Lateral Raise With Towel On Wall

| English Name | Lateral Raise with Towel on Wall |
|---|---|
| Difficulty | Beginner |
| Movement Patterns | Push Pattern |
| Muscle Contraction Types | Isometric |
| Primary Muscle (EN) | Lateral Deltoid |
| Muscle Groups | Shoulder Muscles |
|---|---|
| Workout Type | Isolated |
| Required equipment | No equipment |
💠 Exercise guide
✅ The Lateral Raise with Towel on Wall is a variation of the lateral raise that involves applying gentle pressure with the palms or forearms against a towel and sliding it smoothly along the wall. This movement effectively targets the middle deltoid while improving scapular control. It’s suitable for most training levels, especially when you want to practice proper arm abduction and scapulohumeral rhythm without using weights.

💠 How to perform the exercise

Preparation
✅ Stand next to the wall with your feet hip-width apart, knees slightly bent, and your torso and pelvis in a neutral position.
✅ Place a towel between your forearm (or palm) and the wall; keep your elbow slightly bent (~10–20 degrees).
✅ Depress and slightly rotate your shoulder blades outward (avoid shrugging). Keep your chest down, core gently engaged, and neck neutral.
✅ The distance from the wall should roughly match the length of your forearm; ensure the towel can slide smoothly.
✅ Maintain natural breathing: exhale during the upward phase, inhale as you return.
Execution method
✅ Apply gentle pressure to the towel and slowly move your arm away from your body in the frontal plane or slightly in the scapular plane (~30° forward) until your arm is roughly at shoulder height.
✅ Pause for 1–2 seconds at the top while maintaining even pressure against the wall; avoid fully locking your elbow.
✅ On the way down, lower your arm with controlled eccentric motion, keeping consistent contact between the towel and the wall.
✅ Recommended tempo: 2–1–2 seconds (up–pause–down), for 10–15 repetitions.
Coaching tips and recommendations
✔ Do not shrug your shoulders; keep the range of motion within a pain-free zone.
✔ You may slightly rotate your thumb upward/outward to improve subacromial space.
✔ Keep a slight bend in your elbow and avoid swinging your body or using momentum.
✔ Keep your chest down and ribs tucked; if your lower back arches, reduce the range of motion.
✔ Movement focus: “Arm moves outward — scapula rotates upward smoothly.” The Serratus Anterior and Lower Trapezius should be active, not just the Upper Trapezius.
Benefits of the exercise
1️⃣ Targeted strengthening of the middle deltoid without using weights
2️⃣ Improves shoulder stability and scapulohumeral rhythm in overhead patterns
3️⃣ Enhances activation of the Serratus Anterior and Lower Trapezius for proper upward scapular rotation
4️⃣ A safe option for warm-ups or post-shoulder workout recovery
5️⃣ Increases proprioception and neuromuscular control of the shoulder
6️⃣ Reduces reliance on momentum and trunk compensations
7️⃣ Suitable for small spaces or home workouts (just a wall and a towel)
8️⃣ Transfers well to dumbbell or cable lateral raises by reinforcing correct movement patterns
9️⃣ Helps improve upper body posture (avoiding shoulder shrugging)
🔟 Simple, low-risk, and easily adjustable by varying the amount of pressure applied to the wall
Muscles involved in the exercise
✅ In the lateral raise, the middle deltoid is the primary mover responsible for arm abduction. The initial phase of the motion is supported by the supraspinatus. Simultaneously, for proper upward scapular rotation and adequate subacromial space, the Serratus Anterior works in synergy with the lower, middle, and upper fibers of the trapezius, while the rotator cuff muscles stabilize the humeral head. In the towel-on-wall variation, the isometric pressure applied through the palm reinforces this movement pattern.
Main muscles
Synergistic muscles
Stabilizers
Dynamic Stabilizers

Middle Deltoid Muscle
🔹 The middle deltoid is one of the three parts of the deltoid muscle. Its primary function is to lift the arm outward (abduction) and assist in stabilizing the shoulder during overhead movements. Due to its position on the side of the shoulder, it has the greatest impact on creating the rounded, muscular shape of the shoulders.
