Dumbbell Windmill
| English Name | Dumbbell Windmill |
|---|---|
| Difficulty | Advanced |
| Movement Patterns | Rotation / Anti-Rotation |
| Muscle Contraction Types | Concentric, Isometric |
| Primary Muscle (EN) | External Oblique |
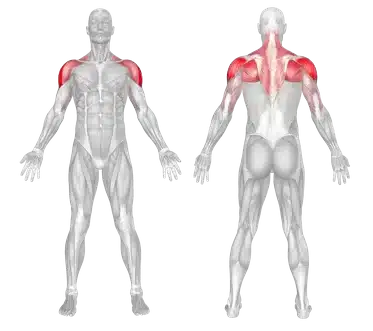
| Muscle Groups | Abdominal muscles Shoulder Muscles |
|---|---|
| Workout Type | Balanced Functional Stretching |
| Required equipment | Dumbbell |
💠 Exercise guide
The dumbbell windmill is a compound, rotational exercise that combines shoulder stability and hip mobility with core strength. It is an effective movement for improving trunk control, range of motion, and injury prevention in athletes.
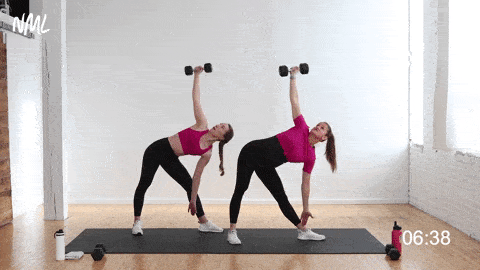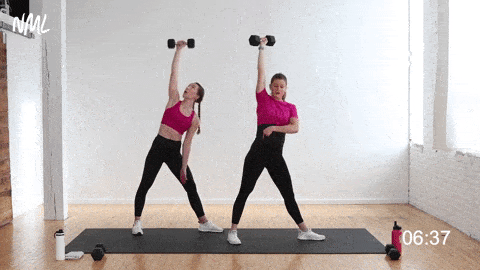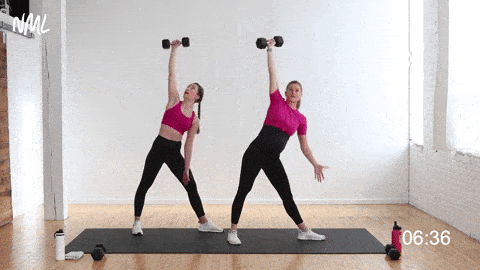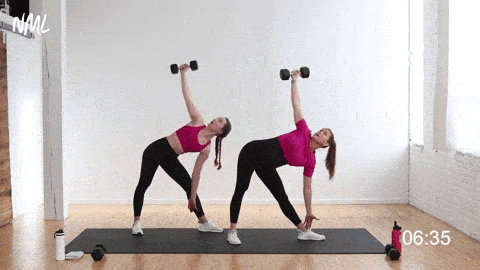
💠 How to perform the exercise

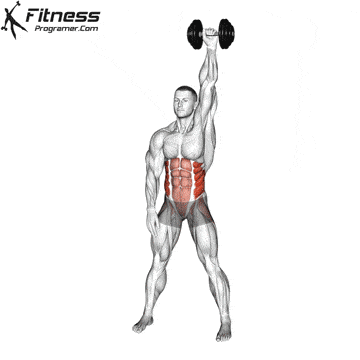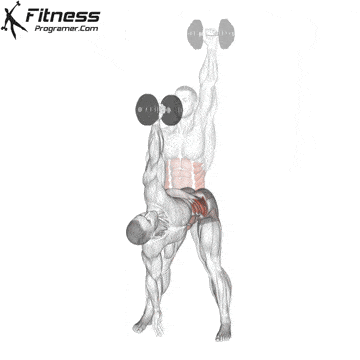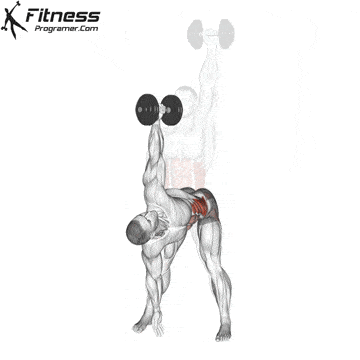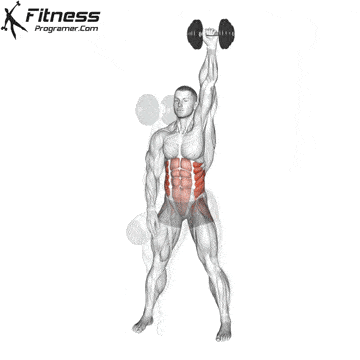
Preparation
✅ Stand with your feet slightly wider than hip-width apart
✅ Hold a dumbbell overhead with your right hand, left hand at your side
✅ Position your feet at an angle (left foot facing forward, right foot slightly turned out)
✅ Keep your torso upright and your core engaged
Execution method
✅ Keep the dumbbell stable overhead
✅ With shoulder stability maintained, bend your torso down to the left
✅ At the same time, lower your left hand toward your left foot or the floor
✅ Keep your gaze fixed on the dumbbell overhead
✅ Slowly and with control, return to the standing position
✅ Repeat on each side
Coaching tips and recommendations
✔ Do not lock your knees; keep your feet firmly planted
✔ Always keep your gaze on the dumbbell overhead
✔ Avoid bending from the lower back; initiate the movement from the hips
✔ Keep your abs tight and engaged
✔ Perform the movement slowly, smoothly, and with full control
Benefits of the exercise
🔹 Strengthening lateral and core power:
Strong activation of the oblique and core muscles enhances trunk control during athletic movements.
