Introduction
🔷 Anatomy and Function of the Arm Muscles Based on Gray’s Anatomy
The arm is one of the most important parts of the upper limb, enabling a wide range of movements from fine and precise actions to powerful and explosive motions. The muscles in this region, by providing a combination of strength, endurance, and coordination, play a fundamental role in all daily and athletic activities—from the simple flexion of the elbow when lifting an object to the execution of powerful movements in intense sports.
✅ According to Gray’s Anatomy, the arm muscles are divided into two main groups:
The anterior group, responsible for flexion of the elbow and shoulder
The posterior group, responsible for extension of the elbow and stabilization of the arm joint
These muscles not only control the movement of the forearm and hand but also play a key role in stabilizing the shoulder and elbow joints. Major muscles such as the biceps brachii, triceps brachii, and brachialis are particularly important in powerful movements. Alongside them, smaller muscles like the coracobrachialis and anconeus assist in stabilization and precise control of movements.
Understanding these muscles is highly important, as it improves the quality of sports and bodybuilding training, helps prevent injuries to the shoulder, elbow, and wrist, and contributes to increasing muscular strength and endurance in daily activities.
In the following sections, based on reliable sources—especially Gray’s Anatomy—the structure, function, innervation, and related exercises of each of these muscles will be examined in detail to provide a comprehensive understanding of their roles in the body.

1️⃣ Anterior Muscles
Anterior Compartment - Flexor
Front of the Arm
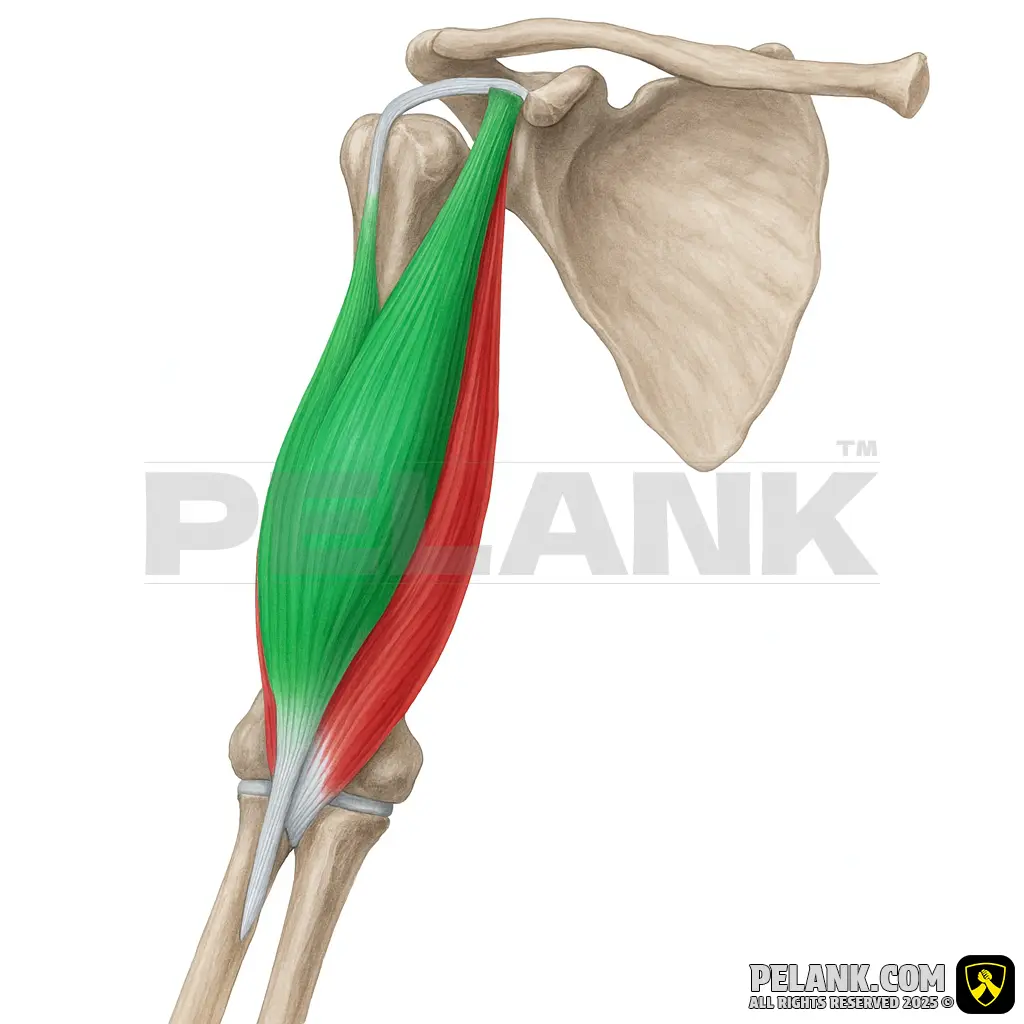
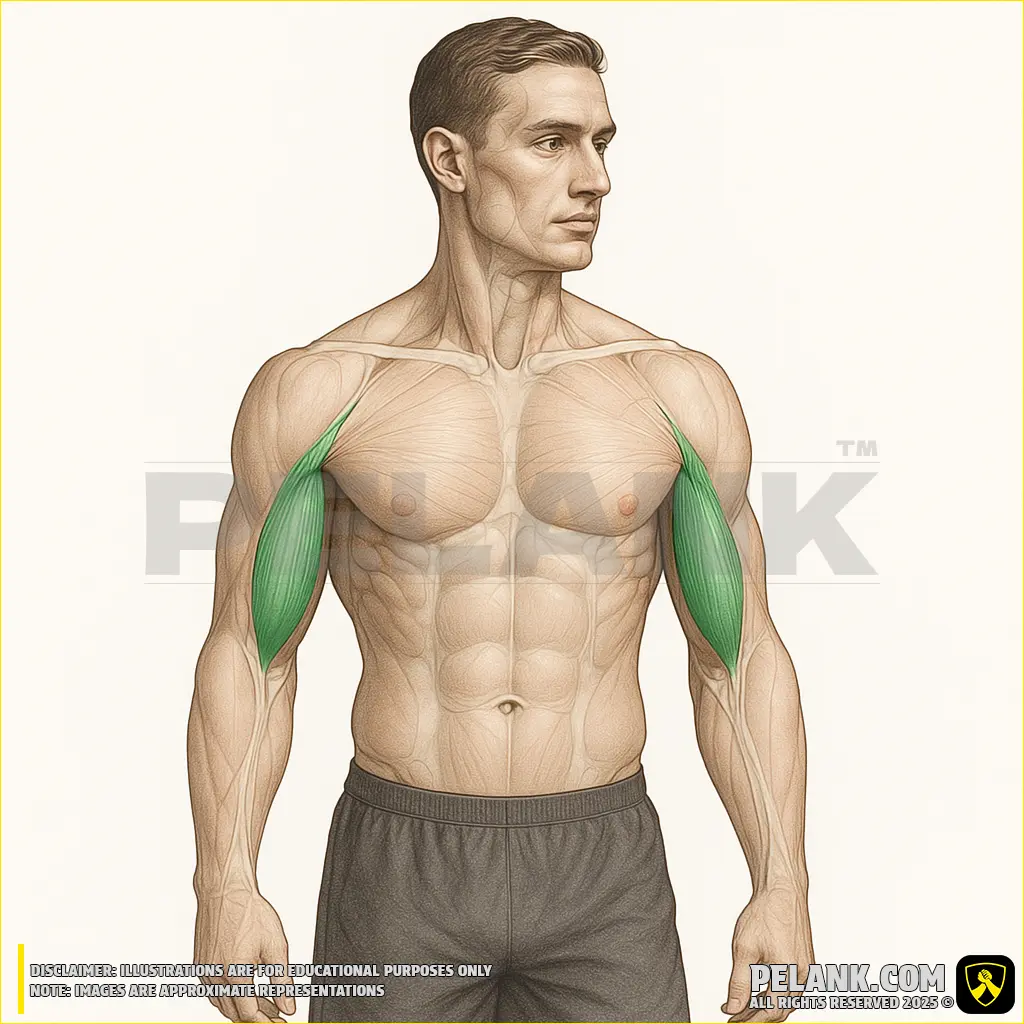
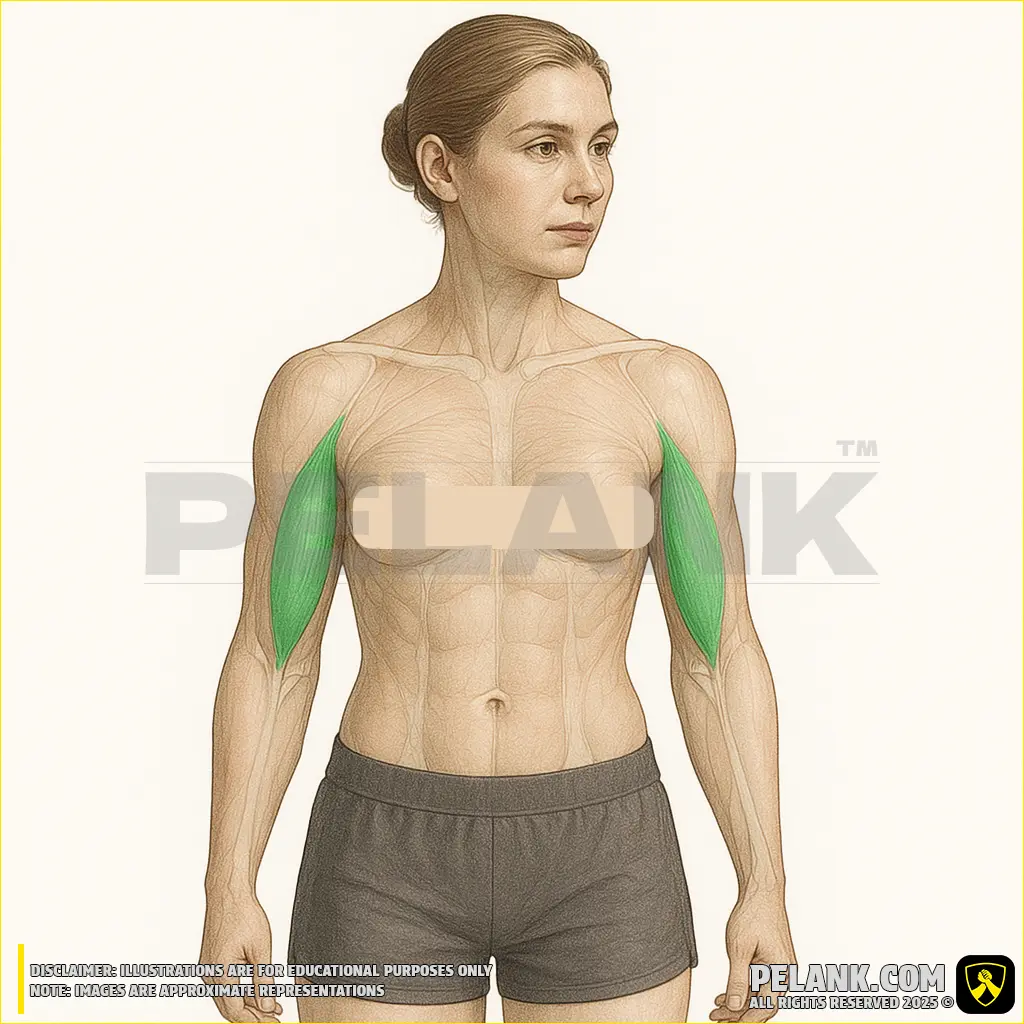
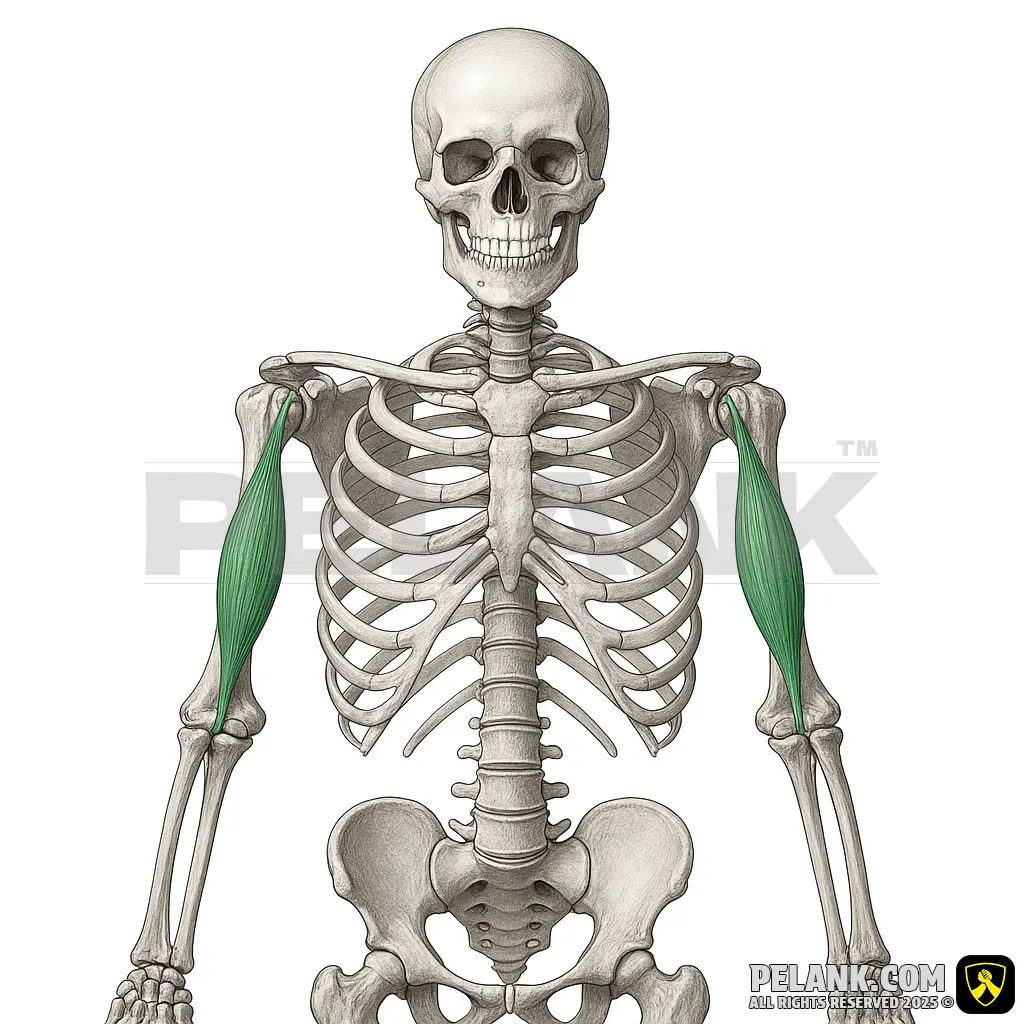
Biceps Brachii Muscle
