One-Arm Medicine Ball Slam
| English Name | One Arm Medicine Ball Slam |
|---|---|
| Difficulty | Advanced |
| Exercise Types | پویا |
| Primary Muscle (EN) | Rectus Abdominis |
| Muscle Groups | Abdominal muscles Chest muscles Full body Shoulder Muscles |
|---|---|
| Workout Type | Explosive Functional Strength training |
| Required equipment | Exercise ball |
💠 Exercise guide
The One-Arm Medicine Ball Slam is a high-intensity, explosive functional exercise that transfers force from the upper body to the lower body through the core. This movement not only strengthens the abdominals and midsection but also engages multiple muscle groups throughout the body, boosting fat burning and overall fitness.
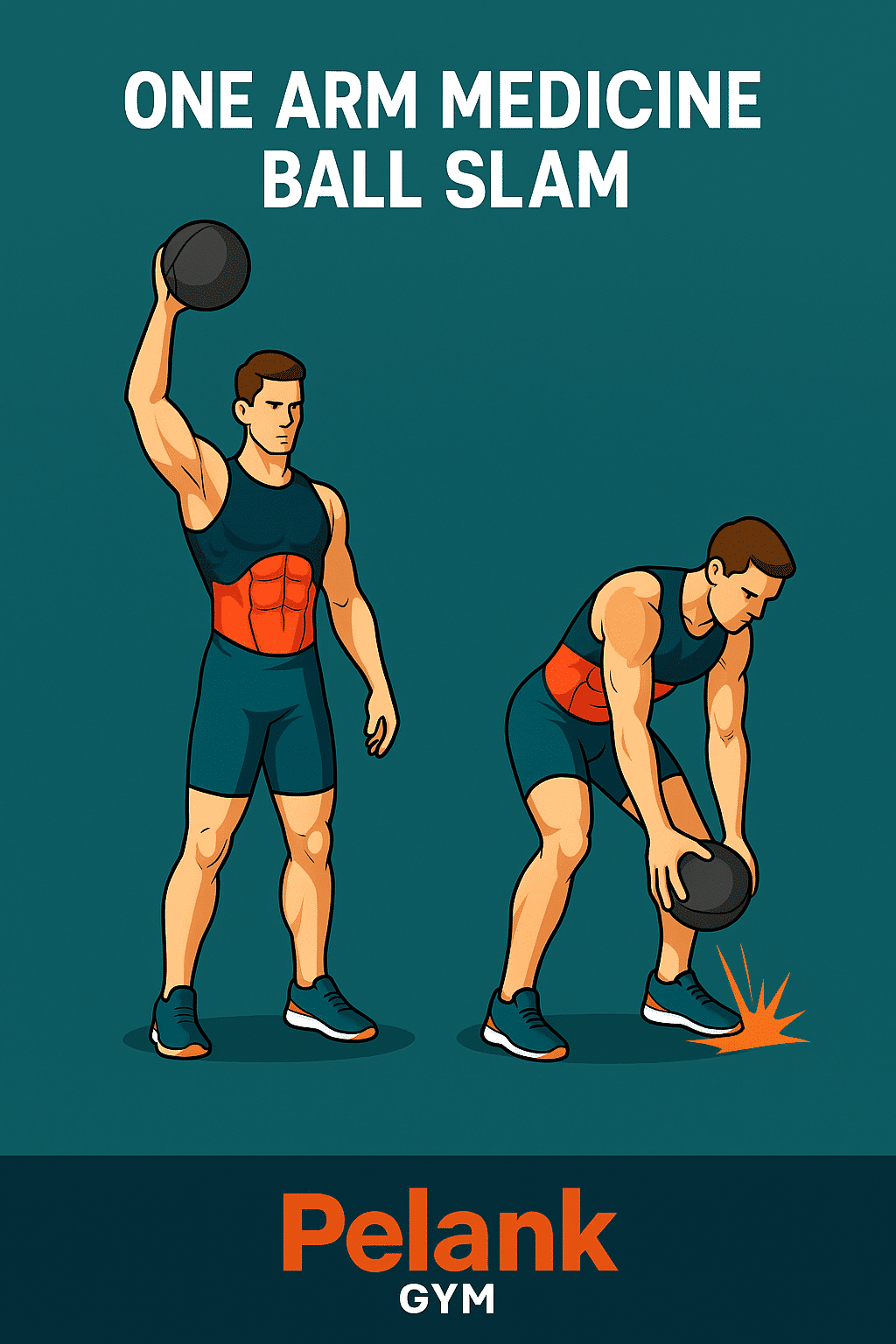
💠 How to perform the exercise

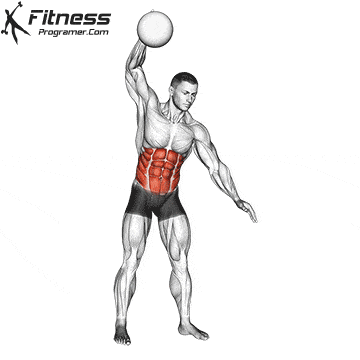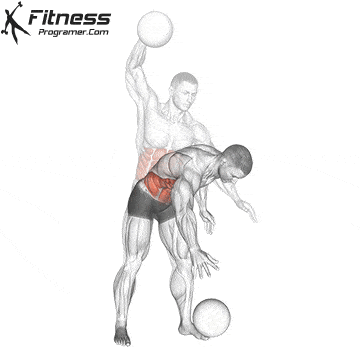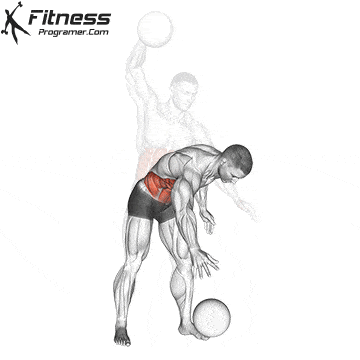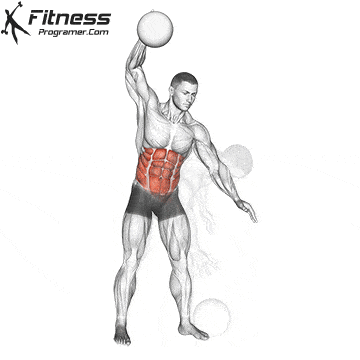
Preparation
✅ Stand tall holding the medicine ball in your right hand at your side
✅ Feet shoulder-width apart, knees slightly bent
✅ Keep the torso upright, core engaged, and eyes facing forward
Execution method
✅ Raise the ball overhead with one hand
✅ In one explosive motion, slam the ball forcefully toward the ground
✅ As you slam, allow the torso to hinge slightly forward and the knees to absorb the impact
✅ Repeat the movement in a controlled manner, then switch to the other hand
Coaching tips and recommendations
✔ Don’t rely solely on the arm; power should be generated from the core
✔ Keep the abs engaged during the movement to prevent torso rotation or collapse
✔ Exhale during the slam to increase intra-abdominal pressure
✔ Use a non-bouncing (dead) ball to avoid it rebounding toward your face or feet
Benefits of the exercise
