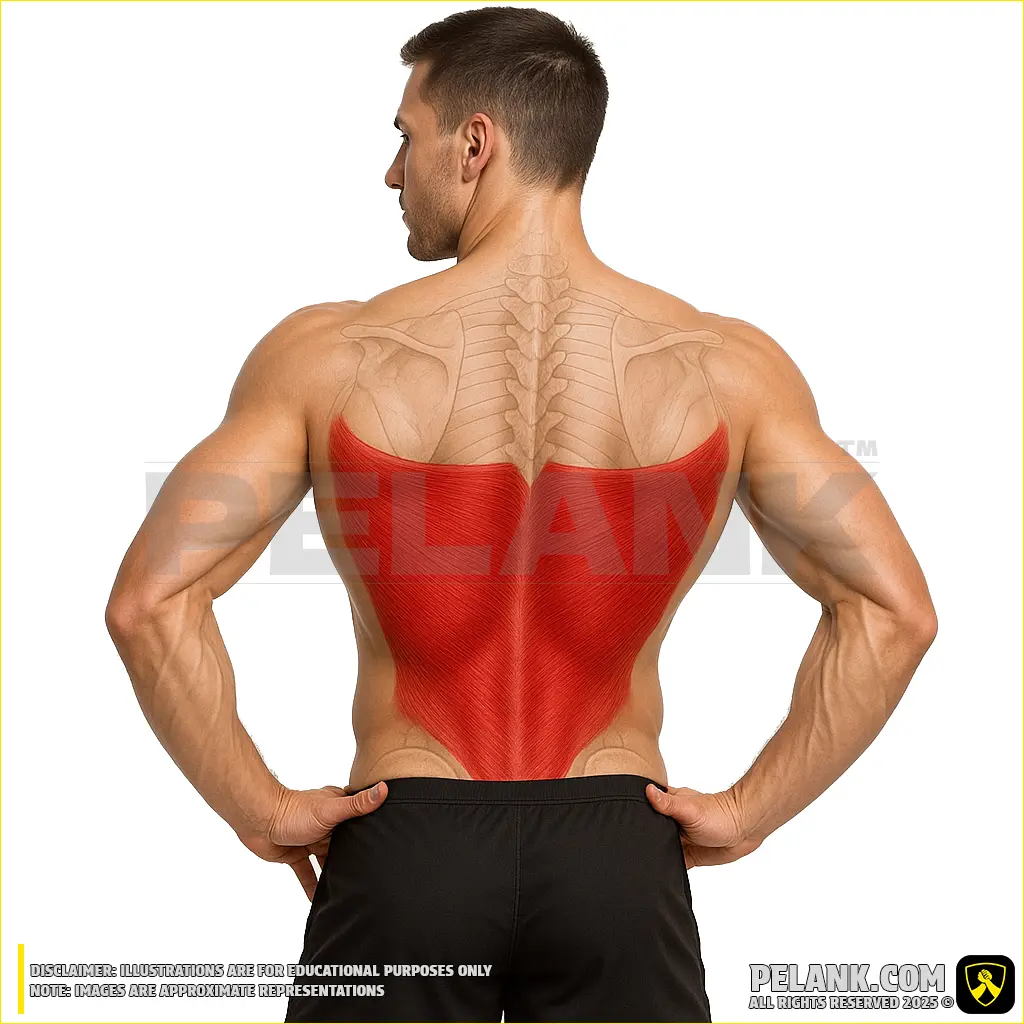
Lever High Row

| English Name | Lever High Row (Plate-Loaded High Row) |
|---|---|
| Difficulty | Intermediate |
| Movement Patterns | Pull Pattern |
| Muscle Contraction Types | Mixed (Con + Ecc) |
| Primary Muscle (EN) | Latissimus Dorsi |
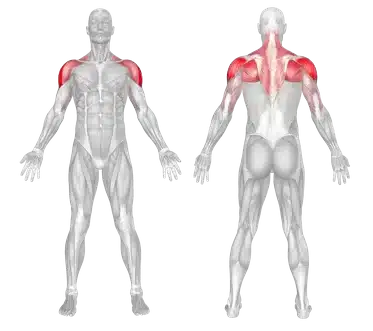
| Muscle Groups | Back muscles Shoulder Muscles |
|---|---|
| Workout Type | Strength training |
| Required equipment | Machine |
💠 Exercise guide
✅ The lever high row is one of the most effective exercises for strengthening and building the mid and lower back muscles. Its movement pattern combines elements of the lat pulldown and the seated row, but with greater control and more focused tension on the back and lower scapular muscles.
💠 How to perform the exercise

Preparation
✅ Sit on the machine and adjust the seat so that the handles are slightly above shoulder level.
✅ Keep your feet firmly planted on the floor or foot pads to stabilize your body throughout the movement.
✅ Keep your chest up and back straight, with your shoulders pulled down and back.
✅ Grip the handles with a neutral (palms facing each other) or pronated (palms facing down) grip.
✅ Before initiating the pull, slightly retract and depress your shoulder blades to establish a stable starting position.
Execution method
1️⃣ Inhale deeply, fully extending your arms and feeling a complete stretch in your lats.
2️⃣ Exhale and slowly pull the handles down and back, focusing on driving the movement with your elbows rather than your wrists.
3️⃣ At the bottom of the motion, when your shoulder blades come close together, pause for 1 second to achieve full contraction in your back.
4️⃣ With control, inhale as you return the handles to the starting position; don’t let the weight rise abruptly.
5️⃣ Perform the movement through a full range of motion with a steady tempo (2 seconds down – 3 seconds up).
Coaching tips and recommendations
✔ Keep your chest up throughout the movement and avoid rounding your back.
✔ Drive your elbows back and slightly downward rather than straight toward your body to place greater emphasis on the lats and mid-back.
✔ As you return to the starting position, don’t let your shoulders rise; they should remain down and back.
✔ Keep your wrists aligned with your forearms to prevent unnecessary joint stress.
✔ Avoid swinging or using momentum — the movement should be fully controlled without assistance from the torso.
