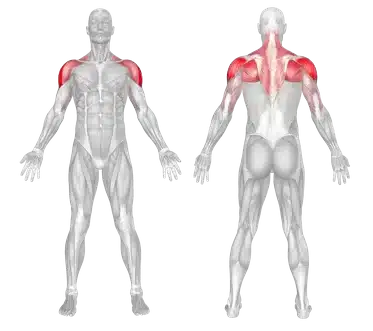
Wall Slide Shoulder Exercise with Foam Roller

| English Name | Serratus Wall Slide With Foam Roller |
|---|---|
| Difficulty | Beginner |
| Exercise Types | pull, static |
| Primary Muscle (EN) | Serratus Anterior |
| Muscle Groups | Chest muscles Shoulder Muscles Trapezius |
|---|---|
| Workout Type | Recovery Stretching |
| Required equipment | Foam roller |
💠 Exercise guide
The Scapular Wall Slide with Foam Roller is designed to strengthen the serratus anterior and improve the stability and mobility of the shoulder blades. Using a foam roller increases muscle activation and enhances shoulder control.

💠 How to perform the exercise

Preparation
✅ Stand facing a wall and place a foam roller at shoulder height.
✅ Position your forearms on the foam roller, elbows bent at 90 degrees, and palms facing each other.
Execution method
✅ Press your forearms into the foam roller and protract your shoulder blades forward.
✅ While maintaining this pressure, slowly slide your forearms upward along the roller as far as your range of motion allows.
✅ Then gently return to the starting position.
✅ Keep your core engaged throughout and avoid arching your lower back.
Coaching tips and recommendations
✔ Focus on moving the shoulder blades forward and upward.
✔ Avoid shrugging your shoulders during the exercise.
✔ Perform the movement slowly and with full control; avoid quick or jerky motions.
✔ Stop if you experience pain or discomfort and consult a professional.
Benefits of the exercise
1️⃣ Strengthens the serratus anterior and enhances shoulder stability
2️⃣ Increases shoulder mobility and flexibility
3️⃣ Helps prevent shoulder injuries such as impingement
4️⃣ Improves posture and reduces rounded shoulders
5️⃣ Suitable for rehabilitation after shoulder injuries
6️⃣ Builds body awareness of scapular movement
7️⃣ Can be done at home or in the gym with minimal equipment
8️⃣ Beneficial for athletes in swimming, volleyball, and basketball
9️⃣ Improves coordination between shoulder and scapular muscles
🔟 Reduces the risk of scapular winging
💠 Muscles engaged in the movement
This exercise primarily targets the serratus anterior, which plays a key role in stabilizing and upwardly rotating the shoulder blades. The upper and lower trapezius and the rotator cuff muscles also act as synergists and stabilizers.
Main muscles
Synergistic muscles
Stabilizers
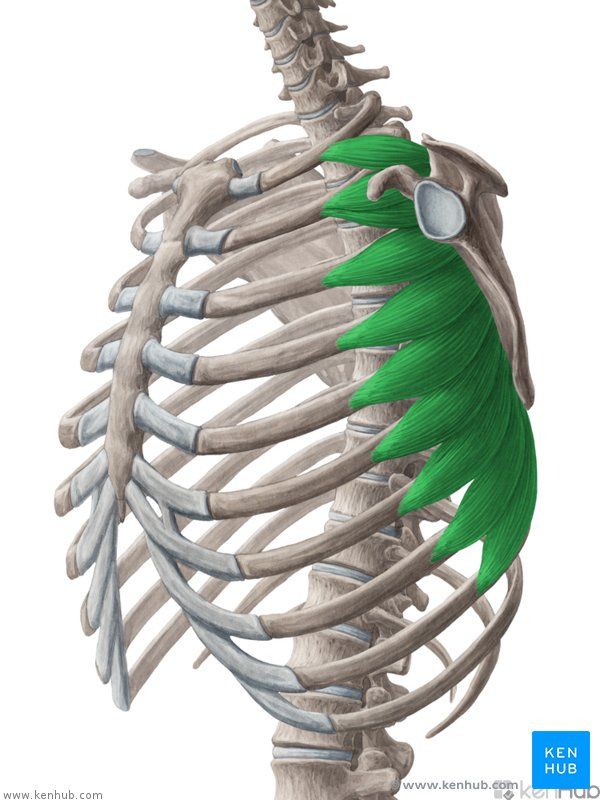
Serratus Anterior Muscle
Serratus Anterior Muscle
The serratus anterior is one of the most important muscles for scapular stabilization and movement. Named for its saw-toothed shape as it attaches to the ribs, this muscle plays a key role in maintaining scapular balance and stability. It is highly active during forward pushing movements such as throwing, punching, and push-ups. Strengthening the serratus anterior improves shoulder range of motion, increases endurance in athletic activities, and helps prevent shoulder pain and instability.