🔹 Increased explosive strength of the core and upper body:
This exercise is one of the few movements that strengthens the abdominals through real-life dynamics such as throwing or striking.
🔹 Unilateral engagement for muscular balance:
The single-arm version challenges the torso with anti-rotational control, helping to strengthen balance and core stability.
🔹 High calorie burn and elevated heart rate:
An excellent movement for ramping up workout intensity in a short time, making it ideal for HIIT.
🔹 Force transfer through the full kinetic chain:
From hand to foot, the entire body works in coordination to transfer energy—a key element in functional strength training.
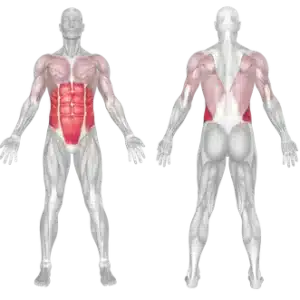
💠 Muscles engaged in the movement
In this full-body exercise, the core serves as the center of power generation and force transfer. The single-arm slam activates the obliques and anti-rotational muscles more intensely, while the legs, arms, and back support the movement and ensure smooth execution.
Main muscles
Synergistic muscles
Stabilizers
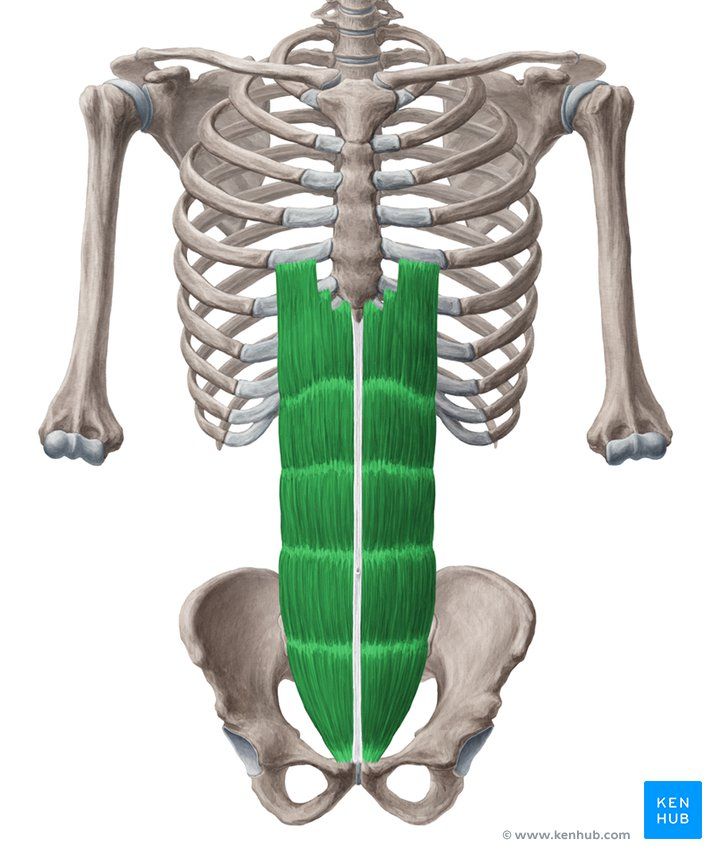
Rectus Abdominis (Six-Pack Muscle)
Rectus Abdominis Muscle
The rectus abdominis is one of the most important muscles in the anterior abdominal wall, located vertically on both sides of the linea alba. This muscle is responsible for flexing the trunk, stabilizing the spine, and compressing the abdominal viscera.
The “six-pack” appearance seen in athletes results from the presence of tendinous intersections on this muscle. Strengthening the rectus abdominis through bodybuilding, gymnastics, and martial arts exercises significantly improves overall body performance.
✅ Effective exercises for this muscle include crunches, leg raises, planks, and ab wheel rollouts, which help strengthen its power and endurance.
