Body Fat Percentage Calculator
Pelank Life ©
Knowing your body-fat percentage is one of the most important markers of health and fitness, because unlike weight and BMI, it accurately shows how much of your body is made of fat versus muscle, water, and lean tissue. 🤓✨
When you know your body-fat percentage, you can plan your journey correctly—whether your goal is fat loss, muscle gain, or achieving your ideal physique. This advanced Pelank calculator helps you get the most accurate scientific estimate within seconds, compare your results with global standards, and build a smarter path toward your progress. 🚀📊
Body Fat Percentage Calculator
Calculate body fat using the US Navy formula or a BMI-based method.
Pelank Life | Body Health Assessment
The Best Body Health Calculators Using Scientific Methods
Developed by Pelank Life ©
Body Fat Percentage Interpretation
Your body fat percentage (Body Fat %) isn’t just a random number; it shows how much of your body is made of essential fat, functional fat, and excess fat—and knowing this is one of the most important steps for your health, athletic performance, and achieving your ideal physique. 📊🔥
That’s why the Pelank calculator gives you a precise, science-based interpretation of your results, so you can clearly understand which category you fall into and what you should do next—without any confusion.
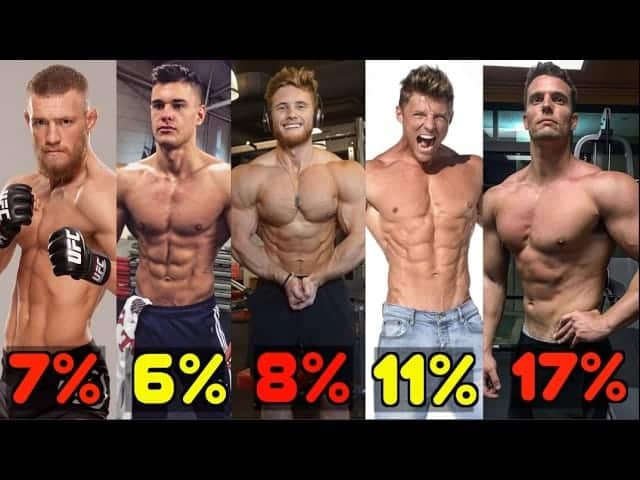

✅ Standard Body Fat Percentage Chart (Men / Women)
Global Classification Based on ACSM & ACE
Category | Men’s Body-Fat Percentage | Women’s Body-Fat Percentage | Quick Description |
|---|---|---|---|
🟧 Essential Fat | 2% – 5% | 10% – 13% | Essential Fat for Vital Body Functions 🧬 |
🟦 Athletes | 6% – 13% | 14% – 20% | Ideal for bodybuilders, endurance athletes, and competitive athletes 🏆 |
🟩 Fitness | 14% – 17% | 21% – 24% | Athletic appearance, defined muscles, and a high level of health 💪✨ |
🟨 Acceptable | 18% – 24% | 25% – 31% | Good overall health, the typical body-fat range for the general population 😊 |
🟥 Obese | 25%+ | 32%+ | High risk of metabolic and cardiovascular problems ❤️⚠️ |
🧬 1. Essential Fat
🔹 Men: 2–5%
🔹 Women: 10–13%
🔥 Role: Keeps you alive! Required for hormones, organ protection, and normal body function.
⚠️ Levels below this range are dangerous and unhealthy.
🏆 2. Athletes Level
🔹 Men: 6–13%
🔹 Women: 14–20%
🚀 Peak performance: strength, endurance, high metabolism
💡 Usually achieved with strict diet, consistent training, and precise weight control
💥 Highly visible muscles and clear definition
💪 3. Fitness Level
🔹 Men: 14–17%
🔹 Women: 21–24%
⭐ The best range for aesthetics + health
😍 Muscles are visible but not as sharp as elite athletes
⚖️ Great balance of energy, style, and overall health
🙂 4. Acceptable Range
🔹 Men: 18–24%
🔹 Women: 25–31%
📌 The most common range in the general population
❤️ Usually not harmful, but not ideal for peak fitness
⚠️ A good starting point if your goal is fat loss or improving shape
⚠️ 5. Obese
🔹 Men: 25% and above
🔹 Women: 32% and above
⚠️ High risk: diabetes, heart disease, high blood pressure, hormonal issues
💡 With proper nutrition + training, fat loss is completely achievable
🎯 Reasonable goal: move toward the Acceptable or Fitness range
🧬 1. Essential Fat
🔹 Men: 2–5%
🔹 Women: 10–13%
🔥 Role: Keeps you alive! Required for hormones, organ protection, and normal body function.
⚠️ Levels below this range are dangerous and unhealthy.
🏆 2. Athletes Level
🔹 Men: 6–13%
🔹 Women: 14–20%
🚀 Peak performance: strength, endurance, high metabolism
💡 Usually achieved with strict diet, consistent training, and precise weight control
💥 Highly visible muscles and clear definition
💪 3. Fitness Level
🔹 Men: 14–17%
🔹 Women: 21–24%
⭐ The best range for aesthetics + health
😍 Muscles are visible but not as sharp as elite athletes
⚖️ Great balance of energy, style, and overall health
🙂 4. Acceptable Range
🔹 Men: 18–24%
🔹 Women: 25–31%
📌 The most common range in the general population
❤️ Usually not harmful, but not ideal for peak fitness
⚠️ A good starting point if your goal is fat loss or improving shape
⚠️ 5. Obese
🔹 Men: 25% and above
🔹 Women: 32% and above
⚠️ High risk: diabetes, heart disease, high blood pressure, hormonal issues
💡 With proper nutrition + training, fat loss is completely achievable
🎯 Reasonable goal: move toward the Acceptable or Fitness range
What Is Body Fat Percentage?
Body Fat Percentage (BF%) tells you what portion of your total body weight is made up of fat. For example, if you weigh 80 kg and 16 kg of that is fat, then your body-fat percentage is:
20% BF 🤓📊
Unlike weight and BMI, this metric shows you how much of your body is made of active, metabolically functional muscle and how much is inactive tissue (fat). And this is exactly how you find out whether your actual weight is healthy or unhealthy.
✅ 🧬 Types of Body Fat
Fat isn’t just fat! Your body has three main types of fat, and understanding them is essential for interpreting your body-fat percentage 👇