🔹 This part of the deltoid is less involved than the anterior section in daily activities and requires specific training for strengthening. Weakness in this muscle can lead to narrower shoulders and limited overhead movement. Strengthening it improves muscular balance in the shoulder and helps prevent shoulder injuries.

✅ Persian Name: Deltoid Miani | Deltoid Janebi
✅ Latin Name: Lateral Deltoid | Middle Deltoid
✅ Common Names: Middle part of the deltoid muscle | Middle head of the shoulder
✅ Location:
🟡 Located on the lateral side of the shoulder, between the anterior and posterior deltoids.
🟡 A superficial muscle covering the shoulder joint that, along with the other two parts, shapes the size and form of the shoulder.
🟡 The primary muscle responsible for moving the arm away from the body (abduction) and plays a role in shoulder joint stabilization.
✅ 🔹 Origin
✔ Acromion process of the scapula (Acromion of Scapula)
✅ 🔹 Insertion
✔ Deltoid tuberosity on the humerus bone (Deltoid Tuberosity, Humerus)
✅ 🔹 Function
📌 Primary functions of the middle deltoid:
✔ Arm abduction – moving the arm outward from the body
✔ Stabilizing the shoulder joint during overhead movements
✔ Assisting lateral arm movements in resistance training exercises
📌 Movements that activate the middle deltoid:
✔ Raising the arm sideways (such as lateral raises)
✔ Overhead movements (such as shoulder press)
✔ Lateral arm movements in sports like volleyball and swimming
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Types
✔ A combination of ✔ A combination of slow-twitch fibers (Type I) and fast-twitch fibers (Type II).
✔ Predominantly composed of slow-twitch fibers for controlled and endurance movements
✔ Plays a significant role in stability and sustained strength during shoulder activities
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ A key muscle in all lateral and overhead movements
✔ Essential in swimming, volleyball, basketball, handball, and gymnastics
✔ Weakness in this muscle reduces arm control and increases the risk of shoulder injury
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Strength and Endurance
✔ Plays a key role in sustained overhead activities such as volleyball and weightlifting
✔ Requires focused training for strengthening, as it is less engaged in daily exercises
✅ 🧠 Innervation
✔ Axillary nerve (C5, C6), which controls the movements of this muscle.
✅ 🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Posterior Circumflex Humeral Artery
✔ Thoracoacromial Artery
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ One of the most important muscles for shoulder width and muscular shape
✔ Involved in all lateral and overhead exercises such as swimming, volleyball, and throwing
✔ Weakness can cause muscular imbalances and increase stress on the shoulder joint
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Interaction with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Strong connection with the anterior deltoid, posterior deltoid, and rotator cuff muscles
✔ Weakness in this muscle can cause excessive strain on the anterior deltoid and upper back muscles
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ Weakness in this muscle can lead to limited lateral movements and increased stress on the shoulder joint.
✔ Improper use of heavy weights during lateral exercises may cause shoulder tendon inflammation.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Strength Training Exercises for the Middle Deltoid
1️⃣ Dumbbell Lateral Raise – the most effective exercise for strengthening this muscle
2️⃣ Overhead Shoulder Press – directly engages the middle deltoid
3️⃣ Cable Lateral Raise – provides continuous tension on the muscle
4️⃣ Arm Raises with Resistance Bands – enhances muscular endurance
5️⃣ Reverse Fly with Bands or Dumbbells – fully activates the muscle through its range of motion
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery
✔ Stretching the arm out to the sides with gentle pressure toward the body
✔ Using a foam roller to reduce tension and accelerate recovery
✅ Fun Fact
✔ The middle deltoid greatly influences the V-shaped appearance of the upper body. Athletes with broad, well-defined shoulders typically have a well-developed middle deltoid.
✅ Practical Tip
✔ Improper form and incomplete execution of lateral raises reduce middle deltoid activation and place extra strain on other muscles. For better results, perform the movement through the full range of motion with proper control.
🔴 Name and Location: A superficial muscle located at the sides of the shoulder joint, responsible for moving the arm away from the body (abduction).
🟠 Anatomy: Originates from the acromion of the scapula and inserts into the deltoid tuberosity of the humerus.
🟡 Function:
✔ Lifting the arm out to the side
✔ Stabilizing the shoulder during overhead movements
🟢 Physiology: Contains slow-twitch fibers suited for controlled and endurance movements.