The biceps brachii is one of the main muscles at the front of the arm, consisting of two heads—a short head and a long head—and plays an important role in elbow flexion and forearm rotation. This muscle is engaged in all strength training and daily activities that require bending the elbow or rotating the forearm.
Strengthening this muscle improves performance in weightlifting, bodybuilding, martial arts, and daily activities.
🖼️ Image Gallery
Click on the images to enlarge them.
🔷 Full Description
Click on the title to read the sections.
✅ Persian Name: Do Sare Bazoei
✅ Latin Name: Biceps Brachii
✅ Common Name: Arm / Front of the Arm
✅ Location:
🟡 Located in the anterior (front) part of the arm, extending from the shoulder to the forearm.
🟡 Consists of two heads—a short head and a long head—that originate from the scapula (shoulder blade).
🟡 Positioned at the front of the arm, it enables movement by flexing the elbow and rotating the forearm.
✅ 🦾 Origin
✔ Long head: originates from the supraglenoid tubercle of the scapula
✔ Short head: originates from the coracoid process of the scapula
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ It attaches to the radius bone in the forearm.
✔ It has a thick sheath called the bicipital aponeurosis, which connects to the forearm muscles.
✅ 📌 Classification and Function
The biceps brachii consists of two main heads:
1️⃣ Long Head
✔ Responsible for shoulder stability and assisting with arm movements.
✔ More active during pulling exercises (such as pull-ups) and overhead movements.
2️⃣ Short Head
✔ Plays a primary role in elbow flexion.
✔ More active during direct biceps exercises, such as dumbbell and barbell curls.
✅ Main Functions:
✔ Elbow flexion – lifting the forearm toward the upper arm.
✔ Forearm supination – rotating the forearm upward (such as opening a bottle).
✔ Assisting shoulder movements – involved in raising the arm.
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Type
✔ A combination of fast-twitch fibers (Type II) and slow-twitch fibers (Type I) It consists of both.
