Introduction
✅ The gluteal and pelvic muscles not only contribute to the strength, stability, and shaping of the lower body, but also functionally stand out as one of the most important muscle groups in the body. According to Gray’s Anatomy, these muscles go beyond hip movement, acting as the body’s center of balance and stability in all daily and athletic activities.
These muscles play a vital role in basic movements like walking, running, jumping, twisting, and quick changes of direction. Additionally, the gluteal muscles and the deep pelvic muscles are key to stabilizing the hip joint, protecting the knees, maintaining proper spinal alignment, and preventing injuries in the lower back and knees.
🔹 According to the classification in Gray’s Anatomy, the pelvic and gluteal muscles are divided into three main groups:
✔ Superficial gluteal muscles: including the gluteus maximus, gluteus medius, and gluteus minimus, which are responsible for hip extension, abduction, and internal rotation.
✔ Deep pelvic muscles: consisting of the piriformis, internal obturator, external obturator, superior and inferior gemellus muscles, and the quadratus femoris, which handle external hip rotation and pelvic stabilization.
✔ Tensor fasciae latae (TFL): which, through the iliotibial band, helps stabilize the knee and control lateral movements of the hip.
From explosive and powerful movements in sports like weightlifting and sprinting to everyday activities such as standing, walking, and sitting, the gluteal and pelvic muscles play a fundamental role in overall body function and health. Weakness in these muscle groups can lead to pelvic imbalances, a higher risk of knee injuries, decreased athletic performance, and chronic lower back pain.
🔹 In this comprehensive review, we’ll analyze the structure, function, and significance of the gluteal and pelvic muscles, as well as explore the most effective ways to strengthen them and prevent injuries.

1. Superficial Gluteal Muscles
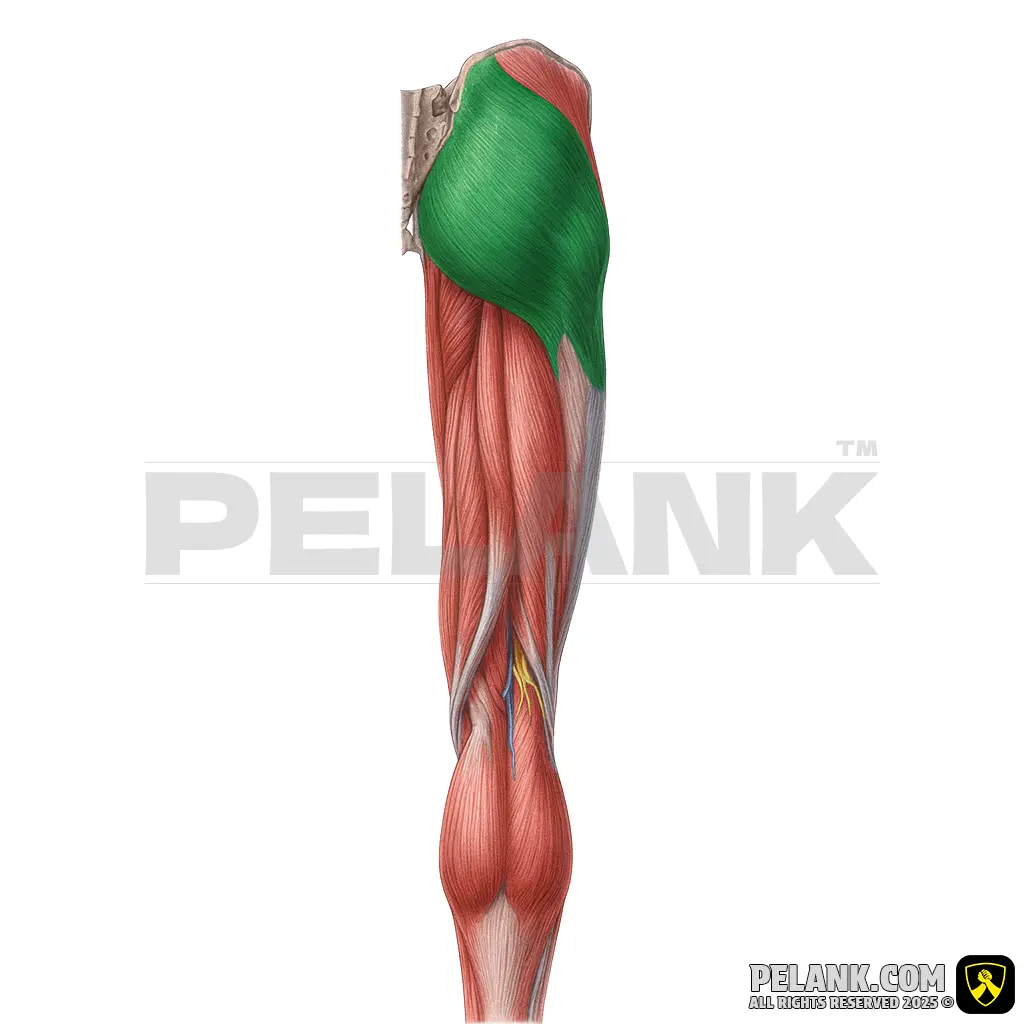
Gluteus Maximus Muscle
✅ The gluteus maximus is one of the most important and powerful muscles in the body, playing a crucial role in hip movement, balance, and pelvic stability. It is vital in strength-based exercises such as squats, deadlifts, and running, enhancing hip extension and pelvic stability.
🔷 Detailed description
Click on the title to read each section.
✅ Persian Name: Sorini Bozorg
✅ Latin Name: Gluteus Maximus
✅ Common Name: Buttock Muscle, Glutes
✅ Location:
🟡 Located at the back of the pelvis, lying over the other gluteal and thigh muscles.
🟡 It is the largest and most superficial muscle in the gluteal region.
🟡 Originates from the ilium (hip bone) and sacrum, attaching to the iliotibial band and the femur.
✅ 🦾 Origin
✔ Posterior surface of the ilium (Ilium)
✔ Posterior surface of the sacrum (Sacrum) and coccyx (Coccyx)
✔ Sacrotuberous ligament (Sacrotuberous Ligament)
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ Iliotibial band (IT Band)
✔ Gluteal tuberosity of the femur
✅ 📌 Function
1️⃣ Hip extension (moving the hip backward, as in deadlifts and climbing stairs)
2️⃣ External rotation of the hip (turning the thigh outward, like in lateral lunges)
3️⃣ Hip abduction and adduction (moving the thigh away from or toward the body, depending on muscle fibers)
4️⃣ Stabilizing the pelvis and knee through the iliotibial band (IT Band)
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Types
✔ Contains fast-twitch fibers (Type II) for powerful movements like deadlifts and squats.
✔ Also includes slow-twitch fibers (Type I) to maintain balance and stability during static positions.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Movement and Athletic Performance
✔ Bodybuilding: Engaged in key exercises like squats, deadlifts, and hip thrusts.
✔ Running and Jumping: Generates the force needed for propulsion and acceleration.
✔ Endurance and Balance: Supports static activities such as prolonged standing and walking.
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ The strongest muscle in the body when it comes to hip extension power.
✔ Weakness can lead to pelvic imbalance, increased lumbar lordosis (excessive lower back curve), knee pain, and reduced athletic performance.
🧠 Innervation
✔ Inferior gluteal nerve (L5, S1, S2)
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Superior and inferior gluteal arteries
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Weightlifting: Drives hip extension in deadlifts, squats, lunges, and hip thrusts
✔ Running and Jumping: Aids in acceleration and pelvic stabilization
✔ Resistance Sports: Enhances knee and pelvic stability for dynamic movements
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Interaction with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Works alongside the gluteus medius and minimus to control hip movements
✔ Collaborates with the hamstrings for hip extension and pelvic stabilization
✔ Stabilizes the knee through the iliotibial band (IT Band)
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ Weakness in the gluteus maximus increases the risk of lower back pain, knee problems, and poor balance.