🔵 Innervation: Axillary nerve, which controls the movements of this muscle.
🟣 Importance: Plays a vital role in swimming, volleyball, gymnastics, and weightlifting.
🟤 Exercises: Lateral raise, shoulder press, cable lateral raise.
⚫ Fun Fact: The key muscle responsible for shoulder width and the V-shaped upper body appearance.
Supraspinatus Muscle
🔹 The supraspinatus muscle is one of the four main rotator cuff muscles and plays a vital role in stabilizing the glenohumeral (shoulder) joint. It is especially important in initiating arm abduction before the middle deltoid activates. Additionally, it helps prevent shoulder dislocation and enhances joint stability.
🔹 The supraspinatus muscle is often undertrained in daily workouts, but its weakness is one of the most common causes of shoulder pain and injuries such as shoulder impingement syndrome. Therefore, athletes and bodybuilders should pay special attention to strengthening this muscle.
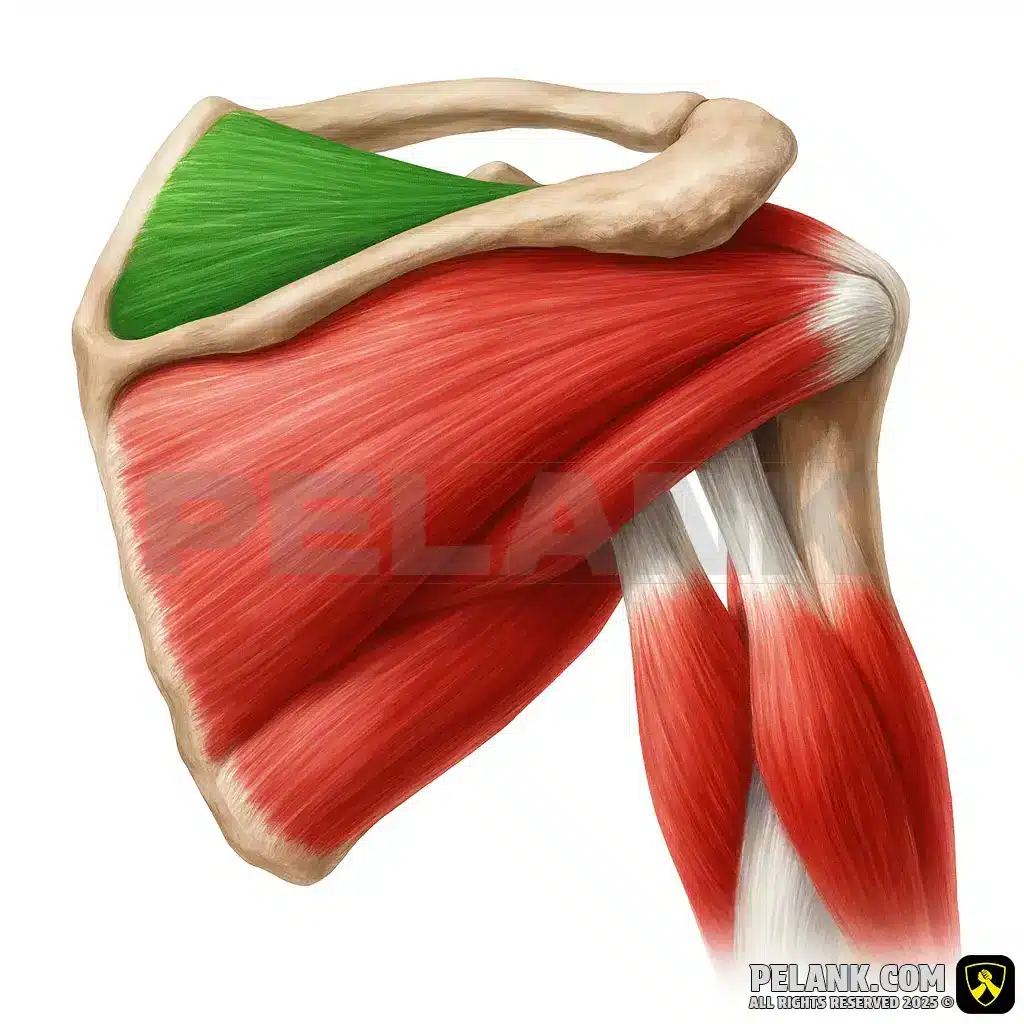
✅ Persian Name: Fogh-e Khari
✅ Latin Name: Supraspinatus
✅ Common Names: Upper Scapular Muscle | Superior Rotator Cuff Muscle
✅ Location:
🟡 Located at the upper part of the scapula, within the supraspinous fossa.