✔ Fast-twitch fibers are activated during powerful movements, such as heavy biceps curls.
✔ Slow-twitch fibers help maintain muscle endurance throughout the day.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Motor and Athletic Performance
✔ It plays a role in all pulling and strength movements of the arm, such as pull-ups, push-ups, deadlifts, and shoulder presses.
✔ Athletes in bodybuilding, weightlifting, boxing, wrestling, and gymnastics need to strengthen this muscle.
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ This muscle has both strength and endurance, being active in repetitive movements (such as swimming) and explosive movements (such as weightlifting).
✔ Weakness in this muscle leads to reduced grip strength, decreased arm endurance, and a higher risk of elbow and shoulder injuries.
🧠 Innervation
✔ The musculocutaneous nerve (C5–C6) is responsible for controlling this muscle.
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ The brachial artery is the main blood supply for this muscle.
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Bodybuilding: Active in all arm strength exercises, such as dumbbell and barbell curls.
✔ Martial arts: Assists with punching in boxing, judo, and wrestling.
✔ Gymnastics: Important in movements like pull-ups, planks, and hanging.
✔ Team sports: Plays a role in throws in basketball, volleyball, and American football.
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Connection with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Works with the brachialis muscle to flex the elbow.
✔ Has a close relationship with the forearm muscles and affects grip strength.
✔ Strengthening this muscle improves shoulder stability and helps prevent elbow injuries.
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ Tearing or straining of the long head of the biceps is the most common injury, especially in weightlifting and intense sports.
