways in cancer cells:
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16595650
Comprehensive review on the anti-cancer potential of withanolides:
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19692202
⚠️ Important note:
This evidence is primarily based on cell and animal studies; there are currently no strong clinical trials in humans supporting cancer treatment. Therefore, ashwagandha should never replace standard cancer therapies and is only considered a promising area of future research.
2️⃣ Neurogenesis and Neural Cell Growth
🧪 Some animal studies suggest that ashwagandha may:
✔️ Stimulate neurite outgrowth (neuronal branching)
✔️ Prevent neuronal degeneration
🔗 Example:
Study on neurite outgrowth and neuroprotection with Withanolide A in animal models:
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14669250
✨ Potential conclusion: These mechanisms may help explain improvements in memory, focus, and protection of the brain against stress and aging; however, more clinical data in humans are needed before making definitive claims.
3️⃣ Neuroprotection
🧬 In animal models of Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease, ashwagandha has been shown to:
✔️ Reduce oxidative stress in the brain
✔️ Limit the accumulation of toxic proteins (such as β-amyloid)
✔️ Improve cognitive function in animals
🔗 Example references:
Neuroprotective effects of ashwagandha in Alzheimer’s disease models:
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21496408
Review of the neuroprotective potential of Withania somnifera:
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25263125
⚠️ Emphasis again: These findings are promising but do not yet mean “treatment of Alzheimer’s or Parkinson’s disease in humans”; for now, they should be viewed as an emerging research area.
4️⃣ Anti-Aging and Cellular Health
💡 Due to a combination of effects:
✔️ Antioxidant activity
✔️ Anti-inflammatory effects
✔️ Reduced stress and cortisol levels
Some researchers consider ashwagandha a potential candidate for slowing certain aspects of the cellular aging process.
In animal studies, ashwagandha supplementation has been associated with:
✔️ Reduced oxidative markers
✔️ Improved endogenous antioxidant status (such as SOD and catalase)
These effects have been observed.
🔗 Related review:
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23560637
👀 However, no long-term human studies are currently available showing that it directly increases lifespan or slows aging. For now, it can be stated that:
“Ashwagandha likely supports cellular health and youthfulness indirectly by reducing stress and inflammation.”
5️⃣ Effects on Social Anxiety
🧪 Data on social anxiety are still limited and inconsistent, but:
Some trials suggest that ashwagandha may improve overall anxiety and social functioning;
In individuals with occupational or academic stress, reductions in general stress may indirectly decrease fear of social situations.
🔗 Example of a study on stress and overall well-being that also reported improvements in social relationships:
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31517876
✅ Summary:
Direct evidence on “Social Anxiety Disorder” is limited;
However, through stress reduction and mood improvement, it may help reduce social anxiety in some individuals; it should not replace psychotherapy or medication in severe cases.
6️⃣ Thyroid Effects
🧾 Limited but important human studies:
In a clinical trial involving individuals with subclinical hypothyroidism, 8 weeks of ashwagandha supplementation led to:
✔️ Increased T3 and T4 levels
✔️ Reduced TSH
Compared to the placebo group.
🔗 Sample study:
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28829155
✨ Conclusion:
In individuals with mild hypothyroidism, it may help improve thyroid function.
However, in those with hyperthyroidism or active autoimmune thyroid disease (such as Graves’ disease), this stimulation may be problematic.
⚠️ Therefore:
For individuals with thyroid disorders, consulting a physician before using ashwagandha is essential;
Ashwagandha cannot replace thyroid medications, but in certain situations, it may serve as an adjunct therapy.
🧷 Summary of Emerging Benefits
✅ Promising evidence in the following areas:
✔️ Anti-cancer effects in laboratory models
✔️ Neurogenesis and neuroprotection
✔️ Thyroid support in mild hypothyroidism
✔️ General stress reduction that may indirectly improve social anxiety
⚠️ However, for all of these areas, it is important to note that:
❌ Large, long-term human clinical trials are still limited
❌ These effects should not replace standard treatments (for cancer, thyroid disorders, or neurological diseases)
Types of Ashwagandha Supplements
Supplement Forms
1️⃣ Powder
Powder Form
🌿 Ashwagandha powder is typically made from ground, dried root and undergoes the least amount of processing.
🧪 Its withanolide content is low and highly variable.
🍵 Suitable for use in smoothies or hot beverages; however, its bitter, earthy taste causes many people to avoid the powder form.
⚠️ Due to the lack of precise standardization, its effects are not predictable.

2️⃣ Capsules
✔ The most common form of use in the global market.
🧪 Capsule contents may include:
✅ Plain powder
✅ Standardized extract
Or a combination of multiple extracts.
📏 Advantage: precise and controllable dosing
⚠️ Important note: always look for the term “Standardized Extract” or a specified withanolide percentage on the label.

3️⃣ Standardized Extract
Standardized extracts provide the most effective and consistent results.
🔬 In these extracts, the percentage of withanolides is clearly defined (for example, 5% or 10%), ensuring that each dose delivers a precise amount of active compounds.
📈 Advantages:
✅ Greater potency
✅ Better absorption
✅ Consistent product quality with every serving
✅ Stronger scientific evidence
⚠️ Typically more expensive than powder or basic capsule forms.

🔥 Comparison of Three Well-Known Global Extracts
KSM-66 vs Sensoril vs Shoden
🌿 KSM-66
Full-Spectrum Root Extract
Extracted exclusively from the root
Full-spectrum: all natural withanolides are preserved
Mild, sustained activity suitable for long-term use
Strong scientific support for: stress, testosterone, muscle, and sleep
Withanolide content: typically 5%
Advantage: natural effects without strong sedation
🌱 Sensoril
Root + Leaf Extract
A combination of root + leaf
Leaves contain higher levels of Withaferin A → faster and stronger effects
Suitable for severe stress, anxiety, and relaxation
Withanolide content: typically 10% or 12%
Advantage: faster and more potent effects
⚠️ May cause sedation or drowsiness in some individuals.
🍃 Shoden
High-Potency Extract
One of the newest specialized extracts
Standardized to 35% withanolides → extremely potent
Higher absorption (greater bioavailability) at lower doses
Suitable for those who want a low dose with strong effects
✔ The best option for high-potency formulations
🧬 Differences in withanolides across extract types
🧪 Why is the withanolide percentage important?
Withanolides are the main active compounds in ashwagandha
Higher percentage → greater potency
But: the type of withanolides also matters
KSM-66 → natural and balanced (root-based)
Sensoril → higher Withaferin A content (leaf-based)
Shoden → highly concentrated and very potent
✔ Therefore, a higher percentage is not always better—it should be chosen based on the intended use.