🟡 This muscle is part of the rotator cuff group, which stabilizes the shoulder joint.
🟡 Responsible for initiating arm abduction (moving the arm away from the body) and assisting in shoulder stabilization during arm movements.
✅ 🔹 Origin
✔ Supraspinous fossa of the scapula (Supraspinous Fossa of Scapula)
✅ 🔹 Insertion
✔ Superior facet of the greater tubercle of the humerus (Greater Tubercle of Humerus)
✅ 🔹 Function
📌 Primary functions of the supraspinatus muscle:
✔ Initiates arm abduction – moving the arm outward away from the body during the first 15 degrees
✔ Assists in stabilizing the shoulder joint throughout arm movements
✔ Prevents shoulder dislocation during heavy or sudden movements
📌 Movements that activate the supraspinatus:
✔ Raising the arm in lateral raises and resistance shoulder exercises
✔ Assisting shoulder joint stabilization in sports like tennis, volleyball, basketball, and swimming
✔ Throwing and pulling movements that require high control
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Types
✔ A combination of ✔ A combination of slow-twitch fibers (Type I) and fast-twitch fibers (Type II).
✔ Predominantly composed of slow-twitch fibers, which enhance the muscle’s endurance during prolonged and controlled movements.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ An important muscle for controlling overhead movements and stabilizing the shoulder in sports like swimming, volleyball, and basketball
✔ Active in light resistance and stretching exercises to prevent shoulder injuries
✔ Weakness in this muscle increases the risk of shoulder joint injuries and reduces range of motion
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Strength and Endurance
✔ A small but crucial muscle for shoulder stability and movement control
✔ Requires controlled training to strengthen without excessive strain
✅ 🧠 Innervation
✔ Suprascapular nerve (C5, C6), which controls the movements of this muscle.
✅ 🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Suprascapular artery
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ A key muscle for stabilizing the shoulder joint and preventing dislocation
✔ Active in throwing sports, tennis, basketball, gymnastics, and weightlifting
✔ Weakness can increase the likelihood of shoulder pain and injuries
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Interaction with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Strong synergy with the middle deltoid, other rotator cuff muscles (infraspinatus, teres minor, subscapularis), and pectoral muscles
✔ Weakness in this muscle increases stress on the deltoid and shoulder joint
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ One of the most commonly injured muscles prone to tears and inflammation.
✔ Weakness or inflammation of this muscle can lead to Shoulder Impingement Syndrome.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Strength Training Exercises for the Supraspinatus
1️⃣ Lateral Raise with Light Dumbbells – gradual strengthening without excessive strain
2️⃣ External Rotation with Resistance Band – improves muscle control and strength
3️⃣ Isometric Shoulder Exercises – helps stabilize the shoulder joint without injury
4️⃣ Controlled movements within the natural range of motion – prevents excessive stress on the muscle
5️⃣ Physiotherapy exercises to improve rotator cuff function
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery
✔ Stretching the arm across the body to improve flexibility and reduce muscle tension
✔ Using a foam roller to enhance blood flow and decrease inflammation
✅ Fun Fact
✔ The supraspinatus muscle initiates arm abduction, but after the first 15 degrees, the middle deltoid takes over this function.
✅ Practical Tip
✔ Strengthening the supraspinatus with light weights and resistance bands is the best way to prevent injury and improve shoulder function.
🔴 Name and Location: A deep muscle located on the top of the scapula, and part of the rotator cuff.
🟠 Anatomy: Originates from the supraspinous fossa of the scapula and inserts into the greater tubercle of the humerus.
🟡 Function:
✔ Initiates arm abduction (moving the arm away from the body)
✔ Stabilizes the shoulder during arm movements
🟢 Physiology: Predominantly composed of slow-twitch fibers for precise and stable movement control.