✔ Weakness in this muscle can cause problems with elbow flexion and reduced hand strength.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Main Exercises for Strengthening the Biceps Brachii
1️⃣ Barbell Curl – the best exercise for mass and strength
2️⃣ Hammer Curl – places more emphasis on the long head
3️⃣ Cable Curl – focuses on a full range of motion
4️⃣ Chin-ups – combines strength and endurance training
5️⃣ Preacher Curl – strengthens the short head and increases muscle isolation
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery Movements
✔ Arm stretch against the wall to improve flexibility
✔ Massage and muscle release to reduce tension after exercise
✅ 🔍 Interesting Fact
✔ Contrary to popular belief, the biceps brachii is just one of several muscles responsible for elbow flexion, and the brachialis muscle is actually the strongest elbow flexor!
✅ 💡 Practical Tip
✔ For maximum growth, perform exercises for this muscle with different grip widths (close, medium, wide) to engage both the short and long heads!
🔴 Name and Location: A muscle at the front of the arm with two heads—short and long.
🟠 Anatomy: Originates from the scapula and inserts into the radius bone.
🟡 Function: Flexes the elbow, supinates the forearm, and assists with shoulder movements.
🟢 Physiology: A mix of strength and endurance fibers, essential in bodybuilding workouts.
🔵 Innervation: Musculocutaneous nerve (C5–C6).
🟣 Importance: Active in bodybuilding, boxing, gymnastics, and team sports.
🟤 Exercises: Barbell curls, hammer curls, chin-ups, cable curls.
⚫ Fun Fact: For complete development, target both heads with a variety of exercises!
Brachialis Muscle
The brachialis is a deep and very strong muscle located at the front of the arm, lying directly beneath the biceps brachii. This muscle plays the primary role in elbow flexion and, unlike the biceps brachii, has no function in forearm rotation.
✅ Why is this muscle important?
✔ It is the strongest elbow flexor—even stronger than the biceps brachii!
✔ It is essential for overall arm thickness and size.
✔ Strengthening this muscle improves performance in sports such as weightlifting, wrestling, and bodybuilding.

🔷 Full Description
Click on the title to read the sections.
✅ Persian Name: Azole Bazoei
✅ Latin Name: Brachialis
✅ Common Name: Brachialis
✅ Location:
🟡 Located directly beneath the biceps brachii at the front of the arm.
🟡 Originates from the middle of the humerus and attaches to the forearm bone.
🟡 Unlike the biceps brachii, it attaches to the ulna and is only responsible for elbow flexion.
✅ 🦾 Origin
✔ The anterior surface of the distal half of the humerus bone
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ The ulna bone in the forearm, especially the coronoid process
✅ 📌 Classification and Function
✔ The strongest elbow flexor regardless of forearm position
✔ Unlike the biceps brachii, it has no role in forearm supination
✔ Active at all elbow angles (whether the hand is rotated or not)
✔ More engaged in movements where the palm faces down (pronation), such as reverse barbell curls and hammer curls
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Type
✔ A combination of slow-twitch (Type I) and fast-twitch (Type II) fibers
✔ Fast-twitch fibers are activated during powerful movements like heavy lifting
✔ Slow-twitch fibers assist with endurance and elbow control
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Motor and Athletic Performance
✔ Plays a key role in all strength and pulling movements of the arm
✔ Highly active in boxing, weightlifting, gymnastics, and wrestling
✔ Weakness in this muscle leads to reduced elbow flexion strength
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ A very strong but less recognized muscle that deserves focused training
✔ Weakness in this muscle reduces arm strength and increases strain on the biceps brachii
🧠 Innervation
✔ The musculocutaneous nerve (C5–C6) controls this muscle.
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ The brachial artery
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Bodybuilding: Active in exercises like hammer curls and reverse barbell curls
✔ Martial Arts: Plays a vital role in gripping opponents in judo and wrestling
✔ Team Sports: Engaged in ball throwing in basketball and handball
✔ Weightlifting: Involved during pulling movements in deadlifts and clean and jerk
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Connection with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Works together with the biceps brachii and brachioradialis muscles to flex the elbow
✔ Excessive strain on this muscle can lead to elbow pain (Tennis Elbow)
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ Weakness in this muscle reduces elbow flexion strength and increases strain on the biceps brachii
✔ Strain or inflammation of this muscle can cause pain in the inner part of the elbow
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Main Exercises to Strengthen the Brachialis Muscle
1️⃣ Reverse Barbell Curl – the best exercise for maximal brachialis engagement
2️⃣ Hammer Curl – places more focus on the long head of the brachialis
3️⃣ Reverse Cable Curl – provides constant tension on the muscle
4️⃣ Chin-ups (underhand grip) – combines pulling and strengthening
5️⃣ Resistance band exercises – help improve muscle endurance
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery Movements
✔ Arm and forearm stretches to increase flexibility
✔ Massage and muscle release to reduce tension after exercise
✅ 🔍 Interesting Fact
✔ The brachialis muscle is stronger than the biceps brachii in everyone, but because it lies beneath it, it is less visible!
✅ 💡 Practical Tip
✔ If you want thicker arms, focus on training the brachialis! The biceps brachii is more visible from the front, but the brachialis adds overall thickness to the sides of the arm.
🔴 Name and Location: A strong muscle located beneath the biceps brachii at the front of the arm
🟠 Anatomy: Originates from the humerus and attaches to the ulna
🟡 Function: The strongest elbow flexor, with no effect on forearm rotation
🟢 Physiology: Contains both strength and endurance fibers, essential for power sports
🔵 Innervation: Musculocutaneous nerve (C5–C6)
🟣 Importance: Active in bodybuilding, wrestling, gymnastics, and weightlifting
🟤 Exercises: Reverse barbell curls, hammer curls, reverse cable curls
⚫ Interesting Fact: Stronger than the biceps brachii but less visible
Coracobrachialis Muscle
The coracobrachialis is a small but important muscle on the inner side of the arm, originating from the coracoid process of the scapula and attaching to the humerus. This muscle functions in flexion and adduction of the arm toward the body and contributes to shoulder stabilization.
✅ Why is this muscle important?
✔ It is vital for strengthening shoulder pulling and pushing movements.
✔ Plays a key role in sports that require pulling and adducting the arm, such as gymnastics and weightlifting.
✔ Helps stabilize the arm and increase strength in movements like bench press and push-ups.

🔷 Full Description
Click on the title to read the sections.
