What is HIIT training? A complete 10 part guide
High-intensity interval training (HIIT) workouts
HIIT (High Intensity Interval Training)
HIIT (High-Intensity Interval Training) workouts 🔥 are a powerful and efficient style of exercise where short bursts of high-intensity effort are combined with intervals of rest or low-intensity movement ⏱️. This training method is designed to push the body to its maximum capacity within a limited period, helping you achieve more in less time.
Why has HIIT become so popular? 💡
In today’s fast-paced world, many people struggle to find enough time for long, traditional workouts. HIIT provides a quick, effective, and flexible solution for busy lifestyles. In under 30 minutes, you can complete a session that promotes intense fat burning, enhances heart health ❤️, and significantly boosts your overall fitness level.
Because of its efficiency and impressive results, HIIT has become the top choice for individuals who want noticeable progress, improved energy, and better health—all with minimal time investment 🚀🔥.
What is HIIT?
Difference from cardio / intervals
HIIT (High-Intensity Interval Training) workouts, also known as high-intensity interval training, are a dynamic and innovative approach to fitness that has gained tremendous popularity among both athletes and beginners in recent years 🔥. This method involves alternating short bursts of intense physical effort—such as sprinting, jumping, or other explosive movements—with intervals of rest or low-intensity activity ⏱️.
The fundamental principle of HIIT is to challenge the body by bringing it close to its maximum physical capacity during these high-intensity intervals, followed by periods of recovery that allow the body to regain enough energy for the next round 💪. This powerful cycle of effort and rest is repeated multiple times in a single workout session, creating a training style that is efficient, highly effective, and ideal for improving overall performance and endurance 🚀.

🏃♂️ The difference between HIIT and traditional cardio workouts
In classic cardio workouts—such as walking, jogging, or cycling at a steady pace—the intensity stays moderate and the exercise duration is usually much longer 🚴♂️. During these sessions, the heart rate remains relatively stable, and the body burns energy at a consistent, predictable rate. This makes traditional cardio effective but generally slower in producing major changes in fitness or fat loss.
In contrast, HIIT creates sharp spikes in intensity during short bursts of effort, causing the heart rate to rise rapidly and forcing the body to work at a much higher capacity 🔥. These intense intervals are then followed by recovery periods—either complete rest or light movement—to help the body return closer to its normal rhythm ⏱️.
This repeated cycle of explosive effort + recovery significantly boosts metabolic activity, not only during the workout but long after it ends. This extended calorie-burning phase is known as the afterburn effect (EPOC), and it is one of the key reasons HIIT is so effective for enhanced fat burning, improved endurance, and overall better fitness results 💪🚀.
🔄 Work and rest intervals
Each HIIT session is typically made up of several repeated “cycles” that follow a structured rhythm of intensity and recovery 🔁. Every cycle contains two essential phases:
- Work Interval ⚡
During this phase, the athlete performs a high-intensity or explosive movement at maximum—or near-maximum—effort. This often includes 20 to 40 seconds of fast, powerful exercises such as sprinting, jumping jacks, burpees, or jump squats. The goal here is to push the body to work as hard as possible within a short window of time. - Rest / Recovery Interval ⏱️
Following the intense effort, a brief period is dedicated to full rest or very light activity, typically lasting 30 to 60 seconds. This may involve slow walking, deep breathing, or simply standing still. The purpose of this recovery phase is to allow the heart rate to drop and prepare the body for the next round of exertion.
These alternating work–rest cycles are commonly repeated 4 to 10 times, depending on the workout plan and the individual’s fitness level. As a result, a complete HIIT session usually lasts 10 to 30 minutes, making it a time-efficient yet highly effective training method for improving performance, endurance, and overall conditioning 💪🔥.
✅ In summary
HIIT is a highly efficient training method designed to maximize workout effectiveness within a short period of time, allowing individuals to achieve remarkable results even with tight schedules 🔥. By combining intense bursts of effort with brief recovery intervals, HIIT significantly increases calorie burn, enhances both cardiovascular and muscular performance, and helps people stay consistently motivated—even when they’re short on time ⏱️💪.
