The Comprehensive Guide to Omega-3 Supplements
🐟 Omega-3: The Complete Scientific Guide to Benefits, Dosage, Sources, and the Best Fish Oil Supplements
✅ Did you know a simple Omega-3 deficiency can affect your heart, brain, mood, inflammation, skin, and even your athletic performance? Omega-3 isn’t just a healthy fat; it’s one of the most essential nutrients for the body, with dozens of scientific studies confirming its vital role in general health and even disease prevention.
✅ But here’s the thing most people don’t know:
Not all Omega-3s are alike! EPA, DHA, and ALA each have different functions, and the real impact of Omega-3 depends on the type, dosage, and quality of the supplement you choose.
✔️ In this comprehensive guide, you’ll learn:
✔️ Exactly what Omega-3 does in the body
✔️ What benefits it has for the heart, brain, joints, and skin
✔️ What the best dosage is for different goals
✅ Is EPA more important, or DHA?
Does Omega-3 actually help with depression, inflammation, or athletic recovery?
Risks, side effects, and important tips for buying a high-quality supplement
🎯 This article is written so that after reading it, you will have no unanswered questions about Omega-3. If you want to know exactly whether this supplement is right for you, don’t miss the rest of the content.
Omega-3 Supplement
Pelank Supplement ©
✅ Omega-3
🥗 Omega-3 is a group of essential fatty acids that the body needs but cannot produce, so it must be obtained through food or supplements.
❤️ These fatty acids play a vital role in heart health, brain function, vision, inflammation control, and cellular health.
✔️ The three main types of Omega-3 include ALA (plant-based 🌱), EPA, and DHA (marine-based 🐟), each having a different function in the body and varying absorption rates.

✅ Why did Omega-3 become one of the best-selling supplements in America?
🔥 In recent years, Omega-3 has become one of the best-selling nutritional supplements in America 🇺🇸—and it’s not just a trend!
There are several important reasons behind this popularity:
🔬 Strong Scientific Backing: Hundreds of reputable studies have shown that EPA and DHA significantly contribute to heart health, lowering triglycerides, improving mood, reducing inflammation, and even athletic performance.
🍔 Modern Diet and Omega-3 Deficiency: Many Americans have low fish consumption and suffer from a chronic Omega-3 deficiency—leading them to turn to supplements.
👨👩👧 Diverse Consumer Groups: Athletes, seniors, pregnant women, students, office workers, and even children all have separate reasons for taking Omega-3.
📢 Increased Awareness: The public’s familiarity with the benefits of Omega-3 and its vital role in health has led to continuous growth in the consumption of this supplement.
⭐ This combination of factors has kept Omega-3 at the top of the list of popular supplements in America for years.
✅ Types of Omega-3 Supplements
✨ Today, Omega-3 is produced in various forms, and choosing the right one can completely change the results of its consumption.
1️⃣ Fish Oil
✔️ The most common and popular type of Omega-3, rich in EPA and DHA.
Suitable for: Heart health, brain health, reducing inflammation, and general consumption.
2️⃣ Algae Oil
✔️ The best source of Omega-3 for vegetarians and vegans.
✔️ High purity, free of marine contaminants, rich in DHA and sometimes EPA.
3️⃣ Plant-Based Omega-3
ALA
✔️ Extracted from flaxseed, chia, walnuts, and some vegetable oils.
✔️ Important Note: The conversion of ALA to EPA/DHA in the body is very low, so it does not have a strong therapeutic effect.
4️⃣ Krill Oil
Krill Oil
✔️ Extracted from tiny marine creatures called krill.
✔️ Advantages: Better absorption, higher natural antioxidant (astaxanthin), less fishy smell.
5️⃣ Concentrated Omega-3s
✔️ Chemical Forms and Concentration
✔️ Produced in Triglyceride, Ethyl Ester, Phospholipid, and Re-esterified TG forms.
✔️ Suitable for high doses, therapeutic purposes, or faster results.
What is Omega-3 and what is its role in the body?
✅ Definition of Essential Fatty Acids
🟩 Essential Fatty Acids (EFAs) are a group of fats that the body needs for survival, cellular health, and proper organ function, but it cannot produce them. These fats must be supplied through diet or supplements. The two main families of these acids include Omega-3 and Omega-6, which each have different roles in the body; however, Omega-3 has special importance due to its anti-inflammatory effects and vital function in the brain, heart, and nervous system.

✅ Why Can't the Body Produce Omega-3?
🟩 The human body lacks the necessary enzyme to produce Omega-3; this is why these fats are designated as “essential.” The body’s metabolic pathways can convert some fatty acids, but the production of EPA, DHA, or even ALA is practically impossible.
✔️ This is why regular intake of Omega-3 through seafood, plant sources, or supplements is absolutely essential for proper bodily function.
✅ The Role of Omega-3 in Cell Structure
🟩 Omega-3 forms a crucial part of the Cell Membrane and gives cells flexibility, resilience, and better material transport capabilities.
🟩 DHA is especially abundant in the membranes of nerve and visual cells; sufficient Omega-3 ensures better cell signaling and reduces inflammation in tissues.
✅ The Role of Omega-3 in the Brain
🧠 Over 30% of the brain’s fats are composed of DHA; this is why Omega-3 is vital for neuronal function, focus, mood, and nervous system health.
✔️ Research has shown that Omega-3 deficiency can affect mood, memory, cognitive function, and even the risk of depression.