✅ Persian Name: Azole Raaste Shakami
✅ Latin Name: Rectus Abdominis | Six-Pack
✅ Common Name: Abs
✅ Location:
🟡 This muscle is located on the front of the abdomen, on both sides of the Linea Alba.
🟡 It originates from the lower ribs and extends to the pelvis.
🟡 It has horizontal tendinous bands that create the six-pack appearance.
✅ 🦾 Origin
✔ Costal cartilage of ribs 5, 6, and 7
✔ Xiphoid process of the sternum
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ Pubic crest of the pelvic bone
✔ Pubic symphysis
✅ 📌 Classification and Function
✔ Flexion of the trunk – such as during a crunch
✔ Compression of abdominal contents – aids in exhalation and increases intra-abdominal pressure
✔ Maintaining the strength of the abdominal wall and spinal balance
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Type
✔ Mostly composed of slow-twitch (Type I) fibers to maintain body endurance.
✔ Contains fast-twitch (Type II) fibers for rapid and powerful movements, such as explosive crunches.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Motor and Athletic Performance
✔ Plays a key role in all abdominal and core exercises, such as crunches, leg raises, and planks.
✔ Responsible for maintaining body balance and preventing lower back injuries.
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ One of the most important muscles for body stability, especially in endurance sports.
✔ Weakness in this muscle can lead to lower back pain and decreased body balance.
🧠 Innervation
✔ Thoracoabdominal nerves – T7 to T12
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Superior and inferior epigastric arteries
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Bodybuilding – Active in all abdominal exercises such as crunches, planks, and V-ups.
✔ Martial arts – Helps increase endurance and abdominal resilience.
✔ Gymnastics and CrossFit – Plays a key role in movements such as toe-bar, leg lifts, and V-sit.
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Connection with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Works in coordination with the internal and external oblique muscles to create rotational movements of the trunk.
✔ Collaborates with the erector spinae and gluteal muscles to stabilize the spine and pelvis.
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ Weakness in this muscle leads to core instability and lower back pain.
✔ Strain and muscle tightness due to heavy training or improper execution of abdominal exercises.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Main exercises to strengthen the rectus abdominis muscle:
1️⃣ Standard Crunches – The most effective exercise for strengthening the middle of the abdomen
2️⃣ Leg Raises – Focuses on the lower part of the rectus abdominis
3️⃣ Plank – Improves core endurance and stability
4️⃣ Ab Wheel Rollout – A challenging exercise for deep abdominal muscle engagement
5️⃣ V-Sit Hold – Strengthens the abdominal muscles and enhances core control
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery Movements
✔ Cobra Stretch – Opens up and aids in the recovery of the abdominal muscles
✔ Cat-Cow Stretch – Increases core flexibility
✅ Interesting Fact
✔ The rectus abdominis is one of the strongest endurance muscles in the body, capable of staying active for long periods, even in static movements like the plank!
✅ Practical Tip
✔ To fully strengthen the six-pack, exercises should include both endurance (like planks) and strength (like crunches and leg raises) training.
🔴 Name and Location: Located on the front of the abdomen, from the lower ribs to the pelvis.
🟠 Anatomy: It has tendinous bands that divide it into several sections.
🟡 Function: Trunk flexion, abdominal compression, and core stabilization.
🟢 Physiology: A combination of slow-twitch and fast-twitch fibers for endurance and strength.
🔵 Innervation: Thoracoabdominal nerves T7-T12
🟣 Importance: Key role in bodybuilding, CrossFit, martial arts, and gymnastics
🟤 Exercises: Crunches, leg raises, planks, ab wheel rollouts, V-sits
⚫ Interesting Fact: A resilient muscle with high endurance capacity in static exercises.
External Oblique Muscle
External Oblique Muscle
The external oblique muscle is one of the most important lateral abdominal muscles, located on both sides of the torso. This muscle performs essential functions such as trunk rotation and lateral flexion, abdominal compression, and assists in breathing.
✅ The external oblique muscle is the largest and most superficial lateral abdominal muscle, and due to the direction of its fibers, it slopes downward and forward (similar to the motion of putting your hand in your pocket).
✅ This muscle is highly activated in exercises such as twisting crunches, bicycle crunches, side planks, and Russian twists, playing a key role in core stability and rotational movements.
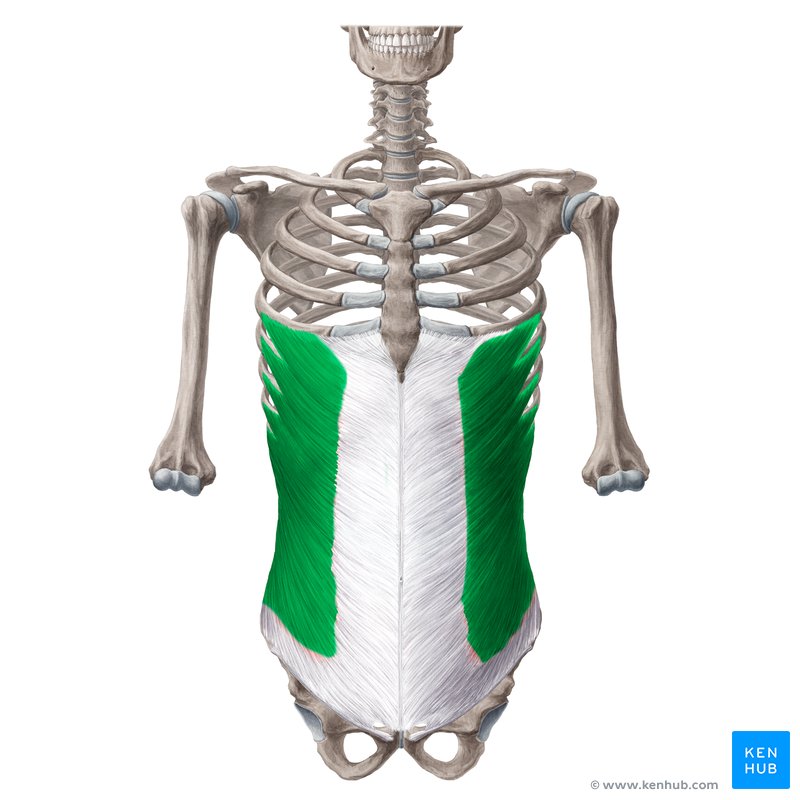
✅ Persian Name: Azole Mayel Khareji
✅ Latin Name: External Oblique
✅ Common Name: Side Abs | External Obliques
✅ Location:
🟡 This muscle extends on both sides of the abdomen, from the lower ribs to the pelvic bone.