🔹 Improving balance and bilateral coordination:
An effective exercise for enhancing functional performance in sports such as tennis, volleyball, or boxing.
🔹 Increasing hip and spinal mobility:
The lateral bending in this exercise helps maintain flexibility and spinal health.
🔹 Active shoulder stability:
Holding the dumbbell overhead provides beneficial isometric stress on the shoulder, especially for overhead athletes.
🔹 Application in injury-prevention training:
This exercise is a popular component of warm-ups or stability routines for athletes.
💠 Muscles engaged in the movement
In this rotational movement, the primary stress is placed on the core muscles, particularly the obliques. Alongside them, the hamstrings, glutes, and shoulder stabilizers are engaged to maintain proper positioning.
Main muscles
Synergistic muscles
Stabilizers
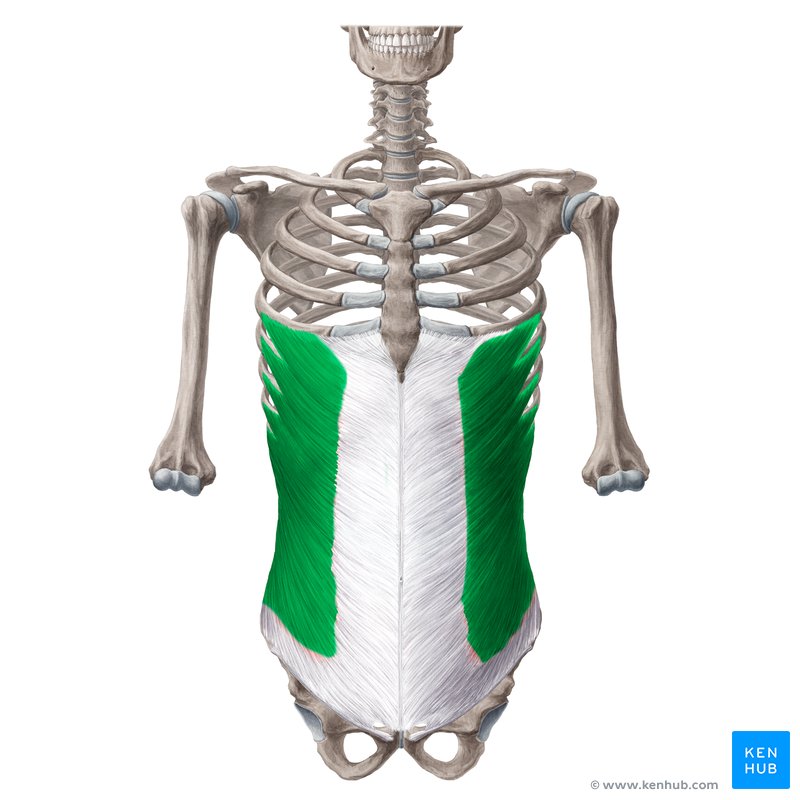
External Oblique Muscle
External Oblique Muscle
The external oblique muscle is one of the most important lateral abdominal muscles, located on both sides of the torso. This muscle performs essential functions such as trunk rotation and lateral flexion, abdominal compression, and assists in breathing.
✅ The external oblique muscle is the largest and most superficial lateral abdominal muscle, and due to the direction of its fibers, it slopes downward and forward (similar to the motion of putting your hand in your pocket).
✅ This muscle is highly activated in exercises such as twisting crunches, bicycle crunches, side planks, and Russian twists, playing a key role in core stability and rotational movements.
✅ Persian Name: Azole Mayel Khareji
✅ Latin Name: External Oblique
✅ Common Name: Side Abs | External Obliques
✅ Location:
🟡 This muscle extends on both sides of the abdomen, from the lower ribs to the pelvic bone.
🟡 It is the largest and most superficial lateral abdominal muscle.
🟡 It has fibers that run diagonally from top to bottom and from back to front.
✅ 🦾 Origin
✔ Ribs 5-12 – The origin of this muscle begins from the outer surface of these ribs.
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ Linea Alba – A fibrous connective tissue structure located at the center of the abdomen.