Its ability to deliver fast, visible results, boost endurance, and keep workouts exciting has made HIIT one of the most popular, effective, and widely recommended training styles in the fitness world today 🚀🔥.
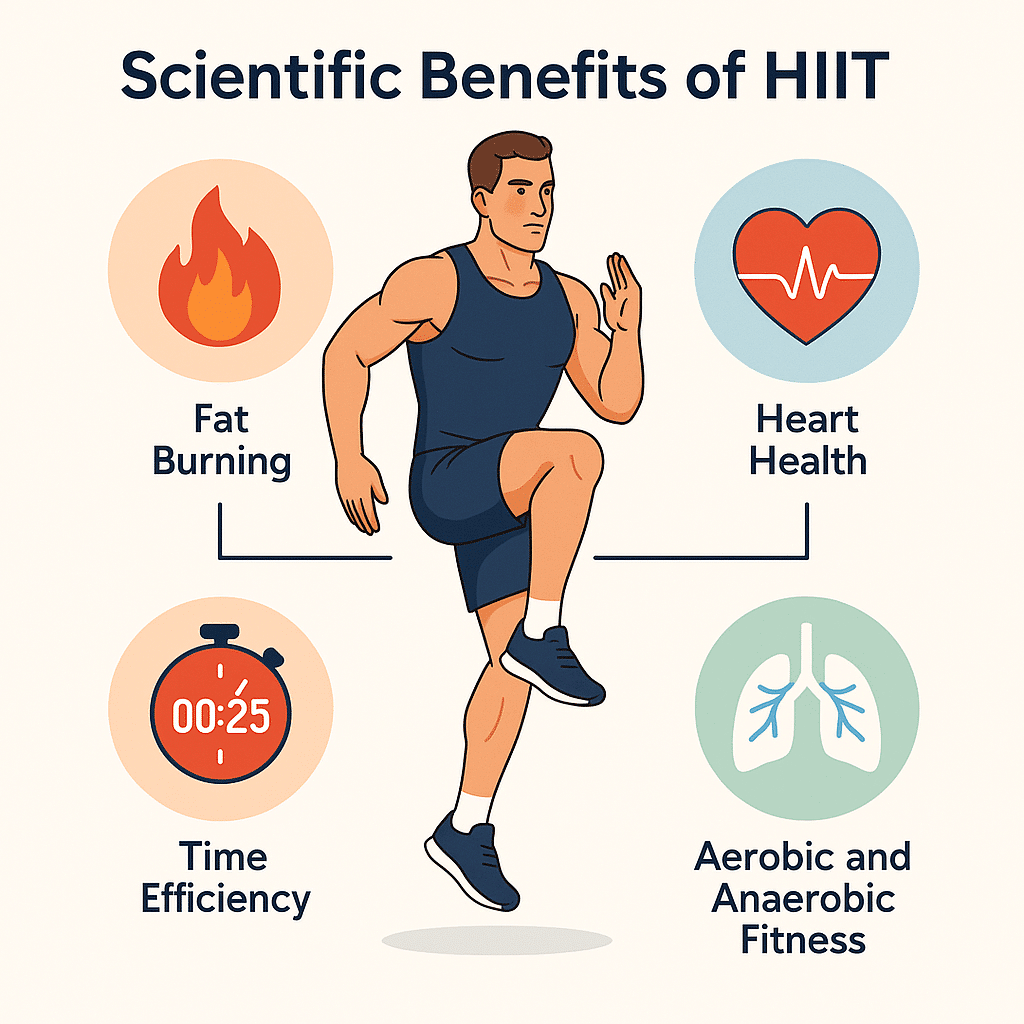
Scientific benefits of HIIT
Fat burning / time efficiency / heart health / aerobic and anaerobic benefits
🔥 Faster fat burning
One of the biggest reasons behind HIIT’s growing popularity is its powerful ability to accelerate fat loss in a short amount of time 🔥. Numerous studies show that HIIT can burn more calories in less time compared to steady-state aerobic activities like jogging or running at a constant pace. This makes it an ideal option for people who want efficient and noticeable results.