✅ Persian Name: Azole Gharabi Bazoei
✅ Latin Name: Coracobrachialis
✅ Common Name: Inner Arm Muscle
✅ Location:
🟡 Located on the inner part of the arm, near the shoulder and beneath the biceps brachii.
🟡 Originates from the coracoid process of the scapula and inserts mid-way along the humerus.
🟡 Responsible for flexing and adducting the arm toward the body.
✅ 🦾 Origin
✔ Coracoid process of the scapula bone.
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ Medial surface of the humerus bone.
✅ 📌 Classification and Function
✔ Shoulder flexion – assists in raising the arm forward.
✔ Adduction – pulling the arm toward the body.
✔ Helps stabilize the shoulder joint during resistance movements.
✔ Unlike the biceps brachii, it does not participate in rotational movements.
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Type
✔ A combination of slow-twitch (Type I) and fast-twitch (Type II) fibers.
✔ Primarily designed for endurance and fine control of arm movements.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Motor and Athletic Performance
✔ Assists in stabilizing the arm during sports such as swimming, wrestling, and gymnastics.
✔ Provides support in movements like bench press, push-ups, and throws.
✔ Helps shoulder stability during pull-ups and chin-ups.
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ A relatively small but vital muscle for maintaining shoulder and arm stability.
✔ Weakness in this muscle reduces shoulder stability and increases strain on the biceps brachii.
🧠 Innervation
✔ The musculocutaneous nerve (C5–C7) is responsible for controlling this muscle.
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Brachial artery
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Bodybuilding: Stabilizes the arm during exercises like bench press and dumbbell flyes.
✔ Martial arts: Active in movements such as gripping opponents in wrestling and MMA.
✔ Gymnastics and swimming: Helps with arm balance and shoulder stabilization.
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Connection with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Works alongside the biceps brachii and anterior deltoid muscles in flexing the arm.
✔ Helps stabilize the glenohumeral (shoulder) joint.
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ Inflammation of the muscle (Coracobrachialis Syndrome) causing pain in the inner arm and shoulder area.
✔ Weakness in this muscle may lead to shoulder instability and reduced bench press strength.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Main Exercises to Strengthen the Coracobrachialis Muscle
1️⃣ Dumbbell Bench Press – helps stabilize the shoulder and increase muscle strength
2️⃣ Cable Crossover – strengthens arm adduction movements
3️⃣ Dumbbell Fly – engages the muscle during arm opening and closing motions
4️⃣ Hammer Curl – provides indirect stress to the coracobrachialis
5️⃣ Neutral Grip Pull-ups – assists in strengthening shoulder stabilization
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery Movements
✔ Arm stretch against the wall to improve flexibility.
✔ Massage and muscle release to reduce tension after exercise.