✔ Iliac Crest – The upper portion of the pelvic bone.
✔ Inguinal Ligament – A band that runs between the pelvis and the groin area.
✅ 📌 Classification and Function
✔ Trunk Rotation – For rotating the abdomen and sides, such as in bicycle crunches.
✔ Lateral Flexion – In bending to the side, like in side planks.
✔ Compression of Abdominal Contents – Helps increase intra-abdominal pressure, such as during a strong exhalation.
✔ Maintaining trunk stability and assisting in strength movements like deadlifts and squats.
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Type
✔ It has a combination of ✔ A combination of slow-twitch fibers (Type I) and fast-twitch fibers (Type II). ✔ For maintaining balance and power movements.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Motor and Athletic Performance
✔ It is active in all twisting and lateral exercises, such as Russian twists and twisting crunches.
✔ Responsible for core stability during weightlifting and stretching movements.
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ This muscle has high endurance due to its activity in all daily and athletic movements.
✔ Its weakness can lead to trunk imbalance and reduced spinal stability.
🧠 Innervation
✔ Intercostal Nerves T7-T11
✔ Subcostal Nerve – T12
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Posterior Intercostal Arteries
✔ Superior & Inferior Epigastric Arteries
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Bodybuilding and Fitness: Plays a crucial role in rotational and lateral abdominal movements such as Russian twists and side planks.
✔ Martial Arts: This muscle plays an important role in rotation and body stability during punching, kickboxing, wrestling, and MMA.
✔ Yoga and Pilates: Helps improve flexibility and body balance.
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Connection with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Interacts with the internal oblique muscles, rectus abdominis, and lumbar muscles to create lateral and rotational movements of the torso.
✔ Works together with the gluteal muscles and erector spinae in trunk stability and spinal balance.
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ Weakness of this muscle leads to trunk weakness, sagging sides, and spinal imbalance.
✔ Muscle strain may occur due to intense abdominal exercises or excessive twisting movements.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Main exercises to strengthen the external oblique muscle:
1️⃣ Russian Twists – The most effective movement for strengthening trunk rotation
2️⃣ Bicycle Crunches – Builds power and endurance in the sides
3️⃣ Side Plank – Increases trunk stability and balance
4️⃣ Oblique Crunches – Enhances size and definition of the sides
5️⃣ Dumbbell Side Bends – Increases strength in lateral movements
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery Movements
✔ Cobra Stretch – Enhances flexibility and aids in abdominal muscle recovery
✔ Side Stretch – Reduces tension and improves the range of motion in the sides
✅ Interesting Fact
✔ The external oblique muscle is one of the most important rotational and stabilizing muscles of the body, and it is automatically activated in all daily movements!
✅ Practical Tip
✔ If you want to strengthen and shape your sides, a combination of resistance exercises and endurance movements (such as side planks) is the best option!
🔴 Name and Location: Superficial lateral abdominal muscle, from the lower ribs to the pelvis
🟠 Anatomy: Has diagonal fibers running from top to bottom and forward
🟡 Function: Rotation, lateral flexion, abdominal compression
🟢 Physiology: A combination of slow-twitch and fast-twitch fibers
🔵 Innervation: Intercostal nerves T7-T11 and T12
🟣 Importance: Plays a key role in abdominal exercises, martial arts, bodybuilding, and yoga
🟤 Exercises: Russian Twists, Side Planks, Bicycle Crunches, Dumbbell Side Bends
⚫ Interesting Fact: A muscle that is active in all daily and athletic movements.
Hamstring Muscles
Hamstring Muscles
The hamstring muscles are a group of three main muscles located at the back of the thigh: the biceps femoris, semitendinosus, and semimembranosus. They originate from the pelvis and extend down to the bones of the lower leg (tibia and fibula). Functionally, they play a crucial role in bending (flexing) the knee and extending the hip joint.
These muscles also play a vital role in pelvic stability and in controlling movements involved in running, jumping, and changing direction during sports. Injuries in this area are common, especially in speed-based activities. Regular strengthening and stretching of the hamstring group help reduce injury risk, increase speed, and improve overall lower limb performance.

✅ Persian name: Hamstring Muscles | Hamstrings
✅ Latin name: Hamstring Muscles
✅ Common name: Back Thigh Muscles
✅ Location:
🟡 Situated in the posterior thigh, between the pelvis and the lower leg
🟡 Composed of three main muscles:
Biceps Femoris Muscle: located in the posterolateral part of the thigh.
Semitendinosus Muscle: located in the middle of the back of the thigh.
Semimembranosus: located deep and on the inner side of the thigh
🟡 All of these muscles originate from the pelvic area (ischial tuberosity) and attach to the bones of the lower leg (tibia or fibula).