1️⃣ Essential Fat
📍 The minimum amount of fat required for survival and normal body function
🧠 Role: regulates hormones, supports brain health, builds cell membranes, and protects organs
🔹 Men: around 2–5%
🔹 Women: around 10–13% (due to hormonal functions)
⚠️ Dropping below this level puts the body in a dangerous state
2️⃣ Subcutaneous Fat
📍 Fat stored directly under the skin
👀 The visible fat you see on the belly, sides, thighs, and arms
⭐ Role: protection and energy storage
💡 A major part of your appearance and body shape is determined by this type of fat
🔥 Strength training + proper nutrition = the best way to reduce it
3️⃣ Visceral Fat
📍 The dangerous fat stored around internal organs like the liver, intestines, and pancreas
⚠️ This fat isn’t visible, but it’s the most harmful type for your health
🔥 Directly linked to:
- Insulin resistance
- Heart problems
- Inflammation
- High blood pressure
- Type 2 diabetes
💡 It’s usually assessed more accurately by measuring waist circumference
✅ Why Are Weight and BMI Not Enough?
It’s very simple:
Weight = muscle + water + bone + fat
But BMI only compares weight to height—it has no idea what’s happening inside your body! 😅
For example:
🔹 Two people with the same height and weight:
Person 1: 12% body fat → lots of muscle, healthy, athletic
Person 2: 30% body fat → high fat, higher risk of metabolic issues
But their BMI is identical!
So:
❌ BMI cannot tell you:
- Your actual body-fat amount
- Your muscle-to-fat ratio
- Your metabolic health
- Visceral fat levels
- The true status of athletes or bodybuilders
✅ Body-fat percentage is the only metric that:
- Explains your appearance 😍
- Clearly reflects your health status 🔬
- Is essential for fat loss / muscle building programs 💪
- Measures real progress over time 📉📈
🎯 Summary
Your body-fat percentage is the most accurate metric that shows what your body is made of—not just how much you weigh. Understanding the different types of fat and how they affect your body helps you choose smarter training and nutrition strategies, leading to faster, healthier, and more targeted results. 🚀🔥
Methods for Measuring Body Fat
To accurately determine how much of your body weight comes from fat, there are several measurement methods—each with different advantages, accuracy levels, and costs. Below, I’ve explained the most complete and scientifically reliable techniques in simple terms so the user can understand the basis on which the Pelank calculator provides its results.
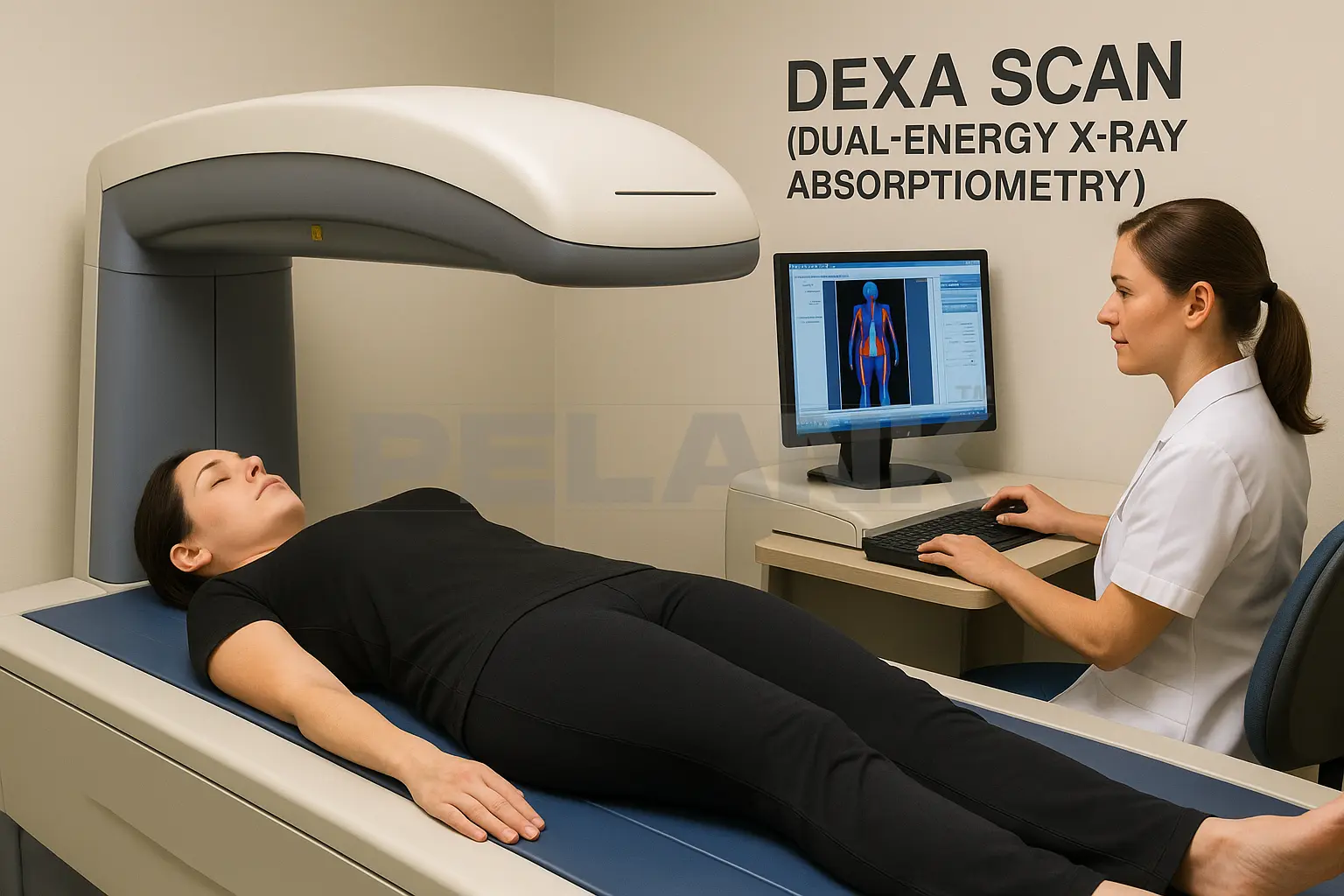
✅ DEXA Scan
Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry
📌 The Most Accurate Method for Measuring Body Fat
DEXA is an X-ray scan that uses two different energy levels to compare how beams pass through various tissues. This technology can measure fat, muscle, bone, and even fat distribution across your body with extremely high precision.
🎯 Advantages
- Very high accuracy (Golden Standard)
- Distinguishes between visceral and subcutaneous fat
- Separate analysis for arms, legs, and torso
- Ideal for sports science and medical research
⚠️ Disadvantages
- Expensive
- Limited availability
- Exposes you to a very small amount of radiation
- Not suitable for frequent everyday use
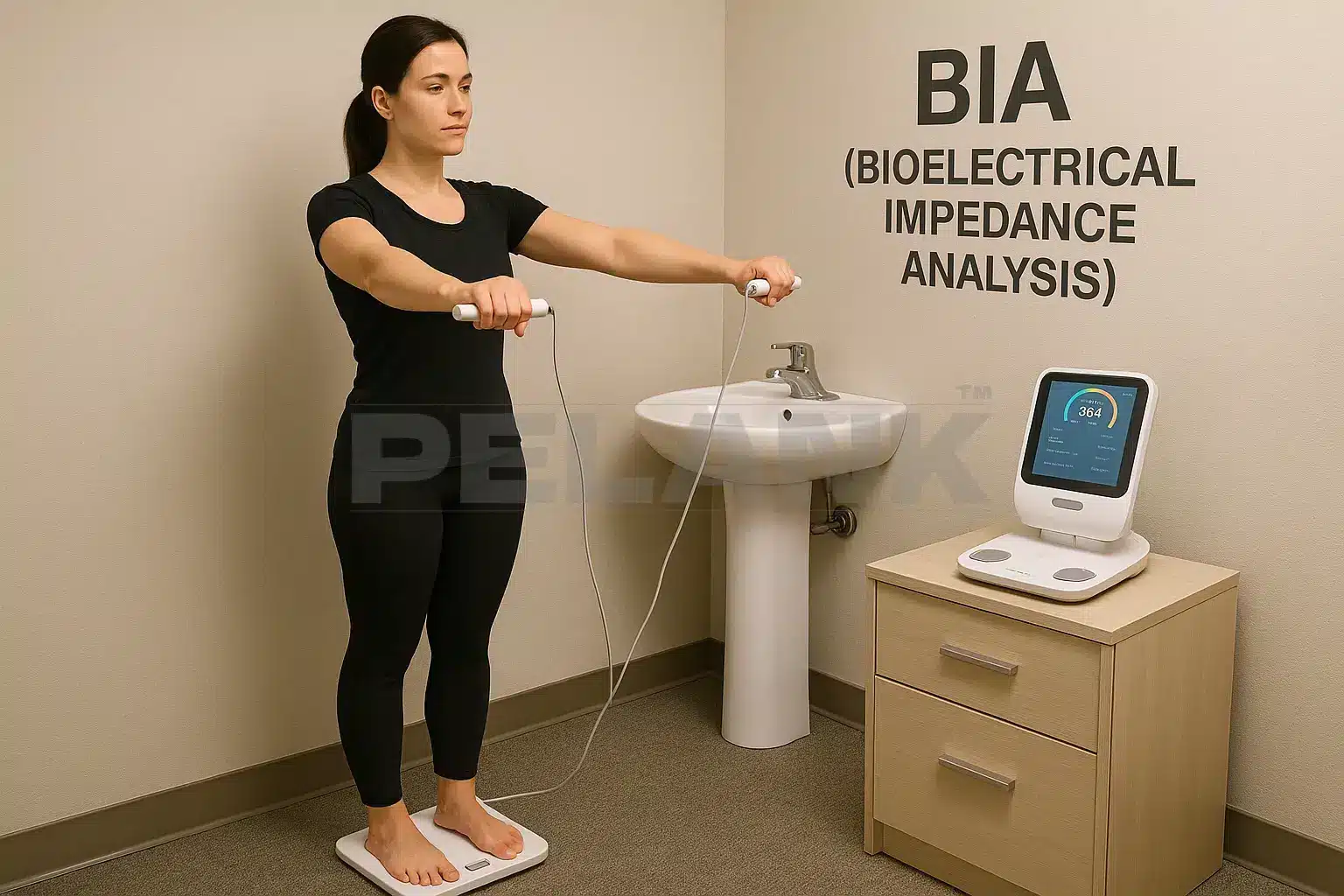
✅ BIA
Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis
📌 Those Smart Home Scales (BIA Method)
In this method, a mild, harmless electrical current passes through your body. The current travels faster through muscle and slower through fat; the device estimates your body-fat percentage based on this difference in resistance.
🎯 Advantages
- Fast, simple, and painless
- Easy to use at home
- Great for tracking changes over time
- Affordable
⚠️ Disadvantages
- Moderate accuracy
- Affected by hydration, food intake, exercise, temperature
- Cheap models can be highly inaccurate