✔ If desired, you can perform the exercise unilaterally (one arm at a time) to correct muscular imbalances.
Benefits of the exercise
1️⃣ Strengthens and increases the thickness of the mid and lower back muscles.
2️⃣ Engages the lats, trapezius, rear deltoids, and rhomboids fully.
3️⃣ Helps correct posture and improve shoulder girdle stability.
4️⃣ Enhances pulling strength for compound movements such as pull-ups and deadlifts.
5️⃣ Suitable for beginners due to the guided motion of the machine.
6️⃣ Reduces spinal stress compared to barbell or dumbbell rows.
7️⃣ Allows full focus on muscle contraction without worrying about body balance.
8️⃣ Compatible with both hypertrophy and strength training programs.
9️⃣ Shoulder-joint friendly thanks to controlled movement mechanics.
🔟 Improves symmetry, strength, and endurance of the back muscles for daily and athletic activities.
Muscles involved in the exercise
✅ In this movement, the arms are pulled from a high position downward and backward, making the latissimus dorsi the primary driver responsible for shoulder adduction and extension. Simultaneously, the scapular retractors — including the trapezius, rhomboids, teres major, and rear deltoids — assist in drawing the shoulder blades together and downward. The arm muscles contribute to force transmission, while the core muscles help maintain body stability.
Main muscles
Synergistic muscles
Stabilizers
Dynamic Stabilizers
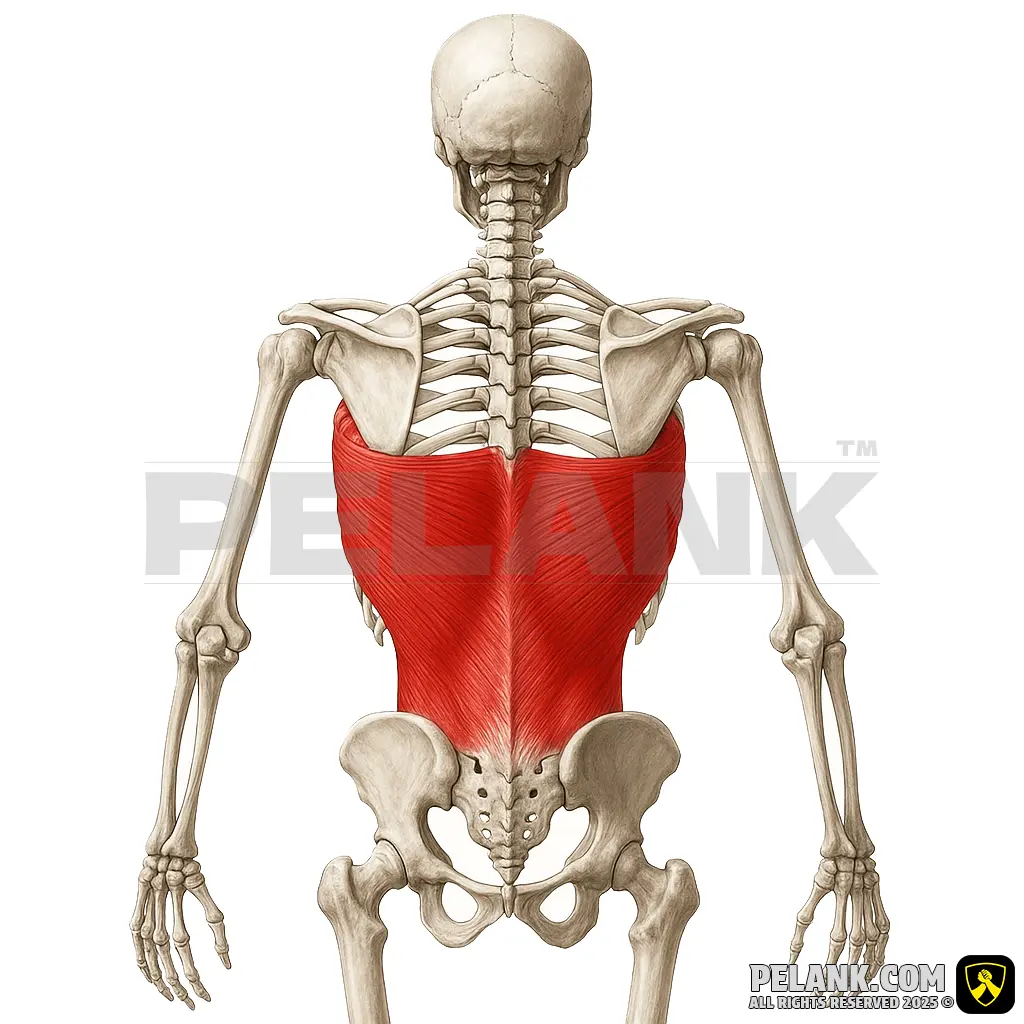
Latissimus Dorsi Muscle
✅ The latissimus dorsi is one of the strongest and widest superficial muscles of the back, playing a vital role in pulling movements, back extension, and internal rotation of the arm. This muscle extends from the lower spine to the humerus and is responsible for generating pulling force in exercises such as pull-ups, push-ups, and rowing. Strengthening this muscle increases pulling strength, improves body shape, and reduces the risk of back and shoulder injuries.
✅ Persian Name: Poshti bozorg
✅ Latin Name: Latissimus Dorsi
✅ Common Name: Lat
✅ Location:
🟡 A superficial muscle that connects from the lower spine, ribs, and pelvis to the humerus (upper arm bone).
🟡 A large, broad muscle located on both sides of the back, covering most of the lumbar and dorsal regions.
🟡 Responsible for pulling movements, arm adduction, and internal rotation of the arm.
✅ 🦾 Origin
✔ Lower six thoracic vertebrae (T7-T12)
✔ Lumbar vertebrae (L1-L5)
✔ Sacrum
✔ Iliac crest
✔ Lower ribs (9th to 12th)
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ Humerus (intertubercular groove)
✅ 📌 Function and Roles
🔹 The latissimus dorsi plays a role in various movements, including pulling, arm adduction, and internal rotation of the shoulder:
1️⃣ Pulling the arm down and back (Adduction)
✔ Like pulling the bar down during a lat pulldown exercise.