🟡 Main functions of these muscles:
▪️ Flexing the knee joint
▪️ Extending the hip joint
▪️ Stabilizing the pelvis and controlling movements during activities such as walking, running, jumping, and sudden stops
🦾 1. Biceps Femoris Muscle
🔹 Long Head
✅ Origin:
✔ Ischial Tuberosity
✅ Insertion:
✔ Head of the Fibula
✅ Functions:
✔ Knee Flexion
✔ Hip Extension
✔ Pelvic stabilization during walking and running
✅ Innervation:
✔ Tibial Nerve Tibial Nerve (L5, S1, S2)
🔹 Short Head
✅ Origin:
✔ Linea Aspera of the Femur
✅ Insertion:
✔ Head of the Fibula
✅ Functions:
✔ Involved only in knee flexion
✔ Does not play a role in hip extension
✅ Innervation:
✔ Common Peroneal Nerve Common Peroneal Nerve (L5, S1, S2)
🦾 2. Semitendinosus Muscle
✅ Origin:
✔ Ischial Tuberosity
✅ Insertion:
✔ Proximal medial surface of the tibia (Pes Anserinus)
✅ Functions:
✔ Knee Flexion
✔ Hip extension
✔ Internal rotation of the lower leg when the knee is bent
✔ Pelvic stabilization during movement
✅ Innervation:
✔ Tibial Nerve Tibial Nerve (L5, S1, S2)
🦾 3. Semimembranosus Muscle
✅ Origin:
✔ Ischial Tuberosity
✅ Insertion:
✔ Posterior part of the medial condyle of the tibia
✅ Functions:
✔ Knee Flexion
✔ Hip extension
✔ Internal rotation of the lower leg when the knee is bent
✔ Stabilization of the hip and knee joints
✅ Innervation:
✔ Tibial Nerve Tibial Nerve (L5, S1, S2)
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Types
✔ The hamstring muscles consist of a combination of Type I (slow-twitch) and Type II (fast-twitch) fibers.
✔ Type I fibers are utilized in endurance activities such as long-distance running and continuous walking.
✔ Type II fibers are activated during powerful, jumping, and explosive movements such as sprinting, quick changes of direction, and throwing.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Movement and Athletic Performance
✔ They play a key role in knee flexion, hip extension, jumping, squats, lunges, deadlifts, sprinting, and running.
✔ The hamstrings help prevent knee hyperextension during running and jumping, contributing to the dynamic stability of the hip and knee joints.
✔ These muscles are highly active in decelerating movements and sudden changes of direction, especially in sports such as soccer, basketball, and track and field.
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ Regular strengthening of the hamstrings leads to:
🔹 Reduced risk of hamstring tears, especially during explosive movements
🔹 Prevention of anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injuries
🔹 Improved muscular balance between the front and back of the thigh
🔹 Enhanced performance in strength training, sprinting, and acrobatic movements
🧠 Innervation
✔ Biceps Femoris:
▪️ Long Head: Tibial Nerve (L5, S1, S2)
▪️ Short Head: Common Peroneal Nerve (L5, S1, S2)
✔ Semitendinosus:
▪️ Tibial Nerve (L5, S1, S2)
✔ Semimembranosus:
▪️ Tibial Nerve (L5, S1, S2)
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Deep Femoral Artery (Profunda Femoris)
✔ Perforating Branches of the Deep Femoral Artery
✔ Popliteal Artery – especially in the posterior knee region to support the hamstrings distally
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Bodybuilding: The hamstrings are heavily engaged in strength exercises such as squats, deadlifts, and lunges, especially during the hip extension phase and in controlling the return of movements.
✔ Running and jumping: During the swing phase of running, the hamstrings are responsible for knee flexion and shock absorption upon landing. They also generate the initial force for sprints, vertical jumps, and quick changes of direction.
✔ Team sports such as soccer and basketball: They play a key role in explosive movements, acceleration, sudden deceleration, and knee stability.
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Connection with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ The hamstrings, along with the semitendinosus and semimembranosus, help stabilize and control movements of the knee and hip, especially during compound or weightlifting exercises.
✔ They reduce excessive stress on the knee joint and create a strength balance with the quadriceps.
✔ During forward trunk flexion, the interaction between the hamstrings and the erector spinae is essential for maintaining balance.
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ The hamstrings are among the most commonly injured muscles in professional athletes, particularly during high-speed movements and sudden changes of direction.