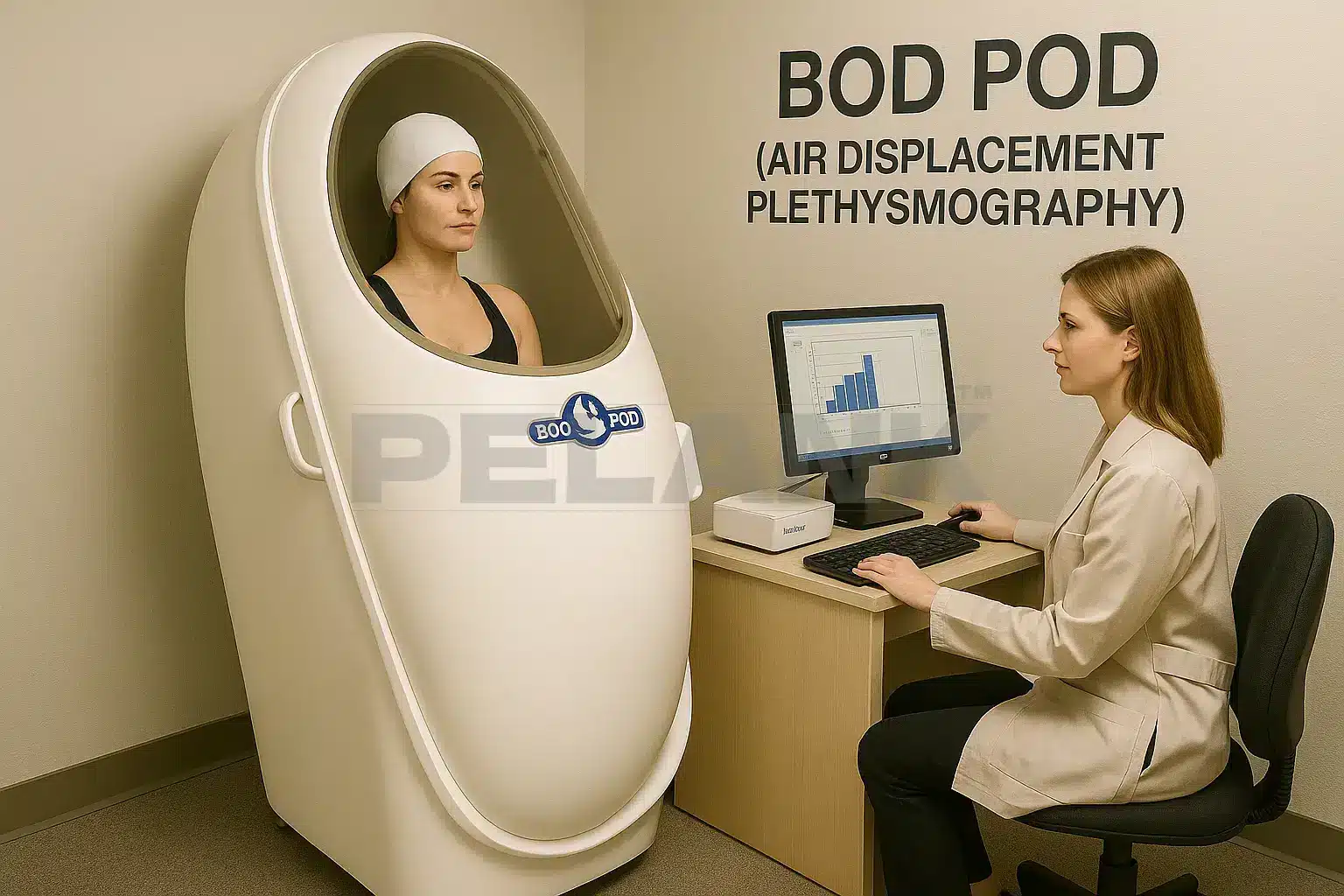
✅ BodPod
Air Displacement Plethysmography
📌 Body-Fat Measurement Using Air Displacement (Bod Pod)
You sit inside an egg-shaped chamber, and the device measures changes in air pressure to calculate your body volume. Then, by combining this with your weight, it estimates your body-fat percentage.
🎯 Advantages
- High accuracy (close to DEXA)
- Fast (2–3 minutes)
- Non-invasive and completely safe
⚠️ Disadvantages
- Requires specialized equipment
- Relatively expensive
- Can be affected by breathing and small movements
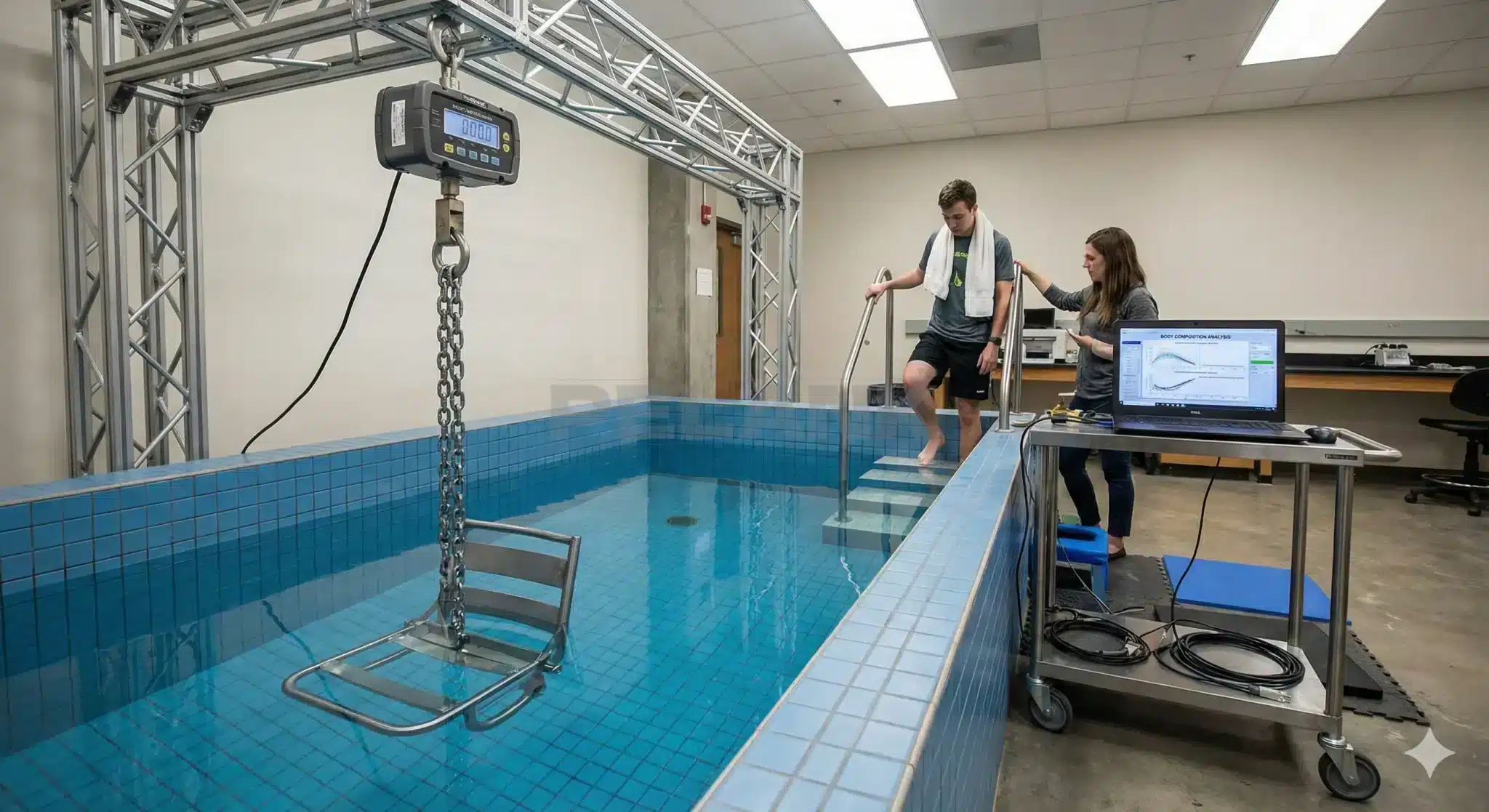
✅ Hydrostatic Weighing
Underwater Weighing
📌 A Classic and Highly Accurate Method
In this method, the person is fully submerged in water. Because fat is less dense, it floats more easily, while muscle is heavier in water. By measuring weight underwater and on land, the device calculates body-fat percentage.
🎯 Advantages
- High accuracy
- A long-standing method widely validated in research
⚠️ Disadvantages
- Uncomfortable or difficult for some people
- Requires a skilled operator
- Limited availability
- Not practical or affordable for home use