2️⃣ Internal rotation of the arm
✔ Like moving the arm inward during swimming and ball throwing.
3️⃣ Extension of the arm backward
✔ Like pulling the arm backward during pull-ups and rowing exercises.
✅ Main Functions:
✔ Lowering the arm and generating pulling force
✔ Assisting in shoulder stabilization during sports movements
✔ Increasing muscular endurance in strength exercises
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Types
✔ A combination of slow-twitch fibers (Type 1) for endurance and fast-twitch fibers (Type 2) for power movements.
✔ The middle section contains more slow-twitch fibers and is active during sustained pulling movements.
✔ The lower section has fast-twitch fibers used in explosive power movements.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Motor and Sports Performance
✔ The most important muscle in pulling movements such as pull-ups, swimming, and weightlifting.
✔ Plays a significant role in rowing, swimming, wrestling, and gymnastics.
✔ Strengthening this muscle increases pulling power, improves endurance, and reduces lower back injuries.
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ This muscle plays a key role in all pulling and strengthening movements of the upper body.
✔ Weakness in this muscle reduces endurance and increases stress on the lumbar and cervical vertebrae.
🧠 Innervation | Neural Control
✔ Thoracodorsal nerve (C6, C7, C8)
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Thoracodorsal artery
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Vital in sports such as bodybuilding, swimming, wrestling, rock climbing, and gymnastics.
✔ Plays a key role in shot put, cable pulling, weightlifting, and swimming.
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Relationship with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Interacts with the deltoid muscle, rotator cuff muscles, and teres major muscle.
✔ Weakness in this muscle leads to reduced pulling strength and pain in the lower back and shoulders.
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ Strain or weakness in this muscle can lead to lower back problems and pain in the upper back and shoulders.
✔ Weakness increases stress on the lumbar and cervical vertebrae.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Key Exercises to Strengthen the Latissimus Dorsi
1️⃣ Pull-Ups – The most effective exercise for full lat engagement
2️⃣ Lat Pulldown – Increases arm pulling strength
3️⃣ Bent-Over Barbell Rows – Builds size and strength in the back
4️⃣ One-Arm Dumbbell Rows – Strengthens the lateral and upper sections of the muscle
5️⃣ Deadlifts – Enhances endurance and strengthens the entire posterior chain
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery Exercises
✔ Overhead Lat Stretch – Improves range of motion and reduces muscle tension