✔ Common injuries include:
▫️ Strain
▫️ Partial or complete tear
✔ Weakness or tightness in the hamstrings can lead to:
▫️ Reduced control of knee movements
▫️ Increased risk of ACL injury
▫️ Hip joint instability
✔ Regular strengthening and stretching exercises can play a crucial role in injury prevention.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Key Exercises to Strengthen the Biceps Femoris Muscle
1️⃣ Romanian Deadlift
🔹 Primary emphasis on the long head of the biceps femoris
🔹 Increased controlled stretch during the lowering phase
🔹 Strengthens power and control in the hamstrings and hips
2️⃣ Single-Leg Squat
🔹 Isolated activation in the lower limb
🔹 Enhances neuromuscular balance and joint control
🔹 Applies effective load to the hamstrings and supporting muscles
3️⃣ Reverse Lunges
🔹 Engages both heads of the biceps femoris
🔹 Improves dynamic function of the hip and knee joints
🔹 Suitable for injury prevention and rehabilitation
4️⃣ Swiss Ball Hamstring Curls
🔹 Focus on both concentric and eccentric phases of the muscle
🔹 Improves muscular endurance and core control
🔹 Can be performed at home or in minimally equipped environments
5️⃣ Resistance Band Glute Bridge
🔹 Simultaneous activation of the glutes and hamstrings
🔹 Ideal for strengthening the posterior chain
🔹 Enhances stability in the hip region
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery Movements
✔ Standing Hamstring Stretch
▪️ Reduces tension in the back of the thigh
▪️ Improves flexibility and decreases muscle stiffness
✔ Cobra Stretch
▪️ Although primarily designed for the spine, it also aids hamstring function by enhancing stretch in the posterior chain
▪️ A suitable addition for recovery after strength training
✅ 🧠 Interesting Fact
✔ The short head of the biceps femoris, unlike the long head and other hamstring muscles, does not originate from the pelvis but from the linea aspera of the femur.
🔹 For this reason, some anatomical sources do not classify it as a true part of the hamstring group.
🔹 This muscle only affects the knee joint and plays no role in hip movements.
✅ 🛡️ Practical Tip
✔ The hamstrings are among the most common injury-prone areas in athletes, especially during high-speed movements or sudden changes of direction.
🔹 To reduce the risk of hamstring strains or tears:
▪️ Incorporate eccentric strengthening exercises (such as the Nordic Hamstring) into your program.
▪️ Perform both dynamic and static stretching regularly before and after training.
▪️ Pay close attention to maintaining a strength balance between the quadriceps and hamstrings.
🔴 Name and Location:
A group of muscles located in the posterior thigh, consisting of three muscles:
▫️ Biceps Femoris
▫️ Semitendinosus
▫️ Semimembranosus
These muscles originate from the pelvis and attach to the bones of the lower leg (tibia and fibula).
🟠 Anatomy:
All originate from the ischial tuberosity (the sitting bone of the pelvis), except for the short head of the biceps femoris, and they function in knee flexion and hip extension.
The biceps femoris has two distinct heads (long and short) with different innervations.
🟡 Function:
✔ Knee Flexion
✔ Hip Extension
✔ Assisting in stabilization of the pelvis and knee during movement
✔ Internal rotation of the leg by the semimembranosus and semitendinosus
✔ External rotation of the leg by the long head of the biceps femoris
🟢 Physiology:
✔ A combination of slow-twitch (Type I) and fast-twitch (Type II) fibers
✔ Slow-twitch fibers support long-term endurance
✔ Fast-twitch fibers power explosive movements and jumps
🔵 Innervation:
✔ Biceps Femoris:
▫️ Long Head: Tibial Nerve (L5–S2)
▫️ Short Head: Common Peroneal Nerve (L5–S2)
✔ Semitendinosus and Semimembranosus:
▫️ Tibial Nerve (L5–S2)
🟣 Functional Importance:
✔ Play a key role in sports such as running, jumping, squats, lunges, deadlifts, soccer, and basketball
✔ Stabilize the pelvis and protect the knee during dynamic movements
✔ The hamstrings are especially active in decelerating movements and quick changes of direction
🟤 Recommended Exercises:
1️⃣ Romanian Deadlift
2️⃣ Reverse Lunge
3️⃣ Resistance Band Glute Bridge
4️⃣ Standing Hamstring Stretch
5️⃣ Swiss Ball exercises for strengthening control and stability
⚫ Interesting Fact:
The short head of the biceps femoris, unlike the other hamstring muscles, does not originate from the pelvis and only acts on the knee; for this reason, some sources do not consider it a “true” member of the hamstring group.
Gluteus Maximus Muscle
Gluteus Maximus Muscle
The gluteus maximus is one of the most important and powerful muscles in the body, playing a key role in hip movement, balance, and pelvic stability. It’s essential for strength-based activities like squats, deadlifts, and running, where it drives hip extension and helps maintain pelvic stability.