🔵 Innervation: Suprascapular nerve, which controls this muscle.
🟣 Importance: Plays a vital role in controlling overhead movements and preventing shoulder injuries.
🟤 Exercises: Light lateral raises, external rotations with resistance bands, physiotherapy exercises.
⚫ Fun Fact: It initiates the abduction movement, but after 15 degrees, the middle deltoid takes over.
Anterior Deltoid Muscle
🔹 The anterior deltoid is one of the three parts of the deltoid muscle. Its primary functions are moving the arm forward (flexion), internal rotation, and assisting in horizontal shoulder movements. This muscle plays a key role in many upper-body exercises, especially strength training movements like bench press, front raises, and throwing actions.
🔹 The anterior deltoid is one of the most important muscles involved in pressing and pushing movements. Due to its engagement in many strength exercises, it is often well-developed among athletes and bodybuilders. However, overusing this muscle without strengthening the posterior shoulder muscles (posterior deltoid and rotator cuff) can lead to muscular imbalances and increase the risk of shoulder injuries.

✅ Persian Name: Deltoid Ghodami
✅ Latin Name: Anterior Deltoid
✅ Common Names: Front part of the deltoid muscle | Anterior head of the shoulder
✅ Location:
🟡 Located at the front of the shoulder, forming the anterior part of the deltoid muscle.
🟡 Originates from the clavicle and lies over the upper part of the humerus.
🟡 Alongside the middle and posterior parts of the deltoid, it acts as part of the shoulder cap and assists in arm movements.
✅ 🔹 Origin
✔ Anterior surface of the lateral third of the clavicle (Clavicle – Anterior Surface of Lateral Third)
✅ 🔹 Insertion
✔ Deltoid tuberosity on the humerus bone (Deltoid Tuberosity, Humerus)
✅ 🔹 Function
📌 Primary functions of the anterior deltoid:
✔ Arm flexion – moving the arm forward (like raising the hand in front of the body)
✔ Internal rotation of the arm – rotating the arm inward toward the body
✔ Assisting in horizontal adduction – moving the arm inward on a horizontal plane (such as during a chest fly)
✔ Helping stabilize the shoulder joint during upper-body movements
📌 Movements that activate the anterior deltoid:
✔ Raising the arm forward (such as front raises)
✔ Throwing movements (ball throws, javelin throws)
✔ Moving weights in pressing and fly exercises
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Types
✔ A combination of fast-twitch fibers (Type II) and slow-twitch fibers (Type I)
✔ Predominantly composed of fast-twitch fibers for rapid and powerful movements
✔ This characteristic makes the anterior deltoid highly active in explosive and strength exercises like weightlifting and throwing
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Active in all pressing, throwing, and forward arm-raising exercises
✔ Plays a key role in strength sports, bodybuilding, weightlifting, boxing, and discus throwing
✔ An important muscle in daily activities such as lifting objects and carrying items
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Strength and Endurance
✔ Requires high strength for pressing exercises and overhead movements
✔ Overdevelopment can lead to muscular imbalances and increase the risk of shoulder injuries
✅ 🧠 Innervation
✔ Axillary nerve (C5, C6), which controls the movements of this muscle.
✅ 🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Posterior Circumflex Humeral Artery
✔ Thoracoacromial Artery
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ One of the key muscles for pushing and pressing movements in bodybuilding and weightlifting
✔ Active in throwing sports, swimming, boxing, gymnastics, and pulling movements
✔ Weakness can reduce pressing strength and increase the risk of shoulder injury
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Interaction with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Closely connected with the middle deltoid, pectoralis major, rotator cuff muscles, and triceps brachii
✔ Weakness in this muscle can lead to excessive strain on the shoulder joint and reduced upper body strength
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ One of the muscles prone to inflammation and strain due to high activity in upper-body training
✔ Weakness can cause excessive strain on the pectoral and shoulder muscles, leading to shoulder injuries
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Strength Training Exercises for the Anterior Deltoid
1️⃣ Front Raise with Dumbbells – the most important exercise for strengthening the anterior deltoid
2️⃣ Overhead Shoulder Press with Dumbbells or Barbell – high engagement of the anterior deltoid
3️⃣ Arnold Press – simultaneous strengthening of all deltoid parts with emphasis on the anterior head
4️⃣ Incline Bench Press – combined strengthening of the anterior deltoid and pectoralis major
5️⃣ Close-Grip Push-ups – bodyweight exercise targeting this muscle
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery
✔ Stretching the arm forward and across the body to improve flexibility and prevent muscle tightness
✔ Using a foam roller to reduce muscle tension and enhance blood flow
✅ Fun Fact
✔ The anterior deltoid is most engaged in throwing movements, which is why athletes in discus, javelin, and boxing typically have a very strong anterior deltoid.