✔ Insufficient strengthening can lead to muscle spasms and pain in the gluteal region.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Strength Training Exercises to Build the Gluteus Maximus
1️⃣ Deadlifts – the primary movement for hip extension
2️⃣ Hip Thrusts – directly target the gluteus maximus
3️⃣ Weighted Squats – a compound exercise strengthening both glutes and hamstrings
4️⃣ Lunges – work the gluteus maximus while challenging balance
5️⃣ Glute Bridge – an excellent exercise to engage the muscle at home
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery Exercises
✔ Glute Stretch to relieve muscle spasms and enhance function
✔ Pigeon Pose to increase gluteal flexibility and reduce lower back tension
✅ 🔬 Interesting Fact:
✔ The gluteus maximus plays the biggest role in shaping and powering the lower body.
✔ In professional athletes, this muscle is often highly developed due to intense training.
✅ 💡 Practical Tip:
✔ To better activate the gluteus maximus during workouts, start with activation exercises like bodyweight glute bridges and lunges before your main training.
🔴 Name and Location: The largest and most superficial muscle in the gluteal region, attaching to the hip bone (ilium) and the femur.
🟠 Anatomy: Originates from the ilium and sacrum, attaching to the gluteal tuberosity of the femur and the iliotibial band.
🟡 Function: Hip extension, external rotation, and stabilization of the pelvis and knee.
🟢 Physiology: A blend of slow-twitch and fast-twitch muscle fibers, providing both strength and endurance.
🔵 Innervation: Inferior gluteal nerve (L5, S1, S2)
🟣 Importance: Active during weightlifting, running, jumping, and lower body movements
🟤 Exercises: Deadlifts, hip thrusts, squats, lunges, glute bridges
⚫ Interesting Fact: The most important muscle for… shaping and strengthening the lower body, as well as preventing lower back pain.
Gluteus Medius Muscle
✅ The gluteus medius is one of the most important muscles of the pelvic region, playing a primary role in abduction (moving the thigh away from the body) and stabilizing the pelvis during walking. Weakness in this muscle can lead to issues such as knee pain, pelvic drop, and reduced balance.
🔷 Detailed description
Click on the title to read each section.
✅ Persian Name: Sorini Miyani
✅ Latin Name: Gluteus Medius
✅ Common Name: Glute Med
✅ Location:
🟡 Located on the side of the pelvis, positioned between the gluteus maximus and gluteus minimus.
🟡 Extends along the posterior-lateral aspect of the pelvis and provides much of the strength needed to stand on one leg.
🟡 Originates from the ilium and attaches to the femur.
✅ 🦾 Origin
✔ External surface of the ilium, between the anterior and posterior gluteal lines
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ Lateral surface of the greater trochanter of the femur
✅ 📌 Function
1️⃣ Hip abduction (moving the thigh away from the midline, like side leg raises)
2️⃣ Hip internal rotation (performed by the anterior fibers)
3️⃣ Hip external rotation (performed by the posterior fibers)
4️⃣ Pelvic stabilization during walking (prevents the pelvis from dropping on the opposite side when standing on one leg)
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Types
✔ A mix of slow-twitch fibers (Type I) for endurance and fast-twitch fibers (Type II) for explosive movements.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Movement and Athletic Performance
✔ Bodybuilding: Engaged during squats, deadlifts, lunges, and hip thrusts.
✔ Running and Quick Direction Changes: Plays a key role in thigh and pelvic stability.
✔ Balance and Body Stability: Crucial during walking, running, and jumping.
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ A key muscle for pelvic balance and lateral hip movements.
✔ Weakness can lead to issues such as a waddling gait (Trendelenburg gait) and knee problems.
🧠 Innervation
✔ Superior gluteal nerve (L4, L5, S1)
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Superior gluteal artery
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Bodybuilding: Engaged in lateral movements, lunges, squats, and deadlifts
✔ Running and Jumping: Plays a crucial role in direction changes and injury prevention
✔ Balance-focused Sports: Important in yoga, Pilates, and functional training exercises
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Interaction with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Works in coordination with the gluteus maximus, gluteus minimus, and hamstrings for stable movements.
✔ Supports the knee and pelvis to prevent balance-related injuries.
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ Weakness in the gluteus medius can cause pelvic drop during walking (known as the Trendelenburg sign).
✔ Strain or spasms in this muscle may lead to hip pain and walking difficulties.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Strength Training Exercises to Target the Gluteus Medius
1️⃣ Lateral Lunges – activate the hip abductors
2️⃣ Clamshells – strengthen external rotation and hip stability
3️⃣ Side-Lying Leg Raises – build lateral thigh strength
4️⃣ Banded Glute Bridge – enhance stability and functional strength
5️⃣ Sumo Squats – increase activation of the gluteus medius
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery Exercises
✔ Glute Stretch to relieve muscle tension
✔ Pigeon Pose to improve flexibility and prevent tightness
✅ 🔬 Interesting Fact:
✔ The gluteus medius is notably stronger in runners and functional athletes, as it plays a key role in controlling lateral movements.
✅ 💡 Practical Tip:
✔ Weakness in this muscle can lead to knee issues like Runner’s Knee Syndrome and lower back pain, so incorporating lateral strengthening exercises is essential.
🔴 Name and Location: The lateral muscle of the pelvis, situated between the gluteus maximus and gluteus minimus.
🟠 Anatomy: Originates from the ilium and attaches to the greater trochanter of the femur
🟡 Function: Hip abduction, internal and external rotation of the hip, pelvic stabilization
🟢 Physiology: A combination of slow-twitch and fast-twitch muscle fibers for both endurance and strength.
🔵 Innervation: Superior gluteal nerve (L4, L5, S1)
🟣 Importance: Key for balance, explosive sports, and pelvic injury prevention
🟤 Exercises: Lateral lunges, clamshells, sumo squats, banded glute bridges
⚫ Interesting Fact: Weakness in the gluteus medius can cause a waddling gait and lead to knee problems.
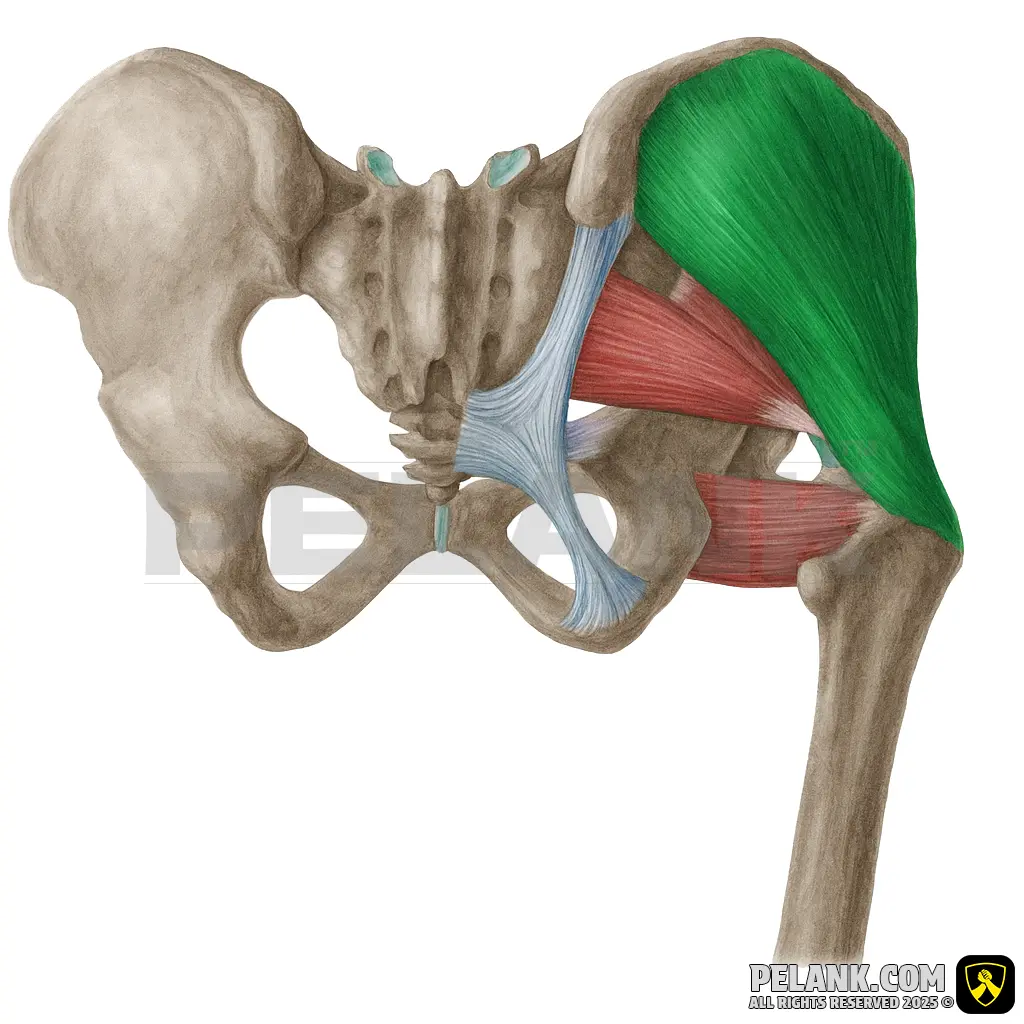
Gluteus Minimus Muscle
✅ The gluteus minimus is the smallest and deepest of the gluteal muscles. Working together with the gluteus medius, it contributes to hip abduction, pelvic stabilization, and internal rotation of the hip. Weakness in this muscle can reduce pelvic motor control and cause issues such as gait imbalance.