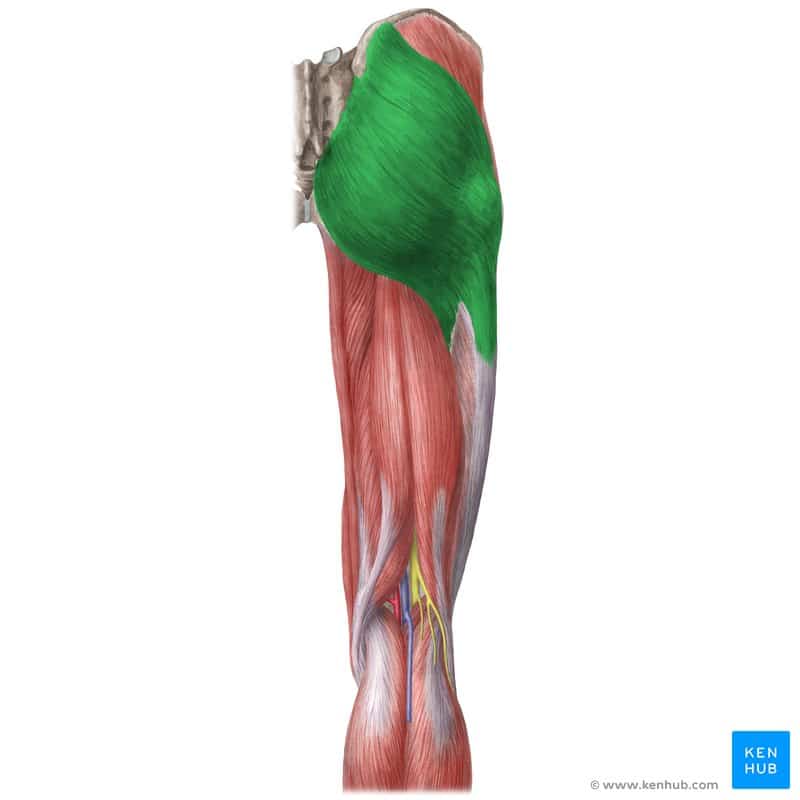
✅ Persian Name: Sorini Bozorg
✅ Latin Name: Gluteus Maximus
✅ Common Name: Buttock Muscle, Glutes
✅ Location:
🟡 Located at the back of the pelvis, lying over the other gluteal and thigh muscles.
🟡 It is the largest and most superficial muscle in the gluteal region.
🟡 Originates from the ilium (hip bone) and sacrum, attaching to the iliotibial band and the femur.
✅ 🦾 Origin
✔ Posterior surface of the ilium (Ilium)
✔ Posterior surface of the sacrum (Sacrum) and coccyx (Coccyx)
✔ Sacrotuberous ligament (Sacrotuberous Ligament)
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ Iliotibial band (IT Band)
✔ Gluteal tuberosity of the femur
✅ 📌 Function
1️⃣ Hip extension (moving the hip backward, as in deadlifts and climbing stairs)
2️⃣ External rotation of the hip (turning the thigh outward, like in lateral lunges)
3️⃣ Hip abduction and adduction (moving the thigh away from or toward the body, depending on muscle fibers)
4️⃣ Stabilizing the pelvis and knee through the iliotibial band (IT Band)
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Types
✔ Contains fast-twitch fibers (Type II) for powerful movements like deadlifts and squats.
✔ Also includes slow-twitch fibers (Type I) to maintain balance and stability during static positions.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Movement and Athletic Performance
✔ Bodybuilding: Engaged in key exercises like squats, deadlifts, and hip thrusts.
✔ Running and Jumping: Generates the force needed for propulsion and acceleration.
✔ Endurance and Balance: Supports static activities such as prolonged standing and walking.
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ The strongest muscle in the body when it comes to hip extension power.
✔ Weakness can lead to pelvic imbalance, increased lumbar lordosis (excessive lower back curve), knee pain, and reduced athletic performance.
🧠 Innervation
✔ Inferior gluteal nerve (L5, S1, S2)
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Superior and inferior gluteal arteries
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Weightlifting: Drives hip extension in deadlifts, squats, lunges, and hip thrusts
✔ Running and Jumping: Aids in acceleration and pelvic stabilization
✔ Resistance Sports: Enhances knee and pelvic stability for dynamic movements
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Interaction with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Works alongside the gluteus medius and minimus to control hip movements
✔ Collaborates with the hamstrings for hip extension and pelvic stabilization
✔ Stabilizes the knee through the iliotibial band (IT Band)
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ Weakness in the gluteus maximus increases the risk of lower back pain, knee problems, and poor balance.
✔ Insufficient strengthening can lead to muscle spasms and pain in the gluteal region.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Strength Training Exercises to Build the Gluteus Maximus
1️⃣ Deadlifts – the primary movement for hip extension
2️⃣ Hip Thrusts – directly target the gluteus maximus
3️⃣ Weighted Squats – a compound exercise strengthening both glutes and hamstrings
4️⃣ Lunges – work the gluteus maximus while challenging balance
5️⃣ Glute Bridge – an excellent exercise to engage the muscle at home
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery Exercises
✔ Glute Stretch to relieve muscle spasms and enhance function
✔ Pigeon Pose to increase gluteal flexibility and reduce lower back tension
✅ 🔬 Interesting Fact:
✔ The gluteus maximus plays the biggest role in shaping and powering the lower body.
✔ In professional athletes, this muscle is often highly developed due to intense training.