✔ Wall Lat Stretch – Increases flexibility during pulling movements
✅ Interesting Fact:
✔ The latissimus dorsi is one of the broadest muscles in the human body and plays a role in numerous daily and sports movements.
✅ Practical Tip:
✔ To better strengthen this muscle, combine compound exercises like deadlifts and pull-ups with isolation movements such as lat pulldowns.
🔴 Name and Location: A broad back muscle extending from the lower spine to the arm
🟠 Anatomy: Originates from lumbar and thoracic vertebrae and ribs, attaching to the humerus
🟡 Function: Pulling, lowering, and internal rotation of the arm
🟢 Physiology: A mix of slow- and fast-twitch fibers for endurance and strength
🔵 Innervation: Thoracodorsal nerve (C6, C7, C8)
🟣 Importance: Active in bodybuilding, swimming, wrestling, weightlifting, and rock climbing
🟤 Exercises: Pull-ups, lat pulldown, rowing, deadlifts, arm stretches
⚫ Interesting Facts: One of the broadest muscles in the body and the key muscle in pulling movements
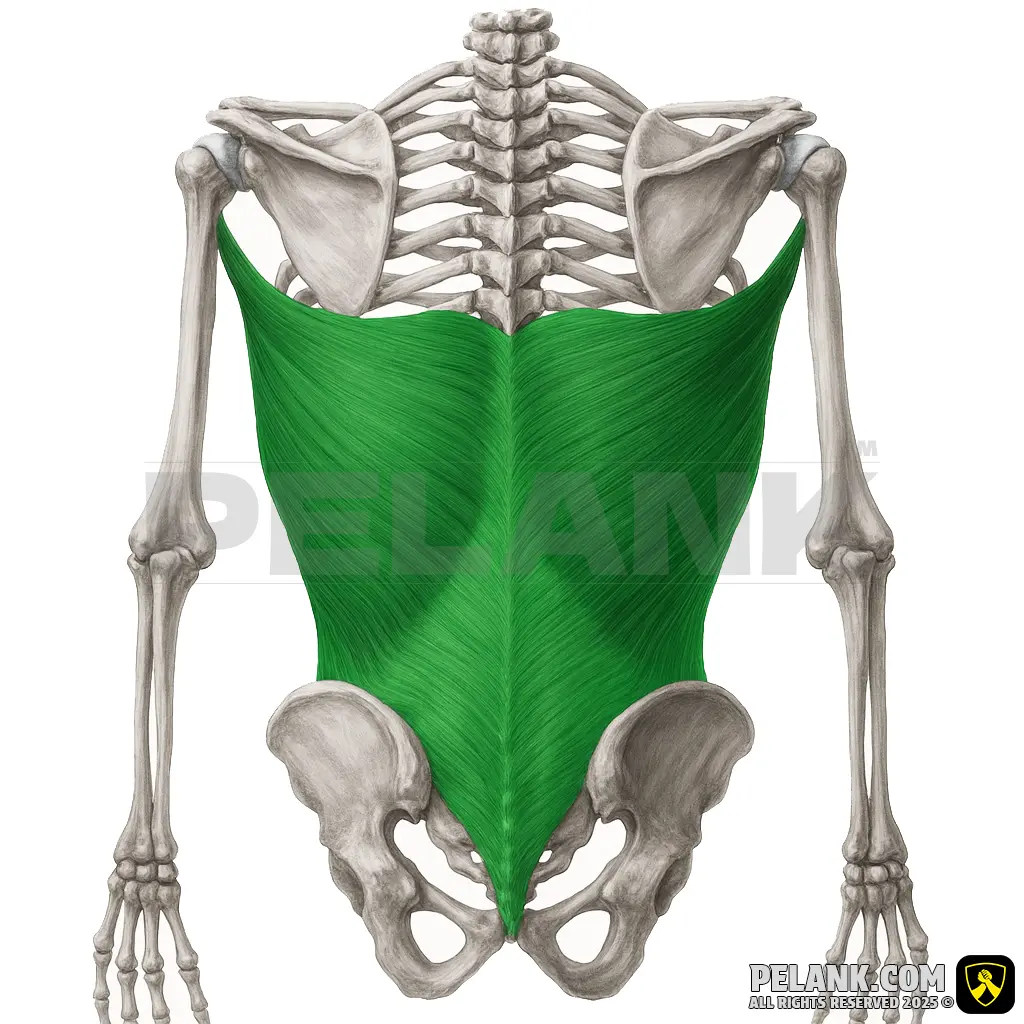
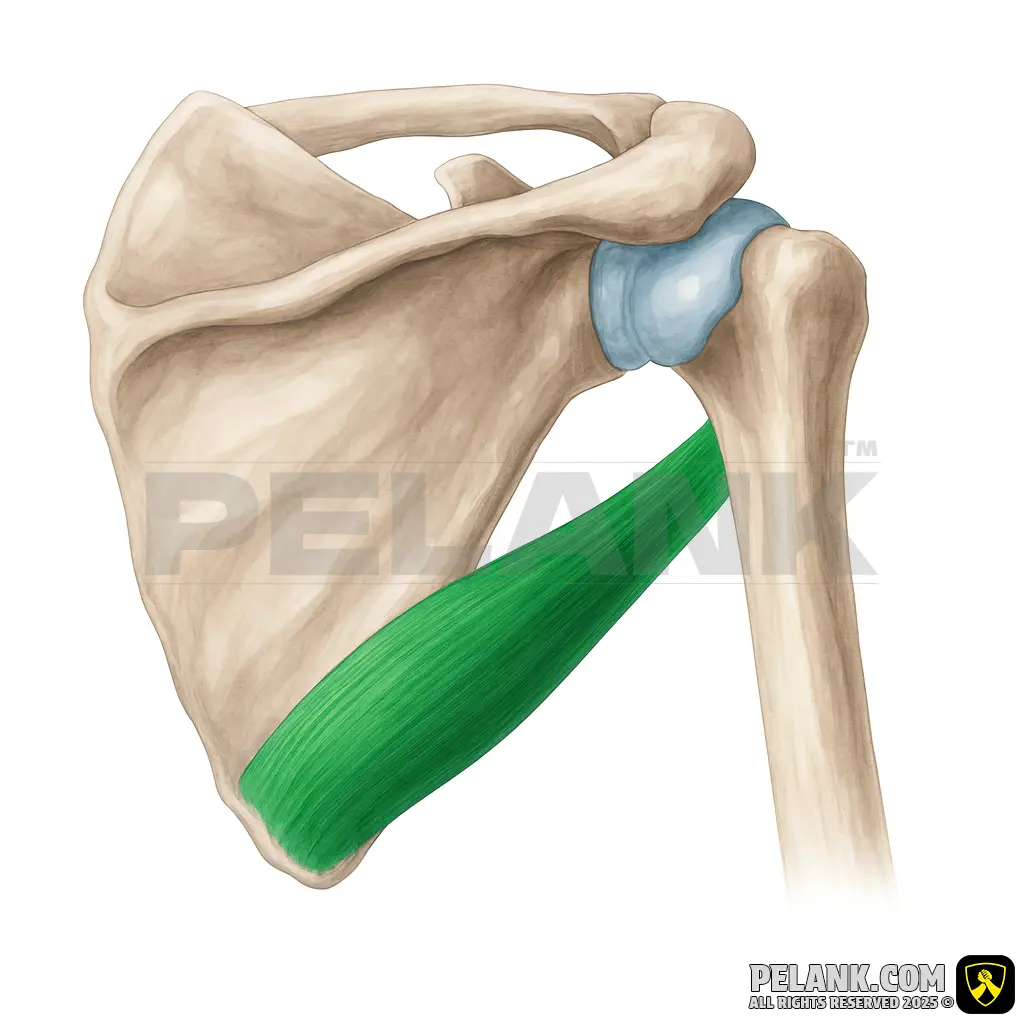
Teres Major Muscle
🔹 The teres major is one of the muscles located at the back of the shoulder, positioned next to the latissimus dorsi and often considered its assisting muscle. It plays a key role in pulling and upper body strength movements such as pull-ups, rows, and deadlifts.
🔹 Unlike the teres minor, which is part of the rotator cuff, the teres major does not contribute to rotator cuff stabilization and is more involved in larger arm movements. Weakness in this muscle can lead to reduced pulling and lowering strength and increased strain on the rotator cuff muscles.
✅ Persian Name: Gerde Bozorg
✅ Latin Name: Teres Major
✅ Common Names: Small Lat Muscle | Shoulder Support Muscle
✅ Location:
🟡 Positioned on the posterior (back) side of the shoulder, beneath the teres minor and adjacent to the latissimus dorsi.
🟡 Originates from the scapula and inserts into the humerus.
🟡 Responsible for internal rotation of the arm, shoulder adduction, and extension. It also contributes to shoulder joint stabilization.
✅ 🔹 Origin
✔ Inferior angle and lateral border of the scapula (Inferior Angle of Scapula)
✅ 🔹 Insertion
✔ Medial lip of the intertubercular sulcus of the humerus (Medial Lip of Intertubercular Sulcus of Humerus)
✅ 🔹 Function
📌 Primary functions of the teres major:
✔ Internal rotation of the arm – rotating the arm inward
✔ Adduction of the arm – bringing the arm closer to the body
✔ Extension of the arm – moving the arm backward
📌 Movements that activate the teres major:
✔ Pulling exercises such as pull-ups and rows
✔ Resistance training like lat pulldowns and deadlifts
✔ Power movements such as shot put and javelin throws
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Types
✔ A combination of ✔ A combination of slow-twitch fibers (Type I) and fast-twitch fibers (Type II).