🔷 Detailed description
Click on the title to read each section.
✅ Persian Name: Sorini Koochak
✅ Latin Name: Gluteus Minimus
✅ Common Name: Glute Min
✅ Location:
🟡 Located beneath the gluteus medius, on the outer surface of the ilium.
🟡 A deep muscle situated close to the hip joint.
🟡 Originates from the ilium and attaches to the greater trochanter of the femur.
✅ 🦾 Origin
✔ External surface of the ilium, between the anterior and inferior gluteal lines
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ Anterior surface of the greater trochanter of the femur
✅ 📌 Function
1️⃣ Hip abduction (moving the thigh away from the body, assisting the gluteus medius)
2️⃣ Hip internal rotation (along with the anterior fibers of the gluteus medius)
3️⃣ Pelvic stabilization during walking (similar to the gluteus medius, preventing pelvic drop)
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Types
✔ A combination of slow-twitch fibers (Type I) for endurance and fast-twitch fibers (Type II) for quick movements.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Movement and Athletic Performance
✔ Walking and running: Controls pelvic balance during each step.
✔ Bodybuilding: Assists in squats, lunges, and glute bridges.
✔ Agility and quick direction changes: Stabilizes the pelvis during lateral movements.
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ A small but vital muscle for controlling the hip joint and stabilizing the pelvis.
✔ Weakness can lead to pelvic instability and issues such as knee pain and lower back pain.
🧠 Innervation
✔ Superior gluteal nerve (L4, L5, S1)
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Superior gluteal artery
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Pelvic stability exercises: including lateral and balance movements.
✔ Running and agility: stabilizes the pelvis during multi-directional movements.
✔ Yoga and Pilates: supports balance and hip joint flexibility.
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Interaction with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Works together with the gluteus medius for hip abduction and internal rotation.
✔ Stabilizes the hip joint to reduce stress on the knees and spine.
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ Weakness in this muscle can cause balance problems, pelvic drop, and knee pain.
✔ Strain or inflammation may lead to hip pain and walking difficulties.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Strength Training Exercises to Target the Gluteus Minimus
1️⃣ Lateral Lunges – activate the abductor muscle fibers
2️⃣ Clamshells – strengthen internal rotation and hip stability
3️⃣ Side-Lying Leg Raises – build lateral thigh strength
4️⃣ Banded Glute Bridge – improve stability and functional strength
5️⃣ Banded Monster Walks – enhance gluteus minimus activation during lateral movements
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery Exercises
✔ Glute Stretch to relieve muscle spasms
✔ Pigeon Pose to improve flexibility and reduce muscle tension
✅ 🔬 Interesting Fact:
✔ The gluteus minimus plays a major role in hip joint stability and is directly involved in controlling pelvic position during movement.
✅ 💡 Practical Tip:
✔ Weakness in this muscle can lead to balance issues, a higher risk of knee injuries, and hip pain—making targeted strengthening exercises essential.
🔴 Name and Location: A deep muscle in the gluteal region, located beneath the gluteus medius
🟠 Anatomy: Originates from the ilium and attaches to the greater trochanter of the femur
🟡 Function: Hip abduction, internal rotation of the thigh, and pelvic stabilization during walking
🟢 Physiology: A mix of slow-twitch and fast-twitch muscle fibers providing both control and endurance.
🔵 Innervation: Superior gluteal nerve (L4, L5, S1)
🟣 Importance: Stabilizes the hip joint, controls balance, and helps prevent knee and lower back injuries
🟤 Exercises: Lateral lunges, clamshells, banded glute bridges, and monster walks
⚫ Interesting Fact: Weakness in this muscle leads to pelvic instability and balance problems.
2.Hip & Knee Stabilizer Muscle
Tensor Fasciae Latae - TFL Muscle
✅ The tensor fasciae latae (TFL) is a small yet powerful muscle located on the lateral side of the pelvis. It connects to the iliotibial band (IT band) and plays a key role in stabilizing both the pelvis and the knee, as well as contributing to hip abduction, internal rotation, and flexion. Weakness or tightness in this muscle may lead to iliotibial band syndrome and knee problems.

🔷 Detailed description
Click on the title to read each section.
✅ Persian Name: Keshandeh Niyam Pahn
✅ Latin Name: Tensor Fasciae Latae (TFL)
✅ Common Name: TFL
✅ Location:
🟡 Located on the lateral side of the hip, just in front of the gluteus medius.
🟡 A narrow, long muscle running along the outer thigh, connecting to the iliotibial band.
🟡 Originates from the ilium and extends down to the area near the knee.
✅ 🦾 Origin
✔ External surface of the ilium near the anterior superior iliac spine (ASIS)
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ Iliotibial band (IT Band), which attaches to the lateral surface of the tibia at Gerdy’s tubercle.
✅ 📌 Function
1️⃣ Hip abduction (moving the thigh away from the body’s midline)
2️⃣ Hip flexion (helping lift the thigh forward, like raising the knee)
3️⃣ Internal rotation of the thigh (rotating the front of the thigh inward)
4️⃣ Stabilizing the knee joint via the iliotibial band (IT band)
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Types
✔ A combination of slow-twitch fibers (Type I) for endurance and fast-twitch fibers (Type II) for quick movements.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Movement and Sports Performance
✔ Running and quick direction changes: stabilizing the knee during side-to-side movements and acceleration.
✔ Explosive sports: such as soccer, basketball, and agility-based activities.
✔ Balance movements: helping maintain knee stability during activities like walking and skating.
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ A vital muscle for stabilizing the pelvis and knee during movement activities.
✔ Tightness in this muscle can lead to knee pain and inflammation of the iliotibial band, commonly known as IT Band Syndrome.
🧠 Innervation
✔ Superior gluteal nerve (L4, L5, S1)
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Superior gluteal artery
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Agility sports and running: stabilizing the knee and pelvis during rapid direction changes.
✔ Balance exercises: maintaining body control in activities like yoga and Pilates.
✔ Strength training: assisting in squats, lunges, and lateral movements.
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Interaction with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Works together with the gluteus medius and minimus to abduct the thigh and stabilize the pelvis.
✔ Controls the iliotibial band to prevent knee instability.
✅ 💉 Vulnerabilities and Potential Issues
✔ Excessive tightness in this muscle can cause pain on the outer side of the knee, known as IT Band Syndrome.