✅ 🔍 Interesting Fact
✔ The coracobrachialis is one of the smallest muscles of the arm but plays a vital role in shoulder stabilization!
✅ 💡 Practical Tip
✔ If you experience weakness in the bench press or shoulder pulling movements, you should strengthen the coracobrachialis!
🔴 Name and Location: A small muscle inside the arm originating from the coracoid process of the scapula.
🟠 Anatomy: Originates from the scapula and attaches to the humerus.
🟡 Function: Flexes and adducts the arm, stabilizes the shoulder.
🟢 Physiology: Contains strength and endurance fibers, aids shoulder movements.
🔵 Innervation: Musculocutaneous nerve (C5–C7).
🟣 Importance: Active in power sports, wrestling, gymnastics, and bodybuilding.
🟤 Exercises: Bench press, cable crossover, dumbbell fly, neutral grip pull-ups.
⚫ Interesting Fact: The smallest arm muscle but key in shoulder stabilization!
2️⃣ Posterior Muscles
Posterior Compartment - Extensor
Back of the Arm
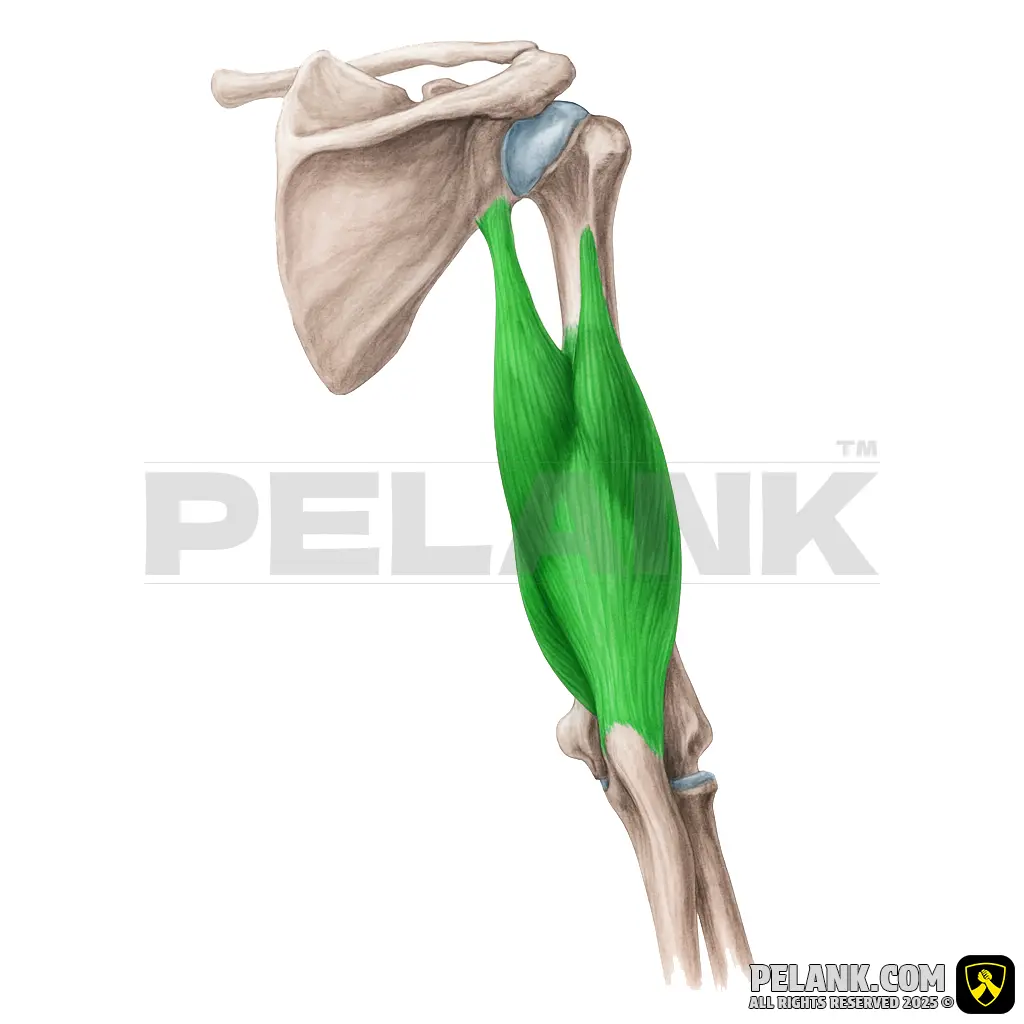
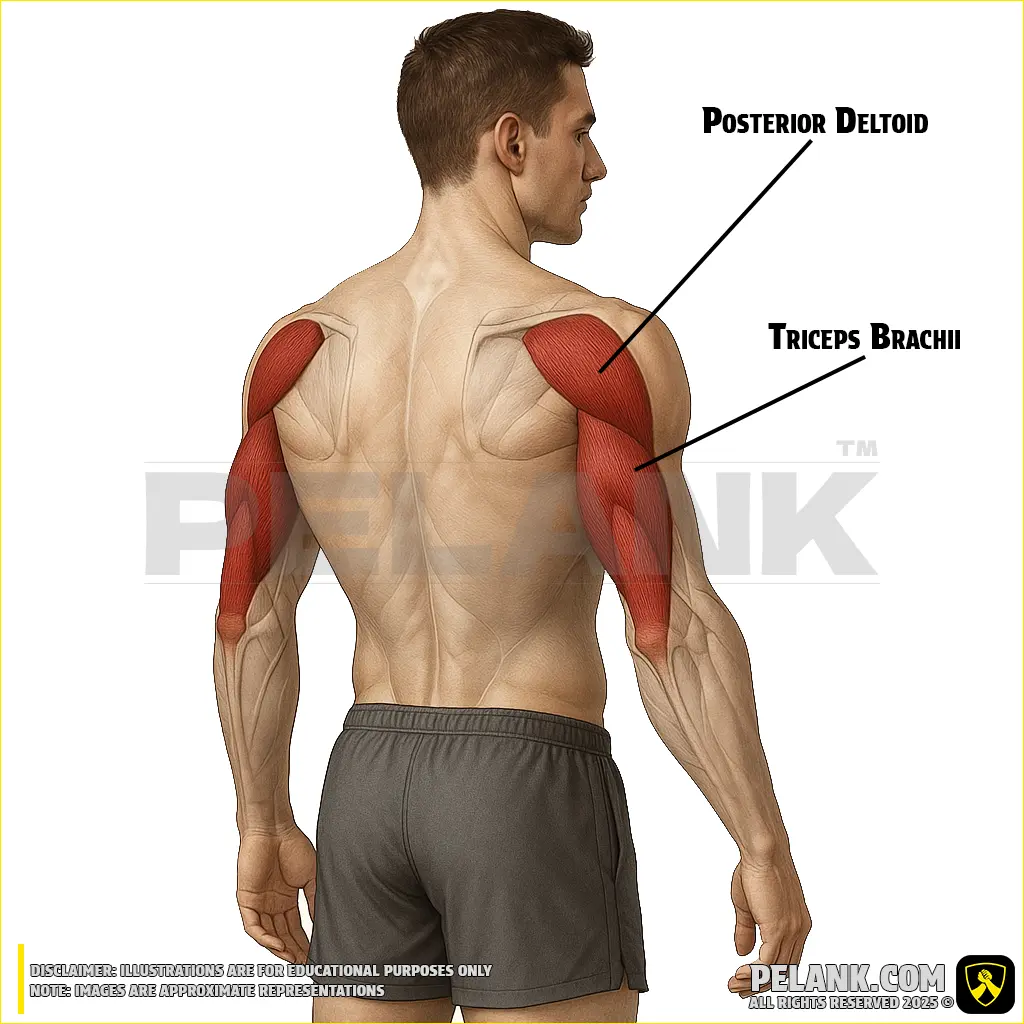
Triceps Brachii Muscle
The triceps brachii is one of the strongest muscles of the posterior arm, with its primary function being elbow extension and generating force in pushing movements. This muscle has three heads (long, medial, and lateral), all located at the back of the arm, and they attach to the ulna in the forearm.
✅ Why is this muscle important?
✔ The sole muscle responsible for elbow extension and essential in strength movements.
✔ Stabilizes the elbow and shoulder joints during pressing exercises like the bench press.
✔ Directly impacts strength gains in bodybuilding, gymnastics, boxing, and weightlifting.
🖼️ Image Gallery
Click on the images to enlarge them.
🔷 Full Description
Click on the title to read the sections.
✅ Persian Name: Azole Se Sare Bazoei
✅ Latin Name: Triceps Brachii
✅ Common Name: Back of the Arm
✅ Location:
🟡 Located in the posterior (back) part of the arm, extending from the scapula to the forearm bone.
🟡 Composed of three heads: long, medial, and lateral.
🟡 Responsible for elbow extension and assists in shoulder stabilization.
✅ 🦾 Origin
✔ Long Head: originates from the infraglenoid tubercle of the scapula
✔ Medial Head: originates from the posterior surface of the humerus, below the lateral head
✔ Lateral Head: originates from the posterior surface of the humerus, above the medial head
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ Ulna bone – olecranon process
✅ 📌 Classification and Function
The three main heads of the triceps brachii muscle are:
1️⃣ Long Head
✔ The strongest head and the only one originating from the scapula.
✔ Besides extending the elbow, it plays a role in arm movements and shoulder stabilization.
✔ More active in movements that involve pulling weight behind the body, such as parallel dips.
2️⃣ Medial Head
✔ Located beneath the lateral head and more active during strength and endurance movements.
✔ Plays a greater role in light, repetitive exercises like cable triceps extensions.
3️⃣ Lateral Head
✔ Responsible for muscle mass and the V-shape appearance of the back of the arm.