🧪 Standardization: HPLC vs UV
Which is better?
🔬 HPLC
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography
✔ The most accurate and reliable method for measuring active compounds
✔ Allows separation of different withanolides
✔ The most transparent standard for laboratory testing
💎 Conclusion: If the label says HPLC-tested, it indicates excellent quality.
🔦 UV Spectrophotometry
UV Spectrophotometry Method
✔ Cheaper and faster
✔ Lower accuracy
✔ Cannot differentiate between similar compounds
⚠️ The withanolide percentage may be overestimated
🔍 Golden tip for you:
It is recommended to always choose HPLC-standardized extracts—such as KSM-66, Sensoril, and Shoden.
Ashwagandha Dosage
Dosage Guidelines
1️⃣ Reduce stress and anxiety
🌿 Effective dosage in studies: [16]
✔️ 300 mg of KSM-66 twice daily (600 mg total)
✔️ 250–500 mg of Sensoril once daily
📌 Results: reduced anxiety and a 27–30% reduction in cortisol
🔗 Source:
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23439798
2️⃣ Sleep Improvement
🌙 Effective dosages: [17]
✔️ 120–300 mg of standardized extract
✔️ 600 mg before bedtime (in some studies)
📌 Results: improved sleep quality, reduced sleep latency, and increased relaxation.
3️⃣ Testosterone Increase
💊 Effective dosages in studies: [18]
✔️ 600 mg per day (KSM-66) → 14–17% increase in testosterone
✔️ 300 mg twice daily for 8 weeks
📌 Best response observed in:
✔️ Men with high stress
✔️ Overweight men or those with low–normal testosterone levels
4️⃣ Athletic Performance and Strength Gains
🏋️ Effective dosages: [19]
✔️ 300 mg of KSM-66 twice daily (8 weeks)
✔️ 600–700 mg of AG or Shoden extract
📌 Results:
✔️ Increased 1RM
✔️ Increased muscle mass
✔️ Reduced muscle damage (CK)
5️⃣ Improved Fertility and Sexual Health
💊 Typical dosage: [20]
✔️ 600 mg of standardized root extract (8 weeks)
📌 Results:
✔️ Improved sperm quality
✔️ Increased libido
✔️ Increased testosterone and DHEA-S
6️⃣ Anti-inflammatory Effects and Recovery
🌿 Effective dosage: [21]
✔️ 250–600 mg per day
📌 Results:
✔️ Reduced CRP and IL-6
✔️ Improved recovery and reduced muscle soreness
7️⃣ Cognition, Memory, and Focus
🎯 Effective dosages: [22]
✔️ 300–600 mg of standardized extract
✔️ Or “sustained-release” formulas, one capsule daily
📌 Results:
✔️ Improved working memory
✔️ Better focus
✔️ Reduced stress and improved sleep → enhanced cognitive function
⭐ Dosage Comparison of Different Extracts
KSM-66 / Sensoril / Shoden
Extract | Typical Dosage | Absorption Characteristics | Potency |
|---|---|---|---|
🌿 KSM-66 | 300–600 mg/day | Stable, slow absorption | Best for stress + exercise |
🌱 Sensoril | 125–250 mg/day | Fast absorption | Best for anxiety and sleep |
🍃 Shoden | 120 mg/day | Very high bioavailability | Best for strong effects at low doses |
🔍 Why does Sensoril require a lower dose?
✔️ Due to higher Withaferin A content and stronger biological activity.
🔍 Why is Shoden more potent?
✔️ Standardized to 35% withanolides (the highest concentration)
🚨 Maximum Safe Dosage
Upper Safety Limit
Based on clinical trial data: [23]
🧪 Safe daily dose: 600–1000 mg of standardized extract
🧪 Maximum dose reported in studies: up to 1250 mg without serious adverse effects
⚠️ Intake above 1500 mg/day may cause:
❌ Gastrointestinal issues
❌ Drowsiness
❌ Thyroid changes in sensitive individuals
✨ Quick Dosage Guide
Purpose | Dosage |
|---|---|
Stress | 600 mg/day |
Sleep | 300–600 mg before bedtime |
Testosterone | 600 mg/day |
Muscle and strength | 600 mg/day |
Fertility | 600 mg/day |
Anti-inflammatory | 250–600 mg/day |
Cognition | 300–600 mg/day |
Ashwagandha dosing timing
Timing
1️⃣ Morning vs Night Use
🌞 Morning Use
Suitable for:
✔️ Reducing daily stress
✔️ Improving focus and sustained energy
✔️ Managing cortisol levels throughout the day
📌 Advantage:
✅ By modulating the HPA axis, ashwagandha helps balance the body’s response to daily stressors.
✅ A better choice for individuals who experience morning anxiety or work-related pressure.
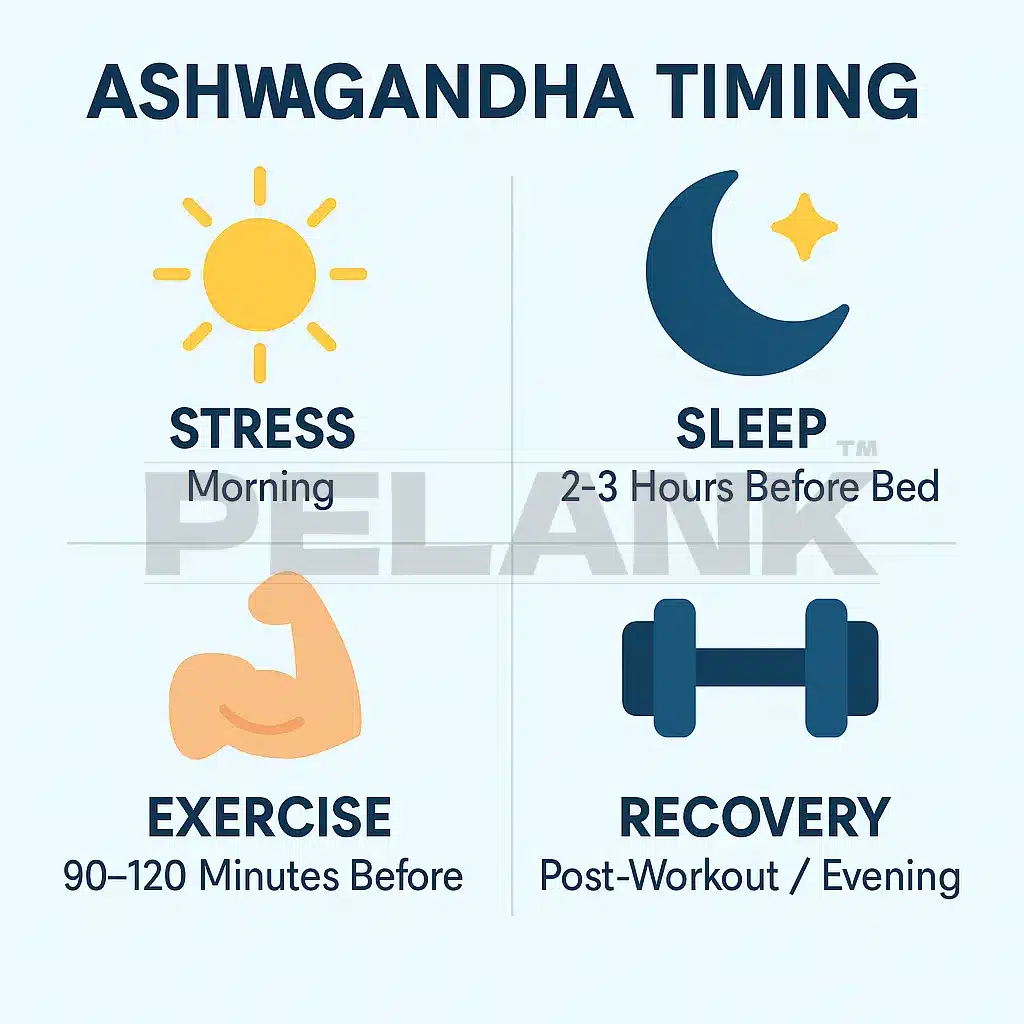
🌙 Night Use
Suitable for:
✔️ Improved sleep
✔️ Reducing nighttime anxiety
✔️ Relaxation before sleep
📌 Advantage:
✅ Some individuals experience calming and relaxing effects from ashwagandha within 2–3 hours after intake.