✅ Practical Tip
✔ Overdeveloping the anterior deltoid without balancing it with the posterior deltoid can lead to muscular imbalances and increased stress on the shoulder joint.
🔴 Name and Location: A superficial muscle located at the front of the shoulder joint, originating from the clavicle.
🟠 Anatomy: Part of the deltoid muscle that, along with the middle and posterior deltoids, surrounds the shoulder and attaches to the humerus.
🟡 Function:
✔ Arm flexion – moving the hand forward
✔ Internal rotation of the arm – rotating the hand inward
✔ Horizontal adduction – assisting in bringing the arm inward on a horizontal plane
🟢 Physiology: Composed mainly of fast-twitch fibers, which provide power and speed in pressing movements.
🔵 Innervation: Axillary nerve, which controls the movements of this muscle.
🟣 Importance: Plays a vital role in pressing exercises, throwing, bodybuilding, boxing, and strength sports.
🟤 Exercises:
✔ Front raise
✔ Shoulder press
✔ Arnold press
✔ Incline bench press
✔ Close-grip push-ups
⚫ Fun Fact: One of the most utilized muscles in throwing and pressing movements, which, if overdeveloped, can lead to muscular imbalances and shoulder injuries.
Infraspinatus Muscle
🔹 The infraspinatus muscle is one of the four key rotator cuff muscles, playing a crucial role in stabilizing and controlling the shoulder joint. It is essential for external rotation of the arm and maintaining shoulder joint stability.
🔹 This muscle is actively engaged in many athletic movements such as throwing, pulling weights, and rotational shoulder actions. Weakness in the infraspinatus can lead to shoulder joint instability, reduced range of motion, and an increased risk of injuries like rotator cuff tendon tears.

✅ Persian Name: Tahte Khari
✅ Latin Name: Infraspinatus
✅ Common Name: External Rotator of the Shoulder | Posterior Rotator Cuff Muscle
✅ Location:
🟡 Located on the posterior (back) side of the scapula, within the infraspinous fossa.
🟡 It is part of the rotator cuff muscle group responsible for external rotation and stabilization of the shoulder.
🟡 Its primary function is to externally rotate the arm and prevent excessive displacement of the humeral head in the glenohumeral joint.
✅ 🔹 Muscle Origin
✔ Infraspinous fossa of the scapula
✅ 🔹 Muscle Insertion
✔ Greater tubercle of the humerus
✅ 🔹 Muscle Function
📌 Primary functions of the infraspinatus muscle:
✔ External rotation of the arm – rotating the arm outward
✔ Stabilizing the shoulder joint against sudden forces
✔ Controlling throwing and rotational shoulder movements
📌 Movements involving activation of the infraspinatus:
✔ External rotation of the arm in resistance exercises (e.g., band external rotations)
✔ Throwing movements such as ball throws, javelin throws, and discus throws
✔ Resistance-based exercises like lateral pulls and controlled shoulder movements
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Types
✔ A combination of ✔ A combination of slow-twitch fibers (Type I) and fast-twitch fibers (Type II).
✔ Contains a higher proportion of slow-twitch fibers, which contribute to endurance and shoulder joint control.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ A key muscle for controlling rotational movements and stabilizing the shoulder in sports like swimming, baseball, basketball, and weightlifting
✔ Engaged in light resistance and stretching exercises to prevent shoulder injuries
✔ Weakness in this muscle can lead to shoulder instability and reduced range of motion.
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ A small but essential muscle for controlling and stabilizing shoulder movements
✔ Requires controlled exercises to enhance stability and prevent tendon inflammation
✅ 🧠 Innervation
✔ Suprascapular nerve (C5, C6), which controls the function of this muscle.