✔ Weakness in this muscle leads to reduced balance and knee stability during running and walking.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Strength Training Exercises to Enhance the TFL
1️⃣ Lateral Lunges – activate the thigh’s side movements
2️⃣ Monster Walks with resistance band – strengthen the iliotibial band function
3️⃣ Clamshells with resistance band – improve internal rotation strength of the thigh
4️⃣ Side-Lying Leg Raises – enhance hip abduction performance
5️⃣ Single-Leg Squats – boost stability of the knee and pelvis
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery Exercises
✔ TFL stretch to relieve muscle tension
✔ Iliotibial band stretch to help prevent knee issues
✅ 🔬 Interesting Fact:
✔ The TFL muscle directly influences knee and hip function and is especially active in runners and athletes who perform frequent lateral movements.
✅ 💡 Practical Tip:
✔ Excessive tightness in this muscle can lead to inflammation and knee pain, so incorporating regular stretching and muscle release exercises is essential.
🔴 Name and Location: A narrow muscle on the lateral side of the hip, positioned in front of the gluteus medius.
🟠 Anatomy: Originates from the anterior superior iliac spine (ASIS) and attaches to the iliotibial band (IT band).
🟡 Function: Hip abduction, flexion, internal rotation, and knee stabilization.
🟢 Physiology: Composed of a mix of slow-twitch and fast-twitch muscle fibers, providing both agility and endurance.
🔵 Innervation: Superior gluteal nerve (L4, L5, S1)
🟣 Importance: Stabilizes the knee and pelvis, enhances balance, and helps prevent lateral knee injuries
🟤 Exercises: Lateral lunges, monster walks, clamshells, single-leg squats
⚫ Interesting Notes: Plays a key role in knee stability and helps prevent IT Band Syndrome.
3. Deep Gluteal Muscles
Piriformis Muscle
✅ The piriformis is one of the deep gluteal muscles, located in the posterior pelvic region around the hip joint. It plays an important role in external rotation of the hip, stabilization of the hip joint, and controlling pelvic movement during walking and running. Since the sciatic nerve passes alongside—or in some individuals, through—this muscle, tightness or spasm can lead to piriformis syndrome and sciatic pain.

🔷 Detailed description
Click on the title to read each section.
✅ Persian Name: Golabi-Shakel
✅ Latin Name: Piriformis
✅ Common Name: External Rotator of the Thigh
✅ Location:
🟡 Located in the posterior pelvis, beneath the gluteus maximus muscle.
🟡 Originates from the inner surface of the sacrum and attaches to the greater trochanter of the femur.
🟡 The sciatic nerve usually passes beneath this muscle, but in some people, it may pass through it.
✅ 🦾 Origin
✔ Anterior surface of the sacrum near the sacral foramina (sacral holes)
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ Greater trochanter of the femur
✅ 📌 Function
1️⃣ External rotation of the thigh (turning the leg outward during walking or movement)
2️⃣ Hip abduction when the hip joint is flexed (helping move the thigh outward while sitting)
3️⃣ Stabilizing the hip joint during walking and running
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Types
✔ A mix of slow-twitch (Type I) fibers for pelvic stabilization and fast-twitch (Type II) fibers for quick movements.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Movement and Sports Performance
✔ Balance and agility sports: crucial for stabilizing the hip joint and preventing excessive pelvic rotation.
✔ Running and quick direction changes: active in twisting movements of the thigh.
✔ Strength training: involved in exercises like squats, deadlifts, and lunges.
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ A vital muscle for maintaining pelvic stability during movement.
✔ Weakness or spasms can lead to sciatic pain and reduced hip flexibility.
🧠 Innervation
✔ Nerve to Piriformis (L5, S1, S2)
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Superior and inferior gluteal arteries
✔ Internal pudendal artery
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Stabilizes the hip joint in sports like soccer, basketball, and weightlifting.
✔ Active in rotational thigh movements found in activities such as dance, kickboxing, and MMA training.
✔ Plays a key role in strengthening the pelvis and lower spine to help prevent back pain and movement issues.
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Interaction with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Works alongside other external rotators of the thigh, such as the quadratus femoris and the superior and inferior gemellus muscles.
✔ Stabilizes the hip joint and pelvis against sudden movements.
✅ 💉 Vulnerabilities and Potential Issues
✔ Piriformis Syndrome:
🚨 Muscle spasms can compress the sciatic nerve, causing sciatica—sharp, shooting pain radiating from the pelvis down the leg.
✔ Weakness in this muscle may lead to hip instability and increased stress on the knee and lower back joints.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Strength Training Exercises to Strengthen the Piriformis
1️⃣ Lateral Lunges – enhance pelvic strength and control
2️⃣ Clamshells – strengthen external rotation of the thigh
3️⃣ Banded Glute Bridge – stabilize the pelvis and hip joint
4️⃣ Monster Walks with resistance band – improve function and reduce pressure on the sciatic nerve
5️⃣ Deadlifts with focused thigh control – strengthen pelvic stabilizers
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery Exercises
✔ Piriformis stretch to relieve tension and prevent Piriformis Syndrome
✔ Pigeon Pose to increase flexibility and improve muscle function
✔ Foam rolling the gluteal area to reduce muscle tightness and prevent spasms
✅ 🔬 Interesting Fact:
✔ In about 15% of people, the sciatic nerve passes through the piriformis muscle, which can increase their risk of developing Piriformis Syndrome and sciatica pain.
✅ 💡 Practical Tip:
✔ Excessive tightness in this muscle can irritate the sciatic nerve, causing pain in the lower back, pelvis, and leg. Therefore, regular stretching and muscle release exercises are essential.
🔴 Name and Location: A deep muscle in the pelvis, located beneath the gluteus maximus and close to the sciatic nerve
🟠 Anatomy: Originates from the anterior surface of the sacrum and attaches to the greater trochanter of the femur
🟡 Function: External rotation of the thigh, abduction when the hip is flexed, and pelvic stabilization
🟢 Physiology: A combination of slow-twitch and fast-twitch muscle fibers, providing endurance and motor control.
🔵 Innervation: Nerve to Piriformis (L5, S1, S2)
🟣 Importance: Stabilizes the hip joint, helps prevent sciatica pain, and reduces knee and lower back problems
🟤 Exercises: Lateral lunges, clamshells, banded glute bridges, monster walks
⚫ Interesting Note: In about 15% of people, the sciatic nerve passes through this muscle, which can lead to sciatic nerve issues.
Obturator Internus Muscle
✅ The obturator internus is one of the deep gluteal muscles, playing an important role in external rotation of the hip and stabilization of the hip joint. Located on the inner side of the pelvis, it works together with the other external rotator muscles to provide pelvic stability and control hip movements.

🔷 Detailed description
Click on the title to read each section.
✅ Persian Name: Sedadi Dakheli
✅ Latin Name: Obturator Internus
✅ Common Name: External Rotator of the Thigh
✅ Location:
🟡 A deep muscle in the pelvic region originating from the internal surface of the obturator membrane and surrounding bones.
🟡 It travels backward through the lesser sciatic foramen to attach to the femur.
✅ 🦾 Origin
✔ Internal surface of the obturator membrane
✔ Margins of the pubis and ischium bones
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ Greater trochanter of the femur
✅ 📌 Function
1️⃣ External rotation of the thigh (turning the leg outward)
2️⃣ Hip abduction when the hip is flexed (moving the thigh outward while sitting)
3️⃣ Stabilization of the femoral head within the acetabulum (hip joint stabilization)
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Types
✔ Contains slow-twitch (Type I) fibers for endurance and stabilization, and fast-twitch (Type II) fibers for external rotation and explosive movements.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Movement and Sports Performance
✔ Thigh and pelvic rotational movements: important in sports like soccer, taekwondo, and kickboxing
✔ Pelvic stability during walking and running: prevents sudden hip joint rotation
✔ Enhances strength and stability of the knee and pelvis: supports precise movements in strength training and functional sports
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ A vital muscle for thigh stability, active with every step and rotational movement.
✔ Weakness can lead to issues like improper pelvic rotation, hip joint pain, and reduced power in dynamic sports activities.