✔ Predominantly composed of slow-twitch fibers, which enhance the muscle’s endurance during pulling and resistance-based movements.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ A key muscle in all upper-body pulling and resistance movements
✔ Plays a vital role in weightlifting, gymnastics, swimming, climbing, and stretch-based sports
✔ Weakness in this muscle can reduce the ability to pull the body upward and perform pulling movements effectively.
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Strength and Endurance
✔ A strength-endurance muscle that plays an essential role in all upper-back movements.
✔ When weak, it places excessive strain on the rotator cuff muscles and the shoulder joint.
✅ 🧠 Innervation
✔ Lower Subscapular Nerve (C5, C6, C7)
✅ 🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Circumflex Scapular Artery
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ A crucial muscle in bodybuilding, weightlifting, swimming, climbing, and pulling movements
✔ Actively engaged in all rowing, pull-up, deadlift, and lat pulldown exercises
✔ If weak, it can reduce pulling strength and increase stress on the shoulder joint.
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Interaction with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Strong synergy with the latissimus dorsi, teres minor, rotator cuff muscles, and posterior deltoid
✔ Weakness in this muscle can increase stress on the glenohumeral (shoulder) joint and reduce the arm’s range of motion.
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ Weakness in the teres major may lead to reduced control during pulling movements and increased stress on the shoulder joint.
✔ Overuse and improper exercise execution can result in inflammation and muscle strain.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Strength Training Exercises for the Teres Major
1️⃣ Pull-Ups – One of the best exercises to strengthen this muscle
2️⃣ Lat Pulldown – An effective workout for increasing muscle strength
3️⃣ Single Arm Row – Combines strengthening of the teres major and back muscles
4️⃣ Medicine Ball Throws – Enhances explosive power of the muscle
5️⃣ Deadlift – Boosts endurance and strength of the teres major
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery
✔ Overhead and backward arm stretches to improve flexibility and prevent muscle tightness
✔ Using a foam roller to relieve tension and enhance blood circulation
✅ Fun Fact
✔ The teres major is often referred to as the “lat helper” due to its position and supportive role alongside the latissimus dorsi.
✅ Practical Tip
✔ Strengthening the teres major enhances performance in all pulling and rowing movements, but improper form can place excessive stress on the shoulder joint.
🔴 Name and Location:
A superficial muscle located at the back of the shoulder, next to the latissimus dorsi, involved in upper-body pulling and strength movements.
🟠 Anatomy: Originates from the lower part of the scapula and inserts into the humerus.
🟡 Function:
✔ Internal rotation of the arm
✔ Arm adduction
✔ Arm extension
🟢 Physiology: Primarily composed of slow-twitch fibers to support endurance during pulling movements.
🔵 Innervation: Lower subscapular nerve, which controls the movements of this muscle.
🟣 Importance: Plays a key role in bodybuilding, weightlifting, climbing, and swimming.
🟤 Exercises: Pull-ups, lat pulldowns, rows, deadlifts.
⚫ Fun Facts: Known as the “lat helper” in pulling and resistance movements.
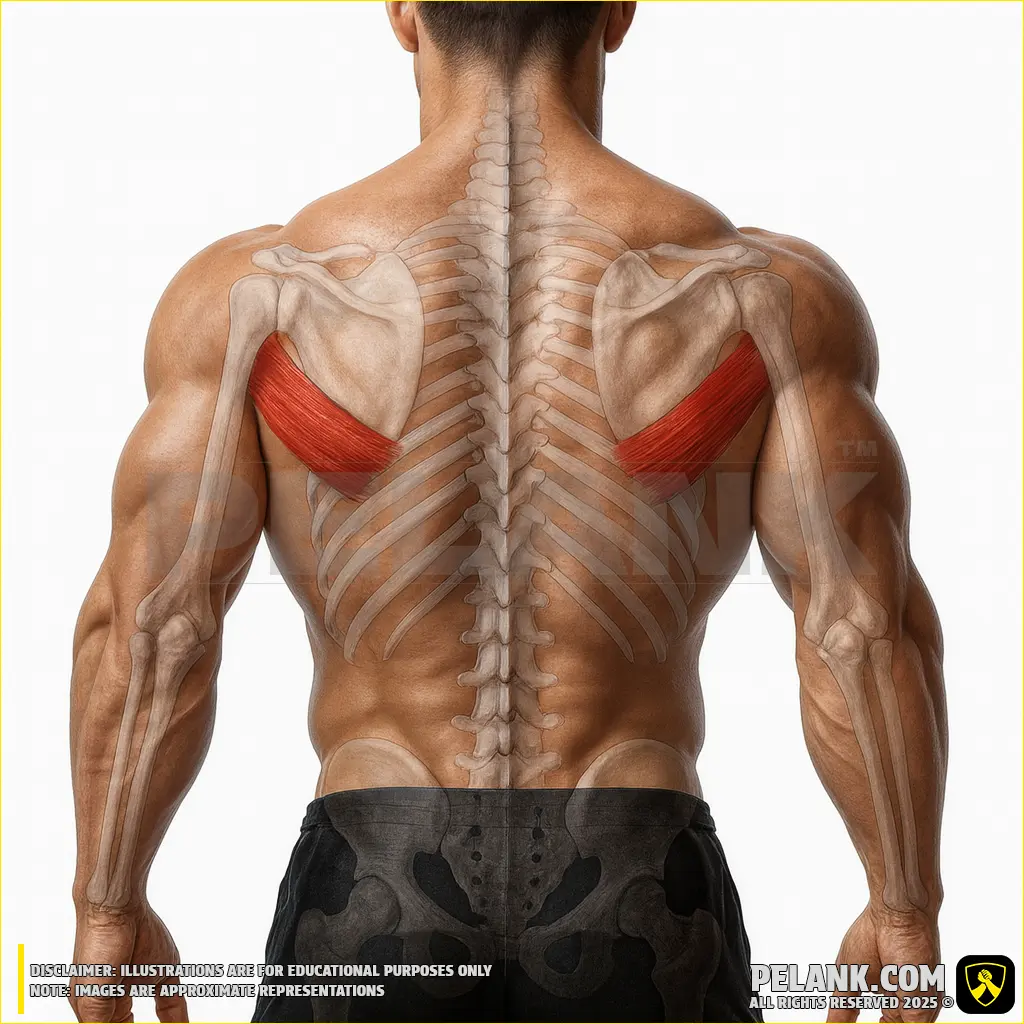
Rhomboid Major Muscle
✅ The rhomboid major is one of the superficial muscles of the back, located between the spine and the scapula. Positioned alongside the rhomboid minor, it functions to retract the scapula toward the spine, stabilize the shoulder, and assist in scapular movements. Strengthening this muscle helps improve posture, prevent shoulder drooping, and reduce pain in the area between the shoulder blades.