✔️ This is why DHA is considered one of the most important fats for fetal and childhood brain development.
✅ The Role of Omega-3 in the Eye
👁️ DHA is one of the main components of the retina, and its deficiency can lead to dry eyes, visual impairment, and inflammatory eye disorders.
✔️ Sufficient Omega-3 intake can help lubricate tears, protect retinal cells, and reduce eye inflammation.
✅ The Role of Omega-3 in Reducing Inflammation
🔥 Omega-3 possesses a strong anti-inflammatory property and helps the body control inflammation and accelerate tissue repair by producing molecules called Resolvins and Protectins.
✔️ This characteristic is one of the main reasons why Omega-3 is valuable for heart health, reducing joint pain, lowering systemic inflammation, and improving conditions like arthritis.
Types of Omega-3
🐟 EPA: Key Functions
✔️ EPA, or Eicosapentaenoic Acid, is one of the most important marine omega-3 fatty acids. Its primary role in the body is to reduce inflammation, improve heart health, and regulate triglycerides.
✔️ EPA is involved in the formation of anti-inflammatory molecules such as resolvins. For this reason, it is extremely important for individuals suffering from joint inflammation, heart disease, oxidative stress, and maintaining mental health.
✔️ Higher doses of EPA have also shown a positive effect on depression and mood in some studies.

🧠 DHA: Role in the brain, eyes, and growth
✔️ DHA, or Docosahexaenoic Acid, plays the biggest role among all types of Omega-3s in the brain and nervous system.
✔️ More than 30% of the fats in the brain and about 90% of the fats in the retina are made of DHA, which is why this fatty acid is essential for vision, focus, learning, memory, and nervous system health.
✔️ DHA plays a crucial role in fetal brain development, the evolution of the nervous system in children, and cognitive health in the elderly. A deficiency can be linked to cognitive or visual problems.
🌱 ALA: Plant Source and Conversion Limitations
✔️ ALA, or Alpha-Linolenic Acid, is the plant-based type of Omega-3, found in sources like flaxseed, chia, walnuts, and canola oil.
✔️ For the body to use ALA, it must first convert it into EPA and DHA, but this conversion is very limited in humans: Approximately 5% is converted to EPA, and less than 1% is converted to DHA.
✔️ For this reason, ALA is beneficial for overall health, but it is not sufficient for therapeutic effects or serious benefits like heart and brain health, and it cannot replace marine sources of EPA/DHA.
🌊 The Difference Between Plant, Animal, and Marine Omega-3
Omega-3 is offered in three main groups, and each one has a different quality and effectiveness:
🟦 Marine Omega-3 (EPA + DHA):
The most effective and absorbable form of Omega-3 with the greatest scientific backing. Best sources: fatty fish, fish oil, algal oil, krill oil.
🟩 Plant Omega-3 (ALA):
Suitable for general health and vegetarians, but with less therapeutic effect. Best sources: flaxseed, chia, walnuts.
🟥 Non-Marine Animal Omega-3:
Found in animal products such as fortified eggs or grass-fed meat, but the EPA/DHA content is much lower than marine sources.
🔍 Summary: For real scientific benefits—especially for the heart, brain, eyes, and inflammation—EPA and DHA are essential and are only found in marine sources or reputable supplements.
Scientific Benefits of Omega-3
Based on reputable studies
✅ Omega-3 is one of the few supplements where dozens of reputable studies have confirmed its effects on the health of the heart, brain, joints, eyes, skin, pregnancy, and even athletic performance.
🔸 In this section, we will review all the scientific benefits of EPA and DHA in a precise and categorized manner.
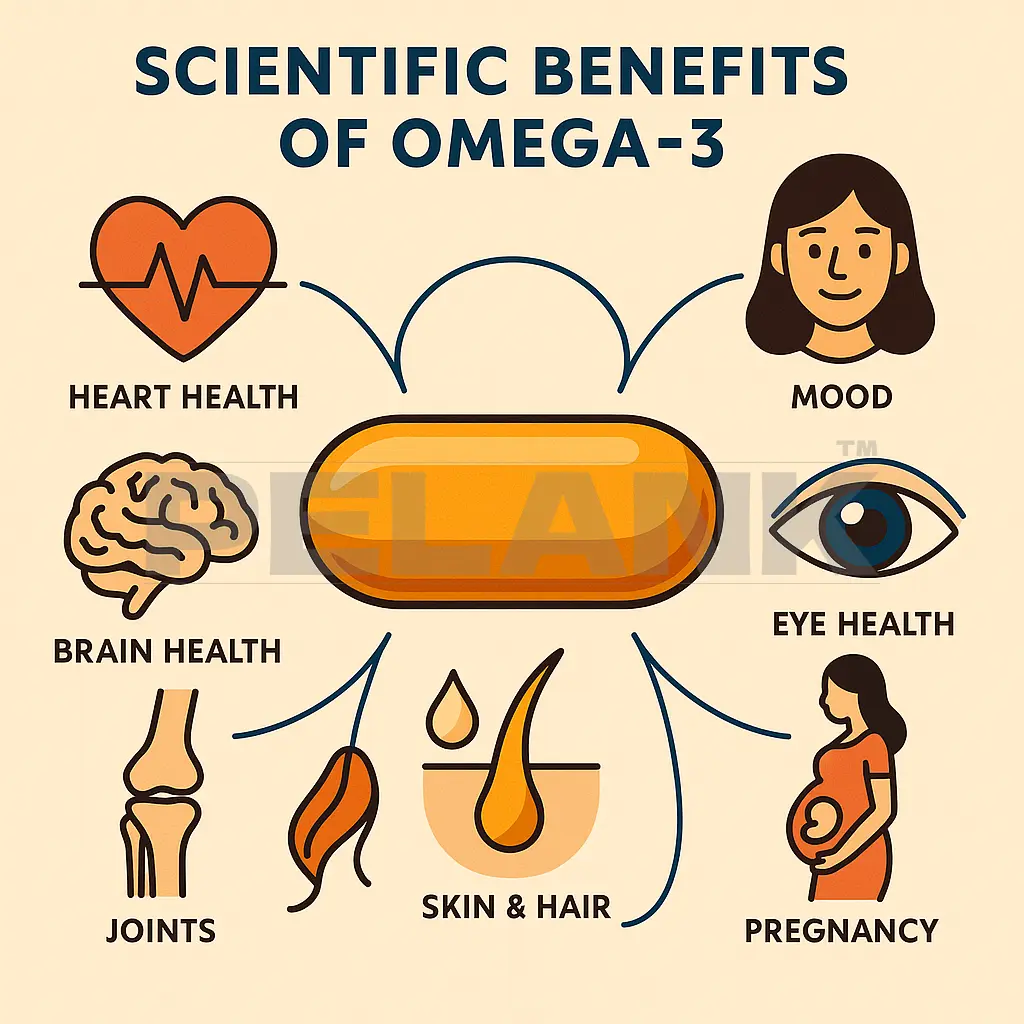
1️⃣ Cardiovascular Health
❤️ Reduced Triglycerides
Omega-3, particularly EPA, is one of the most effective natural substances for lowering blood triglycerides.