🧠 Innervation
✔ Nerve to Obturator Internus (L5, S1, S2)
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Obturator artery
✔ Inferior gluteal artery
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Precise control of thigh and pelvic movements in sports like running, jumping, and skating
✔ Strength training: involved in rotational movements and pelvic stabilization during squats and lunges
✔ Martial arts: enhances rotational power and pelvic stability for powerful kicks
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Interaction with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Works together with the superior and inferior gemellus muscles, quadratus femoris, and obturator externus to stabilize and rotate the thigh
✔ Controls pelvic rotation and reinforces knee stability during lateral movements
✅ 💉 Vulnerabilities and Potential Issues
✔ Weakness in this muscle can reduce control over pelvic movements and increase the risk of knee injuries.
✔ Excessive tightness may put pressure on the sciatic nerve, leading to pelvic pain.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Strength Training Exercises to Strengthen the Obturator Internus
1️⃣ Clamshells with resistance band – enhance thigh rotational strength
2️⃣ Monster Walks with resistance band – stabilize and strengthen the pelvis
3️⃣ Side-Lying Leg Raises – improve rotational function and balance
4️⃣ Lateral Lunges – increase pelvic and knee stability
5️⃣ Banded Glute Bridge – strengthen pelvic stabilizers
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery Exercises
✔ Hip rotation stretch to improve flexibility and relieve muscle tension
✔ Foam rolling on the obturator internus muscle to reduce tightness and prevent hip joint pain
✅ 🔬 Interesting Fact:
✔ Due to its complex pathway through the pelvis, the obturator internus is one of the harder muscles to activate and requires targeted training.
✅ 💡 Practical Tip:
✔ Weakness in this muscle can lead to improper pelvic rotation and increased stress on the knee, making strengthening exercises essential for athletes.
🔴 Name and Location: A deep muscle in the pelvis, located near the hip joint and the obturator foramen
🟠 Anatomy: Originates from the internal surface of the obturator membrane and attaches to the greater trochanter of the femur
🟡 Function: External rotation of the thigh, stabilization of the hip joint, and abduction when the hip is flexed
🟢 Physiology: A mix of slow-twitch and fast-twitch muscle fibers, providing both endurance and movement power.
🔵 Innervation: Nerve to Obturator Internus (L5, S1, S2)
🟣 Importance: Stabilizes the hip joint, controls pelvic rotation, and helps prevent knee injuries
🟤 Exercises: Clamshells, Monster Walks, lateral lunges, banded glute bridges
⚫ Interesting Note: Due to its complex anatomical path, this muscle is challenging to activate and requires focused, targeted training.
Obturator Externus Muscle
✅ The obturator externus is one of the deep pelvic muscles and belongs to the group of hip external rotators. It originates from the outer surface of the obturator membrane and the surrounding bones, attaching to the intertrochanteric fossa of the femur. Its primary functions are external rotation of the hip, stabilization of the hip joint, and assisting in pelvic control.

🔷 Detailed description
Click on the title to read each section.
✅ Persian Name: Sedadi Khareji
✅ Latin Name: Obturator Externus
✅ Common Name: External Rotator of the Thigh
✅ Location:
🟡 Located in the anterior and lower part of the pelvis, beneath the gluteal muscles and near the hip joint.
🟡 Unlike the obturator internus, which extends inside the pelvis, the obturator externus lies on the external surface of the obturator bone.
✅ 🦾 Origin
✔ External surface of the obturator membrane
✔ Margins of the pubis and ischium bones
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ Trochanteric fossa of the femur
✅ 📌 Function
1️⃣ External rotation of the thigh (turning the leg outward)
2️⃣ Stabilization of the femoral head within the acetabulum (hip joint stabilization)
3️⃣ Control of pelvic movements during standing and walking
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Types
✔ A combination of slow-twitch (Type I) fibers for endurance and stabilization, and fast-twitch (Type II) fibers for rapid thigh rotation.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Movement and Sports Performance
✔ Thigh and pelvic rotational movements: important in sports like soccer, taekwondo, and kickboxing
✔ Pelvic stability during walking and running: prevents improper rotation of the thigh and knee
✔ Balance control during lateral movements: essential in sports like skiing, skating, and basketball
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ A key muscle for stabilizing the thigh and knee, involved in virtually all lower-body movements.
✔ Weakness can lead to issues such as improper pelvic rotation, hip joint pain, and decreased power in functional sports activities.
🧠 Innervation
✔ Obturator nerve (L3, L4)
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Obturator artery
✔ Inferior gluteal artery
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Strength training: supports movements like squats, lunges, and deadlifts
✔ Martial arts: provides precise control of thigh rotation during lateral strikes
✔ Running and quick direction changes: stabilizes the pelvis during running and helps reduce injury risk
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Interaction with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Works in coordination with the obturator internus, superior and inferior gemellus, and quadratus femoris muscles to stabilize and rotate the thigh.
✔ Supports the hip joint and helps control excessive knee rotation.
✅ 💉 Vulnerabilities and Potential Issues
✔ Weakness in this muscle can cause excessive pelvic and knee rotation, increasing stress on the hip joint and leading to inner thigh pain.
✔ Excessive tightness may limit hip range of motion and reduce flexibility.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Strength Training Exercises to Strengthen the Obturator Externus
1️⃣ Clamshells with resistance band – strengthen external rotation of the thigh
2️⃣ Monster Walks with resistance band – stabilize and strengthen the pelvis
3️⃣ Lateral Lunges – increase pelvic and knee stability
4️⃣ Banded Glute Bridge – strengthen pelvic stabilizers
5️⃣ Resistance band external thigh rotations – precisely activate the muscle
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery Exercises
✔ Hip rotation stretch to improve flexibility and relieve muscle tension
✔ Foam rolling on the obturator externus area to reduce tightness and prevent hip joint pain
✅ 🔬 Interesting Fact:
✔ The obturator externus plays a crucial role in fine rotational movements of the thigh. Although it is rarely trained in isolation, its proper function is essential for controlling knee and pelvic alignment.
✅ 💡 Practical Tip:
✔ Weakness in this muscle can lead to improper thigh rotation and increase the risk of knee injuries, making targeted strengthening exercises essential for athletes.
🔴 Name and Location: A deep muscle in the pelvis, near the hip joint, located on the external surface of the obturator foramen
🟠 Anatomy: Originates from the external surface of the obturator membrane and attaches to the trochanteric fossa
🟡 Function: External rotation of the thigh, stabilization of the hip joint, and prevention of unstable knee movements
🟢 Physiology: A mix of slow-twitch and fast-twitch muscle fibers, providing both endurance and movement power.
🔵 Innervation: Obturator nerve (L3, L4)
🟣 Importance: Stabilizes the hip joint, controls pelvic rotation, and helps prevent knee injuries
🟤 Exercises: Clamshells, Monster Walks, lateral lunges, banded glute bridges
⚫ Interesting Note: This muscle plays a key role in thigh rotational movements, and weakness in it can increase stress on the knee.
Superior Gemellus Muscle
✅ The superior gemellus is one of the deep gluteal muscles that, together with the other external hip rotators, is responsible for stabilizing the hip joint and producing external rotation of the hip. Though small, this powerful muscle plays an important role in controlled pelvic movements and maintaining hip joint stability.

🔷 Detailed description
Click on the title to read each section.
✅ Persian Name: Doqoloye Foghouni
✅ Latin Name: Superior Gemellus
✅ Common Name: Small External Rotator of the Thigh
✅ Location:
🟡 A small, deep muscle in the gluteal region situated among the external rotators of the thigh.
🟡 Located above the obturator internus and beneath the piriformis muscle.
🟡 Functions as part of the pelvic and thigh stabilization system alongside the inferior gemellus, obturator internus and externus, quadratus femoris, and piriformis muscles.