🟡 It is the largest and most superficial lateral abdominal muscle.
🟡 It has fibers that run diagonally from top to bottom and from back to front.
✅ 🦾 Origin
✔ Ribs 5-12 – The origin of this muscle begins from the outer surface of these ribs.
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ Linea Alba – A fibrous connective tissue structure located at the center of the abdomen.
✔ Iliac Crest – The upper portion of the pelvic bone.
✔ Inguinal Ligament – A band that runs between the pelvis and the groin area.
✅ 📌 Classification and Function
✔ Trunk Rotation – For rotating the abdomen and sides, such as in bicycle crunches.
✔ Lateral Flexion – In bending to the side, like in side planks.
✔ Compression of Abdominal Contents – Helps increase intra-abdominal pressure, such as during a strong exhalation.
✔ Maintaining trunk stability and assisting in strength movements like deadlifts and squats.
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Type
✔ It has a combination of ✔ A combination of slow-twitch fibers (Type I) and fast-twitch fibers (Type II). ✔ For maintaining balance and power movements.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Motor and Athletic Performance
✔ It is active in all twisting and lateral exercises, such as Russian twists and twisting crunches.
✔ Responsible for core stability during weightlifting and stretching movements.
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ This muscle has high endurance due to its activity in all daily and athletic movements.
✔ Its weakness can lead to trunk imbalance and reduced spinal stability.
🧠 Innervation
✔ Intercostal Nerves T7-T11
✔ Subcostal Nerve – T12
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Posterior Intercostal Arteries
✔ Superior & Inferior Epigastric Arteries
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Bodybuilding and Fitness: Plays a crucial role in rotational and lateral abdominal movements such as Russian twists and side planks.
✔ Martial Arts: This muscle plays an important role in rotation and body stability during punching, kickboxing, wrestling, and MMA.
✔ Yoga and Pilates: Helps improve flexibility and body balance.
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Connection with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Interacts with the internal oblique muscles, rectus abdominis, and lumbar muscles to create lateral and rotational movements of the torso.
✔ Works together with the gluteal muscles and erector spinae in trunk stability and spinal balance.
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ Weakness of this muscle leads to trunk weakness, sagging sides, and spinal imbalance.
✔ Muscle strain may occur due to intense abdominal exercises or excessive twisting movements.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Main exercises to strengthen the external oblique muscle:
1️⃣ Russian Twists – The most effective movement for strengthening trunk rotation
2️⃣ Bicycle Crunches – Builds power and endurance in the sides
3️⃣ Side Plank – Increases trunk stability and balance
4️⃣ Oblique Crunches – Enhances size and definition of the sides
5️⃣ Dumbbell Side Bends – Increases strength in lateral movements
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery Movements
✔ Cobra Stretch – Enhances flexibility and aids in abdominal muscle recovery
✔ Side Stretch – Reduces tension and improves the range of motion in the sides
✅ Interesting Fact
✔ The external oblique muscle is one of the most important rotational and stabilizing muscles of the body, and it is automatically activated in all daily movements!
✅ Practical Tip
✔ If you want to strengthen and shape your sides, a combination of resistance exercises and endurance movements (such as side planks) is the best option!
🔴 Name and Location: Superficial lateral abdominal muscle, from the lower ribs to the pelvis
🟠 Anatomy: Has diagonal fibers running from top to bottom and forward
🟡 Function: Rotation, lateral flexion, abdominal compression
🟢 Physiology: A combination of slow-twitch and fast-twitch fibers
🔵 Innervation: Intercostal nerves T7-T11 and T12
🟣 Importance: Plays a key role in abdominal exercises, martial arts, bodybuilding, and yoga
🟤 Exercises: Russian Twists, Side Planks, Bicycle Crunches, Dumbbell Side Bends
⚫ Interesting Fact: A muscle that is active in all daily and athletic movements.
Internal Oblique Muscle
Internal Oblique Muscle
🔹 The internal oblique muscle is one of the deep lateral abdominal muscles located beneath the external oblique muscle.
🔹 This muscle plays a crucial role in trunk rotation, lateral flexion, abdominal compression, and maintaining trunk stability.
🔹 The direction of its fibers is opposite to that of the external oblique, extending upward and forward.
✅ The internal oblique muscle is highly active in exercises such as twisting crunches, bicycle crunches, side planks, and Russian twists, playing a key role in core stability and rotational movements.