Beyond the calories burned during the workout itself, HIIT also boosts EPOC (Excess Post-Exercise Oxygen Consumption)—commonly known as the afterburn effect. This means your body continues burning calories for hours after the session is over, keeping your metabolism elevated and increasing overall energy expenditure ⏱️🔥.
Research strongly supports this effect. For example, a study published in the journal Obesity (2012) showed that individuals who performed HIIT experienced greater reductions in abdominal fat over several weeks compared to those in the control group, highlighting HIIT’s effectiveness for fat loss and improved body composition 💪📉.

⏱️ Time efficiency
One of the greatest advantages of HIIT is its remarkable effectiveness in a short period of time 🔥. Although a typical HIIT session lasts only 15 to 30 minutes, its high intensity makes it just as effective—and in many cases even more effective—than traditional 60-minute workouts.
Numerous studies support this efficiency. For example, research published in PLOS One (2014) showed that even very short HIIT programs—such as three 20-minute sessions per week—can improve key health markers as much as longer, steady-state aerobic routines ⏱️💪.
This time-saving benefit makes HIIT an ideal choice for people with busy schedules, allowing them to achieve impressive, meaningful results without dedicating long hours to exercise 🚀.
❤️ Positive impact on heart health
Contrary to popular belief, HIIT workouts are not harmful to heart health—on the contrary, they can greatly enhance cardiovascular function ❤️🔥. During HIIT, the heart rate repeatedly rises to near-maximum levels and then returns to a resting state. This intermittent challenge strengthens the heart muscle over time, improves its pumping efficiency, and increases overall aerobic capacity.
Scientific evidence supports these benefits. A meta-analysis published in the British Journal of Sports Medicine (2018) found that HIIT significantly improves aerobic capacity and heart health in individuals with coronary artery disease—as long as proper safety guidelines are followed 📈💓.
💨 Improved aerobic and anaerobic performance
In addition to boosting aerobic endurance—the body’s ability to deliver oxygen to the muscles during prolonged activity—HIIT is also extremely effective at improving anaerobic capacity, which refers to the body’s ability to generate energy without oxygen during short, intense bursts of effort 🔥💨.
Research strongly supports these benefits. A study published in Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise (2008) found that individuals who performed HIIT experienced significant increases in both VO₂max (maximum oxygen consumption) and anaerobic power 💪📈.
These improvements demonstrate that HIIT is an efficient and versatile training method capable of enhancing performance not only for professional athletes but also for everyday individuals seeking better overall fitness 🚀.
📊 Scientific studies and statistics (with references)
- Obesity (2012): This study examined the impact of HIIT on abdominal fat reduction and the increase in EPOC (afterburn effect). Result: HIIT led to a significantly greater decrease in abdominal fat compared to traditional steady-state aerobic exercise 🔥📉.
- PLOS One (2014): This research compared HIIT with traditional aerobic training in terms of time efficiency and overall effectiveness. Result: HIIT produced similar—or even superior—health and fitness benefits in far less time, highlighting its exceptional time-saving value ⏱️💪.
- British Journal of Sports Medicine (2018): A comprehensive meta-analysis focusing on cardiac patients undergoing HIIT. Result: HIIT resulted in substantial improvements in cardiovascular function and aerobic capacity, demonstrating its effectiveness when performed under proper safety guidelines ❤️📈.
- Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise (2008): This study investigated the effects of HIIT on VO₂max and anaerobic performance. Result: Participants experienced significant improvements in both maximum oxygen consumption and anaerobic power, confirming HIIT’s strong impact on overall physical performance 🚀💨.