✅ Persian Name: Dandane-ye Ghodami
✅ Latin Name: Serratus Anterior
✅ Common Name: Boxer’s Muscle
✅ Location:
🟡 Located on the lateral aspect of the chest, over the upper ribs
🟡 Originates from the upper ribs and attaches to the medial border of the scapula
🟡 Its primary role is scapular stabilization and protraction (moving the scapula forward)
✅ 🦾 Origin
✔ Ribs 1 to 8 or 9
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ Medial border of the scapula
✅ 📌 Function
✔ Scapular protraction – assists movements such as punching and throwing
✔ Stabilizes the scapula against the rib cage – prevents instability and scapular winging
✔ Upward rotation of the scapula – during arm elevation above the head
✔ Supports pushing movements like push-ups and bench press
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Type
✔ A combination of slow-twitch fibers (Type I) for endurance and fast-twitch fibers (Type II) for rapid movements
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Movement and Athletic Performance
✔ Active in all throwing and punching movements, such as in boxing
✔ Primary scapular stabilizer during exercises like push-ups and bench press
✔ Assists scapular rotation when lifting objects overhead (e.g., weightlifting and discus throwing)
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ A key muscle for shoulder stability and joint injury prevention
✔ Weakness can cause scapular winging, leading to limited upper body movement
🧠 Innervation
✔ Long thoracic nerve
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Thoracodorsal artery
✔ Posterior intercostal arteries
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Boxing and MMA: responsible for powerful and rapid punching motions
✔ Weightlifting: aids proper scapular rotation during heavy lifts
✔ Bodybuilding and fitness: active in pushing exercises such as push-ups, dips, and bench press
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Interaction with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Works in coordination with the trapezius, deltoid, and pectoralis major muscles for proper shoulder stabilization and movement
✔ Poor scapular stabilization due to weakness in this muscle can lead to shoulder pain and decreased athletic performance
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ Weakness in this muscle can cause “scapular winging,” reducing shoulder range of motion
✔ Spasms or weakness may lead to interscapular pain and decreased shoulder stability
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Key Exercises to Strengthen the Serratus Anterior
1️⃣ Scapular push-ups – directly activate and strengthen the muscle
2️⃣ Resistance band punches – simulate punching motions to build strength
3️⃣ Wall slides with resistance band – aid in scapular strengthening and stabilization
4️⃣ Push-ups plus (push-ups with added scapular protraction) – increase muscle endurance
5️⃣ Scapular control exercises with bands – enhance muscle stability
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery Movements
✔ Chest & scapular stretch – improves flexibility and prevents muscle tightness
✔ Scapular mobility drills – enhance control and strengthen the shoulder joint
✅ Fun Fact
✔ The serratus anterior is highly developed in boxers and throwing athletes, which is why it is often called the “boxer’s muscle.”
✅ Practical Tip
✔ If you experience pain or imbalance in the shoulder when raising your arm, this muscle is likely weak. Strengthening and mobility exercises can help improve its function.