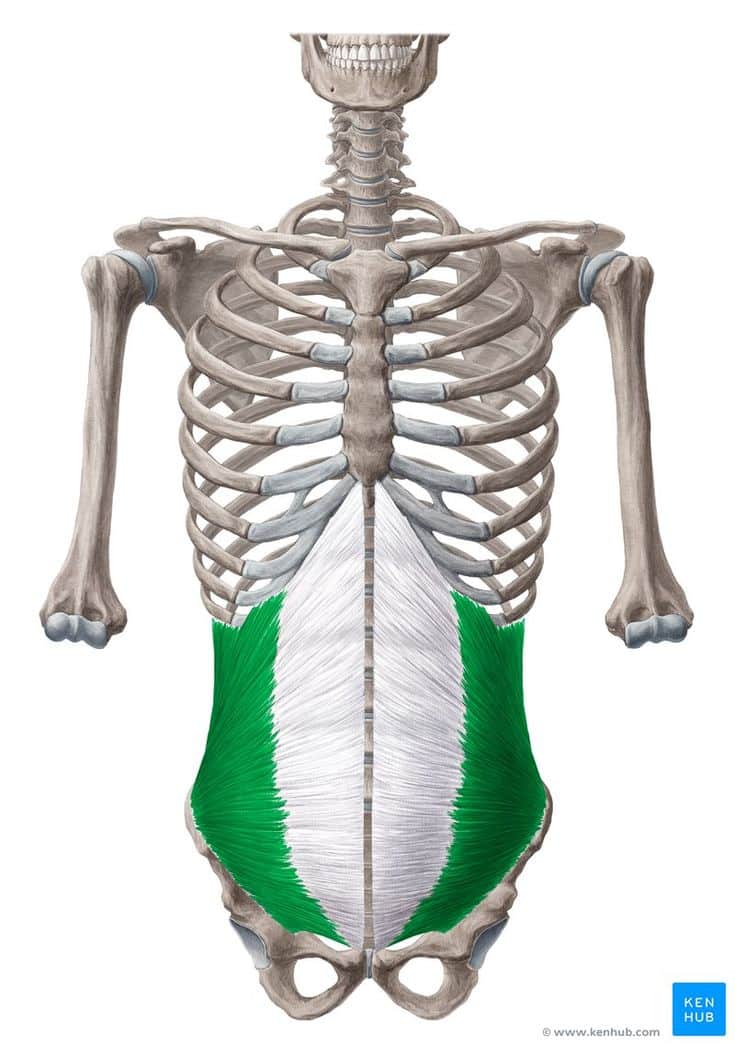
✅ Persian Name: Azole Mayel Dakheli
✅ Latin Name: Internal Oblique
✅ Common Name: Deep Side Abs | Internal Obliques
✅ Location:
🟡 This muscle lies beneath the external oblique, extending from the lower ribs to the pelvis and the Linea Alba.
🟡 It is deeper than the external oblique, but in some areas, it lies on top of the transverse abdominis muscle.
🟡 Its fibers run diagonally from bottom to top, opposite to the external oblique.
✅ 🦾 Origin
✔ Iliac Crest – The upper portion of the pelvic bone.
✔ Thoracolumbar Fascia – A strong connective tissue in the lumbar region.
✔ Inguinal Ligament – A band running between the pelvis and the groin.
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ Ribs 10-12
✔ Linea Alba – Located at the center of the abdomen and connected to the rectus abdominis muscle.
✅ 📌 Classification and Function
✔ Trunk Rotation – Works with the opposite external oblique muscle to create abdominal rotation (such as in Russian twists).
✔ Lateral Flexion – Assists in bending the sides, like in side planks.
✔ Compression of Abdominal Contents – Plays a role in strong exhalation and increasing intra-abdominal pressure.
✔ Maintaining trunk stability and supporting the spine during heavy movements such as deadlifts and squats.
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Type
✔ A combination of ✔ A combination of slow-twitch fibers (Type I) and fast-twitch fibers (Type II). For maintaining endurance and power movements.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Motor and Athletic Performance
✔ Active in all rotational and lateral movements such as bicycle crunches and Russian twists.
✔ Plays a key role in stabilizing the body’s core during weightlifting and athletic movements.
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ It has high endurance and plays a vital role in maintaining spinal and trunk stability.
✔ Weakness in this muscle can lead to trunk imbalance and reduced spinal stability.
🧠 Innervation
✔ Intercostal Nerves T8-T12
✔ Iliohypogastric & Ilioinguinal Nerves
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Posterior Intercostal Arteries
✔ Inferior Epigastric Artery
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Bodybuilding and Fitness: Plays an important role in rotational and lateral movements such as Russian twists and side planks.
✔ Martial Arts: This muscle plays a key role in rotation and body stability during boxing, kickboxing, wrestling, and MMA.
✔ Yoga and Pilates: Helps in stretching movements and improving body balance.
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Connection with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Interacts with the external oblique muscles, rectus abdominis, and transverse abdominis to create rotational and lateral trunk movements.
✔ Works together with the gluteal muscles and erector spinae in trunk stability and spinal balance.
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ Weakness in this muscle can lead to reduced body balance and increased risk of lower back pain.