✅ 🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Suprascapular artery
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ A key muscle in stabilizing the shoulder joint and controlling rotational movements
✔ Active in sports involving throwing, gymnastics, swimming, wrestling, and weightlifting
✔ Weakness in this muscle increases the risk of rotator cuff tears and reduces the power of throwing motions.
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Interaction with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Works closely with the posterior deltoid, other rotator cuff muscles (supraspinatus, teres minor, subscapularis), and the posterior shoulder muscles
✔ Weakness in this muscle increases the load on the shoulder joint and its stabilizing muscles.
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ One of the most commonly injured muscles due to throwing motions and sudden stress.
✔ Weakness or inflammation in this muscle can lead to shoulder pain, and partial or complete rotator cuff tears.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Strengthening Exercises for the Infraspinatus
1️⃣ External Rotation with Resistance Band – one of the most effective exercises to strengthen this muscle
2️⃣ Isometric Shoulder Exercises – enhances shoulder stability
3️⃣ Reverse Fly with Dumbbells – improves muscle strength and endurance
4️⃣ Controlled Range of Motion Exercises – helps prevent tendon inflammation
5️⃣ Physiotherapy Exercises – improves overall rotator cuff function
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery Movements
✔ Outward arm stretches to improve flexibility and reduce muscle tension
✔ Using a foam roller to enhance blood flow and reduce inflammation
✅ Fun Fact
✔ The infraspinatus is one of the most important muscles in throwing movements, and athletes in throwing sports often have a highly developed infraspinatus.
✅ Practical Tip
✔ Strengthening the infraspinatus with light weights and resistance bands is the most effective way to prevent injuries and improve shoulder movement control.
🔴 Name and Location: A deep muscle located on the back of the scapula, beneath the supraspinatus, and part of the rotator cuff group.
🟠 Anatomy: Originates from the infraspinous fossa of the scapula and inserts into the greater tubercle of the humerus.
🟡 Function:
✔ External rotation of the arm
✔ Shoulder stabilization during throwing movements
🟢 Physiology: Predominantly composed of slow-twitch fibers for shoulder joint control and endurance.
🔵 Innervation: Suprascapular nerve, which controls this muscle.
🟣 Importance: Plays a vital role in throwing, rotational movements, and stabilizing the shoulder joint.
🟤 Exercises: Band external rotations, physiotherapy exercises, reverse fly.
⚫ Fun Fact: One of the key muscles for enhancing shoulder control and stability in throwing sports.
Teres Minor Muscle
🔹 The teres minor is one of the four main rotator cuff muscles and works alongside the infraspinatus in external rotation of the arm. In addition to stabilizing the glenohumeral (shoulder) joint, it aids in controlled arm movements during both athletic and everyday activities.
🔹 Unlike the infraspinatus, which has greater power in external rotation, the teres minor plays a more prominent role in stabilizing the shoulder joint and maintaining balance during rotational and resistance movements. Weakness in this muscle can increase stress on the shoulder joint and reduce control in throwing and rotational actions.

✅ Persian Name: Gerde Kochak
✅ Latin Name: Teres Minor
✅ Common Name: Small Shoulder Rotator | Posterior Rotator Cuff Muscle
✅ Location:
🟡 Positioned on the posterior side of the scapula, just below the infraspinatus and above the teres major.
🟡 It is part of the rotator cuff muscle group, responsible for external rotation and stabilization of the shoulder.
🟡 As a small yet essential muscle, it plays a critical role in controlling rotational arm movements and maintaining shoulder joint stability.
✅ 🔹 Muscle Origin
✔ Lateral border of the scapula
✅ 🔹 Muscle Insertion
✔ Greater tubercle of the humerus
✅ 🔹 Muscle Function
📌 Primary functions of the teres minor muscle:
✔ External rotation of the arm – rotating the arm outward
✔ Assists in stabilizing the shoulder joint against lateral forces
✔ Controls resistance movements and helps prevent shoulder dislocation
📌 Movements involving activation of the teres minor:
✔ External rotation of the arm during resistance exercises (e.g., band external rotations)
✔ Shoulder strengthening exercises such as face pulls and bent-over lateral raises
✔ Throwing movements that require high shoulder control (e.g., javelin, ball, and discus throws)
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Types
✔ A combination of ✔ A combination of slow-twitch fibers (Type I) and fast-twitch fibers (Type II).