Who can do HIIT?
Beginners / athletes / individuals with limitations
Due to its flexible structure and the ability to adjust both intensity and duration, HIIT can be an excellent option for a wide range of individuals—regardless of their fitness level or experience 🔥💪. However, to safely enjoy the full benefits of this powerful training method, it is essential to follow proper safety guidelines and take necessary precautions. Doing so ensures a workout that is not only effective but also healthy and sustainable in the long term ⏱️✅.
🟢 Beginners
Beginners can absolutely benefit from HIIT, as long as they start with lower intensity levels and shorter workout durations 🔰💪. It’s best to begin with fewer repetitions and longer rest intervals to allow the body to adapt safely. Proper exercise form is crucial, and performing a thorough warm-up beforehand helps prevent injury and prepares the muscles and joints for high-intensity movement 🔥⏱️.
🔵 Athletes
For semi-professional and professional athletes, HIIT serves as a powerful and highly efficient training tool 🔥💪. It helps elevate both aerobic and anaerobic capacity, supports effective fat burning, and significantly enhances overall performance. Many elite athletes incorporate HIIT into their training routines to add variety, challenge their physical limits, and improve key fitness indicators such as endurance, speed, and power 🚀.
🟡 Individuals with limitations or special conditions
Individuals with certain medical conditions—such as heart disease, high blood pressure, diabetes, severe obesity, or musculoskeletal injuries—should always consult a doctor or qualified health professional before beginning any HIIT program ⚠️👨⚕️.
For older adults or anyone with a history of joint problems or respiratory issues, adjusting the intensity and selecting low-impact exercises is essential. Even in these situations, with proper modifications and supervision, HIIT can safely be incorporated into a rehabilitation or health-improvement plan, offering meaningful benefits while minimizing risk 💪🩺.
⚠️ Warnings and precautions
- Cardiac or respiratory issues: Individuals with heart or lung conditions must obtain medical clearance and follow their doctor’s guidance before beginning any HIIT program ❤️🫁⚠️.
- Current injuries: If there is an active muscle, joint, or bone injury, it must be fully treated before resuming intense exercise. Returning to HIIT should be gradual and carried out under the supervision of a qualified specialist 🩼🧑⚕️.
- Older adults: Seniors can certainly benefit from HIIT if they have a basic level of fitness and access to proper supervision. However, the intensity of movements and the length of rest periods must be carefully adjusted to match their individual needs and physical limitations 👵💪.
- Pregnancy: Pregnant women should only perform specific, modified forms of HIIT—with their doctor’s approval—and should prioritize low-impact, gentle exercises to ensure safety for both the mother and the baby 🤰💛.
Conclusion
HIIT can be performed by most individuals, as long as proper safety guidelines are followed, the right intensity level is selected, and professional advice is sought when necessary 🔒💪. This training method is highly adaptable and can be tailored to a person’s fitness level, age, and medical condition, ensuring both safety and optimal results. With the correct modifications, HIIT becomes an accessible and effective workout approach for a wide range of people 🚀.
Key points before starting HIIT
Warm-up / intensity selection / importance of rest / hydration
🔸 Proper warm-up
Starting each HIIT session with a focused and proper warm-up is absolutely essential 🔥⏱️. Warm-up exercises—such as brisk walking, dynamic stretching, jumping jacks, or gentle lunges—help raise your body temperature, increase blood flow to the muscles, and activate the central nervous system. This preparation ensures your body is ready for the intense movements ahead and significantly reduces the risk of muscle and joint injuries 💪🛡️.

🔸 Choosing appropriate intensity and duration
The intensity of HIIT workouts should always be adjusted based on an individual’s fitness level, age, and medical history 🔧💪. Beginners are encouraged to start with shorter work intervals—such as 20–30 seconds of intense effort—paired with longer rest periods to allow proper recovery. More experienced athletes, on the other hand, can safely increase the intensity or extend the duration of their work intervals as their conditioning improves.