✅ If you struggle with insomnia, racing thoughts at night, or end-of-day stress, nighttime use is more suitable.
⚠️ Note:
Sensoril is generally more sedating and works better for nighttime use.
KSM-66 is more versatile and can be used both in the morning and at night.
2️⃣ Pre-Workout or Post-Workout Use?
🔥 Pre-Workout
Suitable for:
✔️ Reducing the physiological stress of training
✔️ Improving focus
✔️ Better performance during intense workouts
⏱️ Best timing:
✔️ 90–120 minutes before training
📌 Why?
✅ Reduced cortisol → smoother training sessions
✅ Improved neuromuscular focus
✅ Increased fatigue threshold
🧘 Post-Workout
Suitable for:
✔️ Better recovery
✔️ Reduced inflammation
✔️ Lower post-exercise cortisol after high-intensity workouts
📌 When it’s most useful:
✅ If training is done in the evening or at night
✅ If it’s difficult to relax after workouts
✅ If recovery is slow or muscle soreness is significant
3️⃣ With Food or on an Empty Stomach?
🍽️ With Food
Better
✅ Withanolide absorption is fat-soluble → better absorption when taken with food.
✅ Reduces gastrointestinal side effects (such as nausea in some individuals).
📌 Best approach:
✔️ Take with a small meal containing healthy fats
✔️ Such as: eggs, avocado, nuts, Greek yogurt.
🌿 On an Empty Stomach
For faster effects in some individuals
✔️ May slightly speed up onset of effects
⚠️ But the risk of stomach discomfort is higher.
✔️ Suitable for individuals seeking increased morning energy.
4️⃣ Suitable for Shift Work?
Shift Workers
For individuals working night shifts:
🌙 If you work at night:
Take ashwagandha before starting your shift → reduced stress and improved focus
Take it after the shift and before daytime sleep → improved sleep quality
🌅 If you have rotating shifts:
The best timing is your most consistent sleep–wake period
Ashwagandha regulates the “stress rhythm,” not the circadian rhythm
Therefore, take it at the time when you most need relaxation or stress control
✨ Quick Timing Guide
Purpose | Best Time to Take |
|---|---|
Daily stress | Morning |
Sleep | 2–3 hours before sleep |
Focus and energy | Morning or before work |
Exercise (performance enhancement) | 90–120 minutes before training |
Recovery | Immediately after training or in the evening |
Night shift | Before the shift + before daytime sleep |
Gastrointestinal side effects | With food |
Duration of Ashwagandha Effects
Onset of Effects
⏱️ Onset of action
🌿 The onset of ashwagandha’s effects in most individuals occurs within 3 to 7 days.
📌 Early effects commonly reported include:
✔️ Mild reduction in anxiety
✔️ Improved mental calmness
✔️ Easier, more restful sleep
✔️ Better daytime focus
⚠️ However, this is only the initial phase; the primary effects emerge as active compounds gradually accumulate.
📈 Peak Effect Timing
🔥 Based on clinical trials, the peak effects of ashwagandha occur between 6 and 8 weeks.
During this time frame:
✔️ Cortisol reduction reaches its maximum
✔️ Sleep benefits become stable and more pronounced
✔️ Increases in testosterone are observed around weeks 8–12 in studies
✔️ Athletic performance improves significantly
✔️ Mood and focus show the greatest improvements
🔗 References:
Cortisol and stress:
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23439798
Sleep:
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32818573
Testosterone/strength:
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26609282
🔄 Should ashwagandha be cycled or taken continuously?
Cycling vs Continuous Use
Continuous Use
Most scientific studies have evaluated ashwagandha when taken daily and continuously for 6 to 12 weeks.
Conclusion:
✔️ Stable and cumulative effects
✔️ Good tolerability
✔️ No evidence of tolerance or dependence
Cycled Use
Some experts recommend:
✅ 8 weeks of use → 2 weeks off
✔️ This recommendation is based mainly on user experience rather than strict scientific necessity.
📌 Therefore:
✅ If you have a specific therapeutic goal (stress, focus, sleep), continuous use for 8–12 weeks is the best option.
✅ If using ashwagandha for longer than 3 months, it is advisable to include a 10–14 day break every few months to help maintain hormonal balance and reduce the risk of tolerance.
📅 Standard 8–12 Week Protocol
Recommended Protocol
⭐ 8-week protocol (for stress, sleep, focus):
Weeks 1–2 → 300–600 mg/day
Weeks 3–8 → 600 mg/day consistently
Assess sleep quality and stress levels at the end of week 8
⭐ 8–10 week protocol (for muscle, strength, testosterone):
Weeks 1–2 → 300 mg × 2/day
Weeks 3–8 → 600 mg consistently
Strength and muscle growth results typically peak from week 6 onward
🔗 Resistance training study:
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26609282
⭐ 12-week protocol (for fertility and mood-related issues):
600 mg/day (Sensoril or KSM-66)
Testosterone and sperm quality effects are most pronounced at weeks 10–12
🔗 Fertility study:
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35060110
✨ Quick Guide to Effect Timeline
Effect | Onset | Peak |
|---|---|---|
Stress Reduction | 3–7 days | 6–8 weeks |
Sleep | 3–5 days | 4–6 weeks |
Testosterone | 3–4 weeks | 8–12 weeks |
Muscle and strength | 2–4 weeks | 6–8 weeks |
Mood and focus | 1–2 weeks | 6–8 weeks |
Side Effects of Ashwagandha
😐 Common Side Effects
Mild & Common Side Effects
🌿 Mild gastrointestinal issues
Bloating
Nausea
Mild diarrhea
📌 These usually occur when ashwagandha is taken on an empty stomach or at higher doses.