✔ Contains a higher proportion of slow-twitch fibers, which contribute to endurance and shoulder joint control.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ A key muscle for controlling rotational movements and stabilizing the shoulder in sports like swimming, baseball, basketball, and weightlifting
✔ Engaged in light resistance and stretching exercises to prevent shoulder injuries
✔ Weakness in this muscle can lead to shoulder instability and reduced range of motion.
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ A small but essential muscle for controlling and stabilizing shoulder movements
✔ Requires controlled exercises to enhance stability and prevent tendon inflammation
✅ 🧠 Innervation
✔ Axillary nerve (C5, C6), which controls the movements of this muscle.
✅ 🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Posterior circumflex humeral artery
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ A key muscle in stabilizing the shoulder joint and controlling rotational movements
✔ Active in sports involving throwing, gymnastics, swimming, wrestling, and weightlifting
✔ Weakness in this muscle increases the risk of rotator cuff tears and reduces the power of throwing motions.
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Interaction with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Works closely with the posterior deltoid, other rotator cuff muscles (supraspinatus, infraspinatus, subscapularis), and the posterior shoulder muscles
✔ Weakness in this muscle increases stress on the shoulder joint and its stabilizing muscles
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ One of the most commonly injured muscles due to throwing motions and sudden stress.
✔ Weakness or inflammation in this muscle can lead to shoulder pain, and partial or complete rotator cuff tears.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Strengthening Exercises for the Teres Minor
1️⃣ External Rotation with Resistance Band – one of the best exercises to strengthen this muscle
2️⃣ Isometric Shoulder Exercises – improves shoulder stability
3️⃣ Reverse Fly with Dumbbells – enhances muscle strength and endurance
4️⃣ Controlled Range of Motion Exercises – helps prevent tendon inflammation
5️⃣ Physiotherapy Exercises – improves the function of the rotator cuff muscles
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery Movements
✔ Outward arm stretches to improve flexibility and reduce muscle tension
✔ Using a foam roller to enhance blood flow and reduce inflammation
✅ Fun Fact
✔ The teres minor works alongside the infraspinatus in external arm rotation, but it plays a more prominent role in stabilizing the shoulder joint.
✅ Practical Tip
✔ Strengthening the teres minor through controlled exercises is one of the best ways to prevent injuries and improve shoulder movement control.
🔴 Name and Location: A deep muscle located on the back of the scapula, between the infraspinatus and teres major muscles, and part of the rotator cuff group.
🟠 Anatomy: Originates from the lateral border of the scapula and inserts into the greater tubercle of the humerus.
🟡 Function:
✔ External rotation of the arm
✔ Stabilization of the shoulder during rotational and resistance movements
🟢 Physiology: Predominantly composed of slow-twitch fibers for shoulder joint control and endurance.
🔵 Innervation: Axillary nerve, which controls this muscle.
🟣 Importance: Plays a vital role in throwing, rotational movements, and stabilizing the shoulder joint.
🟤 Exercises: Band external rotations, physiotherapy exercises, reverse fly.
⚫ Fun Fact: One of the key muscles for maintaining shoulder strength and balance in power and throwing sports.
Pelank Life | Body Health Assessment
The Best Body Health Calculators Using Scientific Methods
Developed by Pelank Life ©
Muscle training
Pelank is a comprehensive encyclopedia of the body’s muscles, providing an accurate and scientific review of all muscles. Below, you can find muscle groups. By clicking on each muscle group, you will have access to complete information about it, including:
1️⃣ Basic information about the muscle
2️⃣ Muscle anatomy
3️⃣ Muscle physiology
4️⃣ Innervation and blood supply
5️⃣ Importance of the muscle in the body and sports
6️⃣ Strengthening exercises
7️⃣ Scientific and interesting facts
📌 At the end, a summary review of each muscle will be provided.
Body muscles training guide link
🔹 The muscle group engaged in this movement is highlighted in color.
Sharing
References
✅ Official Physical Activity Guidelines
✅ General Overview and Recommendations for the Public
✅ Science-Based and Health-Oriented Education
✅ Policy Making and Comparative Data
Comments