Studies have shown that regular Omega-3 consumption can reduce triglyceride levels by 15% to 30%.
💓 Effect on Blood Pressure
Omega-3 can lower blood pressure, especially in individuals with high blood pressure, by relaxing blood vessels and reducing inflammation in the artery walls.
A reduction in blood pressure has been reported even at moderate doses of Omega-3.
🔥 Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Chronic inflammation is one of the main causes of heart problems.
EPA and DHA help the body reduce inflammation by producing protectins and resolvins; this anti-inflammatory effect is an important factor in heart health.
🫀 Reduced Risk of Heart Disease
Long-term studies have shown that regular consumption of Omega-3 can reduce the risk of heart events such as heart attack and cardiac death.
This effect is due to a combination of benefits including reduced inflammation, lowered triglycerides, improved vascular health, and regulation of heart rate.
2️⃣ Brain and Nervous System Health
🧠 Mood Improvement
DHA and EPA can influence neurotransmitters like serotonin.
This characteristic has made Omega-3 beneficial for people experiencing mood swings.
🙂 Aid in Depression and Anxiety
Many studies have shown that Omega-3 supplements—especially those with a high dose of EPA—have a positive effect in reducing the symptoms of depression and anxiety.
In some cases, its effectiveness has been reported to be close to that of antidepressant medications.
🧩 Cognitive Function and Memory
DHA is vital for neuron function and helps improve brain cell communication, memory, and focus.
This effect also leads to enhanced mental performance in the elderly.
🧓 Reduced Risk of Alzheimer’s Disease
DHA is the most important structural fat in the brain.
Studies have shown that higher levels of DHA in the diet can reduce the risk of diseases like Alzheimer’s or slow down their progression.
3️⃣ Joint Health and Inflammation
🦴 Role in Arthritis
Omega-3 is one of the most well-known supplements for improving the symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis.
This effect is mostly due to the reduction of joint inflammation and decreased morning stiffness.
🔥 Reduced Systemic Inflammation
EPA helps reduce inflammation throughout the entire body.
This is beneficial for conditions like fibromyalgia, chronic pain, and even gastrointestinal inflammation.
4️⃣ Eye Health
👁️ Prevention of Dry Eyes
Omega-3 improves tear flow and reduces dry eyes—especially those caused by excessive use of mobile phones and computers.
🔬 Role of DHA in the Retina
DHA is one of the main components of the retina, and its deficiency can impair eye function.
Adequate consumption of it improves the quality of vision and protects retinal cells.
5️⃣ Skin and Hair Health
✨ Reduced Skin Inflammation
Omega-3, with its anti-inflammatory properties, can reduce skin redness, sensitivity, and inflammation.
🧴 Improved Eczema and Psoriasis
The results of some studies have shown that Omega-3 consumption can reduce the severity of inflammatory skin diseases.
🧪 Role in Skin Cell Membrane Health
DHA and EPA contribute to the softness, flexibility, and moisture of the skin, helping to maintain the health of the cellular layers.
6️⃣ Athletic Performance
💪 Muscle Recovery
Omega-3 helps reduce muscle inflammation after exercise, leading to faster recovery.
🏋️ Support for Muscle Function
DHA plays an important role in neuromuscular communication, and its regular consumption can improve muscle function and contraction.
⚡ Reduced DOMS (Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness)
Studies have shown that Omega-3 can reduce the severity of muscle soreness 24 to 72 hours after exercise.
7️⃣ Pregnancy and Fetal Health
🤰 Role of DHA in Fetal Brain Development
DHA is the main structural component of the fetal brain, and its deficiency is associated with neurodevelopmental problems.
This is why doctors often recommend DHA consumption during pregnancy.