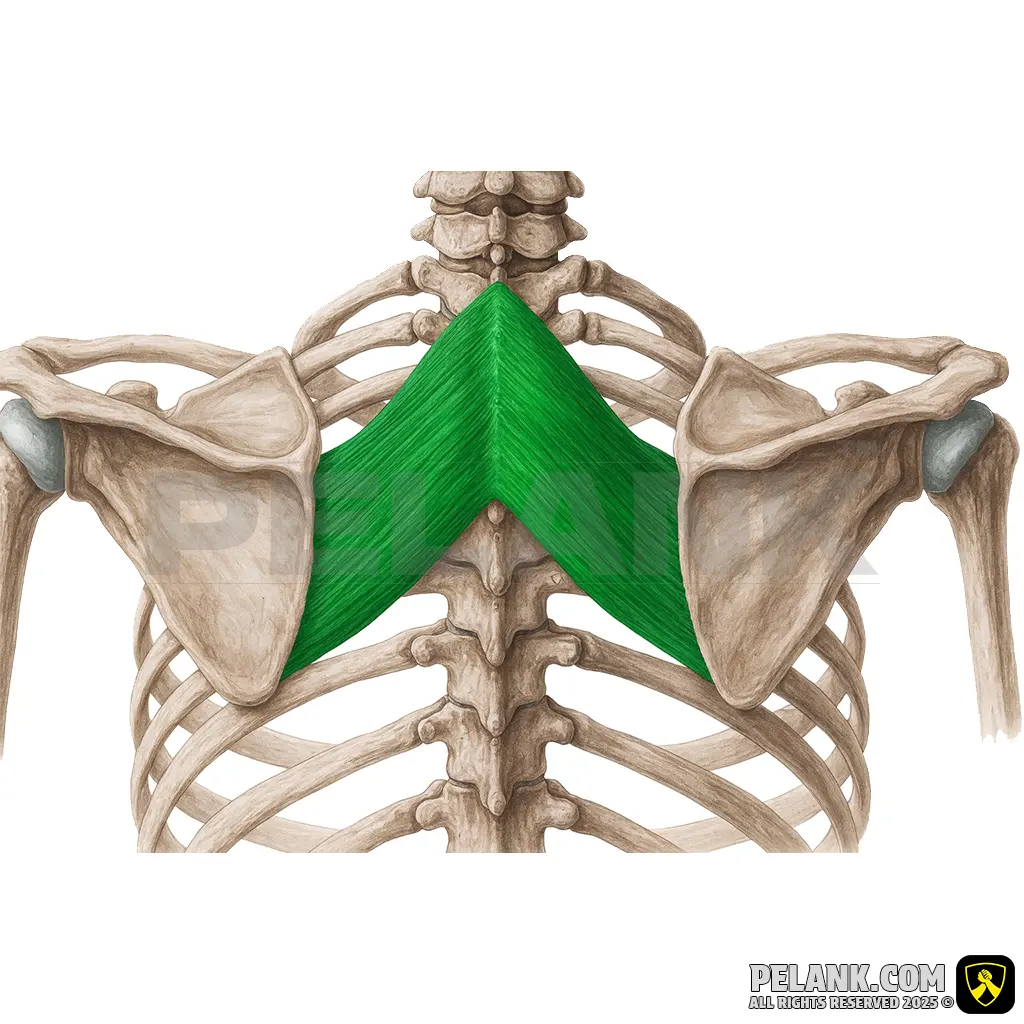
✅ Persian Name: Rhomboid Major
✅ Latin Name: Rhomboid Major
✅ Common Name: Large Rhomboid Muscle
✅ Location:
🟡 A relatively deep muscle located between the thoracic vertebrae and the scapula.
🟡 It lies beneath the trapezius muscle and works in conjunction with the rhomboid minor muscle.
🟡 It plays a key role in scapular retraction and stabilizing the position of the shoulders.
✅ 🦾 Origin
✔ Thoracic vertebrae T2 to T5
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ Medial border of the scapula (from the scapular spine to the inferior angle)
✅ 📌 Function and Responsibilities of the Muscle
🔹 The rhomboid major performs the following functions:
1️⃣ Scapular Retraction
✔ Similar to bringing the shoulder blades closer together during a rowing motion.
2️⃣ Shoulder Stability
✔ Helps maintain the scapula in the proper position to prevent shoulder drooping.
3️⃣ Downward Rotation of the Scapula
✔ Assists in rotating the scapula when lowering the arm.
✅ Main Functions:
✔ Retracting the scapula towards the spine
✔ Stabilizing the scapula for arm movements
✔ Assisting in improving posture and reducing neck strain
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Type
✔ Predominantly composed of slow-twitch fibers (Type 1) for endurance and stability.
✔ Contains fast-twitch fibers (Type 2) for quicker movements, such as sudden shoulder reactions.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Movement and Sports Performance
✔ Plays a key role in rowing, weightlifting, swimming, and martial arts.
✔ Strengthening this muscle enhances shoulder retraction strength and upper body stability.
✔ Weakness in this muscle can lead to shoulder drooping and reduced strength in pulling movements.
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ The strength of this muscle is crucial for shoulder stability and preventing injuries caused by scapular imbalances.