😴 Drowsiness or excessive relaxation
More commonly observed with leaf-based extracts such as Sensoril.
If taken in the afternoon, it may cause an overly calming effect.
🤕 Mild headache
Rare, but reported in some individuals with higher sensitivity.

⚠️ Rare Side Effects
🫀 Mild increases or decreases in blood pressure
Some individuals are sensitive to adaptogenic compounds.
This is usually observed in people with hypertension or those taking blood pressure medications.
🥵 Increased body warmth
In some warm-natured individuals, it may cause a sensation of heat or flushing.
🧠 Transient mood changes
Very rare
May occur at the beginning of use, before neurological effects stabilize.
🦋 Thyroid Effects
Thyroid Effects
🔺 Mild increases in T3 and T4 hormones
Studies indicate that ashwagandha may improve thyroid levels in individuals with mild hypothyroidism.
🔗 Source:
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28829155
🔻 Reduced TSH
This can be dangerous for individuals with hyperthyroidism.
⚠️ Serious warning:
Individuals with the following conditions should consult a physician before use:
🚫 Hyperthyroidism
🚫 Autoimmune thyroid diseases (Hashimoto’s / Graves’)
🚫 Use of thyroid medications (levothyroxine)
🩺 Gastrointestinal Effects
GI Effects
🍽️ Most common GI effects:
Abdominal cramping
Heartburn
Nausea
Mild diarrhea
📌 Solution:
Taking it with food
Dividing the dose into two servings
Choosing KSM-66 instead of Sensoril or Shoden (it is milder)
🚨 High-Risk Dosages
⚠️ Intake above 1500 mg/day may lead to:
Severe nausea
Diarrhea
Deep drowsiness
Low blood pressure
Unwanted hormonal changes
⚠️ Doses above 2000 mg/day have been associated in some case reports with:
Liver toxicity in susceptible individuals
Marked increases in thyroid hormone levels
Severe gastrointestinal issues
🔗 Safety review article:
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33170467
🚫 Warnings
Contraindications & Warnings
❌ Pregnancy
Ashwagandha may have uterotonic effects (stimulating uterine contractions).
Not recommended.
❌ Breastfeeding
There is insufficient evidence → best avoided.
❌ Autoimmune diseases
May mildly stimulate the immune system.
Should be used with caution in autoimmune conditions such as MS, lupus, and RA.
❌ Concomitant use with sedatives / anti-anxiety medications
Increased risk of excessive sedation and drowsiness.
❌ Use with thyroid medications
May alter the required dosage of levothyroxine.
❌ Presence of active liver disease
Rare cases of liver injury have been reported, but the exact cause remains unclear.
✨ Quick Guide to Side Effects
Category | Description |
|---|---|
Common | Gastrointestinal issues, sedation, headache |
Rare | Blood pressure changes, mood changes, flushing |
Thyroid | Increased T3/T4 – caution in hyperthyroidism |
Dangerous | High doses of 1500–2000 mg |
Contraindications | Pregnancy, breastfeeding, active autoimmune diseases, psychiatric medications |
Ashwagandha Drug Interactions
Drug Interactions
⚠️ Important note: This section does not replace medical advice; anyone taking medications should consult a physician or pharmacist before starting ashwagandha.
🦋 Thyroid Medications
🧾 Ashwagandha may slightly increase T3 and T4 levels and reduce TSH in some individuals.
💊 If you are taking levothyroxine or other thyroid medications:
⚠️ The medication’s effect may become stronger, potentially pushing you into a hyperthyroid range.
🩺 TSH and T3/T4 levels should be monitored under medical supervision.
🚫 Generally not recommended for individuals with uncontrolled hyperthyroidism or Graves’ disease.

😴 Benzodiazepines and Sedatives
Such as: diazepam, alprazolam, clonazepam, lorazepam, zolpidem, zopiclone, etc.
😴 Ashwagandha itself has mild sedative effects;
When combined with these medications:
⚠️ Drowsiness, mental fog, and reduced concentration may increase.
🚗 The risk during driving and operating machinery is higher.
📌 If taken together, the ashwagandha dose should be low and must be discussed with a physician.
🙂 Antidepressants
Classes:
SSRIs → such as sertraline, fluoxetine, citalopram
SNRIs → such as duloxetine, venlafaxine
TCAs and others
🧠 Ashwagandha affects GABA and serotonin pathways; theoretically:
It may slightly enhance the sedative or anxiolytic effects of these medications.
⚠️ At high doses combined with multiple psychiatric medications, the risk of drowsiness, confusion, and—at least theoretically—serotonin syndrome may increase (there is no strong clinical evidence, but caution is important).
✅ General rule:
If you are taking one antidepressant → use a moderate dose of ashwagandha under medical supervision.
If you are taking multiple psychiatric medications simultaneously → it is better to avoid ashwagandha unless approved by a psychiatrist.
🦠 Immunotherapy and Autoimmune Medications
Example :
Immunosuppressive drugs (high-dose corticosteroids, methotrexate, cyclosporine, tacrolimus, biologics such as infliximab, etc.)
Medications for autoimmune diseases (RA, MS, lupus, etc.)
🌿 Ashwagandha has shown mild immune-stimulating effects in some studies.
⚠️ Therefore:
In individuals receiving immunotherapy, it could theoretically interfere with the drug’s intended effect (immune suppression).
In some autoimmune diseases, there is a theoretical risk of disease exacerbation (definitive evidence is limited, but caution is warranted).
🚫 Practical recommendation:
If you are using immunosuppressive medications → do not use ashwagandha unless your physician approves it.
🍬 Diabetes Medications
Antidiabetic Drugs
Such as: metformin, glibenclamide, insulin, etc.
🧪 Some small studies suggest that ashwagandha may slightly lower blood glucose levels.
⚠️ When combined with blood sugar–lowering medications:
The risk of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) may increase slightly, especially if you are also following a strict diet or engaging in intense exercise.
Blood glucose should be monitored regularly, and symptoms such as dizziness, cold sweats, and tremors should be taken seriously.