🔴 Name & Location: A superficial muscle over the ribs, attached to the scapula
🟠 Anatomy: Originates from ribs 1 to 8 and inserts into the medial border of the scapula
🟡 Function: Stabilizes and moves the scapula, assisting in throwing and pushing movements
🟢 Physiology: Composed of both slow- and fast-twitch muscle fibers
🔵 Innervation: Long thoracic nerve
🟣 Importance: Essential in boxing, bodybuilding, and overhead activities
🟤 Exercises: Scapular push-ups, resistance band punches, scapular control with bands
⚫ Fun Fact: A vital muscle for throwing and combat athletes
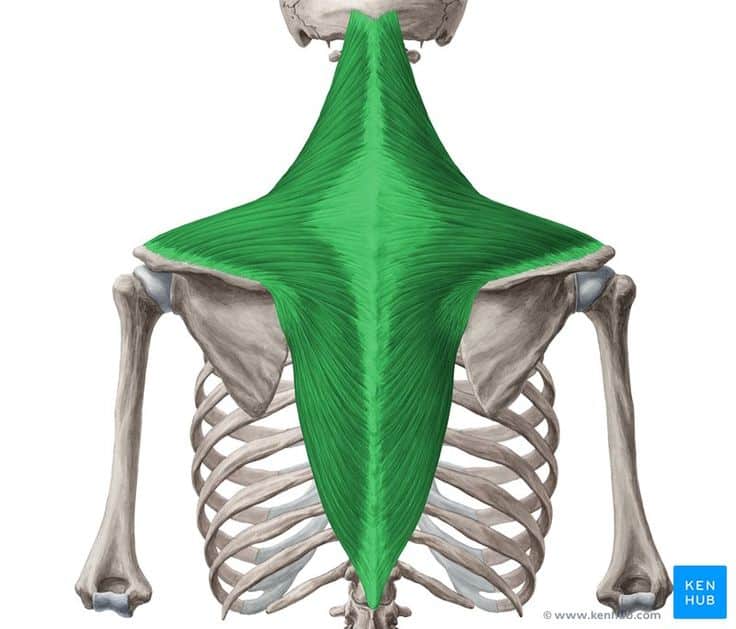
Trapezius muscle
Trapezius Muscle
The trapezius muscle is one of the most important superficial back muscles, extending from the occipital region to the middle of the back. It plays a key role in shoulder movements, scapular stabilization, and neck motions. Strengthening this muscle improves shoulder endurance, reduces neck pain, and enhances overall posture.
✅ Persian Name: Zozanaghei
✅ Latin Name: Trapezius
✅ Common Name: Trapezius muscle
✅ Location:
🟡 A superficial muscle extending from the base of the skull to the twelfth thoracic vertebra (T12).
🟡 Positioned as a broad, diamond-shaped muscle on both sides of the spine.
🟡 Responsible for shoulder movements, scapular stabilization, and assisting neck motions.
✅ 🦾 Origin
✔ Occipital bone
✔ Cervical ligamentum nuchae
✔ Cervical and thoracic vertebrae (C7-T12)
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ Clavicle (lateral third)
✔ Acromion process of the scapula
✔ Spine of the scapula
✅ 📌 Division and Function | Muscle Roles
🔹 The trapezius muscle consists of three main parts, each with different functions:
1️⃣ Upper (Superior) part
✔ Elevates the scapula (like shrugging the shoulders)
✔ Assists in head rotation and neck flexion
2️⃣ Middle part
✔ Retracts the scapula (drawing the shoulder blades closer together)
3️⃣ Lower (Inferior) part
✔ Depresses the scapula (pressing the shoulders downward)
✔ Assists in upward-to-downward rotation of the scapula
✅ Main Functions:
✔ Stabilization and movement of the scapula
✔ Assistance in head and neck movements
✔ Providing stability during shoulder and arm motions
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Types
✔ A combination of slow-twitch fibers (Type 1) for endurance and fast-twitch fibers (Type 2) for rapid movements.
✔ The lower part contains more slow-twitch fibers, aiding in endurance maintenance.
✔ The upper part has a higher proportion of fast-twitch fibers, suited for explosive and quick movements.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Motor and Sports Performance
✔ Plays a key role in weightlifting, bodybuilding, swimming, gymnastics, and wrestling.
✔ Active during overhead press, pull-ups, deadlifts, and rowing movements.
✔ Strengthening this muscle increases neck endurance and reduces injuries caused by spinal stress.
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ This muscle is engaged in all overhead and shoulder movements.
✔ Weakness in this muscle leads to reduced endurance in strength training and increases the risk of shoulder and neck pain.
🧠 Innervation | Neural Control
✔ Accessory nerve (Cranial Nerve XI)
✔ Branches of cervical nerves (C3-C4)
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Transverse cervical artery
✔ Suprascapular artery
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Important in sports such as bodybuilding, weightlifting, swimming, wrestling, and boxing.
✔ Vital for head and neck stability in American football, rugby, and martial arts.
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Relationship with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Works alongside the rhomboid muscles, levator scapulae, and latissimus dorsi in scapular movement and stabilization.
✔ Weakness in this muscle leads to poor posture, neck pain, and limited shoulder mobility.
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ Spasms and tightness in this muscle are common and often cause pain in the neck and upper shoulder area.