✔ Weakness in this muscle may lead to pain between the shoulder blades and reduced arm range of motion.
🧠 Innervation | Neural Control
✔ Dorsal Scapular Nerve (C4, C5)
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Dorsal Scapular Artery
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Effective in sports such as bodybuilding, swimming, rowing, weightlifting, and boxing.
✔ Active in upper body pulling and endurance movements like pull-ups and rowing.
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Connection with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Works with the trapezius, rhomboid minor, and scapular muscles to stabilize and move the shoulder.
✔ Weakness in this muscle increases pressure on the neck muscles and reduces shoulder stability.
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ Weakness in this muscle can lead to chronic pain in the area between the shoulder blades.
✔ Failure to strengthen this muscle can cause shoulder drooping and increased pressure on the neck.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Main Exercises for Strengthening the Rhomboid Major Muscle
1️⃣ Bent-Over Rows – The strongest exercise for this muscle
2️⃣ Wide-Grip Pull-Ups – Strengthens the back and rhomboids
3️⃣ Face Pulls – Enhances shoulder strength and stability
4️⃣ One-Arm Dumbbell Row – Deep activation of muscles between the shoulder blades
5️⃣ Narrow-Grip Lat Pulldown – Improves shoulder and scapular muscle strength
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery
✔ Scapular Stretch – Reduces tension and increases flexibility
✔ Upper Back Stretch – Improves range of motion and reduces stiffness
✅ Interesting Fact:
✔ The rhomboid major muscle is often weakened due to poor posture and slouching, which is why corrective exercises for it are highly recommended.
✅ Practical Tip:
✔ To prevent pain between the shoulder blades, combining strength exercises (like rowing) with stretching exercises (such as upper back and shoulder stretches) is very effective.
🔴 Name and Location: A muscle between the spine and scapula, located beneath the trapezius muscle.
🟠 Anatomy: Originates from the thoracic vertebrae (T2-T5) and attaches to the medial border of the scapula.
🟡 Function: Scapular retraction, stabilizing the shoulder position, downward rotation of the scapula.
🟢 Physiology: Contains slow-twitch fibers for endurance and stability.
🔵 Innervation: Dorsal scapular nerve (C4, C5).
🟣 Importance: Active in bodybuilding, rowing, weightlifting, swimming.
🟤 Exercises: Bent-over rows, pull-ups, face pulls, lat pulldown.
⚫ Interesting Fact: Plays an important role in posture and preventing shoulder drooping.
Posterior Deltoid Muscle
🔹 The posterior deltoid is one of the three parts of the deltoid muscle. Its primary functions are moving the arm backward, external rotation, and assisting in horizontal shoulder movements. Unlike the anterior and middle deltoids, it is less engaged in daily activities but is essential for shoulder muscle balance, strengthening the back, and preventing shoulder injuries.
🔹 The posterior deltoid is directly involved in pulling exercises and weightlifting movements. Weakness in this muscle can lead to shoulder drooping, reduced endurance of the upper back, and an increased risk of injury to the glenohumeral (shoulder) joint.

✅ Persian Name: Deltoid Khalfi | Deltoid Poshti
✅ Latin Name: Posterior Deltoid
✅ Common Names: Posterior part of the deltoid muscle | Posterior head of the shoulder
✅ Location:
🟡 Located on the posterior (back) side of the shoulder, behind the shoulder joint.
🟡 A superficial muscle that, along with the anterior and middle parts, completes the deltoid muscle.
🟡 Primarily responsible for moving the arm backward (extension), external rotation, and assisting in horizontal shoulder movements.
✅ 🔹 Origin
✔ Spine of the scapula (Spine of Scapula)
✅ 🔹 Insertion
✔ Deltoid tuberosity on the humerus bone (Deltoid Tuberosity, Humerus)
✅ 🔹 Function
📌 Primary functions of the posterior deltoid:
✔ Arm extension – moving the arm backward (such as pulling a rope or cable)
✔ External rotation of the arm – rotating the hand outward away from the body
✔ Horizontal adduction – assisting arm movement backward on a horizontal plane (such as reverse fly)
✔ Stabilizing the shoulder joint during pulling and resistance exercises
📌 Movements that activate the posterior deltoid:
✔ Pulling exercises such as rowing, pull-ups, and face pulls
✔ Resistance training like reverse fly, bent-over lateral raise, and rear cable pulls
✔ Sports movements such as javelin throwing and butterfly swimming
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Types
✔ A combination of fast-twitch fibers (Type II) and slow-twitch fibers (Type I)
✔ Composed mostly of fast-twitch fibers for powerful and quick pulling movements
✔ Plays a crucial role in stabilizing pulling actions and enhancing upper back endurance
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ A key muscle in pulling and resistance exercises such as pull-ups, rowing, and reverse fly
✔ Plays an important role in wrestling, gymnastics, weightlifting, and swimming
✔ Weakness in this muscle can cause shoulder drooping and limit pulling movements
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Strength and Endurance
✔ One of the most important muscles for maintaining shoulder balance and preventing injuries from asymmetrical training
✔ Strengthening it improves upper back stability and enhances motor control during strength exercises
✅ 🧠 Innervation
✔ Axillary nerve (C5, C6), responsible for controlling the movements of this muscle.
✅ 🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Posterior Circumflex Humeral Artery
✔ Thoracoacromial Artery
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ A vital muscle for maintaining shoulder muscle balance and preventing rounded shoulders
✔ Plays an important role in pulling, resistance, and sports activities like wrestling and swimming
✔ Weakness can lead to muscular imbalance and increased strain on the front shoulder muscles
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Interaction with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Strong synergy with the middle deltoid, back muscles, rotator cuff muscles, and lower trapezius
✔ Weakness in this muscle can reduce shoulder joint performance and limit range of motion
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ Weakness in the posterior deltoid increases the risk of injury during pressing and pulling exercises.