✅ Solution:
Start with a low dose of ashwagandha
Inform your diabetes physician so medication doses can be adjusted if necessary
🩺 Blood Pressure Medications
Antihypertensives
Example : Losartan, enalapril, amlodipine, bisoprolol, etc.
🌿 Due to its calming and stress-reducing effects, ashwagandha may slightly lower blood pressure in some individuals.
⚠️ When combined with blood pressure medications, especially beta-blockers and potent antihypertensives:
Risk of hypotension (low blood pressure):
Dizziness
Blackout sensation when standing up
Weakness
✅ Recommendation:
Start with a low dose
Monitor blood pressure during the first few days
If a significant drop occurs, discontinue ashwagandha and contact a physician
✨ Quick Guide to Drug Interactions
Drug category | Type of interaction | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|
Thyroid | Increased drug effect, risk of hyperthyroidism | Strict medical supervision, laboratory monitoring required |
Benzodiazepines / Sedatives | Increased drowsiness | Use with caution, avoid driving |
Antidepressants | Enhanced sedative effect, theoretical serotonin risk | Moderate dosing, coordinate with a psychiatrist |
Immunotherapy / Autoimmune | Potential interference with immune suppression | Generally not recommended |
Diabetes | Risk of hypoglycemia | Regular glucose monitoring, low dose |
Blood pressure | Risk of hypotension | Monitor blood pressure, low dose |
Ashwagandha and Bodybuilding
Ashwagandha for Athletes
👨🏻🦱 Effects on Testosterone
Testosterone Enhancement
🧪 Studies show that ashwagandha can increase testosterone levels by 10–15% in male athletes or individuals under high stress.
📌 Reasons:
Reduced cortisol → less inhibition of testosterone production
Improved sleep → increased hormone production
Anti-inflammatory effects → improved testicular function
🔗 Source:
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30854916
💪 Increased Muscle Strength
Strength Gains
🌿 In 8-week resistance training studies, ashwagandha has led to significant increases in 1RM for the bench press and deadlift.
📌 Results:
Increased explosive strength
Increased muscular endurance
Faster progress in resistance training
🔗 Source:
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26609282
🔄 Improved Recovery
Recovery Acceleration
🏋️ Intense training increases cortisol and leads to inflammation and muscle damage.
Ashwagandha works by:
Reducing CK (a marker of muscle damage)
Reduced CRP and IL-6
Reduced oxidative stress
Helps accelerate recovery.
📌 Results:
Less muscle soreness
Greater capacity for the next training session
Lower risk of overtraining

🥱 Fatigue Reduction
Ashwagandha increases VO₂max and reduces perceived fatigue.
📌 Studies show that:
Athletes using ashwagandha demonstrate greater endurance compared to placebo.
Neuromuscular fatigue develops later.
🔗 Source:
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25286463
😴 Improved Sleep
Sleep Optimization
High-quality sleep → faster muscle recovery → better growth.
🌿 Ashwagandha:
Reduces sleep onset time
Improves deep sleep quality
Promotes pre-sleep relaxation by lowering cortisol
🔗 Source:
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32818573
🩸 Post-Workout Cortisol Control
Elevated cortisol after training leads to:
Muscle breakdown
Reduced recovery
Reduced testosterone
Ashwagandha helps suppress this response.
📌 Results:
Improved protein synthesis
Faster recovery
Greater muscle growth
🔗 Source:
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23439798
⭐ Athlete Supplement Protocol
🟢 Goal: Increase in strength and muscle mass
💊 600 mg KSM-66 daily
⏱️ 90–120 minutes before training or with breakfast
📅 Duration: 8 to 12 weeks
🔵 Goal: Recovery and reduced muscle soreness
💊 300–600 mg post-workout
📅 Minimum of 4–6 weeks
🟡 Goal: Natural testosterone increase
💊 600 mg/day (preferably KSM-66)
📅 Main effects from weeks 6–12
🔴 Goal: Focus and stress reduction before competition
💊 300 mg in the morning
💊 300 mg before training / competition
⚠️ For high-stakes competitions, it is best to test this protocol 7–10 days in advance.
🟣 Goal: Better sleep for recovery
💊 300–500 mg before bedtime
📌 Sensoril or Shoden are more sedating.
✨ Quick Guide for the Bodybuilding Section
Purpose | Result | Dosage |
|---|---|---|
Testosterone | ↑ 10–15% | 600 mg/day |
Strength | ↑ Bench/Deadlift | 600 mg/day |
Recovery | ↓ CK / ↓ inflammation | 300–600 mg/day |
Fatigue | ↑ Vo₂max | 300–600 mg/day |
Sleep | ↑ Sleep quality | 300–500 mg/night |
Cortisol | ↓ 20–30% | 600 mg/day |
Common Myths About Ashwagandha
Myths & Misconceptions
❌ Is ashwagandha a steroid?
💊 No, absolutely not!
Ashwagandha is a medicinal herb, not an anabolic steroid.
🌿 Its active compounds are withanolides, which have anti-inflammatory and anti-stress effects—they have no similarity to testosterone or steroid drugs.
📌 This myth likely exists because some studies show a mild increase in testosterone with ashwagandha; however, these changes are natural and limited, not steroid-like.
❌ Is ashwagandha addictive?
Strength Gains
🧠 No. There is no evidence of addiction or dependence.
Unlike sedative medications such as benzodiazepines, ashwagandha:
Does not overstimulate or saturate receptors
Has stable, non-progressive tolerance
Does not cause withdrawal symptoms when discontinued
📌 It can be discontinued at any time without difficulty.
❌ Is ashwagandha safe for everyone?
⚠️ No.
Although ashwagandha is safe for most people, it is not suitable for certain groups:
🚫 Pregnant women
🚫 Individuals with hyperthyroidism
🚫 Patients with autoimmune diseases (MS, RA, lupus)
🚫 Individuals using sedative medications
🚫 People with liver disorders
📌 Therefore, “safe for everyone” is a completely false belief.
❌ Does ashwagandha always cause drowsiness?
😴 No, that’s not the case.
The effects of ashwagandha depend on the extract type, timing of use, and dosage.
🔹 Sensoril → more sedating
🔹 KSM-66 → more balanced and better suited for daytime use
🔹 Shoden → potent, but does not always cause drowsiness
📌 Some people use it to improve focus and energy during the day.
❌ Does ashwagandha always increase testosterone?
🧪 No. This is a common misconception.
Increases in testosterone are only observed under the following conditions:
✔ Men with high stress levels
✔ Individuals with low–normal testosterone levels
✔ Use of 600 mg/day for at least 8–12 weeks
✔ Combined with adequate sleep and regular training
❌ If testosterone levels are already normal and healthy, no significant change usually occurs.