✔ Weakness or lack of strengthening can lead to shoulder drooping and reduced power in overhead movements.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Key Exercises to Strengthen the Trapezius Muscle
1️⃣ Dumbbell or Barbell Shrugs – Increase size and strength of the upper trapezius
2️⃣ Wide-Grip Pull-Ups – Engage the middle and lower parts of the muscle
3️⃣ Deadlifts – Strengthen the entire trapezius muscle
4️⃣ Bent-Over Rows with Barbell or Dumbbells – Target the middle portion of the muscle
5️⃣ Face Pulls with Cable – Enhance strength and endurance of the middle and lower trapezius
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery Exercises
✔ Neck Stretch – Reduces tension in the upper trapezius
✔ Trapezius Stretch – Increases flexibility and reduces spasms
✔ Shoulder Stretch – Improves range of motion
✅ Interesting Fact:
✔ The trapezius muscle plays a crucial role not only in shoulder and neck movements but also in stabilizing the spine and controlling upper body motions.
✅ Practical Tip:
✔ Combining strength exercises (such as deadlifts) with stretching movements (like neck stretches) is highly effective for improving performance and preventing muscle injuries.
🔴 Name and Location: A superficial muscle on both sides of the spine from the neck to mid-back
🟠 Anatomy: Three parts (upper, middle, lower) with distinct functions
🟡 Function: Stabilizes and moves the scapula; assists head and neck movements
🟢 Physiology: Combination of slow- and fast-twitch fibers for endurance and strength
🔵 Innervation: Accessory nerve and cervical nerves (C3-C4)
🟣 Importance: Active in bodybuilding, weightlifting, swimming, and martial arts
🟤 Exercises: Shrugs, deadlifts, pull-ups, rows, neck stretches
⚫ Interesting Fact: The most important muscle for overhead movements and shoulder stabilization
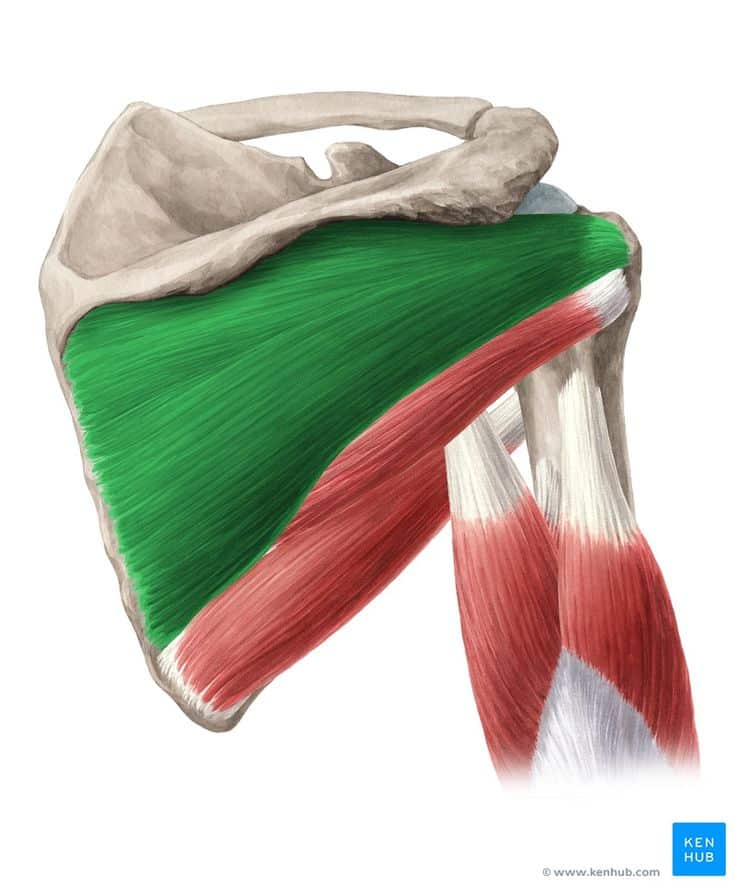
Infraspinatus Muscle
Infraspinatus Muscle
🔹 The infraspinatus muscle is one of the four key rotator cuff muscles, playing a crucial role in stabilizing and controlling the shoulder joint. It is essential for external rotation of the arm and maintaining shoulder joint stability.