🍼 Recommended dose during pregnancy
Most research suggests a daily intake of 200–300 mg of DHA during pregnancy.
8️⃣ Other studied benefits
🫀 Liver health (Fatty Liver)
Omega-3 can reduce liver triglycerides and may be effective in improving non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
🛡️ Immune system enhancement
By reducing inflammation and improving immune cell function, omega-3 helps balance the body’s immune system.
🎯 Help with ADHD
DHA plays a vital role in brain function, and some research has shown that omega-3 consumption can improve the focus and behavior of children with ADHD.
🦴 Effect on bone health
Omega-3 may have a positive effect on bone strength by reducing inflammation and helping with better mineral absorption.
Food Sources of Omega-3
🐟 Fatty fish
Salmon, sardines, mackerel, and so on.
✅ Fatty fish are the best and richest sources of EPA and DHA—the two types of omega-3 that have the greatest impact on heart, brain, and eye health, and inflammation reduction.
✔️ Regular consumption of these fish—at least 2 servings per week—can directly make up for omega-3 deficiency and meet the body’s needs.
The best options include:
🔸 Salmon
🔸 Sardine
🔸 Mackerel
🔸 Halibut, tuna, trout, and herring
✔️ In addition to omega-3, these fish are also good sources of vitamin D, high-quality protein, and selenium.

🌱 Plant-based sources
Chia, flax, walnuts
✅ Plant sources of omega-3 primarily contain ALA. ALA is the plant-based type of omega-3 that the body must convert to EPA and DHA—but as we know, this conversion is very limited (less than 5%).
✔️ Despite this, consuming these foods is beneficial for overall health, high fiber content, and antioxidants.
The best plant-based sources of omega-3:
🔸 Chia Seeds
🔸 Flaxseed
🔸 Walnuts
🔸 Flaxseed oil, canola oil, and soybean oil
These sources are suitable options for vegetarians and vegans, but they do not fully replace marine EPA/DHA on their own.
🧴 Marine and Algae Oils
✅ Oils extracted from marine sources have a high concentration of EPA and DHA and play the most significant role in the therapeutic benefits of omega-3. These oils are also offered as supplements, but they exist in food form as well.
Key types:
🔸 Fish Oil: The most famous and widely used source of omega-3.
🔸 Krill Oil: Better absorption, high astaxanthin, less odor.
🔸 Algal Oil: The best option for vegetarians; a direct source of DHA and sometimes EPA.
🔸 Cod Liver Oil: In addition to omega-3, it is rich in vitamins D and A.
Algal oils are the best alternative for people who cannot consume fish (due to allergies or dietary restrictions).
Daily Requirements and Appropriate Dosage of Omega-3
RDA
✅ Recommended amount for healthy individuals
🟩 The exact daily requirement of omega-3 varies depending on the type (EPA/DHA), but the most reputable scientific bodies typically recommend a daily intake of:
✔️ 250 to 500 mg of EPA + DHA for healthy individuals.
This amount is sufficient for heart and brain health and general inflammation reduction, and it can be supplied through supplements or two servings of fatty fish per week.

✅ Therapeutic dose for triglycerides and inflammatory issues
🟩 To reduce triglycerides and treat inflammatory issues, studies suggest higher doses:
✔️ 1,000 to 4,000 mg (1 to 4 grams) of EPA + DHA per day
Higher doses are usually taken as a concentrated supplement and are beneficial for individuals with heart issues or high triglycerides.
📌 Note: Doses over 3 grams should be taken under a doctor’s supervision, especially if the individual is taking blood-thinning medication.
👧🏻 Appropriate dose for children
🟩 Children’s needs vary depending on age:
✔️ 1–3 years: Approximately 70–100 mg DHA
✔️ 4–8 years: About 100–150 mg of DHA
✔️ 9–13 years: About 150–200 mg of DHA
Children who don’t eat fish or follow a plant-based diet usually need child-specific supplements (containing algal DHA).
🤰🏻 Recommended dosage during pregnancy and breastfeeding
🟩 Pregnancy and breastfeeding are the most critical times for DHA intake because DHA is essential for the development of the brain, eyes, and nervous system of the fetus.
Recommended amount:
✔️ 200 to 300 mg of DHA daily
📌 Some pregnancy supplements contain DHA, but many still don’t have a sufficient dose. For mothers who don’t consume fish, algae oil (Algal DHA) is the best option.
✅ Difference between EPA and DHA
🟩 EPA and DHA serve different roles, and their appropriate dosage varies depending on the intended purpose:
✅ EPA is more for:
- Reducing inflammation
- Lowering triglycerides
- Improving depression and mood
- Heart health
✔️ The EPA dose typically makes up 60 to 70% of therapeutic formulas.
✅ DHA is more for:
- Brain health
- Eye health
- Fetal development
- Cognition and memory
✔️ DHA doses are typically higher in pregnancy or cognitive supplements.
📌 Key point:
✔️ If your goal is to treat inflammation or depression → More EPA
✔️ If your goal is brain, eye, or pregnancy health → More DHA
Types of Omega-3 supplements on the market
✅ Fish Oil
✔️ Fish oil is the most common and popular form of omega-3 supplement, derived from fatty fish like salmon, sardines, and mackerel.
✔️ This type of supplement typically contains EPA and DHA in standard doses and is considered a reliable, cost-effective, and effective option for most people.