✅ 🦾 Origin
✔ External surface of the ischial spine
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ Greater trochanter of the femur, alongside the tendon of the obturator internus muscle
✅ 📌 Function
1️⃣ External rotation of the thigh (turning the leg outward)
2️⃣ Stabilization of the femoral head within the acetabulum (hip joint)
3️⃣ Assists with hip abduction when the hip is flexed
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Types
✔ Slow-twitch (Type I) fibers for long-term hip joint stabilization
✔ Fast-twitch (Type II) fibers for rapid rotational movements
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Movement and Sports Performance
✔ Thigh and pelvic rotational movements: important in sports like soccer, judo, wrestling, and kickboxing
✔ Pelvic stability during walking and running: helps control external rotation of the hip joint
✔ Knee and thigh stability: crucial in endurance sports such as sprinting
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ A small but influential muscle critical for hip joint stability
✔ Weakness can lead to pelvic imbalance, hip pain, and reduced control during rotational movements
🧠 Innervation
✔ Nerve to Obturator Internus (L5, S1)
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Inferior gluteal artery
✔ Internal pudendal artery
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Assists precise thigh rotation in martial arts and agility sports
✔ Enhances pelvic stability during quick direction changes and sudden movements
✔ Plays a vital role in stabilizing the hip joint during walking and running
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Interaction with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Works alongside other external rotators like the obturator internus, piriformis, inferior gemellus, and quadratus femoris to control thigh movements
✔ Stabilizes the hip and knee joints to prevent excessive stress on the pelvis
✅ 💉 Vulnerabilities and Potential Issues
✔ Weakness in this muscle reduces pelvic rotational control and increases stress on the hip and knee joints.
✔ Excessive tightness can cause pelvic pain and limit hip range of motion.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Strength Training Exercises to Strengthen the Superior Gemellus
1️⃣ Clamshells with resistance band – strengthen external rotation of the thigh
2️⃣ Monster Walks with resistance band – stabilize and strengthen the pelvis
3️⃣ Side-Lying Leg Raises – improve rotational function and balance
4️⃣ Banded Glute Bridge – strengthen pelvic stabilizers
5️⃣ Resistance band external thigh rotations – activate the muscle and enhance motor control
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery Exercises
✔ Hip rotation stretch to increase flexibility
✔ Foam rolling on the superior gemellus muscle to reduce tightness and prevent pain
✅ 🔬 Interesting Fact:
✔ The superior and inferior gemellus muscles act like twin guardians stabilizing the hip joint, working together with the obturator internus as a unified functional group.
✅ 💡 Practical Tip:
✔ If you’re experiencing issues with external rotation of the thigh, this muscle may be weak and could benefit from targeted strengthening exercises.
🔴 Name and Location: A small, deep muscle in the pelvis, located between the piriformis and obturator internus
🟠 Anatomy: Originates from the ischial spine and attaches to the greater trochanter of the femur
🟡 Function: External rotation of the thigh, hip joint stabilization, and assists with abduction when the hip is flexed
🟢 Physiology: A blend of slow-twitch and fast-twitch muscle fibers, providing both endurance and rotational movement control.
🔵 Innervation: Nerve to Obturator Internus (L5, S1)
🟣 Importance: Stabilizes the hip joint, controls pelvic rotation, and helps prevent knee injuries
🟤 Exercises: Clamshells, Monster Walks, lateral lunges, banded glute bridges
⚫ Interesting Note: This muscle, together with the inferior gemellus and obturator internus, forms a strong rotational and stabilizing complex in the pelvis.
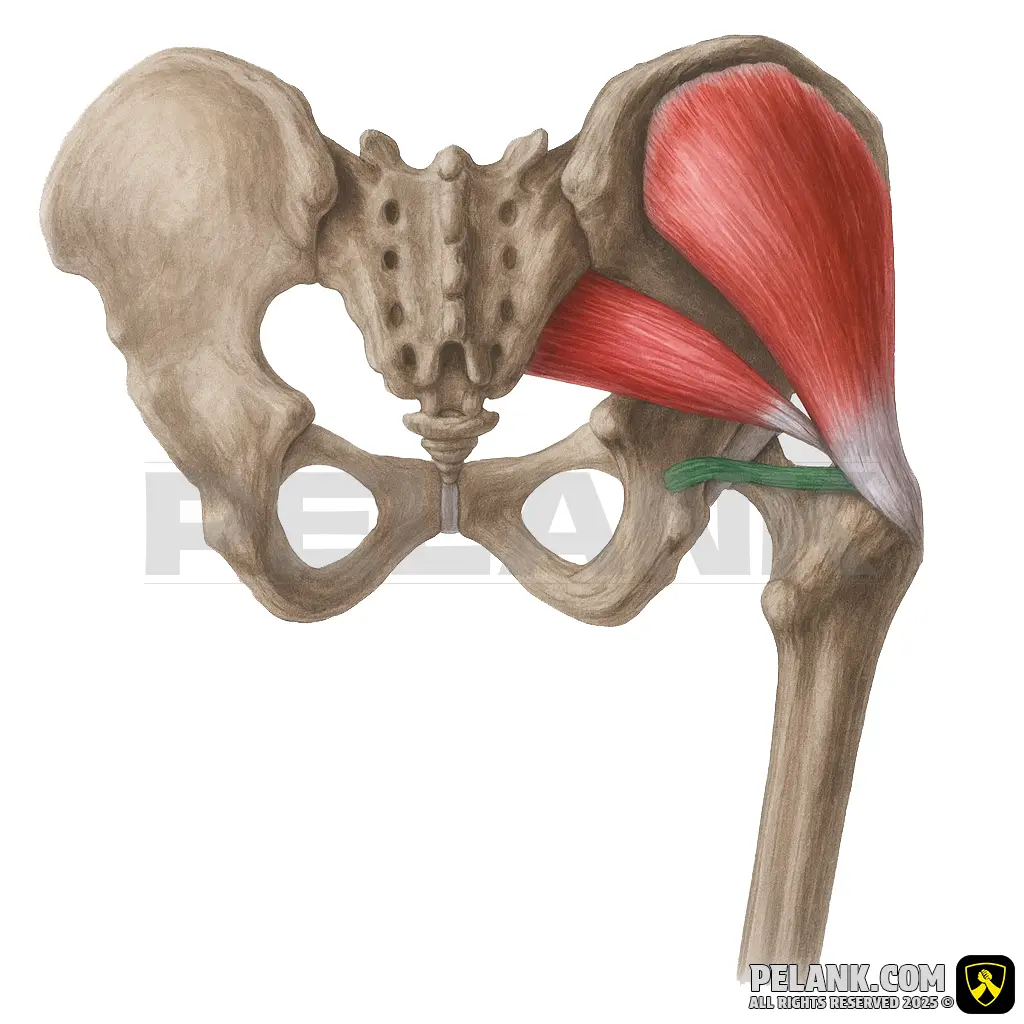
Inferior Gemellus Muscle
✅ The inferior gemellus is one of the deep gluteal muscles that, along with the other external hip rotators, is responsible for stabilizing the hip joint and producing external rotation of the hip. Positioned beneath the superior gemellus, it works alongside the obturator internus and other external rotators to play an important role in maintaining hip joint stability.
🔷 Detailed description
Click on the title to read each section.
✅ Persian Name: Doqolou-ye Tahtani
✅ Latin Name: Inferior Gemellus
✅ Common Name: Small External Rotator of the Thigh
✅ Location:
🟡 Situated in the lower part of the pelvis, adjacent to the Superior Gemellus and the Internal Obturator muscles.
🟡 Located just beneath the Superior Gemellus and above the Quadratus Femoris muscle.
🟡 Together with the Superior Gemellus and Internal Obturator, it forms a functional unit that controls and stabilizes thigh rotation.