🔹 This muscle is actively engaged in many athletic movements such as throwing, pulling weights, and rotational shoulder actions. Weakness in the infraspinatus can lead to shoulder joint instability, reduced range of motion, and an increased risk of injuries like rotator cuff tendon tears.
✅ Persian Name: Tahte Khari
✅ Latin Name: Infraspinatus
✅ Common Name: External Rotator of the Shoulder | Posterior Rotator Cuff Muscle
✅ Location:
🟡 Located on the posterior (back) side of the scapula, within the infraspinous fossa.
🟡 It is part of the rotator cuff muscle group responsible for external rotation and stabilization of the shoulder.
🟡 Its primary function is to externally rotate the arm and prevent excessive displacement of the humeral head in the glenohumeral joint.
✅ 🔹 Muscle Origin
✔ Infraspinous fossa of the scapula
✅ 🔹 Muscle Insertion
✔ Greater tubercle of the humerus
✅ 🔹 Muscle Function
📌 Primary functions of the infraspinatus muscle:
✔ External rotation of the arm – rotating the arm outward
✔ Stabilizing the shoulder joint against sudden forces
✔ Controlling throwing and rotational shoulder movements
📌 Movements involving activation of the infraspinatus:
✔ External rotation of the arm in resistance exercises (e.g., band external rotations)
✔ Throwing movements such as ball throws, javelin throws, and discus throws
✔ Resistance-based exercises like lateral pulls and controlled shoulder movements
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Types
✔ A combination of ✔ A combination of slow-twitch fibers (Type I) and fast-twitch fibers (Type II).
✔ Contains a higher proportion of slow-twitch fibers, which contribute to endurance and shoulder joint control.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ A key muscle for controlling rotational movements and stabilizing the shoulder in sports like swimming, baseball, basketball, and weightlifting
✔ Engaged in light resistance and stretching exercises to prevent shoulder injuries
✔ Weakness in this muscle can lead to shoulder instability and reduced range of motion.
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ A small but essential muscle for controlling and stabilizing shoulder movements
✔ Requires controlled exercises to enhance stability and prevent tendon inflammation
✅ 🧠 Innervation
✔ Suprascapular nerve (C5, C6), which controls the function of this muscle.
✅ 🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Suprascapular artery
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ A key muscle in stabilizing the shoulder joint and controlling rotational movements
✔ Active in sports involving throwing, gymnastics, swimming, wrestling, and weightlifting
✔ Weakness in this muscle increases the risk of rotator cuff tears and reduces the power of throwing motions.
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Interaction with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Works closely with the posterior deltoid, other rotator cuff muscles (supraspinatus, teres minor, subscapularis), and the posterior shoulder muscles
✔ Weakness in this muscle increases the load on the shoulder joint and its stabilizing muscles.
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ One of the most commonly injured muscles due to throwing motions and sudden stress.
✔ Weakness or inflammation in this muscle can lead to shoulder pain, and partial or complete rotator cuff tears.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Strengthening Exercises for the Infraspinatus
1️⃣ External Rotation with Resistance Band – one of the most effective exercises to strengthen this muscle
2️⃣ Isometric Shoulder Exercises – enhances shoulder stability
3️⃣ Reverse Fly with Dumbbells – improves muscle strength and endurance
4️⃣ Controlled Range of Motion Exercises – helps prevent tendon inflammation
5️⃣ Physiotherapy Exercises – improves overall rotator cuff function
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery Movements
✔ Outward arm stretches to improve flexibility and reduce muscle tension
✔ Using a foam roller to enhance blood flow and reduce inflammation
✅ Fun Fact
✔ The infraspinatus is one of the most important muscles in throwing movements, and athletes in throwing sports often have a highly developed infraspinatus.
✅ Practical Tip
✔ Strengthening the infraspinatus with light weights and resistance bands is the most effective way to prevent injuries and improve shoulder movement control.
🔴 Name and Location: A deep muscle located on the back of the scapula, beneath the supraspinatus, and part of the rotator cuff group.
🟠 Anatomy: Originates from the infraspinous fossa of the scapula and inserts into the greater tubercle of the humerus.
🟡 Function:
✔ External rotation of the arm
✔ Shoulder stabilization during throwing movements
🟢 Physiology: Predominantly composed of slow-twitch fibers for shoulder joint control and endurance.
🔵 Innervation: Suprascapular nerve, which controls this muscle.
🟣 Importance: Plays a vital role in throwing, rotational movements, and stabilizing the shoulder joint.