✅ Benefits:
- Suitable for heart, brain health, and reducing inflammation
- Affordable price
- Widely available
📌 Note: The quality of fish oil depends on freshness, purity standards, and oxidation levels.

✅ Krill Oil
✔️ Krill oil is derived from tiny marine creatures called “krill” and is considered one of the most advanced forms of omega-3.
✔️ The omega-3 structure in krill is in the form of phospholipids, which have much higher absorption rates compared to fish oil.
✅ Benefits:
- Better and faster absorption
- Contains astaxanthin (a powerful antioxidant)
- Less fishy smell
📌 This type of supplement is typically more expensive than fish oil, but it is an ideal option for people with sensitive stomachs or those needing better absorption.
✅ Algal Oil
Suitable for vegetarians
✔️ Algal oil is the best choice for vegans and vegetarians.
✔️ This supplement directly contains DHA (and sometimes EPA) and is extracted from marine algae — most fish also get their DHA from these algae.
✅ Benefits:
- Very high purity
- Free from marine contaminants like mercury and PCBs
- Suitable for pregnancy and breastfeeding
📌 Algal oil is considered one of the safest and most sustainable sources of omega-3.
✅ Omega-3 Concentrates
Triglyceride, Ethyl Ester, Phospholipid
✔️ Omega-3 concentrates are designed to deliver higher doses of EPA and DHA in each capsule.
These supplements are produced in various chemical forms:
✅ Triglyceride (TG):
The natural and more absorbable form; usually more expensive but highly effective.
✅ Ethyl Ester (EE):
A processed form that allows for a very high concentration of EPA/DHA in the capsule; requires consumption with fatty foods for better absorption.
✅ Re-Esterified Triglyceride (rTG):
The best form available: high concentration and excellent absorption.
Many professional sports supplements use this form.
✅ Phospholipid:
The form found in krill oil; high absorption and rapid effectiveness.
📌 These supplements are mainly recommended for individuals with high triglycerides, chronic inflammation, professional athletes, or high-dose consumers.
✅ Difference in chemical forms and their absorption rates
✔️ Understanding the chemical form of omega-3 is one of the most important factors in choosing the right supplement:
✅ High absorption:
- rTG
- TG
- Phospholipid (krill oil)
✅ Moderate absorption:
- EE (requires consumption with fatty foods)
✅ High stability:
- Algal oil
- Krill oil (due to astaxanthin)
✅ Best for high doses:
- EE and rTG
📌 Conclusion:
✔️ If you’re looking for daily use → High-quality fish oil or algal oil
✔️ If you need therapeutic use → Concentrate forms of TG or rTG
✔️ If high absorption is important → Krill oil is the best choice.
How to choose a high-quality omega-3 supplement?
✅ Important tips when buying:
🟩 To choose a suitable omega-3 supplement, you should check several key factors:
✔️ Oil quality, EPA/DHA content, lab standards, fish source, and purity level.
✔️ A good supplement should be pure, stable, fresh, and have verified lab results.

📊 EPA/DHA percentage
✅ The most important part of the supplement label is the actual amount of EPA and DHA, not the total fish oil content.
🔸 Many people mistakenly focus on the “Fish Oil 1000 mg” amount, while it may only contain 300 mg of EPA + DHA!
✔️ For a high-quality supplement:
- At least 500 to 800 mg of EPA + DHA per capsule is recommended.
- For therapeutic purposes, higher doses or concentrate forms are better.
🌍 Global Standards
IFOS, USP, NSF
✅ Having reputable standards on the packaging indicates the purity, potency, and safety of the supplement.
Most important standards:
✔️ IFOS (International Fish Oil Standards):
- The most reputable standard for omega-3 worldwide.
- Products with a 5-star IFOS rating are flawless in terms of contamination, freshness, and label accuracy.
✔️ USP (United States Pharmacopeia):
- Confirms that the supplement contains exactly the amount stated on the package.
✔️ NSF / NSF Certified for Sport:
- Suitable for athletes; guarantees the product is free from banned substances.
📌 Having one of these certifications indicates high quality.
✅ Fish Source (Oceanic / Farmed)
The quality of the fatty acid depends on the fish source.
✅ Better sources include:
- Wild salmon
- Sardines
- Mackerel
- Anchovies
- Herring
📌 Farmed fish may have lower levels of contamination or quality unless from a reputable brand.
☣️ Risk of contaminants: Mercury, lead, PCB
✔️ Omega-3 supplements should be tested for the following contaminants:
- Mercury
- Lead
- Cadmium
- PCB and Dioxins
📌 Products with the IFOS standard typically score full marks on these tests and have less concern about contamination.
🧪 Oxidation and Production Date
🟩 Omega-3 is a sensitive fat, and if it oxidizes, it loses its effectiveness and can develop an unpleasant smell and taste.
Therefore, pay attention to the following:
- The production date should be recent.
- The expiration date should be far away.
- The supplement should be in dark packaging.
- It should contain natural antioxidants (like vitamin E).
- It should not have a strong fishy smell or taste when consumed (sign of oxidation).
📌 The best brands publish oxidation levels (TOTOX) in IFOS tests.
How to take omega-3
🕒 Best time to take
🟩 The best time to take omega-3 is with a meal that contains some fat or oil.
✔️ The fat in the food helps increase the absorption of EPA and DHA from the intestines by several times.
✔️ Many nutritionists recommend taking omega-3 during lunch or dinner, as these meals typically contain more fat.

🍽️ Before or after a meal?