It’s crucial that individuals without prior HIIT experience avoid starting at maximum intensity. Instead, they should gradually increase the difficulty and intensity of their sessions over time to ensure steady progress and reduce the risk of injury ⏱️🔥.
🔸 The importance of rest between sets
Rest or recovery intervals between the high-intensity phases of HIIT are essential for both safety and workout quality ⏱️🛡️. Adequate rest—whether active or passive—allows the heart rate and breathing to come down slightly and gives the muscles enough time to recover before the next intense round.
When rest periods are shortened too much, it can lead to excessive fatigue, a noticeable drop in exercise quality, and an increased risk of injury. Maintaining the right balance between effort and recovery is key to achieving safe, effective, and sustainable HIIT results 💪🔥.
🔸 Hydration and recovery
HIIT naturally causes intense sweating and fluid loss, making it essential to drink enough water before, during, and after your workout to stay properly hydrated 💧🔥. In addition, effective recovery—including a gentle cool-down, light stretching, and taking adequate rest between training sessions—supports muscle repair and significantly reduces the likelihood of soreness and stiffness.
Neglecting recovery can lead to decreased performance, a higher risk of injury, and even a loss of motivation to continue exercising. Prioritizing hydration and recovery ensures safer, more enjoyable, and more effective HIIT training 💪🛡️.
Summary
Proper warm-up, choosing the right intensity and duration, allowing adequate rest, and prioritizing hydration and recovery are the essential pillars of safe and successful HIIT training 🔑🔥. By following these guidelines, you can maximize the effectiveness of your workouts while minimizing the risks of injury, excessive fatigue, or burnout. This balanced approach ensures consistent progress and a more enjoyable training experience 💪🚀.
Sample HIIT workout program for home
Without equipment / Exercise structure / Suggested movements
⏰ Introduction
This HIIT program is designed for individuals who want to maximize their results at home—without any special equipment—and in the shortest time possible 🔥🏠. All you need is 20 minutes and a bit of motivation to get started! 💪⏱️

📋 Workout structure
Total duration: 20 minutes⏱️
Pattern: 30 seconds of intense exercise + 30 seconds of rest 🔥
Number of movements: 5 different exercises 💪
Repetitions: Perform each exercise for 3 rounds, completing a total of 15 active sets🚀
💪 Suggested movements
- Jump Squat 🔥
- Burpee 💥
- Jumping Jack ⭐
- Mountain Climber 🏔️💨
- Push-Up / Plank 💪🧱
📊 HIIT Workout Program Table
Round | Movement 1 | Movement 2 | Movement 3 | Movement 4 | Movement 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Round 1 | Jump Squat | Burpee | Jumping Jack | Mountain Climber | Push-Up |
Round 2 | Jump Squat | Burpee | Jumping Jack | Mountain Climber | Plank |
Round 3 | Jump Squat | Burpee | Jumping Jack | Mountain Climber | Push-Up |
Time | 30 seconds | 30 seconds | 30 seconds | 30 seconds | 30 seconds |
After each 30-second exercise, rest for 30 seconds ⏱️. Once you complete all 5 movements, move on to the next round 🔁🔥.
⚠️ Execution Tips
- Before starting the workout, perform 3 to 5 minutes of dynamic warm-up to prepare your body 🔥.
- Make sure to rest between each movement and each round, giving your muscles time to recover ⏱️.
- Drink water regularly and maintain proper form throughout all exercises to prevent injury 💧💪.
- If you’re a beginner, feel free to reduce the intensity or extend the rest periods slightly for a safer start.
After finishing the workout, complete 3 minutes of stretching to cool down and help your body recover effectively 🧘♂️✨.
📝 Summary
This short and effective HIIT program is suitable for all fitness levels and can be performed in almost any space 🔥🏠. Stay consistent, and you’ll soon notice powerful changes in your body, stamina, and overall daily energy levels 🚀💪.