❌ In women, no undesirable hormonal increases have been reported.
✨ Quick Guide to Common Myths
Myth | Reality |
|---|---|
“Ashwagandha is a steroid” | ❌ A medicinal herb → no similarity to steroids |
“Addictive” | ❌ Does not cause dependence |
Safe for everyone | ❌ Some groups should not use it |
Always causes drowsiness | ❌ It depends on the extract type and dose |
Always increases testosterone | ❌ It only affects certain individuals |
How to Choose a High-Quality Supplement
Choosing a Quality Ashwagandha Supplement
Choosing the wrong ashwagandha supplement =
❌ Weak effectiveness
❌ Higher risk of side effects
❌ Money wasted
Choosing the right one =
✅ Maximum effectiveness
✅ High safety
✅ Real, evidence-based results
Let’s break down the best choice step by step:

🧪 Withanolide Percentage
The Most Important Selection Criterion
🌿 Withanolides are the main active compounds in ashwagandha.
The more precisely defined and consistent their percentage, the more reliable the supplement.
📌 Standard ranges:
5% → Balanced, suitable for daily use (KSM-66)
10–12% → More potent, more calming effects (Sensoril)
20–35% → Very potent, lower dosing, suitable for high-potency formulas (Shoden)
⚠️ Be careful:
Some low-quality brands report higher percentages using UV methods, which are not accurate.
True measurement should be done using HPLC.
⚗️ Extract Standardization
🔍 The following should be clearly stated on the label:
✔ Standardized Extract
✔ Clearly specified withanolide percentage
✔ Standardization method: HPLC
Why is this important?
Plain ashwagandha powder contains highly variable levels of active compounds.
Standardized extracts provide consistent and predictable effects.
Nearly all high-quality studies have been conducted using standardized extracts.
If the label only states:
❌ “Ashwagandha Root Powder”
Be aware that the effectiveness is significantly lower.
🧯 Heavy Metals Testing
⚠️ Medicinal plants like ashwagandha can absorb heavy metals:
Lead (Pb)
Arsenic (As)
Mercury (Hg)
Cadmium (Cd)
For this reason, the brand should provide the following:
✔ Certified heavy metal testing
✔ A visible COA (Certificate of Analysis)
✔ Independent third-party laboratory testing
📌 Professional brands usually publish their COA on their website.
🧾 Brand Transparency
A reputable brand should:
🔎 Clearly state the source of the plant
India? USA? Organic farms?
📄 Explain the extraction process
Alcohol-free?
Green extraction?
Water-based?
🧪 Publish quality testing results
COA
Heavy Metals
Microbial Testing
🛡️ Certifications:
USDA Organic
Non-GMO
GMP Certified
Gluten-Free
ISO Lab Tested
The greater the brand transparency → the higher the scientific trust.
🌍 Top 5 Global Ashwagandha Brands
These are brands referenced in scientific studies or recognized for top-tier quality in the U.S. market:
🥇 1. KSM-66 (Ixoreal Biomed)
The most reputable full-spectrum extract in the world
The highest number of clinical trials
5% withanolides
Best for: stress, testosterone, muscle, sleep
🥈 2. Sensoril (Natreon)
Contains root + leaf
10–12% withanolides
Stronger calming effects
Best for: severe anxiety, sleep
🥉 3. Shoden (Arjuna Natural)
35% withanolides (very potent)
Higher bioavailability at lower doses
Best for: rapid effects, premium formulations
⭐ 4. Himalaya Organic Ashwagandha
A classic, organic, well-known brand
Suitable for general use
Lower withanolide percentage compared to specialized extracts
⭐ 5. Gaia Herbs Ashwagandha
Liquid PhytoCaps
Organic, gentle formulation
Suitable for beginners or sensitive users
✨ Quick Guide to Choosing a High-Quality Supplement
Criteria | Why is this important? | What should you choose? |
|---|---|---|
Withanolide percentage | Determines potency | 5–12% for general use; 20–35% for high potency |
Standardized extract | Consistent, evidence-based effects | KSM-66 / Sensoril / Shoden |
Heavy Metal Testing | Prevents contamination | COA + independent laboratory |
Brand transparency | Trust and quality | Brands with complete testing reports |
Brand selection | Effectiveness and safety | KSM-66, Sensoril, Shoden, Gaia, Himalaya |
Who Should / Shouldn’t Use Ashwagandha
Population-Based Guide
👨🏻 Men
✔ Men who benefit the most:
💪 Men under high stress
🩸 Men with low–normal testosterone
🏋️ Athletes or bodybuilders
🧠 Men with anxiety or concentration issues
❌ Men who should use caution:
⚠️ Thyroid disorders (especially hyperthyroidism)
⚠️ Users of sedative medications
⚠️ Active autoimmune diseases
👩🏻 Women
✔ Women who may benefit:
🌿 Women experiencing stress, insomnia, or fatigue
🧠 Women with anxiety or low mood
🏋️ Female athletes needing better recovery
📌 Note: Ashwagandha does not cause abnormal increases in testosterone in women.
❌ Women who should not use it:
🚫 Pregnancy
🚫 Breastfeeding
🚫 Hyperactive thyroid
😟 Stressed Individuals
✔ Suitable for:
🧠 People with work-related stress
📚 Students under academic pressure
📈 Managers and employees with heavy workloads
😵 Individuals with daily anxiety or stress episodes
📌 Ashwagandha works best in individuals with elevated cortisol levels.
❌ Use with caution:
⚠️ Individuals with severe depression or those taking psychiatric medications should inform their physician.
⛹🏻 Athletes
✔ Best candidates for use:
💪 Strength-training athletes
🏃 Endurance athletes
🔥 Individuals experiencing mild overtraining
😴 Athletes with poor sleep quality
📌 In this group, ashwagandha:
Improves athletic performance
Accelerates recovery
Reduces neuromuscular fatigue
❌ Use with caution:
⚠️ Athletes taking sedative medications
⚠️ Athletes with thyroid disorders
🦋 Thyroid Patients
✔ May be beneficial for:
🔹 Individuals with mild (subclinical) hypothyroidism
🔹 Reducing fatigue and stress secondary to thyroid dysfunction
❌ Should not be used by:
🚫 Individuals with hyperthyroidism
🚫 Patients with Graves’ disease
🚫 Those with unstable levothyroxine dosing
⚠️ Ashwagandha may increase T3/T4 levels → dangerous in hyperthyroidism.