✔ Excessive strain during heavy weight training may cause tendon strains and inflammation in the rear shoulder region.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Strength Training Exercises for the Posterior Deltoid
1️⃣ Reverse Fly with Dumbbells – one of the best exercises to strengthen the posterior deltoid
2️⃣ Bent-over Lateral Raise with Dumbbells – effective for increasing muscle size
3️⃣ Face Pull – a specialized exercise to enhance upper back stability
4️⃣ Single Arm Row with Dumbbells – combines strengthening of the posterior deltoid and back muscles
5️⃣ Reverse Cable Fly – provides continuous tension on this muscle
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery
✔ Stretching the arm forward and overhead to improve flexibility and prevent muscle tightness
✔ Using a foam roller to reduce tension and enhance blood circulation
✅ Fun Fact
✔ The posterior deltoid is often undertrained in workout programs but is essential for shoulder stability and endurance.
✅ Practical Tip
✔ Overdeveloping the anterior deltoid without balancing the posterior deltoid can disrupt shoulder muscle balance and increase the risk of shoulder injuries.
🔴 Name and Location: A superficial muscle located at the back of the shoulder joint, responsible for pulling and rotational movements of the arm.
🟠 Anatomy: Originates from the spine of the scapula and inserts into the deltoid tuberosity of the humerus.
🟡 Function:
✔ Moving the arm backward (extension)
✔ External rotation of the arm
✔ Assisting pulling movements in resistance training
🟢 Physiology: Predominantly composed of fast-twitch fibers for powerful and rapid pulling movements.
🔵 Innervation: Axillary nerve, which controls the movements of this muscle.
🟣 Importance: Plays a key role in resistance sports, weightlifting, and gymnastics.
🟤 Exercises: Reverse fly, bent-over lateral raise, face pull, rowing.
⚫ Fun Fact: One of the most important muscles for maintaining shoulder balance and preventing rounded shoulders.
Pelank Life | Body Health Assessment
The Best Body Health Calculators Using Scientific Methods
Developed by Pelank Life ©
Muscle training
Pelank is a comprehensive encyclopedia of the body’s muscles, providing an accurate and scientific review of all muscles. Below, you can find muscle groups. By clicking on each muscle group, you will have access to complete information about it, including:
1️⃣ Basic information about the muscle
2️⃣ Muscle anatomy
3️⃣ Muscle physiology
4️⃣ Innervation and blood supply
5️⃣ Importance of the muscle in the body and sports
6️⃣ Strengthening exercises
7️⃣ Scientific and interesting facts
📌 At the end, a summary review of each muscle will be provided.
Body muscles training guide link
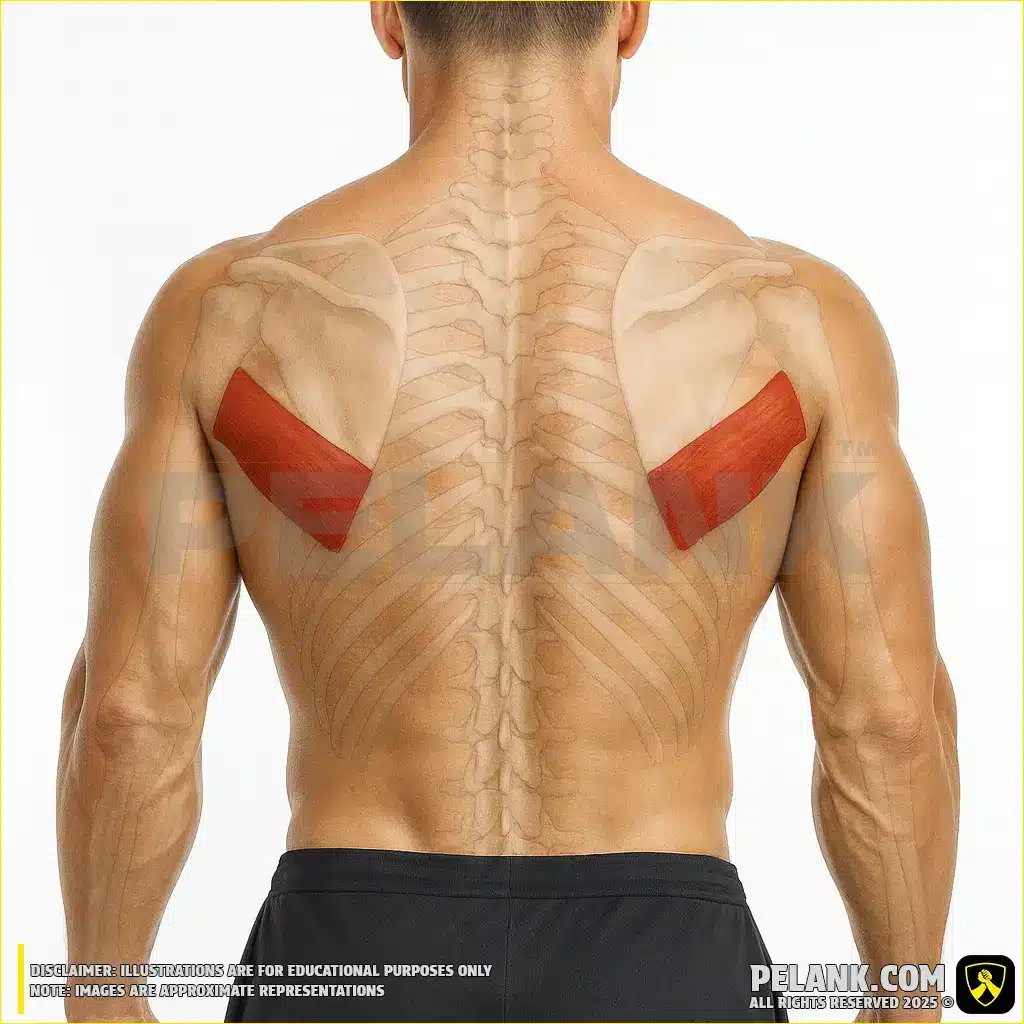
🔹 The muscle group engaged in this movement is highlighted in color.

Mohsen Taheri
References
✅ Official Physical Activity Guidelines
✅ General Overview and Recommendations for the Public
✅ Science-Based and Health-Oriented Education
✅ Policy Making and Comparative Data
Comments