✔ Muscle strain may occur due to sudden rotational movements or intense exercises.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Main exercises to strengthen the internal oblique muscle:
1️⃣ Russian Twists – Enhance rotational power of the torso
2️⃣ Bicycle Crunches – Combine rotation and endurance
3️⃣ Side Plank – Improve core stability and side strength
4️⃣ Oblique Crunches – Increase size and strength in the sides
5️⃣ Dumbbell Side Bends – Build strength in lateral movements
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery Movements
✔ Cobra Stretch – Enhances torso flexibility
✔ Side Stretch – Reduces tension and improves range of motion
✅ Interesting Fact
✔ The internal oblique muscle works in conjunction with the opposite external oblique; that is, the right internal oblique coordinates with the left external oblique in trunk rotation!
✅ Practical Tip
✔ To have strong and firm sides, combine rotational and lateral exercises with weights for better muscle growth!
🔴 Name and Location: Deep lateral abdominal muscle, located beneath the external oblique
🟠 Anatomy: Fibers run opposite to the external oblique, extending upward and inward
🟡 Function: Rotation, lateral flexion, abdominal compression
🟢 Physiology: A combination of slow-twitch and fast-twitch fibers
🔵 Innervation: Intercostal nerves T8-T12 and lumbar nerves
🟣 Importance: Plays a key role in martial arts, bodybuilding, and yoga
🟤 Exercises: Russian Twists, Side Planks, Bicycle Crunches, Dumbbell Side Bends
⚫ Interesting Fact: Works with the opposite external oblique for trunk rotation.
Anterior Deltoid muscle
Anterior Deltoid Muscle
🔹 The anterior deltoid is one of the three parts of the deltoid muscle. Its primary functions are moving the arm forward (flexion), internal rotation, and assisting in horizontal shoulder movements. This muscle plays a key role in many upper-body exercises, especially strength training movements like bench press, front raises, and throwing actions.
🔹 The anterior deltoid is one of the most important muscles involved in pressing and pushing movements. Due to its engagement in many strength exercises, it is often well-developed among athletes and bodybuilders. However, overusing this muscle without strengthening the posterior shoulder muscles (posterior deltoid and rotator cuff) can lead to muscular imbalances and increase the risk of shoulder injuries.
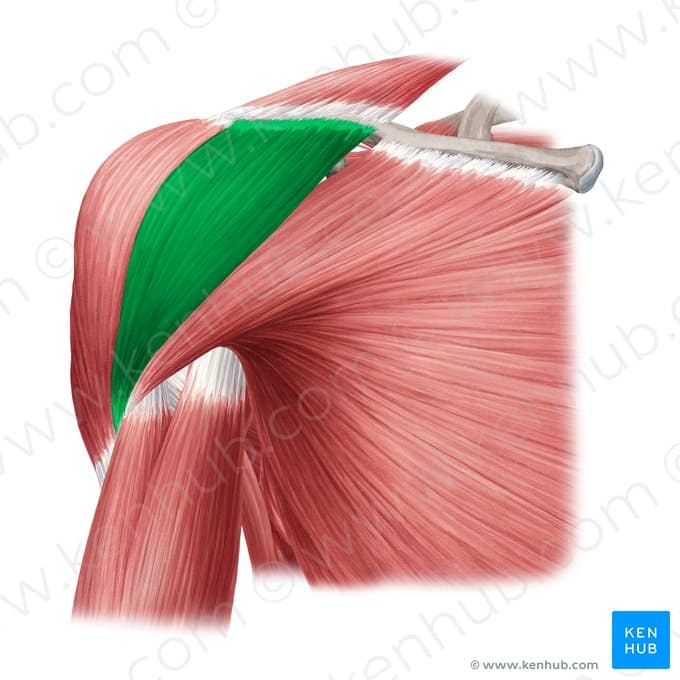
✅ Persian Name: Deltoid Ghodami
✅ Latin Name: Anterior Deltoid
✅ Common Names: Front part of the deltoid muscle | Anterior head of the shoulder
✅ Location:
🟡 Located at the front of the shoulder, forming the anterior part of the deltoid muscle.
🟡 Originates from the clavicle and lies over the upper part of the humerus.
🟡 Alongside the middle and posterior parts of the deltoid, it acts as part of the shoulder cap and assists in arm movements.
✅ 🔹 Origin
✔ Anterior surface of the lateral third of the clavicle (Clavicle – Anterior Surface of Lateral Third)
✅ 🔹 Insertion
✔ Deltoid tuberosity on the humerus bone (Deltoid Tuberosity, Humerus)
✅ 🔹 Function
📌 Primary functions of the anterior deltoid:
✔ Arm flexion – moving the arm forward (like raising the hand in front of the body)
✔ Internal rotation of the arm – rotating the arm inward toward the body
✔ Assisting in horizontal adduction – moving the arm inward on a horizontal plane (such as during a chest fly)
✔ Helping stabilize the shoulder joint during upper-body movements
📌 Movements that activate the anterior deltoid:
✔ Raising the arm forward (such as front raises)
✔ Throwing movements (ball throws, javelin throws)
✔ Moving weights in pressing and fly exercises
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Types
✔ A combination of fast-twitch fibers (Type II) and slow-twitch fibers (Type I)
✔ Predominantly composed of fast-twitch fibers for rapid and powerful movements
✔ This characteristic makes the anterior deltoid highly active in explosive and strength exercises like weightlifting and throwing
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Active in all pressing, throwing, and forward arm-raising exercises
✔ Plays a key role in strength sports, bodybuilding, weightlifting, boxing, and discus throwing
✔ An important muscle in daily activities such as lifting objects and carrying items
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Strength and Endurance
✔ Requires high strength for pressing exercises and overhead movements
✔ Overdevelopment can lead to muscular imbalances and increase the risk of shoulder injuries
✅ 🧠 Innervation
✔ Axillary nerve (C5, C6), which controls the movements of this muscle.