✅ Omega-3 should be taken after or during a meal because:
- It will be better absorbed
- The fishy aftertaste is less likely to occur
- It causes less stomach discomfort
📌 Taking omega-3 on an empty stomach or with no food is usually not recommended.
✅ Taking with vitamin D, K2, or other supplements
✔️ Taking omega-3 with certain supplements can enhance its effects:
1️⃣ Vitamin D:
Both are fat-soluble, and taking them together enhances their absorption. It’s a very common and healthy combination.
2️⃣ Vitamin K2:
This vitamin is beneficial for bone and heart health, and taking it with omega-3 poses no issues. It may even have a synergistic effect.
3️⃣ Magnesium and Zinc:
They do not interfere with omega-3.
4️⃣ Blood thinners (warfarin, aspirin):
Should be taken with caution; high doses may enhance the thinning effect.
5️⃣ Fat-burning supplements:
There are no major interactions, but it’s better not to take them with meals to avoid reducing the absorption of fat burners.
❄️ Store in the fridge or room temperature?
✔️ Omega-3 is a sensitive fat, and if not stored properly, it will oxidize and lose its quality.
1️⃣ Softgel capsules:
They can usually be stored at room temperature in a dry place (away from direct light and heat). If the weather is very hot, the fridge is a better choice.
2️⃣ Omega-3 liquid oil:
It must be stored in the fridge. This form oxidizes faster and needs lower temperatures.
3️⃣ Algal oil:
More stable than fish oil, but storage in a cool, dark place is recommended.
📌 Important note:
If the capsules have a strong fishy smell or cause a bitter taste, they are likely oxidized and should be replaced.
Disadvantages, side effects, and precautions.
🩸 Blood thinning
🔸 Taking high doses of omega-3 (especially over 3000 mg per day) can increase blood-thinning effects.
🔸 This usually doesn’t cause problems for most people, but it can be dangerous for those on blood-thinning medications, increasing the risk of bleeding.

💊 Drug interactions
Warfarin, Aspirin, NSAIDs
🛑 Omega-3 can interact with certain medications, particularly:
- Warfarin
- Aspirin
- Ibuprofen, naproxen, and other NSAIDs
📌 People taking these medications should consult with their doctor before taking high doses, as the blood-thinning effects may be enhanced.
🤢 Digestive issues
🛑 Some people may experience mild digestive side effects when taking omega-3, such as:
- Fishy aftertaste
- Bloating
- Mild stomach pain
- Nausea
📌 These side effects are usually relieved by taking the supplement with food or choosing enteric-coated supplements.
⚠️ Excessive consumption
🛑 Taking too much omega-3 (e.g., more than 4–5 grams per day) can cause side effects:
- Increased risk of bleeding
- Excessive lowering of blood pressure
- Weakened immune system
- Oxidation of fat in the body if consuming low-quality supplements
📌 Excess omega-3 from food usually doesn’t cause issues; the main concern is with high-dose supplements.
🏥 Warning for people with specific health conditions
⛔ Some people should take omega-3 with caution and under medical supervision:
- People with bleeding disorders
- People with diabetes (very high doses may affect blood sugar)
- People with liver problems
- People with very low blood pressure
- Before surgery (it usually needs to be stopped 7–10 days prior)
📌 Omega-3 is also very beneficial during pregnancy, but it’s important to choose types that are free of mercury contamination.
Omega-3 for specific groups
✅ Omega-3 is one of the few supplements with clear, proven benefits for almost everyone. In this section, we take a closer look at how much omega-3 each group needs and what they should keep in mind.
🏋️ Athletes
✔️ Because athletes experience more inflammation, muscle damage, oxidative stress, and higher recovery demands, they usually benefit more from omega-3.
✅ Taking EPA and DHA can
- Speed up recovery
- Reduce DOMS (delayed onset muscle soreness)
- Improve muscle and nerve performance
- Reduce inflammation caused by intense training
✅ Recommended dose for athletes:
1,000–2,000 mg of EPA+DHA

🧓🏻 Seniors
✔️ As we age, the body faces reduced nutrient absorption, chronic inflammation, and declining cognitive function.
✅ Omega-3 offers important benefits for older adults:
- Strengthens memory and helps prevent cognitive decline
- Helps reduce the risk of Alzheimer’s (especially DHA)
- Improves joint health
- Reducing inflammation
- Supports heart health and lowers the risk of stroke
✅ Recommended dose:
500–1,000 mg of EPA+DHA
🧒🏻 Children
✔️ Omega-3—especially DHA—is essential for brain development, vision, and focus in kids.
✅ Key benefits of omega-3 for children:
- Improves learning ability
- Enhances focus (especially in kids with ADHD)
- Supports visual development
- Boosts the immune system
✅ Recommended DHA dose by age:
Ages 1–3: 70–100 mg DHA
Ages 4–8: 100–150 mg DHA
Ages 9–13: 150–200 mg DHA
For children who don’t eat fish, algae oil is the best option.
🌱 Vegetarians and vegans
✔️ Vegetarians typically don’t get enough EPA and DHA because plant sources contain only ALA, and the body converts ALA to EPA and DHA very poorly.
✅ So the best choice for this group is:
- Algal oil, which provides direct DHA (and sometimes EPA) and has very high purity.
✅ Recommended dose:
300–600 mg of DHA daily
❤️ People with heart conditions
✔️ Omega-3 is one of the most important supplements for heart health.