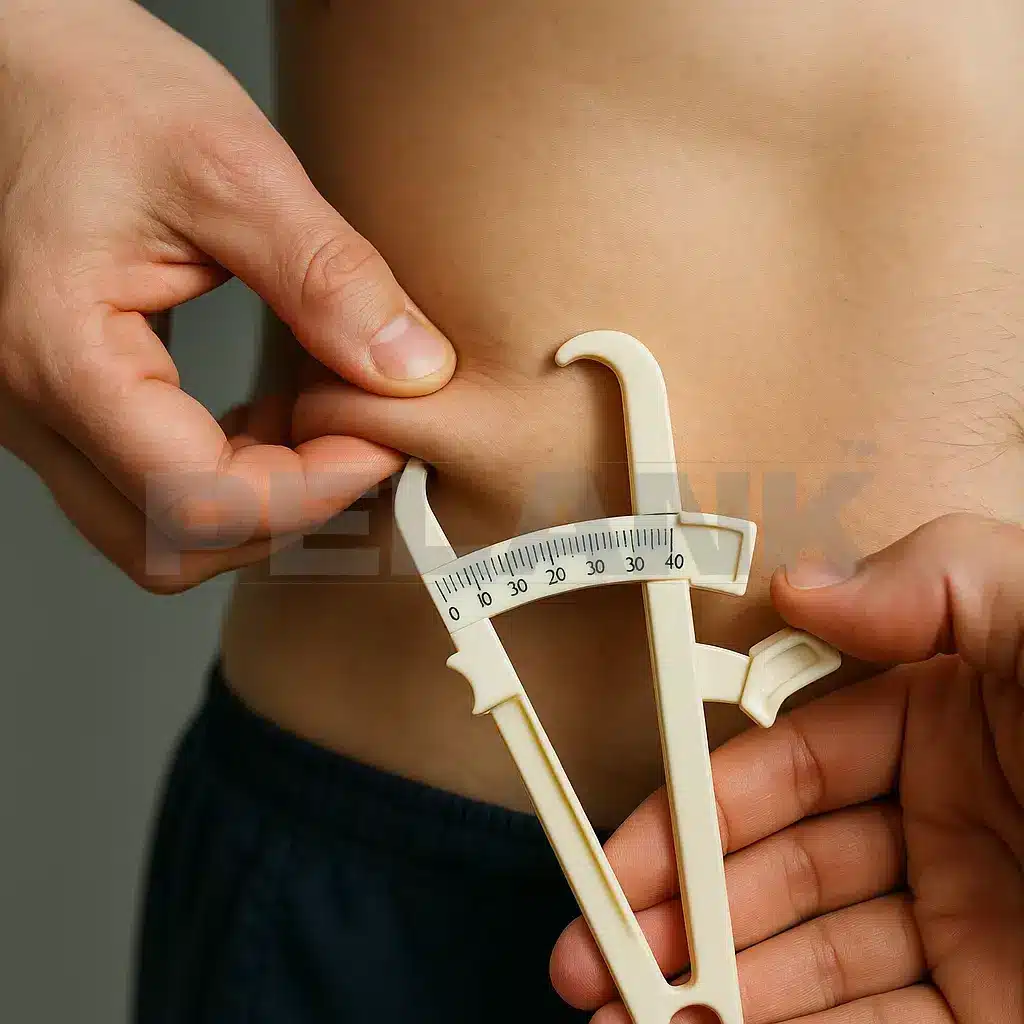
✅ Skinfold
Caliper – Skinfold Measurement
📌 A traditional but effective method
In this method, a caliper is used to measure the thickness of skinfolds at different points on the body (3 to 7 sites). Then, using scientific formulas like Jackson & Pollock, body-fat percentage is estimated.
🎯 Advantages
- Inexpensive
- Can be done at the gym by a trained coach
- Useful for tracking body changes over time
⚠️ Disadvantages
- Accuracy depends heavily on the operator’s skill
- High error margin in very overweight or highly muscular individuals
- Possible mistakes in identifying measurement sites
✅ US Navy Formula
Official U.S. Navy Formula
📌 The foundation of many online calculators
This formula uses measurements of waist circumference, neck circumference, and height (and hip circumference for women) to estimate body-fat percentage using geometric equations.
🎯 Advantages
- Fast, inexpensive, and accessible for everyone
- No special equipment required
- Ideal for accurate calculators like Pelank
- Acceptable accuracy across most populations
⚠️ Disadvantages
- Less accurate than DEXA or BodPod
- Requires precise waist/neck measurements
- Higher error margin in people with uncommon body shapes
✅ Accuracy Comparison of Methods
Accuracy Ranking
Row | Method | Scientific Accuracy | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
🥇1 | DEXA | Very high (±1–2%) | Golden standard |
🥈2 | Hydrostatic | High (±2–3%) | Classic method |
🥉3 | BodPod | High (±3–4%) | Fast and convenient |
4 | Skinfold | Moderate (±3–6%) | Skill-dependent |
5 | BIA | Moderate to low (±3–8%) | Highly dependent on body conditions |
6 | US Navy | Moderate (±4–7%) | Good but not laboratory-level |
✅ Comprehensive Table of Pros and Cons of Each Method
Method | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
DEXA | Most accurate, distinguishes visceral fat | Expensive, slight radiation, limited availability |
BIA | Fast, home-friendly, inexpensive | Low accuracy, highly affected by hydration and food intake |
BodPod | High accuracy, very fast | Rare equipment, expensive |
Hydrostatic | Excellent accuracy | Difficult, requires expertise |
Skinfold | Low cost, suitable for gyms | Accuracy depends on skill |
US Navy | Easy, free, ideal for online use | Moderate accuracy, requires precise measurements |
Body Fat Calculation Formula
How the Formula Works
Body-fat percentage can be measured through laboratory methods such as DEXA or BodPod, but for everyday use, the easiest and most reliable approach is to use validated scientific formulas. In this section, we introduce the best formulas and explain how the Pelank calculator uses them.
✅ US Navy Formula
The most accurate simple and accessible formula
This formula was developed by the U.S. Navy and is one of the most widely used methods for calculating body fat without laboratory equipment.
The calculation is based on body circumference measurements:
📏 For men:
- Neck circumference
- Waist circumference
- Height
📏 For women:
- Neck circumference
- Waist circumference
- Hip circumference
- Height
1️⃣ US Navy Formula – Men
\text{BodyFat} = 86.010 \cdot \log_{10}(Waist – Neck) – 70.041 \cdot \log_{10}(Height) + 36.76
2️⃣ US Navy Formula – Women
\text{BodyFat} = 163.205 \cdot \log_{10}(Waist + Hip – Neck) – 97.684 \cdot \log_{10}(Height) – 78.387
🎯 Why This Formula Is Popular
- Great accuracy compared to home-based methods
- Scientifically validated
- Suitable for most body types
- Lower error rate than cheap BIA devices
⚠️ Important Notes
- Circumference measurements must be accurate
- Use a flexible tape, under clothing, on the correct anatomical points
✅ Skinfold Formula
Jackson & Pollock
This formula is one of the scientifically validated methods approved by ACSM and ISSN. Using a caliper, the thickness of subcutaneous fat is measured at 3, 4, or 7 points on the body.
📌 3-site formula for men:
- Chest
- Abdomen
- Thigh
📌 3-site formula for women:
- Triceps
- Suprailiac
- Thigh
🎯 Very good accuracy — but skill-dependent
If performed by an experienced coach, its accuracy is comparable to BIA and in some cases even better.
⚠️ Limitations
- High error rate in very overweight individuals
- Operator skill is the main factor determining accuracy
✅ Durnin–Womersley Formula
Deurenberg
This formula is simpler than the Navy and Jackson & Pollock methods and uses only BMI + age + sex.
📌 Formula:
\text{BodyFat} = 1.2 \cdot BMI + 0.23 \cdot Age – 10.8 \cdot Sex – 5.4
🔹 Sex = 1 for men, 0 for women
🎯 Advantage
Fast and doesn’t require circumference measurements
⚠️ Limitation
Because it relies only on BMI, it has a high error rate in muscular individuals
Almost unsuitable for bodybuilders
✅ Differences Between Formulas for Men and Women
The bodies of men and women differ in terms of:
- Essential fat percentage
- Hormonal roles
- Fat distribution patterns
- Anatomical structure
Because of this, the formulas are designed separately.
🔵 Men typically store fat in:
- Abdomen
- Waist/sides
- Chest
🔴 Women typically store fat in:
- Hips
- Thighs
- Waist/sides
- Lower-body regions
This is why the Navy formula for women includes hip circumference as an additional measurement.
Ideal Body Fat Percentage for Each Goal
The ideal body-fat percentage isn’t the same for everyone. It depends on your goals, activity level, age, gender, and even genetics. Below, you’ll find the most accurate, science-based ranges recommended for muscle gain, fat loss, general fitness, professional bodybuilding, and overall health.
✅ General Ranges (Without Age Classification)
🔵 Men
Goal | Ideal Body Fat Percentage |
|---|---|
Professional Bodybuilding (Stage Ready) | 5–8% |
Lean Muscle Gain (Lean Bulk) | 10–12% |
Fitness Shape | 12–17% |
General Health | 15–20% |
Fat Loss | 10–15% (target) |
🔴 Women
Goal | Ideal Body Fat Percentage |
|---|---|
Professional Bodybuilding (Stage Ready) | 12–15% |
Lean Muscle Gain (Lean Bulk) | 17–20% |
Fitness Shape | 20–24% |
General Health | 22–30% |
Fat Loss | 18–25% (target) |
⭐ Why do these ranges differ?
- Women have a higher essential fat requirement
- Men store more fat in the abdominal area
- Women store more fat in the hips and thighs
- Hormone levels (estrogen / testosterone) play the main role
✅ Complete Ideal Body-Fat Chart by Age + Gender
This chart is one of the most widely accepted global standards (based on ACSM)
🔵 Men
Age | Essential | Fitness | Average (Normal) | High Fat / Obese |
|---|---|---|---|---|
20–29 | 7–13% | 14–17% | 18–23% | 24%+ |
30–39 | 8–14% | 15–18% | 19–24% | 25%+ |
40–49 | 9–15% | 16–19% | 20–25% | 26%+ |
50–59 | 10–16% | 17–21% | 22–27% | 28%+ |
60+ | 11–17% | 18–22% | 23–29% | 30%+ |
🔴 Women
Age | Essential | Fitness | Average (Normal) | High Fat / Obese |
|---|---|---|---|---|
20–29 | 14–20% | 21–24% | 25–31% | 32%+ |
30–39 | 15–21% | 22–25% | 26–33% | 34%+ |
40–49 | 16–23% | 23–26% | 27–34% | 35%+ |
50–59 | 17–24% | 24–28% | 28–35% | 36%+ |
60+ | 18–25% | 25–29% | 29–36% | 37%+ |
✅ Ideal Body-Fat Percentage for Different Goals
🏆 1) Professional Bodybuilding (Stage Ready)
Men: 5–8%
Women: 12–15%
- Extremely low subcutaneous water
- 100% visible muscle definition
- Unsafe to maintain for long periods
💪 2) Muscle Building (Hypertrophy / Lean Bulk)
Men: 10–12%
Women: 17–20%
- Best range for muscle growth while minimizing fat gain
- Optimal hormonal environment
🔥 3) Fat Loss Phase
Men: aiming for 10–15%
Women: aiming for 18–25%
- Ideal for health + aesthetics
- Achievable without extreme stress on the body
⭐ 4) Fitness Look
Men: 12–17%
Women: 20–24%
- Athletic and well-shaped appearance
- Moderate muscle definition, very healthy
❤️ 5) General Health
Men: 15–20%
Women: 22–30%
- Low obesity risk
- Suitable for a normal, balanced lifestyle
The Difference Between Body-Fat Percentage, BMI, and Weight
Why BF% ≠ BMI ≠ Weight
Many people still think weight or BMI are the best indicators of fitness… but the truth is, these two numbers tell us almost nothing about body composition.
That’s why experts in sports science, medicine, nutrition, and fitness say:
“Body Fat Percentage is the most accurate real-world indicator of health and fitness.”
Let’s break it down 👇
✅ Why Isn’t Weight Enough?
Weight
Weight is simply the sum of:
- Muscle
- Fat
- Water
- Bone
- Glycogen
- Internal organs
👉 By itself, weight doesn’t tell you how much of your body is fat and how much is muscle.
✅ What Is BMI?
BMI, or Body Mass Index, is a very simple formula:
BMI = weight (kg) ÷ height² (m²)
The major problem with BMI:
BMI cannot tell whether your body weight comes from muscle or fat.
✅ What Is Body Fat Percentage (Body Fat %)?
Body-fat percentage tells you:
✔️ What percentage of your total body weight is fat
✔️ How much muscle you have
✔️ What your health and metabolic status look like
✔️ How your physical appearance and body shape are defined
🔥 Visual Explanation
Why can two men who both weigh 80 kg look completely different?
Imagine two people who both weigh 80 kg 👇
🔵 Person A – 12% body fat
Weight: 80 kg
Fat: 9.6 kg
Muscle: high
Appearance: muscular, visible abs
BMI: about 25 (classified as “overweight”!)
Health: excellent
🔴 Person B – 30% body fat
Weight: 80 kg
Fat: 24 kg
Muscle: low
Appearance: belly + love handles
BMI: again 25 (same number!)
Health: high metabolic & cardiovascular risk
👉 Conclusion:
Both weight and BMI are identical, but their bodies are completely different.
This proves BMI cannot reveal the true condition of the body.