🛡️ Individuals with Immune Disorders
❌ Use with extreme caution or avoid:
🚫 Patients with MS
🚫 Patients with lupus
🚫 Patients with active rheumatoid arthritis
🚫 Users of immunosuppressive medications (such as high-dose corticosteroids, methotrexate, cyclosporine)
📌 Reason:
Ashwagandha may mildly stimulate the immune system.
✔ Use only with specialist supervision:
🟡 Individuals with a history of autoimmune disease but currently inactive
🟡 Those not using biologic therapies
👩🏻🦳 Older Adults
✔ May be beneficial for:
🧠 Improved memory
😴 Better sleep
💪 Improved quality of life
🔥 Stress management
❌ Use with caution:
⚠️ Individuals on multiple medications (polypharmacy)
⚠️ Users of blood pressure or sedative medications
⚠️ Those with liver or thyroid disorders
📌 Older adults should start with a low dose (150–300 mg).
✨ Quick Population-Based Guide
Group | Suitable | Not suitable / Use with caution |
|---|---|---|
Men | High stress, training, low–normal testosterone | Active thyroid disease, sedatives |
Women | Stress, sleep, exercise | Pregnancy / breastfeeding, thyroid disorders |
Stressed individuals | Highly suitable | Severe depression + medication |
Athletes | Highly effective | Thyroid disorders |
Thyroid patients | Only mild hypothyroidism | Hyperthyroidism, Graves’ disease |
Autoimmune | – | Active MS, lupus, RA |
Seniors | Beneficial at low doses | Low blood pressure, sedatives |
Pelank Self-Assessment Quiz
“Is ashwagandha right for you?”
👇 Answer each question with “Yes / No”:
🧠 1. Have you experienced significant stress or mental tension in the past week?
😴 2. Do you have sleep problems, difficulty falling asleep, or frequent awakenings?
😓 3. Do you feel that your fatigue is not fully relieved even with rest?
💪 4. Has your training capacity or strength declined over the past month?
🧔 5. Has your doctor told you that your testosterone is in the low–normal range?
📈 6. Do you experience anxiety or intrusive thoughts in daily life?
🍃 7. Are you looking for a natural supplement to manage stress and improve sleep?
⚠️ Precautions (Important!)
If you answer “Yes” to any of the following, you should consult a physician before use:
🦋 8. Do you have an active thyroid condition (especially hyperthyroidism)?
🛡️ 9. Do you have an active autoimmune disease or are you using immunosuppressive medications?
🤰 10. Are you pregnant or planning to become pregnant?
💊 11. Are you taking sedatives, antidepressants, or strong psychiatric medications?
💉 12. Do you have diabetes and use medication?
⭐ Quiz Results
Interpretation Guide
✅ If you answered “Yes” to 4–7 questions:
Ashwagandha is likely to be beneficial for you—especially for stress, sleep, focus, and recovery.
⚠️ If you answered “Yes” to 1–3 questions:
It may be helpful, but it’s best to first clarify your specific goal for use.
🚫 If you answered “Yes” to even one question in the “Precautions” section:
You should consult a physician before using ashwagandha.
Scientific Quick Review Table
Quick Evidence Summary Box
🎯 Goal | 📊 Level of Evidence | 🧪 Scientific outcome | 💊 Standard dosage |
|---|---|---|---|
Stress Reduction | 🅰️ Strong | 27–30% reduction in cortisol, reduced anxiety | 300–600 mg/day (KSM-66) |
Improving sleep | 🅱️ Moderate–strong | Improved sleep quality, reduced sleep onset time | 120–300 mg at night; or 600 mg/day |
Cognitive enhancement | 🅱️ Moderate | Improved focus, memory, and processing speed | 300–600 mg/day |
Male testosterone | 🅱️ Moderate | 10–15% increase in testosterone in stressed or overweight men | 600 mg/day |
Strength and muscle | 🅱️ Moderate | Increased 1RM, increased muscle mass, reduced CK | 600 mg/day (8–12 weeks) |
Anti-inflammatory / recovery | ©️ Emerging | Reduced CRP and IL-6; improved recovery | 250–600 mg/day |
Explanation of evidence levels:
- A = Strong: multiple RCTs + meta-analyses
- B = Moderate: several well-designed RCTs
- C = Emerging: preliminary data / limited studies
Frequently Asked Questions
FAQ
💬 Yes. Most human studies have examined daily use for 6–12 weeks, and no issues have been reported in healthy individuals. However, for longer-term use (several consecutive months), it’s better to take a 10–14 day break every 2–3 months. If you are taking medications, consult your physician.
💬 It does not directly cause weight gain or weight loss. However, by reducing stress and improving sleep, it may help regulate appetite and hormones. In some people, appetite may increase slightly, while in others it may decrease. There is still no strong evidence supporting its use for weight loss.
💬 It is absolutely suitable for women as well—especially for stress, anxiety, sleep, and fatigue. No increase in testosterone has been reported in women, and there are no major hormonal concerns. It is simply not recommended during pregnancy or breastfeeding.
💬 There is no strong direct evidence. Indirectly, by reducing stress and balancing hormones, it may help improve hair health in some individuals, but it should not be considered a treatment for hair loss.
💬 Yes. Many people in the U.S. take ashwagandha with their morning coffee. Ashwagandha may help blunt caffeine-related stress and palpitations. If your caffeine intake is very high or you are prone to anxiety, start with a lower dose first.
💬 Yes. In healthy individuals, no interactions have been observed with multivitamins, whey protein, creatine, or most sports supplements. Just be mindful if your pre-workout formula contains strong stimulants—keep dosages reasonable.
💬 There is no clear evidence of a direct interaction with oral contraceptives. However, since ashwagandha can influence hormones and liver metabolism, if you are using birth control pills, it’s best to consult your physician or gynecologist before long-term use.
💬 It can be helpful for mild to moderate anxiety and everyday stress. However, in severe conditions such as panic disorder or severe generalized anxiety, ashwagandha is not a replacement for psychiatric treatment or psychotherapy and should only be used as a supportive aid.
💬 Some individuals report improved focus, and limited studies suggest cognitive benefits. However, evidence for treating ADHD is still weak. If you are taking ADHD medications (such as methylphenidate/Ritalin), you should coordinate with your physician.
💬 If depression is mild and well-controlled, some physicians in the U.S. consider ashwagandha as a supportive supplement for stress and sleep. However, in moderate to severe depression—especially when strong medications are involved—do not start it on your own; consult a psychiatrist first.
💬 Nothing serious happens; you may simply notice less effect that day. Resume your normal routine the next day and do not double the dose.
💬 Most studies focus on 8–12 week periods, but overall safety data suggest that at standard doses it is well tolerated in most healthy individuals. For very long-term use, it is best to:
- Take a 10–14 day break every 2–3 months
- Have blood tests once a year and check thyroid and liver function, especially if you use other supplements as well.