✅ In heart patients, it can:
- Reduce triglycerides by 15–30%
- Lower cardiac inflammation
- Decrease the risk of heart attack
- Improve heart rhythm
✅ Therapeutic dose:
1,000–4,000 mg of EPA+DHA
(under medical supervision)
🤰 Pregnant women
DHA is essential for fetal brain development. Pregnant and breastfeeding women are among the groups that most critically need DHA.
✅ Benefits:
- Supports optimal fetal brain development
- Supports retinal development
- Helps prevent preterm birth
- Boosts the baby’s intelligence
✅ Recommended dose during pregnancy:
200–300 mg of DHA daily
(preferably from algal oil or mercury-free fish oil)
Omega-3 compared to other supplements
🆚 Omega-3 vs. Omega-6
✔️ Omega-3 and omega-6 are both essential fatty acids, but they have very different effects on the body.
✔️ Omega-3 is anti-inflammatory, while omega-6 (found in vegetable oils and processed foods) is generally pro-inflammatory.
✔️ The main issue with the modern diet is that the omega-6 to omega-3 ratio has become extremely high (15:1 or even 20:1), whereas the natural ratio should be around 3:1.
✔️ This is why supplementing with omega-3 helps restore balance and reduce chronic inflammation.

🐟 Omega-3 (fish oil) vs. krill oil
✔️ Both supplements contain EPA and DHA, but they have important differences:
1️⃣ Fat structure:
Regular omega-3 comes in triglyceride or ethyl ester form, while krill oil is in phospholipid form, which has better absorption.
2️⃣ Natural antioxidant:
Krill oil contains astaxanthin, a very powerful antioxidant that fish oil lacks.
3️⃣ Smell and taste:
Krill oil usually doesn’t have a fishy smell.
4️⃣ Price:
Krill oil is more expensive.
📌 Conclusion:
If you want higher absorption and premium quality → Krill oil
If you want affordability and higher dosing → Fish oil
🌿 Regular omega-3 vs. algal oil
✔️ Algal oil is the best choice for vegetarians and vegans because it directly provides DHA (and sometimes EPA).
🔸 Differences:
1️⃣ Source:
Algal oil comes from marine plants, while fish oil comes from marine animals.
2️⃣ Purity:
Algal oil is extremely pure and free from mercury, lead, and PCBs.
3️⃣ Environmental sustainability:
Producing algal oil has a much smaller environmental impact.
4️⃣ Price:
It’s usually more expensive than fish oil.
📌 Conclusion:
If you’re vegetarian or worried about marine contaminants → Algal oil
If price matters more → Fish oil
💊 Omega-3 vs. multivitamins
✔️ Multivitamins are a blend of vitamins and minerals, while omega-3 is an essential fat supplement with a completely different role.
🅰️ Multivitamins:
Used to correct micronutrient deficiencies (vitamins and minerals).
🅱️ Omega-3:
Supports heart, brain, eye, and joint health and helps reduce inflammation.
✔️ Multivitamins cannot replace omega-3 because none of them contain EPA or DHA.
✔️ Many people—especially athletes and seniors—take both together.
📌 Key takeaway:
Multivitamin = micronutrient support
Omega-3 = vital system health (heart, brain, inflammation)
Frequently Asked Questions
FAQ
Omega-3 is a family of fatty acids; the most important ones are EPA and DHA. Fish oil is one of the most common omega-3 supplements and typically contains EPA and DHA.
EPA is more related to inflammation and triglycerides; DHA plays a structural role in the brain and retina. Which one is “better” depends on your goal (heart/triglycerides vs. brain/pregnancy).
For healthy adults, many nutrition guidelines recommend around 450–500 mg per day (usually as EPA+DHA or the equivalent). If you have underlying conditions, your dose may differ.
The “Fish Oil 1000 mg” number doesn’t matter; what matters is the amount of EPA and DHA. Many 1000 mg capsules contain only about 180 mg of EPA and 120 mg of DHA.
The time of day isn’t very important; consistency matters more. It’s best taken with a meal that contains some fat to improve absorption.
Usually with or after a meal is best, because absorption improves and side effects like fishy burps or heartburn are reduced.
Yes. For high triglycerides, prescription omega-3 at 4 grams per day can lower triglycerides by about 20–30% (self-medicating with OTC omega-3 isn’t recommended).
The strongest evidence is for lowering triglycerides. Some people may experience a slight increase in LDL with certain formulas (especially those high in DHA), so if you have lipid issues, dosing should be adjusted with your doctor.
Some studies report a mild reduction in blood pressure, and the effect may be more noticeable in people with higher baseline blood pressure.
Yes. One of the main reasons people take omega-3 is its anti-inflammatory effects, and in some conditions (like rheumatoid arthritis) it may help. ✔ Only in appropriate doses and under specialist guidance…
In RA, some clinical trials have shown that omega-3 can somewhat improve symptoms and even reduce the need for pain medications, though its effect is not “miraculous.”
DHA is an important structural component of the brain, but supplement results for cognitive enhancement in healthy individuals are not consistently positive. Generally, diet and fish intake should be the priority, with supplements used selectively.
Some studies—especially those using EPA-focused formulas—show promising effects, but omega-3 is NOT a replacement for medical treatment. It should be evaluated alongside standard therapy. ✔ For endurance competitions, yes, but not typically recommended for ordinary days…
There’s no conclusive evidence that supplements prevent Alzheimer’s, but adequate omega-3 intake in the diet is associated with better brain health.