✅ 💡 Practical Tip:
✔ To better activate the gluteus maximus during workouts, start with activation exercises like bodyweight glute bridges and lunges before your main training.
🔴 Name and Location: The largest and most superficial muscle in the gluteal region, attaching to the hip bone (ilium) and the femur.
🟠 Anatomy: Originates from the ilium and sacrum, attaching to the gluteal tuberosity of the femur and the iliotibial band.
🟡 Function: Hip extension, external rotation, and stabilization of the pelvis and knee.
🟢 Physiology: A blend of slow-twitch and fast-twitch muscle fibers, providing both strength and endurance.
🔵 Innervation: Inferior gluteal nerve (L5, S1, S2)
🟣 Importance: Active during weightlifting, running, jumping, and lower body movements
🟤 Exercises: Deadlifts, hip thrusts, squats, lunges, glute bridges
⚫ Interesting Fact: The most important muscle for… shaping and strengthening the lower body, as well as preventing lower back pain.
Deltoid Muscle
Deltoideus Muscle
🔹 The deltoid muscle is one of the most important and voluminous muscles of the shoulder region. Its primary function is to move the arm in various directions and stabilize the shoulder joint. Due to its triangular shape, it is named “deltoid,” derived from the Greek word “Δέλτα” (delta), meaning triangle.
🔹 The deltoid muscle is divided into three distinct heads, each playing a specific role in shoulder movement. The anterior head assists in forward motions and arm flexion, the middle head is responsible for abduction and lifting the arm, and the posterior head supports extension and movements behind the body. This muscle is essential for the stability and strength of the shoulder joint, and its weakness can lead to limited range of motion, reduced shoulder power, and an increased risk of injury.
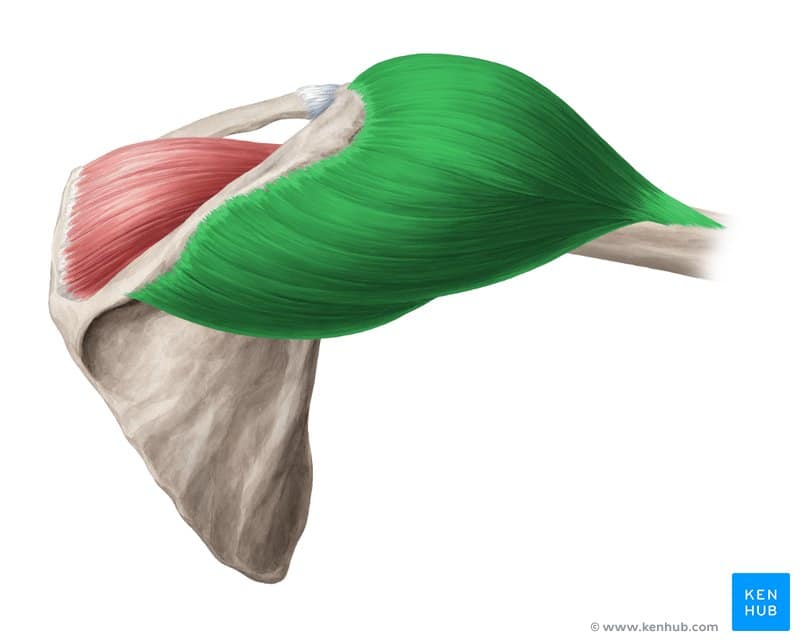
✅ Persian Name: Deltoeid
✅ Latin Name: Deltoideus
✅ Common Name: Shoulder Muscle
✅ Location:
🟡 A superficial muscle located at the top of the upper arm, covering the shoulder joint.
🟡 It forms a cap-like structure over the shoulder joint.
🟡 It directly overlays the head of the humerus and originates from the clavicle, scapula, and the upper part of the arm.
✅ 🔹 Origin
✔ Anterior part: from the outer surface of the clavicle
✔ Middle part: from the acromion, a portion of the scapula
✔ Posterior part: from the spine of the scapula
✅ 🔹 Insertion
✔ All parts of the deltoid muscle insert onto the deltoid tuberosity of the humerus.
✅ 🔹 Function
📌 The deltoid muscle is divided into three parts, each with a specific function:
1️⃣ Anterior Head
- ✔ Moving the arm forward (shoulder flexion)
- ✔ Internal rotation of the arm
- ✔ Assists in horizontal adduction of the arm (moving the arm forward across the body)
2️⃣ Middle Head
- ✔ Lifting the arm outward (shoulder abduction)
- ✔ Assists in stabilizing the shoulder during arm elevation
3️⃣ Posterior Head
- ✔ Moving the arm backward (shoulder extension)
- ✔ External rotation of the arm
- ✔ Assists in horizontal abduction of the arm (moving the arm backward across the body)
📌 Function Summary: The deltoid muscle plays a key role in all shoulder movements and is one of the primary muscles responsible for moving the arm in various directions.