✔ More active in heavy exercises such as close-grip bench press and lying barbell triceps extensions.
✅ Main Functions:
✔ Elbow extension – the primary muscle responsible for straightening the forearm.
✔ Stabilizes the elbow during pressing movements such as push-ups and bench press.
✔ Assists shoulder movements (long head of the muscle).
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Type
✔ A combination of fast-twitch fibers (Type II) and slow-twitch fibers (Type I) ✔ Fast-twitch fibers are activated during powerful and explosive movements such as bench press and dips.
✔ Slow-twitch fibers are important for endurance in continuous movements like push-ups and parallel bar exercises.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Motor and Athletic Performance
✔ Active in all pressing movements such as bench press, push-ups, dips, and parallel bar exercises.
✔ Plays a key role in sports like boxing, weightlifting, gymnastics, and basketball.
✔ Helps stabilize the shoulder joint during overhead movements like shoulder press and clean and jerk.
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ A very strong and essential muscle for increasing upper body strength.
✔ Weakness in this muscle leads to reduced strength in pressing movements and increased strain on the elbow and shoulder.
🧠 Innervation
✔ The radial nerve (C6–C8) is responsible for controlling this muscle.
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Deep brachial artery
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Bodybuilding: Active in triceps exercises, bench press, dips, and lying barbell presses.
✔ Boxing and martial arts: Plays a key role in straight punches and increasing punching power.
✔ Weightlifting: Helps stabilize the elbow during shoulder presses and clean and jerk.
✔ Gymnastics and CrossFit: Vital in movements like parallel bars, pull-ups, and dips.
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Connection with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Works alongside the deltoid and pectoral muscles during pressing movements.
✔ Weakness in this muscle increases strain on the shoulder and elbow, raising the risk of joint injury.
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ Strain or inflammation of the triceps tendon (Triceps Tendinitis) causes pain at the back of the elbow.
✔ Weakness in this muscle may reduce pressing strength and increase strain on the shoulders.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Main Exercises to Strengthen the Triceps Brachii Muscle
1️⃣ Lying Barbell Triceps Extension (Skull Crushers) – targets all heads of the muscle
2️⃣ Parallel Dips – best for strength and endurance
3️⃣ Cable Triceps Pushdown – ideal for muscle isolation
4️⃣ Close-Grip Bench Press – combines triceps and chest muscles
5️⃣ Overhead Dumbbell Triceps Extension – emphasizes the long head more
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery Movements
✔ Triceps stretch to improve flexibility.
✔ Massage and foam rolling to reduce tension after exercise.
✅ 🔍 Interesting Fact
✔ 70% of the arm’s volume comes from the triceps brachii! If you want bigger arms, you need to focus on this muscle.
✅ 💡 Practical Tip
✔ For complete growth, perform exercises at different angles to engage all three heads of the muscle!
🔴 Name and Location: A three-headed muscle located at the back of the arm, extending from the shoulder to the elbow.
🟠 Anatomy: Originates from the scapula and humerus, and attaches to the ulna bone in the forearm.
🟡 Function: Elbow extension, shoulder stabilization, and assisting pressing movements.
🟢 Physiology: Contains both strength and endurance fibers, active in power and endurance arm movements.
🔵 Innervation: Radial nerve (C6–C8), which controls the function of this muscle.
🟣 Importance: Active in bodybuilding, boxing, weightlifting, swimming, CrossFit, and gymnastics.
🟤 Exercises: Parallel dips, close-grip bench press, lying barbell triceps extension, overhead dumbbell triceps extension, cable triceps pushdown.
⚫ Interesting Fact: It makes up 70% of the arm’s volume, so focusing on this muscle is essential for increasing arm size!
Anconeus Muscle
The anconeus is a small but vital muscle located at the posterior aspect of the elbow. It acts as an accessory to the triceps brachii in elbow extension and contributes to the stabilization and control of elbow movements during pushing and pulling actions.
✅ Why is this muscle important?
✔ Assists in elbow extension during powerful movements such as bench press and dips.
✔ Reduces strain on the elbow and helps prevent injuries in repetitive-motion sports.
✔ Stabilizes the elbow during gripping and pulling exercises.

🔷 Full Description
Click on the title to read the sections.
✅ Persian Name: Azole Poshti Aranj
✅ Latin Name: Anconeus
✅ Common Name: Posterior Elbow Muscle
✅ Location:
🟡 Located at the back of the elbow, between the humerus and the ulna.
🟡 Part of the elbow joint’s stabilizing system.
🟡 Acts as a helper muscle to the triceps brachii in extending the elbow.
✅ 🦾 Origin
✔ Humerus – originating from the lateral epicondyle of the humerus.
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ Ulna – on the lateral surface of the olecranon process.
✅ 📌 Classification and Function
✔ Assists in elbow extension alongside the triceps brachii muscle.
✔ Stabilizes the elbow joint during pushing and pulling movements.
✔ Absorbs movement shocks and reduces pressure on the elbow during rapid actions.
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Type
✔ Primarily composed of slow-twitch (Type I) fibers for endurance and control of elbow movements.
✔ Contains fast-twitch (Type II) fibers for sudden and powerful actions such as bench press and dips.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Motor and Athletic Performance
✔ Active in all pushing and pulling movements that require elbow extension.
✔ Provides supportive role in sports such as throwing, wrestling, bodybuilding, gymnastics, and boxing.
✔ Stabilizes the elbow during heavy exercises like bench press and push-ups.
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ Essential for controlling the elbow joint and preventing injury in sports that require repetitive elbow extension.
✔ Weakness in this muscle can lead to elbow inflammation and decreased joint stability.
🧠 Innervation
✔ The radial nerve (C7, C8, T1) is responsible for innervating this muscle.
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Posterior interosseous artery.
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Bodybuilding: Provides support in bench press, lying triceps extensions, and dips.
✔ Boxing and Martial Arts: Helps stabilize the elbow during punching and defense.
✔ Throwing Sports: Plays a key role in volleyball, basketball, handball, and tennis.
✔ Pulling Sports: Contributes to elbow stability in swimming, gymnastics, and CrossFit.
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Connection with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Works alongside the triceps brachii in elbow extension.