🏋️♂️ Why Is BMI Useless for Athletes?
Bodybuilders, CrossFit athletes, and other trained individuals carry a lot of muscle.
High muscle → higher body weight → higher BMI
But their body fat is very low (for example 10–12%).
Even someone like Ronaldo would technically be classified as “overweight” according to BMI! 😅
🧬 Scientific Comparison Table: BMI vs Body Fat %
Criteria | BMI | Body Fat % |
|---|---|---|
Accuracy in identifying body fat | ❌ Low | ✅ Very high |
Suitable for athletes | ❌ Misleading | ✅ Accurate |
Visceral fat detection | ❌ Cannot detect | ✅ Partially possible |
Body-shape assessment | ❌ Zero | ✅ Very accurate |
Medical use suitability | ⚠️ Only for initial screening | ✅ Highly recommended |
Suitable for fitness goal-setting | ❌ No | ⭐ The best metric |
Affected by muscle mass | ❌ Strongly | ✅ Not much |
Affected by height/weight | ✅ Yes | ❌ Much less |
Factors That Influence Body-Fat Percentage
Body-fat percentage isn’t the result of a single factor; it’s shaped by a combination of genetics, hormones, lifestyle, training, nutrition, and sleep—all working together. Below, we break down the most important factors in a clear, scientific way.
1️⃣ 🧬 Genetics
Genetics determines:
- Where your body stores fat (abdomen, sides, thighs, hips)
- Your basal metabolic rate (BMR)
- How much muscle you can naturally build
- How easily you burn or store fat
Examples of genetic influences:
- People with more active LEPR hormone receptors → store fat more easily
- People born with a naturally fast metabolism → lower fat, higher muscle
But 🔥 even genetics can be managed with proper training and nutrition.

2️⃣ 🧪 Hormones
Hormones directly determine whether your body burns fat or stores it.
📌 Key hormones:
🔥 Testosterone
- Increases muscle mass
- Boosts metabolism
- Reduces fat storage
Low testosterone → higher belly fat
😴 Cortisol (stress hormone)
- Elevated levels lead to abdominal fat and emotional overeating
- Less sleep = higher cortisol = more fat gain
🍬 Insulin
- Regulates blood sugar
- Insulin resistance → more fat storage
High-carb diet + low activity → elevated insulin
🌸 Estrogen (in women)
- Promotes fat storage in hips and thighs
- Monthly hormonal changes cause fluctuations in fat and water levels
3️⃣ 😴 Sleep
The Hidden Fat Burner
Sleep is one of the most powerful fat-loss factors.
Lack of sleep causes:
🔸 Increased cortisol
🔸 Lower testosterone
🔸 Higher appetite (due to increased ghrelin)
🔸 Reduced nighttime fat burning
🔸 Fatigue → less daily activity
🔥 With just 7–9 hours of quality sleep, your body burns fat far more efficiently.
4️⃣ 🍽️ Nutrition
Nutrition is the most direct factor influencing body-fat percentage.
Key points:
✔️ Calorie surplus → fat gain
✔️ Calorie deficit → fat loss
✔️ High protein → more muscle + reduced appetite
✔️ Healthy fats (omega-3s, avocado, almonds) → improved hormones
✔️ Simple sugars → insulin spikes → fat storage
🔥 Ideal diet:
High protein + controlled carbs + healthy fats + plenty of fiber
5️⃣ 🏋️♂️Strength Training
Strength training is the most important long-term fat-loss tool.
Because:
✔️ Muscle increases your metabolism
✔️ Your body burns more fat for up to 24 hours after training (afterburn effect)
✔️ It boosts testosterone and growth hormone
🔥 Ideal routine:
3–4 weight-training sessions per week
6️⃣ 🏃♂️ Cardio
Cardio burns calories directly.
✔️ HIIT → fast fat burning
✔️ LISS → steady, sustainable fat loss
✔️ Too much cardio → muscle loss (if protein is low)
🔥 Best combination:
2–3 moderate-intensity cardio sessions per week
7️⃣ 😣 Stress
Chronic stress = high cortisol =
🔸 More belly fat
🔸 Strong cravings for sugary foods
🔸 Poor sleep
🔸 Reduced muscle mass
🔥 Lower stress = better fat loss
Quick strategies:
🔸 Deep breathing
🔸 Meditation
🔸 Walking
🔸 Avoiding caffeine after the afternoon
🟩 Body-fat percentage is shaped by a combination of factors:
✔️ Genetics sets the baseline
✔️ Hormones guide the direction
✔️ Sleep and stress control the speed
✔️ Diet and training are the main drivers
When these factors align correctly, fat loss becomes faster, muscle gain becomes easier, and long-term health improves dramatically.
10 Common Mistakes When Measuring Body-Fat Percentage
If body-fat measurement is done incorrectly, it can produce completely inaccurate results. These mistakes can shift the number by 5% to even 10%!
Below are the most common errors people make and why they matter.