✅ 🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Posterior Circumflex Humeral Artery
✔ Thoracoacromial Artery
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ One of the key muscles for pushing and pressing movements in bodybuilding and weightlifting
✔ Active in throwing sports, swimming, boxing, gymnastics, and pulling movements
✔ Weakness can reduce pressing strength and increase the risk of shoulder injury
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Interaction with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Closely connected with the middle deltoid, pectoralis major, rotator cuff muscles, and triceps brachii
✔ Weakness in this muscle can lead to excessive strain on the shoulder joint and reduced upper body strength
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ One of the muscles prone to inflammation and strain due to high activity in upper-body training
✔ Weakness can cause excessive strain on the pectoral and shoulder muscles, leading to shoulder injuries
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Strength Training Exercises for the Anterior Deltoid
1️⃣ Front Raise with Dumbbells – the most important exercise for strengthening the anterior deltoid
2️⃣ Overhead Shoulder Press with Dumbbells or Barbell – high engagement of the anterior deltoid
3️⃣ Arnold Press – simultaneous strengthening of all deltoid parts with emphasis on the anterior head
4️⃣ Incline Bench Press – combined strengthening of the anterior deltoid and pectoralis major
5️⃣ Close-Grip Push-ups – bodyweight exercise targeting this muscle
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery
✔ Stretching the arm forward and across the body to improve flexibility and prevent muscle tightness
✔ Using a foam roller to reduce muscle tension and enhance blood flow
✅ Fun Fact
✔ The anterior deltoid is most engaged in throwing movements, which is why athletes in discus, javelin, and boxing typically have a very strong anterior deltoid.
✅ Practical Tip
✔ Overdeveloping the anterior deltoid without balancing it with the posterior deltoid can lead to muscular imbalances and increased stress on the shoulder joint.
🔴 Name and Location: A superficial muscle located at the front of the shoulder joint, originating from the clavicle.
🟠 Anatomy: Part of the deltoid muscle that, along with the middle and posterior deltoids, surrounds the shoulder and attaches to the humerus.
🟡 Function:
✔ Arm flexion – moving the hand forward
✔ Internal rotation of the arm – rotating the hand inward
✔ Horizontal adduction – assisting in bringing the arm inward on a horizontal plane
🟢 Physiology: Composed mainly of fast-twitch fibers, which provide power and speed in pressing movements.
🔵 Innervation: Axillary nerve, which controls the movements of this muscle.
🟣 Importance: Plays a vital role in pressing exercises, throwing, bodybuilding, boxing, and strength sports.
🟤 Exercises:
✔ Front raise
✔ Shoulder press
✔ Arnold press
✔ Incline bench press
✔ Close-grip push-ups
⚫ Fun Fact: One of the most utilized muscles in throwing and pressing movements, which, if overdeveloped, can lead to muscular imbalances and shoulder injuries.
Latissimus dorsi muscle
Latissimus Dorsi Muscle
The latissimus dorsi is one of the strongest and widest superficial back muscles, playing a crucial role in pulling movements, backward bending, and internal rotation of the arm. It extends from the lower spine to the humerus and is responsible for generating pulling force in exercises like pull-ups, swimming, and rowing. Strengthening this muscle enhances pulling power, improves body posture, and reduces the risk of lower back and shoulder injuries.
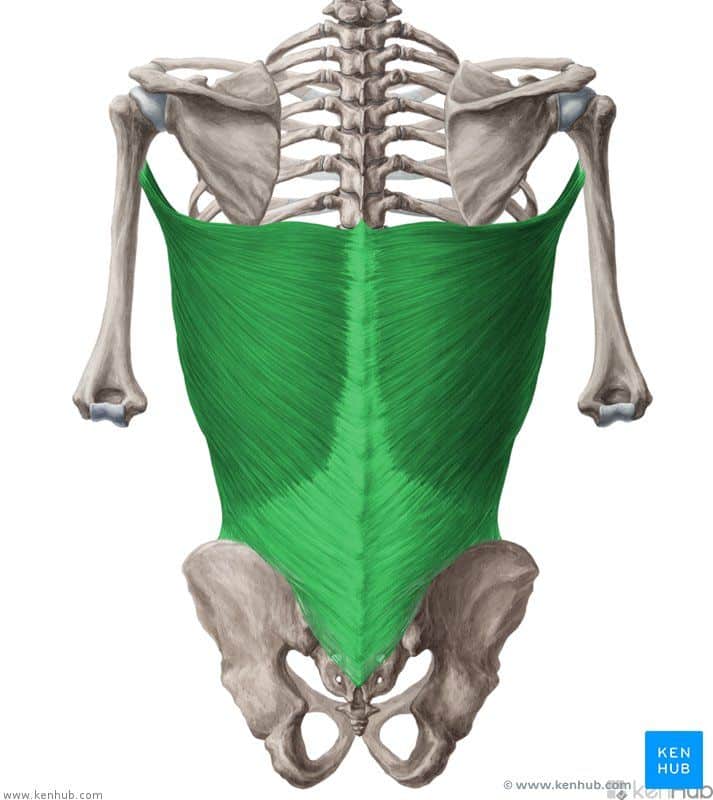
✅ Persian Name: Poshti bozorg
✅ Latin Name: Latissimus Dorsi
✅ Common Name: Lat
✅ Location:
🟡 A superficial muscle that connects from the lower spine, ribs, and pelvis to the humerus (upper arm bone).