🟤 Exercises: Band external rotations, physiotherapy exercises, reverse fly.
⚫ Fun Fact: One of the key muscles for enhancing shoulder control and stability in throwing sports.
Teres Minor Muscle
Teres Minor Muscle
🔹 The teres minor is one of the four main rotator cuff muscles and works alongside the infraspinatus in external rotation of the arm. In addition to stabilizing the glenohumeral (shoulder) joint, it aids in controlled arm movements during both athletic and everyday activities.
🔹 Unlike the infraspinatus, which has greater power in external rotation, the teres minor plays a more prominent role in stabilizing the shoulder joint and maintaining balance during rotational and resistance movements. Weakness in this muscle can increase stress on the shoulder joint and reduce control in throwing and rotational actions.
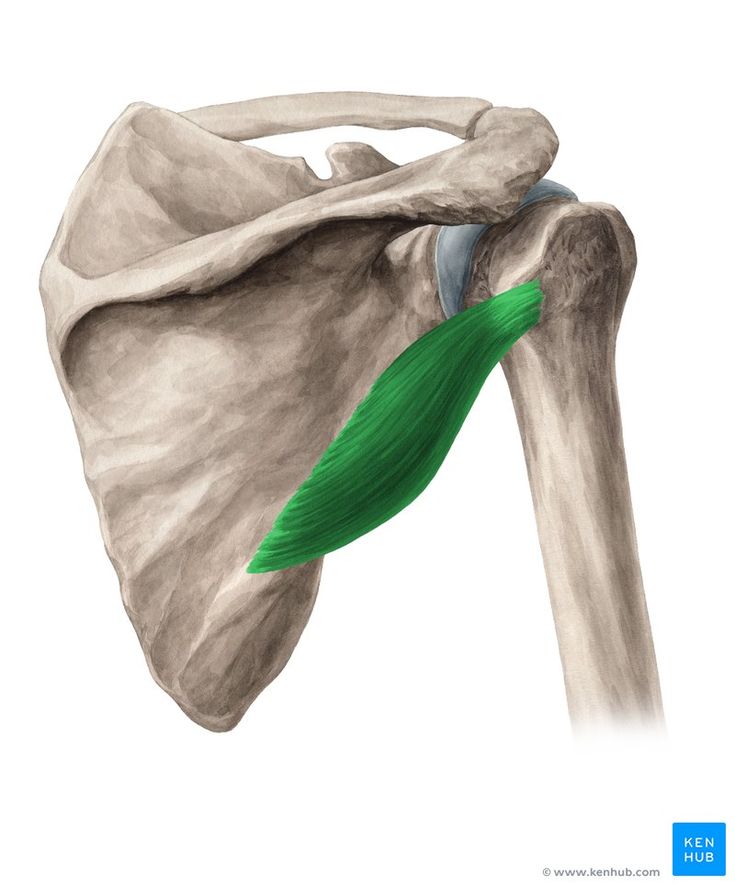
✅ Persian Name: Gerde Kochak
✅ Latin Name: Teres Minor
✅ Common Name: Small Shoulder Rotator | Posterior Rotator Cuff Muscle
✅ Location:
🟡 Positioned on the posterior side of the scapula, just below the infraspinatus and above the teres major.
🟡 It is part of the rotator cuff muscle group, responsible for external rotation and stabilization of the shoulder.
🟡 As a small yet essential muscle, it plays a critical role in controlling rotational arm movements and maintaining shoulder joint stability.
✅ 🔹 Muscle Origin
✔ Lateral border of the scapula
✅ 🔹 Muscle Insertion
✔ Greater tubercle of the humerus
✅ 🔹 Muscle Function
📌 Primary functions of the teres minor muscle:
✔ External rotation of the arm – rotating the arm outward
✔ Assists in stabilizing the shoulder joint against lateral forces
✔ Controls resistance movements and helps prevent shoulder dislocation
📌 Movements involving activation of the teres minor:
✔ External rotation of the arm during resistance exercises (e.g., band external rotations)
✔ Shoulder strengthening exercises such as face pulls and bent-over lateral raises
✔ Throwing movements that require high shoulder control (e.g., javelin, ball, and discus throws)
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Types
✔ A combination of ✔ A combination of slow-twitch fibers (Type I) and fast-twitch fibers (Type II).