1️⃣ Using cheap smart scales
Cheap BIA Scales
⚖️ Many low-cost BIA smart scales:
❌ Send the electrical current only through the lower body
❌ Misinterpret hydration levels dramatically
❌ Have an error margin of 3% to 8%
❌ Change the reading completely if your skin is dry or wet
⚠️ These scales are useful for tracking relative changes, but not for getting an accurate body-fat number.
2️⃣ Measuring waist or neck circumference incorrectly
🪖 With the Navy formula—or any formula—incorrect measurements = incorrect results.
Common mistakes:
❌ Holding the tape too high or too low
❌ Pulling the tape too tight
❌ Measuring over clothing
❌ Misidentifying the navel or side-waist location
❌ Bending forward and changing abdominal shape
🔥 Best method:
✔️ Stand straight, exhale, place the tape on the skin, with no extra tension.
3️⃣ Measuring right after a workout
After a workout, several things happen:
🔸 Body temperature rises
🔸 Hydration levels drop
🔸 Sodium and electrolytes shift
🔸 Muscle size temporarily increases (the pump)
Result?
❌ Scales and formulas give completely inaccurate numbers.
🔥 Best time to measure:
✔️ In the morning after waking up, before eating, on an empty stomach.
4️⃣ Changes in body water levels
Hydration Level
Water balance is the biggest source of error in body-fat measurements.
❌ Dehydration → body-fat percentage appears higher
❌ Excess water → body-fat percentage appears lower
❌ High salt intake → changes electrical resistance
❌ Menstrual cycle → increases water retention and weight
🔥 Your body can fluctuate by 1–3 kg of water throughout the day, which can completely alter BIA readings.
5️⃣ Hormonal conditions in women
Female Hormonal Cycle
In women, the menstrual cycle causes:
🔸 Changes in water retention
🔸 Weight fluctuations
🔸 Abdominal bloating
🔸 Shifts in the body’s electrical impedance
Because of this, measurements taken on different cycle days can vary by 2–4%.
🔥 Best timing for women:
✔️ Days 6–10 of the cycle (lowest water retention).
6️⃣ Using calipers by an inexperienced person
If a skinfold test is done incorrectly:
❌ The wrong site is measured
❌ The skinfold isn’t properly separated
❌ Hand pressure varies each time
❌ Muscle is mistakenly grabbed instead of fat
⚠️ This method is only accurate when performed by a trained professional.
7️⃣ Using old or uncalibrated devices
❌ Old DEXA scanners
❌ Old gym BIA devices
❌ BodPod units without calibration
❌ Old or unstable scales
All of these can show body-fat measurements that are off by several percentage points.
8️⃣ Judging by photos
Visual Estimation
A lot of people see someone’s photo and say:
“Is that 12% body fat? No way, it’s higher!”
But estimating body fat from a photo is highly inaccurate and depends on:
🔸 Lighting
🔸 Angle
🔸 Muscle pump
🔸 Genetics
🔸 Skin thickness
🔸 Fat distribution
9️⃣ Measuring over clothing or with a low-quality tape measure
❌ Measuring over thick clothing
❌ Using a stiff, non-flexible tape
❌ Using a stretched-out fabric tape
Each of these can change the measurement by 1–3 cm,
→ making the formula’s output completely inaccurate.
🔟 Comparing measurements on irregular days
For accurate measurements:
✔️ Always at the same time of day
✔️ Under the same conditions (fasted/before meals/after a shower)
✔️ With the same tools
✔️ In the same phase of the menstrual cycle for women
🔥 Consistency = accuracy
80% of body-fat errors come from incorrect measurement methods—
not from the formula or the scale itself.The Pelank Calculator works accurately only when the input variables are accurate.
How do we reduce body fat percentage?
Reducing body fat doesn’t happen just by “eating less” or “doing tons of cardio.”