Common Mistakes in HIIT and Solutions
Overtraining / Neglecting Warm-Up and Cool-Down / Choosing Incorrect Movements / Not Allowing Enough Rest
Although HIIT workouts are incredibly effective and engaging, they can become harmful or less productive if proper principles aren’t followed ⚠️🔥. Understanding the most common mistakes—and knowing how to avoid them—is essential for maximizing both the safety and effectiveness of this training method. By staying aware and making smart adjustments, you can get the most out of every session while protecting your body 💪🛡️.
🟥 1. Overtraining
Mistake: Many individuals, impressed by the intensity and fast results of HIIT, tend to increase the number of sessions or push the intensity too much. This can lead to excessive fatigue, chronic muscle soreness, decreased performance, a weakened immune system, or even injury ⚠️🔥.
Solution:
- Perform HIIT no more than 2 to 4 times per week.
- Give your body sufficient time to recover, and make sure to include rest days or light workout days.
- Pay close attention to signs of over-fatigue or persistent pain, and take them seriously to prevent injury 💪🛡️.
🟧 2. Neglecting Warm-Up and Cool-Down
Mistake: Some individuals skip the warm-up before HIIT or the cool-down afterward. However, failing to properly prepare the muscles and nervous system greatly increases the risk of injury, muscle cramps, and reduced performance ⚠️🔥.
Solution:
- Always perform 3 to 5 minutes of dynamic warm-up before starting HIIT (dynamic stretches, brisk walking, jumping jacks).
- After finishing the workout, complete 3 to 5 minutes of stretching and light cool-down exercises to promote muscle recovery and prevent stiffness 🧘♂️⏱️.
🟨 3. Choosing Incorrect Movements
Mistake: Using overly complex or heavy movements beyond one’s fitness level—or performing exercises with improper technique—can increase the risk of injury and significantly reduce the effectiveness of the workout ⚠️💥.
Solution:
- Choose exercises that match your current fitness level; beginners should start with simpler, low-impact movements.
- Prioritize proper form and clean execution over speed or the number of repetitions.
- If necessary, seek help from a coach or rely on trusted instructional resources to learn correct technique and avoid harmful mistakes 💪🎯.
🟩 4. Not Allowing Enough Rest
Mistake: Shortening rest periods or ignoring their importance can lead to premature fatigue and significantly reduce the quality of the following sets. Without proper recovery, performance drops and the risk of injury increases ⚠️⏱️.
Solution:
- Stick to the recommended work-to-rest ratios (e.g., 30 seconds of exercise, 30 seconds of rest).
- If you experience extreme fatigue or unusual shortness of breath, allow yourself longer rest periods.
- Remember: the quality of each movement is far more important than completing the workout without adequate rest 💪🔥.
📝 Summary
Avoiding these mistakes and following practical solutions ensures that your HIIT workouts remain both safe and highly effective 🔥💪. Remember, the goal is steady progress, improved fitness, and long-term health—not burnout or injury. Staying mindful and consistent will help you get the best results while keeping your body strong and protected 🛡️🚀.
Difference Between HIIT and Other Training Methods
HIIT vs. Steady-State Aerobic Exercise (Endurance Cardio)
HIIT workouts, as a modern and dynamic training style, differ greatly from other common methods such as steady-state aerobic exercise and traditional weight training 🔥💪. Understanding these distinctions allows you to make smarter training decisions and achieve your fitness goals more effectively.

🏃♂️ HIIT vs. Steady-State Aerobic Exercise (Endurance Cardio)
Steady-state aerobic exercises—such as running at a steady pace, long walks, or gentle cycling—are typically performed at moderate intensity and for longer durations 🚶♂️🚴♀️. In this method, the heart rate remains relatively stable, and most of the fat burning happens during the workout itself.
In contrast, HIIT consists of short bursts of intense activity paired with rest intervals, causing the heart rate to repeatedly rise and fall toward its maximum 🔥⏱️. This alternating pattern not only allows you to burn more calories in less time, but also boosts the afterburn effect (EPOC)—meaning your body continues burning fat even after the workout has ended.