✔ Contains a higher proportion of slow-twitch fibers, which contribute to endurance and shoulder joint control.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ A key muscle for controlling rotational movements and stabilizing the shoulder in sports like swimming, baseball, basketball, and weightlifting
✔ Engaged in light resistance and stretching exercises to prevent shoulder injuries
✔ Weakness in this muscle can lead to shoulder instability and reduced range of motion.
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ A small but essential muscle for controlling and stabilizing shoulder movements
✔ Requires controlled exercises to enhance stability and prevent tendon inflammation
✅ 🧠 Innervation
✔ Axillary nerve (C5, C6), which controls the movements of this muscle.
✅ 🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Posterior circumflex humeral artery
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ A key muscle in stabilizing the shoulder joint and controlling rotational movements
✔ Active in sports involving throwing, gymnastics, swimming, wrestling, and weightlifting
✔ Weakness in this muscle increases the risk of rotator cuff tears and reduces the power of throwing motions.
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Interaction with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Works closely with the posterior deltoid, other rotator cuff muscles (supraspinatus, infraspinatus, subscapularis), and the posterior shoulder muscles
✔ Weakness in this muscle increases stress on the shoulder joint and its stabilizing muscles
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ One of the most commonly injured muscles due to throwing motions and sudden stress.
✔ Weakness or inflammation in this muscle can lead to shoulder pain, and partial or complete rotator cuff tears.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Strengthening Exercises for the Teres Minor
1️⃣ External Rotation with Resistance Band – one of the best exercises to strengthen this muscle
2️⃣ Isometric Shoulder Exercises – improves shoulder stability
3️⃣ Reverse Fly with Dumbbells – enhances muscle strength and endurance
4️⃣ Controlled Range of Motion Exercises – helps prevent tendon inflammation
5️⃣ Physiotherapy Exercises – improves the function of the rotator cuff muscles
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery Movements
✔ Outward arm stretches to improve flexibility and reduce muscle tension
✔ Using a foam roller to enhance blood flow and reduce inflammation
✅ Fun Fact
✔ The teres minor works alongside the infraspinatus in external arm rotation, but it plays a more prominent role in stabilizing the shoulder joint.
✅ Practical Tip
✔ Strengthening the teres minor through controlled exercises is one of the best ways to prevent injuries and improve shoulder movement control.
🔴 Name and Location: A deep muscle located on the back of the scapula, between the infraspinatus and teres major muscles, and part of the rotator cuff group.
🟠 Anatomy: Originates from the lateral border of the scapula and inserts into the greater tubercle of the humerus.
🟡 Function:
✔ External rotation of the arm
✔ Stabilization of the shoulder during rotational and resistance movements
🟢 Physiology: Predominantly composed of slow-twitch fibers for shoulder joint control and endurance.
🔵 Innervation: Axillary nerve, which controls this muscle.
🟣 Importance: Plays a vital role in throwing, rotational movements, and stabilizing the shoulder joint.
🟤 Exercises: Band external rotations, physiotherapy exercises, reverse fly.
⚫ Fun Fact: One of the key muscles for maintaining shoulder strength and balance in power and throwing sports.
Muscle training
Pelank is a comprehensive encyclopedia of the body’s muscles, providing an accurate and scientific review of all muscles. Below, you can find muscle groups. By clicking on each muscle group, you will have access to complete information about it, including:
1️⃣ Basic information about the muscle
2️⃣ Muscle anatomy
3️⃣ Muscle physiology
4️⃣ Innervation and blood supply
5️⃣ Importance of the muscle in the body and sports
6️⃣ Strengthening exercises
7️⃣ Scientific and interesting facts
📌 At the end, a summary review of each muscle will be provided.
Body muscles training guide link
🔹 The muscle group engaged in this movement is highlighted in color.
References
Anatomy and medical books :
- Gray’s Anatomy (one of the standard references in anatomy).
- Netter’s Atlas of Human Anatomy (a famous visual atlas in anatomy).
- Clinically Oriented Anatomy by Keith Moore
Sports and training references :
- Strength Training Anatomy by Frederic Delavier
- Essentials of Strength Training and Conditioning by NSCA
- Well-known articles and training programs by international coaches
Medical databases :
- PubMed (for scientific and research articles)
- MedlinePlus (health and medical information)
- WebMD (for practical and general health information)
Pelank Life | Body Health Assessment
The Best Body Health Calculators Using Scientific Methods
Developed by Pelank Life ©
Comments