It’s a smart combination of nutrition, training, sleep, recovery, stress management, and supplements.
Below, we explain the most reliable science-based principles clearly and directly.
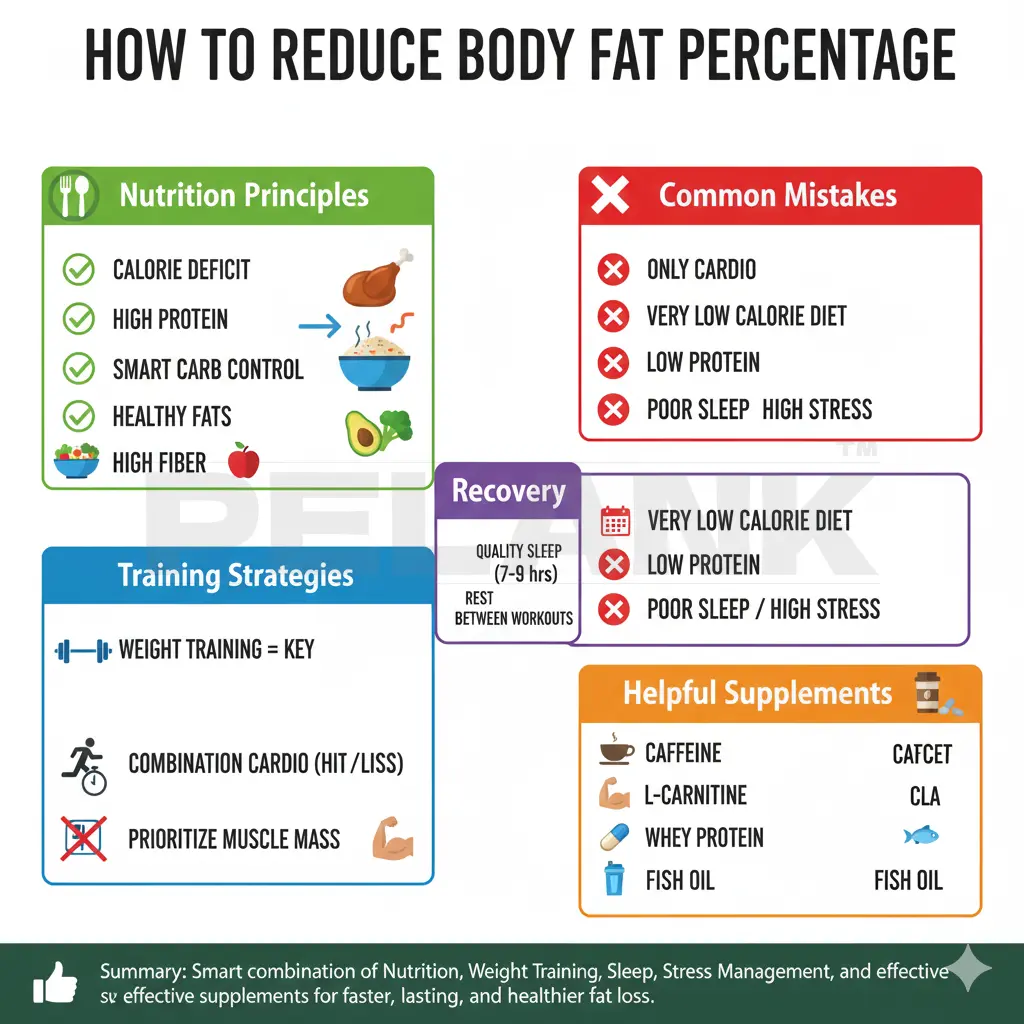
1️⃣ Nutrition principles for fat loss
✔️ 1. Create a Calorie Deficit
No diet burns fat without a calorie deficit.
Standard deficit:
20–30% below your maintenance calories
Not too big → prevents muscle loss
Not too small → prevents metabolic slowdown
✔️ 2. High Protein
Protein helps with:
- Reducing appetite
- Increasing metabolism
- Preventing muscle breakdown
Recommended amount:
1.6 to 2.2 g per kg of bodyweight
✔️ 3. Smart Carb Control
Carb timing matters a lot:
- Before training: a small amount of carbs for energy
- After training: protein + carbs
- Rest days: fewer carbs
✔️ 4. Healthy Fats
(Nuts, avocado, fish, olive oil, eggs)
They improve hormones, reduce inflammation, and keep you satisfied.
✔️ 5. High Fiber
(Vegetables, salads, low-sugar fruits, oats)
Fiber controls appetite and keeps insulin responses balanced.
2️⃣ Training tips
✔️ 1. Resistance Training (Weight Training) = the most important principle
Strength training leads to:
- More muscle
- Higher BMR
- 24-hour fat burning (Afterburn Effect)
Suggested plan:
3–4 sessions per week
✔️ 2. Combined Cardio
HIIT: fast fat burning
LISS: steady fat burning
Golden formula:
2 HIIT sessions + 2 LISS sessions per week
✔️ 3. Prioritize muscle building—not excessive cardio
Too much cardio → muscle loss → lower metabolism
Which means fat comes back more easily later.
3️⃣ Recovery
✔️ 1. High-quality sleep (7–9 hours)
Poor sleep leads to:
Cortisol ↑
Testosterone ↓
Belly fat ↑
Appetite ↑
The best fat-burning “medicine” = enough sleep.
✔️ 2. Low stress
Chronic stress stops fat loss.
Useful methods:
- Walking
- 4-7-8 breathing
- Reducing afternoon caffeine
- Short meditation
✔️ 3. Rest between workouts
Muscle grows during recovery, not in the gym.
4️⃣ Common fat-loss mistakes
❌ Doing only cardio
Without resistance training → muscle loss, less fat loss.
❌ Very low-calorie diets
Metabolism crashes and the body goes into survival mode.
❌ Low protein
With low protein, fat loss is weak even in a deficit.
❌ Training without a plan
No structure → slow progress
A proper plan → faster results
❌ Poor sleep or high stress
The biggest fat-loss killer = bad sleep.
5️⃣ Useful supplements for fat loss
Supplements are not a miracle, but they can be helpful alongside a proper diet and training.
⚡ 1. Caffeine
- Boosts energy
- Increases focus
- Enhances fat burning during workouts
- Best time: 30 minutes before training
🔥 2. L-Carnitine
- Transports fatty acids to the mitochondria
- Helps use fat as energy
- Best effect in people with moderate fat levels
- Dose: 1000–2000 mg
💛 3. CLA (Conjugated Linoleic Acid)
- Moderate but sustained fat-burning effect
- Helps reduce belly fat
💪 4. Whey Protein
- Increases muscle mass
- Helps with satiety
- Improves recovery
- A great tool for hitting daily protein goals
🐟 5. Fish Oil (Omega-3)
- Reduces inflammation
- Improves hormones
- Indirectly supports fat loss
Body fat reduction is a smart combination of:
✔️ Proper nutrition
✔️ Resistance training
✔️ Targeted cardio
✔️ Sufficient sleep
✔️ Stress management
✔️ Choosing effective supplements
When all of these come together, body fat decreases faster, more sustainably, and in a healthier way.
Body Fat Percentage Comparison with Images Examples
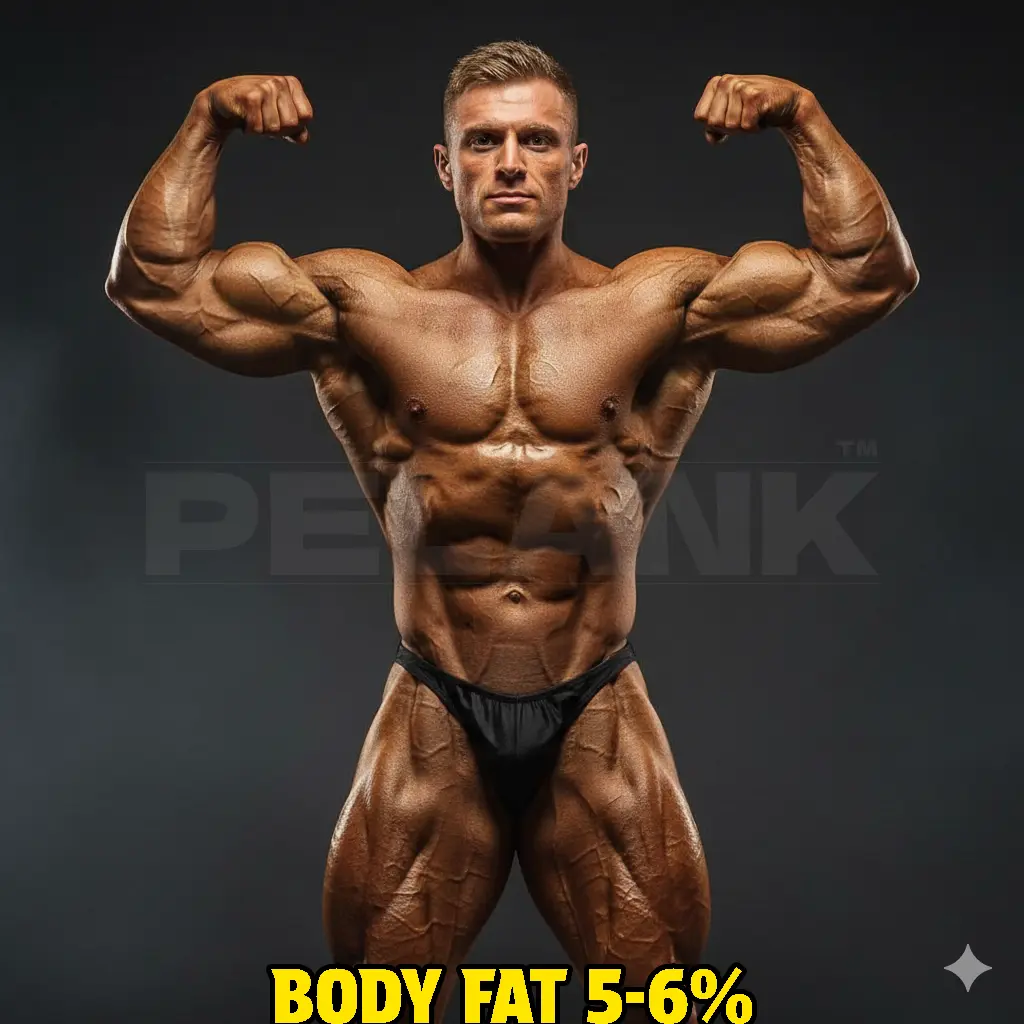
5-6% Body Fat: This level of body fat is typically seen in professional bodybuilders during competition time. Muscles are fully defined, and veins are prominent.