✔ Plays a vital role in stabilizing the elbow joint and preventing sudden, unstable movements.
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ Weakness in this muscle can lead to decreased elbow stability and increased strain on the tendons.
✔ Inflammation and pain caused by repetitive elbow extension movements in throwing sports or bodybuilding.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Key Exercises to Strengthen the Anconeus Muscle
1️⃣ Close-Grip Bench Press – directly engages the muscle during pushing movements.
2️⃣ Parallel Dips – assists in elbow stabilization and strengthens the triceps.
3️⃣ Reverse Triceps Pushdown – increases activation of the anconeus muscle.
4️⃣ Hammer Curl with controlled eccentric phase – emphasizes elbow stabilization.
5️⃣ Stretching and resistance exercises with elastic bands – helps improve flexibility.
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery Movements
✔ Triceps stretch to enhance flexibility.
✔ Muscle massage to relieve tension after intense workouts.
✅ 🔍 Interesting Fact
✔ The anconeus muscle is often overlooked, yet it plays a key role in reducing stress on the elbow joint!
✅ 💡 Practical Tip
✔ If you experience elbow pain during pushing exercises like bench press or dips, your anconeus muscle might be weak and in need of strengthening!
🔴 Name and Location: A small muscle located at the back of the elbow, situated between the humerus and the ulna bones.
🟠 Anatomy: It originates from the lateral epicondyle of the humerus and attaches to the olecranon process of the ulna.
🟡 Function: Assists in elbow extension, stabilizes the elbow joint, and absorbs movement shocks.
🟢 Physiology: Contains both slow-twitch and fast-twitch fibers that contribute to stabilization and powerful movements.
🔵 Innervation: Radial nerve (C7, C8, T1).
🟣 Importance: Active in strength sports, bodybuilding, boxing, throwing sports, CrossFit, and gymnastics.
🟤 Exercises: Close-grip bench press, parallel dips, reverse-grip triceps pushdown, resistance band exercises.
⚫ Interesting Facts: A small but key muscle in elbow stabilization, reducing tendon stress, and preventing elbow injuries!
Interesting and Practical Facts
💪 The biceps brachii plays a role in the speed of arm movement.
✔ In addition to flexing the elbow, it is also active during rapid actions such as throwing a ball or punching, and through rapid contractions helps regulate movement speed.
🦾 The strongest flexor of the elbow is not the biceps brachii.
✔ The brachialis is the strongest elbow flexor, and even when the forearm is rotated, it still carries out the task of elbow flexion.
📏 More than 70% of arm mass comes from the triceps brachii.
✔ To build bigger arms, you should place greater focus on training the triceps brachii, as it makes up more volume than the biceps brachii.
🔄 The only arm muscle that rotates the forearm is the biceps brachii.
✔ In addition to flexing the elbow, this muscle also rotates the forearm upward (as in opening a bottle).
🖐️ The way you grip a weight affects arm development.
✔ A neutral grip engages the brachioradialis more, while a wide grip activates the long head of the biceps brachii.
🏋️ The triceps brachii is the strongest elbow extensor.
✔ Without this muscle, pressing movements such as the bench press or dips would not be possible.
🤲 The coracobrachialis is active in everyday movements.
✔ This small muscle, located beneath the biceps brachii, is responsible for flexing and adducting the arm, and is engaged in simple tasks such as hugging or lifting objects.
🧬 The final shape of the arms depends on genetics.
✔ The length and attachment of the arm muscles to the bones are genetically determined, which is why the shape of the arms differs among individuals.
🧗 Pull-ups with an underhand grip activate the biceps brachii more.
✔ In a standard pull-up the back muscles are more active, but with an underhand grip greater stress is placed on the biceps brachii.
⛓️ Not training the arms leads to weakness in pulling movements.
✔ Weak arms reduce performance in exercises such as pull-ups or climbing, since gripping and pulling depend on them.
⚡ The brachioradialis is the link between the arm and forearm.
✔ This muscle plays a key role in semi-rotational elbow movements and is more active in exercises such as hammer curls.
🛡️ The long head of the triceps brachii increases shoulder stability.
✔ This part of the triceps attaches to the scapula and helps stabilize the shoulder during heavy movements such as the overhead press.
🚨 Excessive pressure can lead to compartment syndrome.
✔ Very intense training without adequate rest may increase muscle pressure and cause severe pain and swelling.
🪶 The biceps brachii becomes less active when lifting light objects.
✔ In this case, the brachialis does most of the work, while the biceps brachii is less involved.
🧘 Isometric contraction is an effective method for improving arm endurance and stability.
✔ Exercises such as static pull-up holds or hand planks are isometric and help enhance endurance and stability, but for complete arm development they should be combined with dynamic movements such as biceps curls or dips.
💧 Arm muscle cramps are mostly related to dehydration.
✔ Such cramps usually occur due to a lack of water or minerals such as potassium.
🎯 The short head of the biceps brachii is harder to develop.
✔ Since it has fewer fibers, achieving greater activation requires focused exercises such as preacher curls.
🛠️ Strong arms reduce the load on the shoulders.
✔ When the arms are strong, the weight of heavy objects is distributed more onto the arms rather than the shoulders.
🥊 Martial artists have stronger arms.
✔ Sports such as boxing and judo, due to the repeated flexion and extension of the elbow, lead to significant strengthening of the arms.
⚖️ Weak arms can disrupt body balance.
✔ If the arms are weaker than the other upper-body muscles, overall body balance and performance in training decrease.
Conclusion
The arm muscles are among the most vital muscle groups in the body, playing key roles not only in strength movements and aesthetic appearance but also in daily and athletic activities. By understanding their anatomy, function, and strengthening tips, you can make your workouts more targeted, prevent injuries, and achieve maximum strength and endurance.
✅ Remember that balancing biceps and triceps training, along with incorporating stretching and recovery exercises, is the key to achieving strong and healthy arms. Get stronger, stay balanced!

Sharing

Mohsen Taheri
Further Reading
Pelank Life | Body Health Assessment
The Best Body Health Calculators Using Scientific Methods
Developed by Pelank Life ©
References
✅ Anatomy and Medical Books
✅ Research Resources and Standardized Terminology Databases
✅ Visual Resources and Professional Anatomy Atlases
✅ Educational Resources – Official Textual and Visual References