Comparison | HIIT | Steady-State Aerobic Exercise |
|---|---|---|
Exercise Intensity | Very High (Interval) | Moderate (Steady) |
Duration | Short (15-30 minutes) | Long (30-60 minutes or more) |
Fat burning | High, even after exercise | During exercise |
Impact on cardiovascular fitness | Very high | Good, but much lower |
Variety of movements | High | Limited (running, cycling, etc.) |
Suitable for busy individuals | Yes | Less |
🏋️♂️ HIIT vs. Traditional Weight Training
Traditional weight training is built around structured sets and repetitions using external weights, with the primary goal of increasing strength and muscle mass 💪🏋️♂️. The intensity is determined by the amount of weight lifted and the number of reps performed, and rest periods are usually longer to allow proper muscular recovery.
In HIIT, however, the emphasis is on high intensity, elevated heart rate, and minimizing rest time 🔥⏱️. Strength-based movements can be included within a HIIT routine, but the core objective is to improve strength, endurance, and fat burning simultaneously. This makes HIIT a more dynamic and time-efficient option for full-body conditioning.
Comparison | HIIT | Traditional Weight Training |
|---|---|---|
Type of Exercise | Aerobic and Strength | Strength (Muscle-focused) |
Activity Intensity | Very High (Interval) | Adjustable (usually moderate or high) |
Rest Time | Short (in seconds) | Longer (1-3 minutes) |
Calorie Burning | Very high | Moderate (depends on workout volume) |
Main Focus | Fat burning, overall fitness | Increase in strength and muscle mass |
Suitable for all levels | Yes (Adjustable) | Requires a stronger technical foundation |
Summary Comparison Table
Features | HIIT | Steady-State Aerobic Exercise | Traditional Weight Training |
|---|---|---|---|
Intensity | Very High (Interval) | Moderate (Steady) | Moderate/High (Muscle-focused) |
Duration | Short | Long | Variable |
Calorie Burning | Very high | High (during exercise) | Moderate |
Increase in strength | Moderate/High | Low | High |
Increase in aerobic endurance | Very high | High | Moderate |
Recovery and Rest | Short | Less required | Longer |
Suitable for busy individuals | Yes | No | Depends on the program |
📝 Summary
HIIT, as a flexible and highly time-efficient training method, is ideal for quick fat burning, improving heart health, enhancing aerobic fitness, and boosting physical strength 🔥💪. However, each type of training has its own unique characteristics, and the best choice depends on your individual goals, physical condition, and personal preferences. Selecting the right method ensures safer progress and more effective long-term results 🚀.
Conclusion and Practical Recommendation
Summary of Benefits / Quick Start Tips
✅ Summary of Benefits
HIIT workouts are among the most efficient and powerful exercise methods for burning fat, improving cardiovascular health, and enhancing both aerobic and anaerobic performance 🔥💪. This training style is especially smart and scientifically supported for individuals with limited time, delivering maximum results in short, intense sessions.
Thanks to its high flexibility, HIIT can be easily adjusted for all fitness levels, making it a practical and effective choice for beginners, intermediates, and advanced athletes alike 🚀✨.
🏁 Quick Start Tips
To get started, try a simple and beginner-friendly routine like the 20-minute equipment-free HIIT workout 🔥.
Begin with a short warm-up to prepare your body.
Choose five basic movements—such as jump squats, burpees, jumping jacks, mountain climbers, and push-ups.
Perform each exercise for 30 seconds with intensity, then rest for 30 seconds.
Complete this sequence for three full rounds, and finish with a few minutes of stretching to cool down and promote recovery 🧘♂️⏱️.