10-12% Body Fat: At this level, muscle definition is good, and the abdominal muscles (six-pack) are clearly visible. Veins are also visible in certain areas.

15-17% Body Fat: At this range, the abdominal muscles may still be slightly visible, but muscle definition is less pronounced. The body shape still appears fit and athletic.

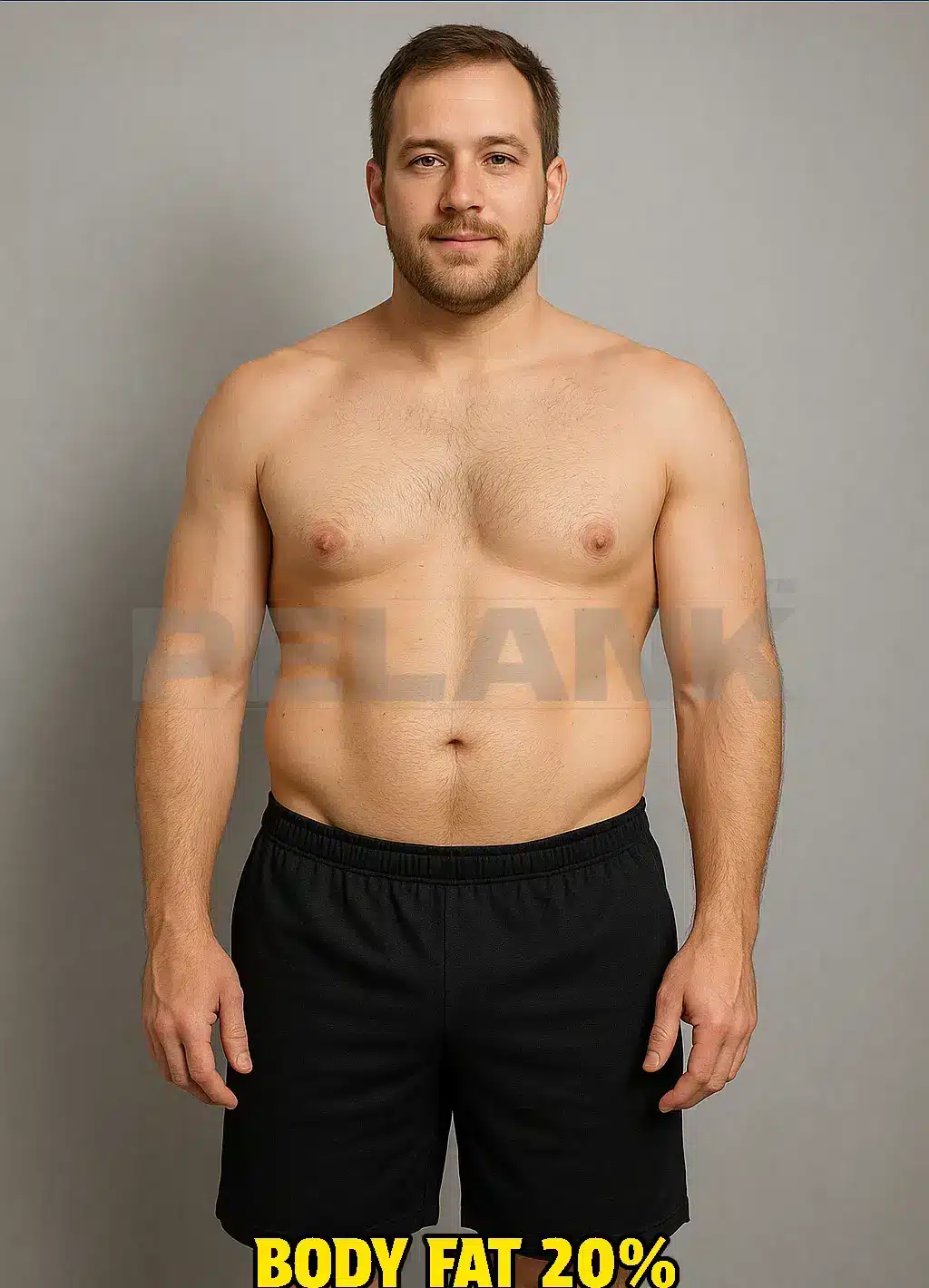
20% Body Fat: At this level, the abdominal muscles are rarely visible, and the body has a smoother appearance. A small amount of fat is noticeable on the abdomen and sides.

25-30% Body Fat: At this level, there is a noticeable accumulation of fat, clearly visible in the abdomen, sides, thighs, and arms. Muscle definition is less apparent, and the body may have a rounder, softer appearance. Typically, individuals in this range fall into the “overweight” or “obesity class 1” category.

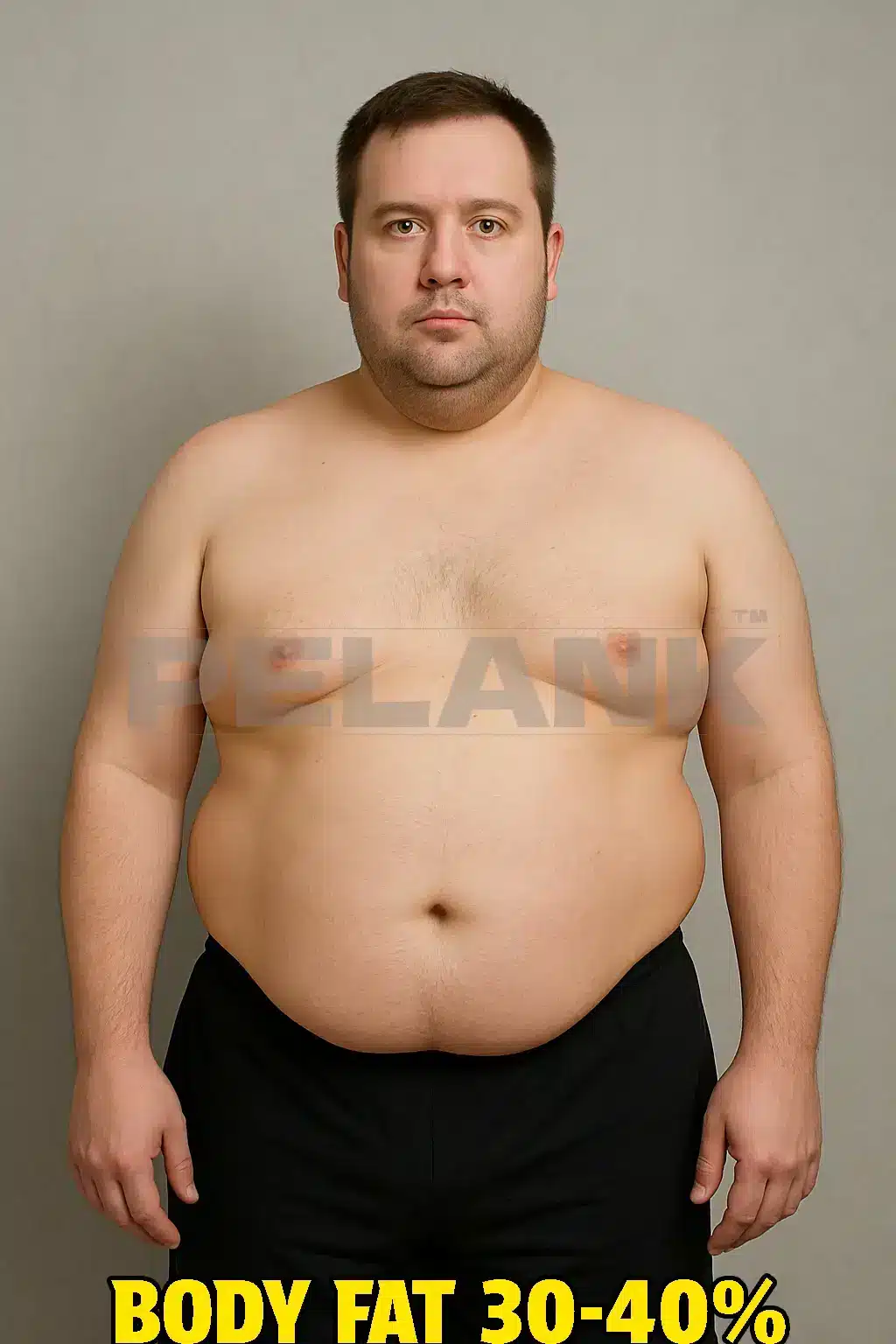
30-40% Body Fat: At this range, body fat accumulation is very high and noticeable. Fat is widely distributed throughout the body, particularly in the abdomen, waist, and chest, creating significant volume. Muscle definition is virtually nonexistent, and body definition has completely disappeared. Individuals in this range are typically classified as “obese,” with an increased risk of weight-related health issues.

+40% Body Fat: This level indicates severe obesity or morbid obesity. The amount of body fat is extremely high and has accumulated uncontrollably throughout the body. Body volume has significantly increased, and physical movement may become difficult. At this range, visceral fat, which surrounds internal organs, is usually very high. This condition is associated with the highest risk of serious and chronic diseases, such as type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, and cardiovascular issues.

Frequently Asked Questions
FAQ
The best time is in the morning, right after waking up, before eating or drinking anything.
At this time:
- Body water levels are more stable
- Food and exercise haven't had an impact yet
- The result variation is minimized
The most accurate methods are:
- DEXA Scan
- Hydrostatic Weighing (Underwater Weighing)
These methods are considered the gold standard in scientific research, with very low error margins.
In general, yes, but it's not accurate.
Lighting, angle, muscle pump, fat distribution, skin thickness, and genetics can make visual guesses completely incorrect.
For a scientific decision, you should use a formula or tool.
Yes.
Women's bodies naturally require more essential fat due to:
- Estrogen hormones
- Menstrual cycle
- Reproductive function
- Energy storage in the hips and thighs
Therefore, comparing women's bodies to men's is not accurate.
For tracking real progress:
Every 6 to 8 weeks.
Weekly measurements are usually influenced by body water fluctuations and are not accurate.
Because they are highly influenced by:
- Body water levels
- Food intake
- Exercise
- Body temperature
- Skin contact with electrodes
- The scale's power source
These scales are good for tracking "overall trends," but not for precise measurements.
Yes!
By:
- Maintaining a mild calorie deficit
- Consuming enough protein
- Doing resistance training
- Getting enough sleep
- Managing stress
You can lose fat while preserving or even gaining muscle.
Yes, with age:
- Metabolism decreases
- Muscle building becomes harder
- The body retains more fat
Therefore, the "healthy" body fat percentage for older individuals is slightly higher.
A lot!
A fluctuation of 1 to 3 kg of body water can cause a 2 to 3% difference in BF%.
Factors like salt intake, stress, lack of sleep, menstruation, and intense workouts can cause water fluctuations.
No, not on its own.
BF% is very important, but for a complete picture, it should be considered alongside:
- Strength
- Athletic performance
- Body measurements
- Daily energy levels
- Overall health

Mohsen Taheri
November 30, 2025