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Types
✔ The deltoid muscle consists of a combination of fiber types. ✔ A combination of slow-twitch fibers (Type I) and fast-twitch fibers (Type II). ✔ It is composed of both fiber types.
✔ The anterior and posterior heads contain more fast-twitch fibers, which are suited for powerful and rapid movements.
✔ The middle head has a higher proportion of slow-twitch fibers, which help maintain muscular endurance during sustained activity.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Plays a key role in all overhead movements, such as shoulder press and bench press.
✔ Crucial for sports like weightlifting, swimming, gymnastics, and wrestling.
✔ Considered one of the primary muscles involved in carrying heavy objects, throwing, and raising the arm.
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Strength and Endurance
✔ The deltoid plays a vital role in maintaining shoulder joint stability, and its weakness can reduce control over shoulder movements.
✔ This muscle is well-suited for both strength and endurance activities and is heavily engaged in many professional sports.
✅ 🧠 Innervation
✔ Axillary Nerve (also known as the underarm nerve) – responsible for controlling deltoid muscle movements and providing sensation to the shoulder area.
✅ 🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Posterior Circumflex Humeral Artery
✔ Thoracoacromial Artery
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Directly involved in all shoulder and arm movements.
✔ A key muscle for athletes in bodybuilding, weightlifting, swimming, boxing, and combat sports.
✔ Strengthening this muscle improves shoulder shape, prevents injuries, and boosts upper body strength.
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Interaction with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Works closely with the rotator cuff muscles, back muscles, and pectoralis major.
✔ Weakness in this muscle can lead to excessive strain on the shoulder and scapular joints, increasing the risk of injury.
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ One of the most injury-prone muscles in bodybuilding and strength sports due to its crucial role in heavy movements.
✔ Common injuries include tears, strains, tendon inflammation, and cramps—often caused by improper use of heavy weights.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Strength Training Exercises for the Deltoid Muscle
1️⃣ Dumbbell or Barbell Shoulder Press – Strengthens all parts of the deltoid
2️⃣ Lateral Raise – Targets the middle head of the deltoid
3️⃣ Bent-Over Reverse Fly – Strengthens the posterior head of the deltoid
4️⃣ Front Raise with Dumbbell or Barbell – Focuses on the anterior head
5️⃣ Arnold Press – Activates all heads of the deltoid simultaneously
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery
✔ Forward and backward shoulder stretches
✔ Wall walks with the hand to improve flexibility
✅ Fun Fact
✔ The deltoid muscle is actually one of the key muscles that shapes and enhances the appearance of the upper body.
✅ Practical Tip
✔ Overtraining the deltoid without strengthening the back and rotator cuff muscles can disrupt shoulder muscle balance.
🔴 Name and Location: A superficial muscle that covers the shoulder joint and originates from the clavicle, scapula, and humerus.
🟠 Anatomy: Composed of three parts—anterior, middle, and posterior—each responsible for different shoulder movements.
🟡 Function:
✔ Anterior: Arm flexion and internal rotation
✔ Middle: Arm abduction and elevation
✔ Posterior: Arm extension and external rotation
🟢 Physiology: A combination of slow- and fast-twitch fibers, allowing for both endurance and explosive power movements.
🔵 Innervation: Axillary nerve, which controls the muscle’s movement and sensation in the shoulder area.
🟣 Importance: Active in all upper-body movements, bodybuilding, weightlifting, swimming, boxing, and combat sports.
🟤 Exercises: Shoulder press, lateral raise, front raise, bent-over raise, Arnold press.
⚫ Fun Fact: A key muscle for shoulder strength and aesthetics, yet one of the most injury-prone muscles during heavy training.
Muscle training
Pelank is a comprehensive encyclopedia of the body’s muscles, providing an accurate and scientific review of all muscles. Below, you can find muscle groups. By clicking on each muscle group, you will have access to complete information about it, including:
1️⃣ Basic information about the muscle
2️⃣ Muscle anatomy
3️⃣ Muscle physiology
4️⃣ Innervation and blood supply
5️⃣ Importance of the muscle in the body and sports
6️⃣ Strengthening exercises
7️⃣ Scientific and interesting facts
📌 At the end, a summary review of each muscle will be provided.
Body muscles training guide link
🔹 The muscle group engaged in this movement is highlighted in color.
References
Anatomy and medical books :
- Gray’s Anatomy (one of the standard references in anatomy).
- Netter’s Atlas of Human Anatomy (a famous visual atlas in anatomy).
- Clinically Oriented Anatomy by Keith Moore
Sports and training references :
- Strength Training Anatomy by Frederic Delavier
- Essentials of Strength Training and Conditioning by NSCA
- Well-known articles and training programs by international coaches
Medical databases :
- PubMed (for scientific and research articles)
- MedlinePlus (health and medical information)
- WebMD (for practical and general health information)
Pelank Life | Body Health Assessment
The Best Body Health Calculators Using Scientific Methods
Developed by Pelank Life ©
Comments