💬 Almost all studies have been conducted in adults over 18 years old. Use in adolescents requires direct medical supervision. For those under 18, it’s better to focus on sleep, nutrition, and non-supplement stress management strategies.
Scientific Sources & References
📚 References
Chandrasekhar K, Kapoor J, Anishetty S.
A prospective, randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled study of safety and efficacy of a high-concentration full-spectrum extract of Ashwagandha root in reducing stress and anxiety in adults. Indian J Psychol Med. 2012. Accessed December 11, 2025.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23439798/Lopresti AL, Smith SJ, Malvi H, Kodgule R.
An investigation into the stress-relieving and pharmacological actions of an ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) extract: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. Accessed December 11, 2025.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31517876/Arumugam V, et al.
Effects of Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) extract on stress and anxiety: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Complement Ther Med. 2024. Accessed December 11, 2025.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1550830724001691Wiciński M, et al.
Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) and its effects on well-being: A comprehensive review. Nutrients. 2025. Accessed December 11, 2025.
https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/17/13/2143Office of Dietary Supplements, National Institutes of Health.
Ashwagandha: Health professional fact sheet. NIH ODS website. Accessed December 11, 2025.
https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Ashwagandha-HealthProfessional/Langade D, Kanchi S, Salve J, Debnath K, Ambegaokar D.
Efficacy and safety of Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) root extract in insomnia and anxiety: A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study. Cureus. 2020. Accessed December 11, 2025.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32818573/Cheah K, et al.
Effect of ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) on sleep: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2021. Accessed December 11, 2025.
https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0257843Gopukumar K, et al.
Efficacy and safety of Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) root extract on cognitive functions in healthy, stressed adults: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. Accessed December 11, 2025.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34858513/
(Free full text: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8632422/)Lopresti AL, Drummond PD, Smith SJ.
A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover study examining the hormonal and vitality effects of ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) in aging, overweight males. Am J Mens Health. 2019. Accessed December 11, 2025.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30854916/Lopresti AL, et al.
Ashwagandha for the treatment of stress and anxiety: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Altern Complement Med. 2019. Accessed December 11, 2025.
https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/1557988319835985Revibe Men’s Health.
Ashwagandha and testosterone: The science behind the link. Revibe Men’s Health website. Accessed December 11, 2025.
https://revibemenshealth.com/blog-and-news/ashwagandha-and-testosterone-the-science-behind-the-link/Wankhede S, Langade D, Joshi K, Sinha SR, Bhattacharyya S.
Examining the effect of Withania somnifera supplementation on muscle strength and recovery: A randomized controlled trial. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2015. Accessed December 11, 2025.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26609282/
(Free full text: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4658772/)Verma N, et al.
Effects of Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) root extract on muscle strength, growth, and endurance during resistance training: A randomized, placebo-controlled trial in men and women. Nutrients. 2024. Accessed December 11, 2025.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38988644/Cheah K.
Ashwagandha for sleep: How does it work? Healthline website. Published 2023. Accessed December 11, 2025.
https://www.healthline.com/health/sleep/ashwagandha-for-sleepMITO Health.
The power of ashwagandha for muscle growth, strength and recovery. MITO Health website. Accessed December 11, 2025.
https://mitohealth.com/blog/the-power-of-ashwagandha-for-muscle-growth-strength-and-recoverySharma AK, Basu I, Dasgupta A.
Efficacy and safety of Ashwagandha root extract in subclinical hypothyroid patients: A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. J Altern Complement Med. 2018. Accessed December 11, 2025.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28829155/Medical News Today.
Can ashwagandha benefit thyroid health? Medical News Today website. Updated 2023. Accessed December 11, 2025.
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/ashwagandha-and-thyroidVerma N, et al.
Safety of Ashwagandha root extract: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study in healthy volunteers. J Diet Suppl. 2021. Accessed December 11, 2025.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33338583/Elgar K.
Ashwagandha: A review of clinical use and efficacy. Nutritional Medicine Institute monograph. Accessed December 11, 2025.
https://www.nmi.health/ashwagandha-a-review-of-clinical-use-and-efficacy/Tohda C, Kuboyama T, Komatsu K.
Dendrite extension by methanol extract of ashwagandha (roots of Withania somnifera) in SK-N-SH cells. Neuroreport. 2000. Accessed December 11, 2025.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10884056/More SV, Koppula S, Kim IS, Kumar H, Kim BW, Choi DK.
The role of bioactive compounds on the promotion of neurite outgrowth. Molecules. 2012. Accessed December 11, 2025.
https://www.mdpi.com/1420-3049/17/6/6728Kurapati KRV, Atluri VS, Samikkannu T, et al.
Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) reverses β-amyloid1–42 induced toxicity in human neuronal cells: Implications in HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders (HAND). PLoS One. 2013. Accessed December 11, 2025.
https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0077624Sehgal N, Gupta A, Valli RK, et al.
Withania somnifera reverses Alzheimer’s disease pathology by enhancing low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein in liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. Accessed December 11, 2025.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22308347/
(Free full text: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3295277/)Kataria H, et al.
Water extract from the leaves of Withania somnifera protects RA differentiated C6 and IMR-32 cells against glutamate-induced excitotoxicity. PLoS One. 2012. Accessed December 11, 2025.
https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0037080Atteeq M, et al.
Evaluating anticancer properties of Withaferin A—a potent Withania somnifera constituent. Front Pharmacol. 2022. Accessed December 11, 2025.
https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2022.975320/fullZhang Q, Yuan L, et al.
Withanolides: Promising candidates for cancer therapy. Front Oncol. 2024. Accessed December 11, 2025.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38176694/Subbaraju GV, Vanisree M, Rao CV, et al.
Ashwagandhanolide, a bioactive dimeric thiowithanolide from the roots of Withania somnifera. J Nat Prod. 2006. Accessed December 11, 2025.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17190461/Jayaprakasam B, Padmanabhan K, Nair MG.
Withanamides in Withania somnifera fruit protect PC-12 cells from β-amyloid induced toxicity. Phytother Res. 2010. Accessed December 11, 2025.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19957250/Verywell Health.
Can ashwagandha help your anxiety? Here’s what the science says. Verywell Health website. 2025. Accessed December 11, 2025.
https://www.verywellhealth.com/ashwagandha-for-anxiety-11745628EatingWell.
The #1 herb to help reduce stress, according to dietitians. EatingWell website. 2025. Accessed December 11, 2025.
https://www.eatingwell.com/best-herb-to-reduce-stress-11717359
Pelank Life | Body Health Assessment
The Best Body Health Calculators Using Scientific Methods
Developed by Pelank Life ©

Mohsen Taheri
December 16, 2025