✅ 🦾 Origin
✔ Superior surface of the ischial tuberosity (Ischial Tuberosity)
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ Greater trochanter of the femur, alongside the tendon of the obturator internus muscle
✅ 📌 Function
1️⃣ External rotation of the thigh (rotating the thigh outward)
2️⃣ Stabilization of the femoral head within the acetabulum (hip joint stabilization)
3️⃣ Assisting thigh abduction when the hip is flexed
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Types
✔ Slow-twitch (Type I) fibers for long-term hip joint stabilization
✔ Fast-twitch (Type II) fibers for rapid rotational movements
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Movement and Sports Performance
✔ Supports rotational movements of the thigh in sports such as soccer, judo, wrestling, and kickboxing
✔ Provides pelvic stability during walking and running, preventing improper hip joint rotation
✔ Helps control knee alignment in endurance sports
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ A small but influential muscle critical for hip joint stability
✔ Weakness can lead to pelvic imbalance, hip pain, and reduced control during rotational movements
🧠 Innervation
✔ Nerve to Quadratus Femoris (L4, L5, S1)
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Inferior gluteal artery
✔ Internal pudendal artery
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Assists precise thigh rotation in martial arts and agility sports
✔ Enhances pelvic stability during quick direction changes and sudden movements
✔ Plays a vital role in stabilizing the hip joint during walking and running
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Interaction with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Works together with other external rotators like the Internal Obturator, Piriformis, Superior Gemellus, and Quadratus Femoris to control thigh movements
✔ Stabilizes the hip and knee joints to prevent excessive strain on the pelvis
✅ 💉 Vulnerabilities and Potential Issues
✔ Weakness in this muscle reduces pelvic rotational control and increases stress on the hip and knee joints.
✔ Excessive tightness can cause pelvic pain and limit hip range of motion.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Strengthening Exercises for the Inferior Gemellus
1️⃣ Clamshells with resistance band – to strengthen external rotation of the thigh
2️⃣ Monster Walk with resistance band – to stabilize and strengthen the pelvis
3️⃣ Side-Lying Leg Raises – to enhance rotational function and balance
4️⃣ Banded Glute Bridge – to strengthen pelvic stabilizers
5️⃣ External thigh rotation with resistance band – to activate the muscle and improve motor control
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery Exercises
✔ Hip Rotation Stretch to improve flexibility
✔ Foam rolling on the Inferior Gemellus to relieve tightness and prevent discomfort
✅ 🔬 Interesting Fact:
✔ The Inferior Gemellus, together with the Superior Gemellus and Internal Obturator, forms a powerful muscle group essential for stabilizing the hip joint.
✅ 💡 Practical Tip:
✔ If you experience instability in your knee while running or performing rotational movements, it might indicate weakness in this muscle, signaling the need for targeted strengthening.
🔴 Name and Location: A small, deep muscle in the pelvis, situated between the Internal Obturator and the Quadratus Femoris muscles.
🟠 Anatomy: Originates from the ischial tuberosity and attaches to the greater trochanter of the femur.
🟡 Function: External rotation of the thigh, stabilization of the hip joint, and assistance with thigh abduction when the hip is flexed.
🟢 Physiology: A blend of slow-twitch and fast-twitch muscle fibers, providing both endurance and rotational movement control.
🔵 Innervation: Nerve to Quadratus Femoris (L4, L5, S1)
🟣 Importance: Stabilizes the hip joint, controls pelvic rotation, and helps prevent knee injuries
🟤 Exercises: Clamshells, Monster Walk, Lateral Lunges, and Banded Glute Bridges
⚫ Interesting Facts: This muscle, together with the Superior Gemellus and Internal Obturator, forms a strong rotational and stabilizing unit within the pelvis.
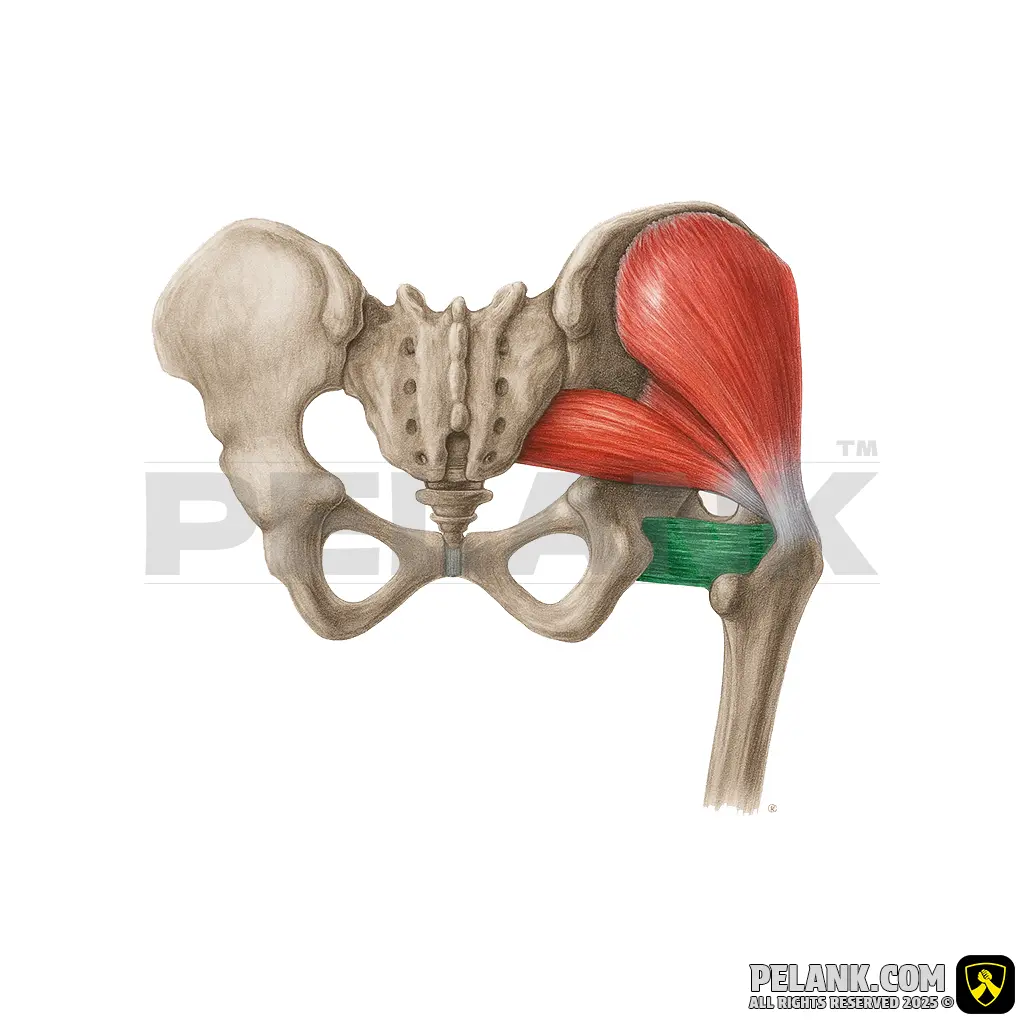
Quadratus Femoris Muscle
✅ The quadratus femoris is one of the deep gluteal muscles belonging to the group of external hip rotators. This short, broad muscle is located behind the hip joint and, together with other external rotators such as the superior and inferior gemelli and the obturator internus and externus, plays an important role in external rotation of the hip and stabilization of the hip joint.
🔷 Detailed description
Click on the title to read each section.
✅ Persian Name: Morabba-ye Ran
✅ Latin Name: Quadratus Femoris
✅ Common Name: External Rotator of the Thigh
✅ Location:
🟡 Positioned in the posterior and lower part of the pelvis, beneath the Inferior Gemellus and above the Adductor Magnus muscle.
🟡 Compared to other external rotators, this muscle is thicker and rectangular in shape.
🟡 Plays a key role in stabilizing the femoral head within the acetabulum and controlling thigh movements.
✅ 🦾 Origin
✔ Lateral surface of the ischial tuberosity (Ischial Tuberosity)
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ Intertrochanteric crest of the femur
✅ 📌 Function
1️⃣ External rotation of the thigh (rotating the thigh outward)
2️⃣ Stabilization of the femoral head within the hip joint
3️⃣ Assisting with thigh adduction in certain movements
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Types
✔ Slow-twitch fibers (Type I) for stabilizing the hip joint during prolonged activities
✔ Fast-twitch fibers (Type II) for generating quick, powerful thigh rotations
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Movement and Sports Performance
✔ Provides stability to the pelvis and thigh in sports like soccer, judo, taekwondo, and basketball
✔ Plays a key role in rotational and control movements of the thigh and pelvis during strength training
✔ Enhances hip joint control in endurance sports such as running and hiking
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ A broad, thick, and powerful muscle that plays a crucial supportive role in rotational movements.