Results are mixed. NIH/ODS notes that a major high-dose trial (EPA 2000 mg + DHA 1000 mg for one year) showed no benefit over placebo. Expectations should be realistic.
This is common. Taking omega-3 with food, splitting the dose, or choosing enteric-coated capsules can help. Sometimes it’s also a sign of poor quality or oxidized oil.
Yes. These side effects are usually mild and may include nausea, heartburn, or diarrhea. Taking omega-3 with food and lowering the dose often helps.
At higher doses, it can increase the risk of bleeding, especially if taken along with blood-thinning medications.
It can. NIH and Mayo Clinic warn that high doses of omega-3 combined with anticoagulant or antiplatelet drugs may increase bleeding risk.
Many doctors recommend temporarily stopping it because of bleeding concerns. The best approach is to check with your surgeon/physician before the procedure.
NIH/ODS recommends consuming 8–12 ounces (about 225–340 g) of low-mercury fish per week during pregnancy and breastfeeding. Evidence for supplements is mixed, so choosing a low-contaminant product and consulting a doctor is important.
Many health sources commonly recommend 200–300 mg of DHA per day, especially if fish intake is low.
NIH states that more research is needed in certain areas, such as ADHD symptoms. For children, the dose and age-appropriate form matter (preferably under medical supervision).
There may be risk, and Mayo clearly notes that safety for people with seafood allergies is “not fully established.” In this case, algal oil and medical guidance are safer options.
Algal oil is a plant-based source of DHA (and sometimes EPA) and is the primary omega-3 option for vegans. NIH recognizes it as a valid omega-3 supplement.
Both contain EPA/DHA, but krill has different compounds (like phospholipids) and natural antioxidants. There is no universal “better”; the choice depends on dose, digestive tolerance, and budget.
The forms differ, and dose/taking with food matters significantly. In general, if your product is in ethyl ester form, taking it with a fatty meal improves absorption. ✔ Yes, there are non-responders, but they’re a very small percentage…
These indicate third-party testing for quality, purity, and label accuracy. The AHA also reminds us that supplements are not tested and approved for effectiveness the way prescription drugs are, so quality certifications matter even more.
Liquids are usually better kept in the fridge; capsules should be stored away from heat and light. If there’s a strong or unpleasant smell/taste, it may indicate oxidation or quality issues.
Some recent studies and reports suggest a possible increase in AFib risk (especially at higher doses or in certain populations), but findings are not consistent or conclusive. If you have a history of arrhythmia or heart problems, it’s best to discuss supplement use with your doctor.
Final Summary
🧾 Omega-3 is one of the most important nutritional supplements in the world because, unlike many others, it has strong scientific support and affects several vital systems in the body at the same time.
🧠 EPA and DHA (marine omega-3s) play the biggest roles in cardiovascular health, lowering triglycerides, controlling inflammation, and supporting the brain and eyes. Deficiency is common—especially in people who eat little fish.
✅ Main benefits of omega-3
❤️ Lowers triglycerides and supports heart health
🔥 Reduces inflammation and helps with joints and arthritis
🧠 Supports brain function, mood, and memory
👁️ Supports eye health (especially DHA in the retina)
🤰 DHA is crucial during pregnancy for fetal brain development
💪 Helps recovery and reduces DOMS in athletes

🧠 Practical consumption guidelines
🕒 Best time to take it
🍽️ Take omega-3 with or after a meal, ideally one that contains some fat, to improve absorption.
📌 Appropriate amounts for most people
⚖️ For healthy adults, 250–500 mg of EPA+DHA per day is usually enough.
🔥 For therapeutic goals like high triglycerides or chronic inflammation, 1–4 grams per day may be required—preferably under medical supervision.
🚫 Important safety note
🩸 If you take blood thinners or have a history of bleeding, consult your doctor before using higher doses.
🛒 Practical tips for choosing the best product
📊 Top priority: the actual EPA+DHA content
🔍 Instead of the “Fish Oil 1000 mg” number, look at the EPA and DHA amounts on the label—these two determine the real effect.
🏅 Second priority: standards and third-party testing
✅ Products with reputable certifications are more trustworthy:
🌍 IFOS
🧪 USP
🏋️ NSF (especially for athletes)
🐟 Third priority: source and purity
🌊 Small ocean fish like sardines and anchovies usually have lower contamination risk.
☣️ Always choose a product that has been tested for contaminants like mercury, lead, and PCBs.
🧊 Fourth priority: freshness and oxidation prevention
🧴 Dark packaging, recent production dates, natural antioxidants like vitamin E, and no strong/rancid smell—these are signs of a high-quality product.
🌱 If you’re vegetarian
🟩 Your best choice is algal oil, since it provides DHA (and sometimes EPA) directly and with high purity.
🎯 Final summary
⭐ If we say it in one sentence:
Omega-3 isn’t a one-dimensional supplement; it’s a long-term investment in heart health, brain function, and inflammation control.
✅ With the right product and proper use, it can become one of the most effective daily supplements you take.
Scientific Sources & References
🇺🇸 Official Government Sources (Government / Federal)
✔️🔬 Scientific sources (PubMed)
✅ Quality standards and third-party testing (for the supplement selection section)
Pelank Life | Body Health Assessment
The Best Body Health Calculators Using Scientific Methods
Developed by Pelank Life ©

Mohsen Taheri
December 6, 2025