🟡 A large, broad muscle located on both sides of the back, covering most of the lumbar and dorsal regions.
🟡 Responsible for pulling movements, arm adduction, and internal rotation of the arm.
✅ 🦾 Origin
✔ Lower six thoracic vertebrae (T7-T12)
✔ Lumbar vertebrae (L1-L5)
✔ Sacrum
✔ Iliac crest
✔ Lower ribs (9th to 12th)
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ Humerus (intertubercular groove)
✅ 📌 Function and Roles
🔹 The latissimus dorsi plays a role in various movements, including pulling, arm adduction, and internal rotation of the shoulder:
1️⃣ Pulling the arm down and back (Adduction)
✔ Like pulling the bar down during a lat pulldown exercise.
2️⃣ Internal rotation of the arm
✔ Like moving the arm inward during swimming and ball throwing.
3️⃣ Extension of the arm backward
✔ Like pulling the arm backward during pull-ups and rowing exercises.
✅ Main Functions:
✔ Lowering the arm and generating pulling force
✔ Assisting in shoulder stabilization during sports movements
✔ Increasing muscular endurance in strength exercises
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Types
✔ A combination of slow-twitch fibers (Type 1) for endurance and fast-twitch fibers (Type 2) for power movements.
✔ The middle section contains more slow-twitch fibers and is active during sustained pulling movements.
✔ The lower section has fast-twitch fibers used in explosive power movements.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Motor and Sports Performance
✔ The most important muscle in pulling movements such as pull-ups, swimming, and weightlifting.
✔ Plays a significant role in rowing, swimming, wrestling, and gymnastics.
✔ Strengthening this muscle increases pulling power, improves endurance, and reduces lower back injuries.
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ This muscle plays a key role in all pulling and strengthening movements of the upper body.
✔ Weakness in this muscle reduces endurance and increases stress on the lumbar and cervical vertebrae.
🧠 Innervation | Neural Control
✔ Thoracodorsal nerve (C6, C7, C8)
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Thoracodorsal artery
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Vital in sports such as bodybuilding, swimming, wrestling, rock climbing, and gymnastics.
✔ Plays a key role in shot put, cable pulling, weightlifting, and swimming.
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Relationship with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Interacts with the deltoid muscle, rotator cuff muscles, and teres major muscle.
✔ Weakness in this muscle leads to reduced pulling strength and pain in the lower back and shoulders.
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ Strain or weakness in this muscle can lead to lower back problems and pain in the upper back and shoulders.
✔ Weakness increases stress on the lumbar and cervical vertebrae.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Key Exercises to Strengthen the Latissimus Dorsi
1️⃣ Pull-Ups – The most effective exercise for full lat engagement
2️⃣ Lat Pulldown – Increases arm pulling strength
3️⃣ Bent-Over Barbell Rows – Builds size and strength in the back
4️⃣ One-Arm Dumbbell Rows – Strengthens the lateral and upper sections of the muscle
5️⃣ Deadlifts – Enhances endurance and strengthens the entire posterior chain
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery Exercises
✔ Overhead Lat Stretch – Improves range of motion and reduces muscle tension
✔ Wall Lat Stretch – Increases flexibility during pulling movements
✅ Interesting Fact:
✔ The latissimus dorsi is one of the broadest muscles in the human body and plays a role in numerous daily and sports movements.
✅ Practical Tip:
✔ To better strengthen this muscle, combine compound exercises like deadlifts and pull-ups with isolation movements such as lat pulldowns.
🔴 Name and Location: A broad back muscle extending from the lower spine to the arm
🟠 Anatomy: Originates from lumbar and thoracic vertebrae and ribs, attaching to the humerus
🟡 Function: Pulling, lowering, and internal rotation of the arm
🟢 Physiology: A mix of slow- and fast-twitch fibers for endurance and strength
🔵 Innervation: Thoracodorsal nerve (C6, C7, C8)
🟣 Importance: Active in bodybuilding, swimming, wrestling, weightlifting, and rock climbing
🟤 Exercises: Pull-ups, lat pulldown, rowing, deadlifts, arm stretches
⚫ Interesting Facts: One of the broadest muscles in the body and the key muscle in pulling movements
Muscle training
Pelank is a comprehensive encyclopedia of the body’s muscles, providing an accurate and scientific review of all muscles. Below, you can find muscle groups. By clicking on each muscle group, you will have access to complete information about it, including:
1️⃣ Basic information about the muscle
2️⃣ Muscle anatomy
3️⃣ Muscle physiology
4️⃣ Innervation and blood supply
5️⃣ Importance of the muscle in the body and sports
6️⃣ Strengthening exercises
7️⃣ Scientific and interesting facts
📌 At the end, a summary review of each muscle will be provided.
Body muscles training guide link
🔹 The muscle group engaged in this movement is highlighted in color.
References
Anatomy and medical books :
- Gray’s Anatomy (one of the standard references in anatomy).
- Netter’s Atlas of Human Anatomy (a famous visual atlas in anatomy).
- Clinically Oriented Anatomy by Keith Moore
Sports and training references :
- Strength Training Anatomy by Frederic Delavier
- Essentials of Strength Training and Conditioning by NSCA
- Well-known articles and training programs by international coaches
Medical databases :
- PubMed (for scientific and research articles)
- MedlinePlus (health and medical information)
- WebMD (for practical and general health information)
Pelank Life | Body Health Assessment
The Best Body Health Calculators Using Scientific Methods
Developed by Pelank Life ©
Comments