✔ Weakness in this muscle can lead to pelvic imbalance and increased strain on other external rotator muscles.
🧠 Innervation
✔ Nerve to Quadratus Femoris (L4, L5, S1)
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Inferior Gluteal Artery
✔ Obturator Artery
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Controls rotational thigh movements in soccer, basketball, martial arts, and skating
✔ Maintains pelvic stability and helps prevent rotational injuries in strength and endurance sports
✔ Assists with thigh adduction during strength training and balance exercises
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Interaction with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Works in coordination with other external rotators such as the Superior and Inferior Gemellus, Internal and External Obturator muscles to stabilize the pelvis
✔ Controls thigh rotation to prevent excessive strain on the knee and hip joints
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ Weakness or imbalance in this muscle can reduce hip joint stability and increase the likelihood of pelvic pain.
✔ Excessive tightness may lead to restricted range of motion in the hip joint.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Strengthening Exercises for the Quadratus Femoris
1️⃣ Clamshells with resistance band – to boost thigh rotational strength
2️⃣ Monster Walk with resistance band – to stabilize and strengthen the pelvis
3️⃣ Side-Lying Leg Raises – to improve rotational function and balance
4️⃣ Banded Glute Bridge – to strengthen pelvic stabilizers
5️⃣ External thigh rotation with resistance band – to activate the muscle and enhance motor control
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery Exercises
✔ Hip Rotation Stretch to enhance flexibility
✔ Foam rolling on the Quadratus Femoris to relieve tightness and prevent discomfort
✅ 🔬 Interesting Fact:
✔ The Quadratus Femoris is one of the thickest external rotator muscles of the thigh, playing a vital supportive role in pelvic stabilization and controlling rotational movements.
✅ 💡 Practical Tip:
✔ If you feel instability in your pelvis during running or rotational movements, this muscle might be weak and could benefit from targeted strengthening exercises.
🔴 Name and Location: A broad, thick muscle located deep in the pelvis, positioned beneath the Inferior Gemellus and above the Adductor Magnus.
🟠 Anatomy: Originates from the ischial tuberosity and attaches to the intertrochanteric crest of the femur.
🟡 Function: External rotation of the thigh, stabilization of the hip joint, and assistance with thigh adduction.
🟢 Physiology: A blend of slow-twitch and fast-twitch muscle fibers, providing both endurance and rotational movement control.
🔵 Innervation: Nerve to Quadratus Femoris (L4, L5, S1)
🟣 Importance: Stabilizes the hip joint, controls pelvic rotation, and helps prevent knee injuries
🟤 Exercises: Clamshells, Monster Walk, Lateral Lunges, and Banded Glute Bridges
⚫ Interesting Fact: This muscle is a key player in controlling rotational movements and stabilizing the pelvis. Although often overlooked, it has a significant impact on athletic performance.
Interesting and Practical Facts
The gluteus maximus is not just about strength!
✔ This muscle is not only the strongest hip extensor, but also plays a vital role in maintaining pelvic balance while standing and walking. 🏋️♂️
The gluteus medius prevents pelvic drop!
✔ If this muscle is weak, the pelvis tilts toward the opposite leg while walking—a condition known as the Trendelenburg sign. 🚶♂️
3. The gluteus minimus — the often-forgotten muscle!
✔ Unlike the gluteus maximus, this muscle primarily contributes to internal rotation of the thigh and pelvic stabilization; weakness here can lead to balance issues. 🤸♀️
4. The Tensor Fasciae Latae can actually cause knee pain!
✔ This muscle affects the knee through the iliotibial (IT) band. When tight, it can lead to IT Band Syndrome and cause knee pain. 🏃♂️
5. The piriformis muscle can be a hidden cause of sciatica pain!
✔ In some people, the sciatic nerve passes through the piriformis muscle, and when this muscle tightens, it can compress the nerve, causing pain. ⚡
6. The external rotator muscles of the thigh play a crucial role in agility!
✔ The internal and external obturator muscles, superior and inferior gemellus, and quadratus femoris all play key roles in quick direction changes and rotational movements. ⚽
7. Weakness in the gluteus maximus can lead to lower back pain!
✔ This muscle helps stabilize the spine and maintain proper posture; when weak, the lower back muscles overcompensate, often leading to back pain. 🚑
8. The strongest external rotator of the thigh is the quadratus femoris!
✔ Among the external rotator muscles, the Quadratus Femoris generates the greatest force for thigh external rotation and plays a key role in stabilizing movements. 🔄
9. The gluteal muscles have a big impact on running speed!
✔ The gluteus maximus, as a powerhouse muscle, provides the force needed for acceleration and explosive jumps. 🏃♀️
10. The gluteus medius is the strongest muscle for maintaining pelvic stability!
✔ This muscle is highly active during one-legged standing and lateral movements, making it essential for athletes to focus on strengthening it. 🏋️♀️
11. 11. Weakness in the gluteal muscles increases the risk of ACL injuries!
✔ The gluteal muscles help control knee rotation and reduce excessive strain on the ACL; weakness in these muscles can raise the risk of injury. ⚠️
12. Tightness in the Tensor Fasciae Latae muscle can lead to lower back pain!
✔ This muscle attaches to the pelvis, and if overly tight or overactive, it can alter pelvic alignment, increasing the curve of the lower back (lordosis). 🩹
13. The upper and lower calf muscles are often overlooked!
✔ These muscles play a key role in external hip rotation and pelvic stability, but they are often neglected in strengthening exercises. 🎯
14. Piriformis strain can reduce the effectiveness of the gluteal muscles!
✔ If the piriformis muscle becomes too tight, it can restrict the function of other gluteal muscles and lead to weakness in hip movements. 🚷
15. Gluteal muscles help reduce lower back pain in pregnant women!
✔ These muscles play a vital role in pelvic stabilization, and strengthening them during pregnancy helps reduce pressure on the spine. 🤰
16. The glute bridge is one of the most effective exercises for activating the gluteus maximus!
✔ The Glute Bridge activates the gluteus maximus more effectively than squats. 🏗️
17. Improving hip mobility enhances the function of the gluteal muscles!
✔ Stretching and mobility exercises, like the Hip Flexor Stretch, can help improve the function of the gluteal muscles. 🤸
18. Weak pelvic muscles can lead to overall body imbalance!
✔ The pelvis is the body’s center of gravity, and weakness in these muscles can cause balance fluctuations and movement coordination issues. ⚖️
19. Stronger glutes reduce pressure on the knees!
✔ These muscles take a significant load off the knee joint during squats, running, and jumping, helping to reduce stress on the knees. 🦵
20. Hip muscles have a significant impact on athletic performance!
✔ The strength of these muscles plays a crucial role in jumping, quick direction changes, running speed, and maintaining balance in various sports. 🏆
Conclusion
✅ The gluteal and pelvic muscles play a vital role in strength, balance, and movement of the body. These muscles are not only essential for basic actions such as walking, running, and jumping, but also contribute to hip joint stability, knee protection, and reducing stress on the spine.
🔹 Weakness or imbalance in these muscles can lead to issues such as lower back pain, pelvic drop, sciatica, and an increased risk of knee injuries. On the other hand, strengthening these muscles improves athletic performance, reduces the likelihood of injury, and enhances the overall quality of daily life.
For strengthening and flexibility, specific exercises like glute bridges, lunges, Monster Walks, and rotational hip movements can be incredibly beneficial. These exercises really help boost the strength and mobility of these muscles, which in turn can prevent future movement issues from popping up.
✅ Ultimately, having strong glutes and pelvis is essential not only for athletes but for everyone, as these muscles have a direct impact on overall body health! 💪🔥
Sharing

Mohsen Taheri
Further Reading
Pelank Life | Body Health Assessment
The Best Body Health Calculators Using Scientific Methods
Developed by Pelank Life ©
References
✅ Anatomy and Medical Books
✅ Research Resources and Standardized Terminology Databases
✅ Visual Resources and Professional Anatomy Atlases
✅ Educational Resources – Official Textual and Visual References