Invitation to Exercise
Try the home HIIT program today! 🔥
You can download or save the suggested routine from this article and start tracking your personal progress. If you need more workouts, guidance, or structured plans, feel free to explore the educational resources and the free HIIT programs available on the Planck website 🏠💪🚀.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
HIIT Workouts
1. Is HIIT better for weight loss?
Yes, HIIT, due to its high intensity and afterburn effect (EPOC), can burn more fat in less time compared to steady-state aerobic exercises.
2. How many times a week should HIIT be done?
For most people, 2 to 4 HIIT sessions per week are sufficient and safe. Doing more than this can lead to fatigue or injury.
3. Is HIIT suitable for women?
Yes, HIIT is absolutely suitable for women and can help with weight loss, body shaping, and improving heart health. The intensity and type of exercises should only be chosen according to one's fitness level.
4. Can beginners do HIIT?
Yes, but beginners should start with simpler exercises, shorter durations, and longer rest periods. Proper form is more important than high intensity.
5. Does HIIT require equipment?
No, most HIIT programs can be done without equipment (using body weight). However, adding dumbbells, bands, or other tools is possible for more variety.
6. Does HIIT increase muscle mass?
HIIT mainly focuses on fat burning and improving endurance, but some strength exercises can also aid in muscle growth. If the main goal is to increase muscle mass, weight training should complement HIIT.
7. Is HIIT dangerous for heart health?
In healthy individuals, HIIT is not only safe but beneficial. However, those with heart conditions or underlying health issues should consult a doctor before starting.
8. How long should a HIIT session be?
Most HIIT programs last between 15 to 30 minutes. Longer sessions are not necessarily more effective and can even be harmful.
9. What happens if we decrease or increase the rest time between exercises?
Decreasing rest time increases the intensity of the workout, but it may cause form to deteriorate and increase the risk of injury. Increasing rest makes the workout lighter but safer; balance is key.
10. Is HIIT suitable for all ages?
Yes, with general health and proper intensity levels, HIIT is suitable for all ages. Even older adults can perform modified, lighter versions of HIIT with guidance from a specialist.
References
- High-Intensity Intermittent Exercise and Fat Loss 🔥
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30765340/ - Systematic Review: The Impact of HIIT on Health Indicators 📊
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37204620/ - A Systematic Review: The Impact of HIIT on Health Outcomes 🧪
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24144531/ - HIIT for Cardiovascular Disease Patients: A Meta-Analysis ❤️
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34279621/ - HIIT for Cardiovascular Disease Patients: A Meta-Analysis ❤️
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24144531/ - HIIT Improves Aerobic and Anaerobic Performance 💪💨
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36983289/ - HIIT: Science and Application 📘
https://us.humankinetics.com/products/hiit-science - HIIT: Science and Application 📘
https://us.humankinetics.com/products/hiit-science - High-Intensity Interval Training: Is It Right for You? 🤔🔥
https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/fitness/in-depth/high-intensity-interval-training/art-20046356 - High-Intensity Interval Training: Is It Right for You? 🤔🔥
https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/fitness/in-depth/high-intensity-interval-training/art-20046356 - Interval Training for a Stronger Heart ❤️💪
https://www.heart.org/en/healthy-living/fitness/fitness-basics/interval-training-for-a-stronger-heart - Benefits of HIIT for Fat Loss and Insulin Sensitivity 🔥🩸
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29127602/ - Beginner HIIT Workouts You Can Do at Home 🏠💥
https://www.health.harvard.edu/exercise-and-fitness/interval-training - HIIT: Evidence and Guidelines 📚
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37939367/ - HIIT: Evidence and Guidelines 📚
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37939367/
Pelank Life | Body Health Assessment
The Best Body Health Calculators Using Scientific Methods
Developed by Pelank Life ©
Founder of Pelank Platform (6+ years) | Founder & Manager of Galaxy Gym (11+ years) | M.Sc. Student in Exercise Physiology & Nutrition | Certified Fitness & Conditioning Coach | Official Member of the Bodybuilding & Physical Fitness Federation
- This author does not have any more posts.


