Medicine Ball Overhead Throw
| English Name | Medicine Ball Overhead Throw |
|---|---|
| Difficulty | Advanced |
| Movement Patterns | Push Pattern |
| Muscle Contraction Types | Concentric |
| Primary Muscle (EN) | Anterior Deltoid |
| Muscle Groups | Chest muscles Shoulder Muscles Triceps muscles |
|---|---|
| Workout Type | Explosive Functional Strength training |
| Required equipment | Exercise ball |
💠 Exercise guide
The Medicine Ball Overhead Throw is an excellent explosive exercise for developing upper body power and enhancing force transfer from top to bottom. Widely used in athletic programs—especially in CrossFit and combat training—it simultaneously engages the shoulders, chest, and core muscles, helping to improve overall physical performance.
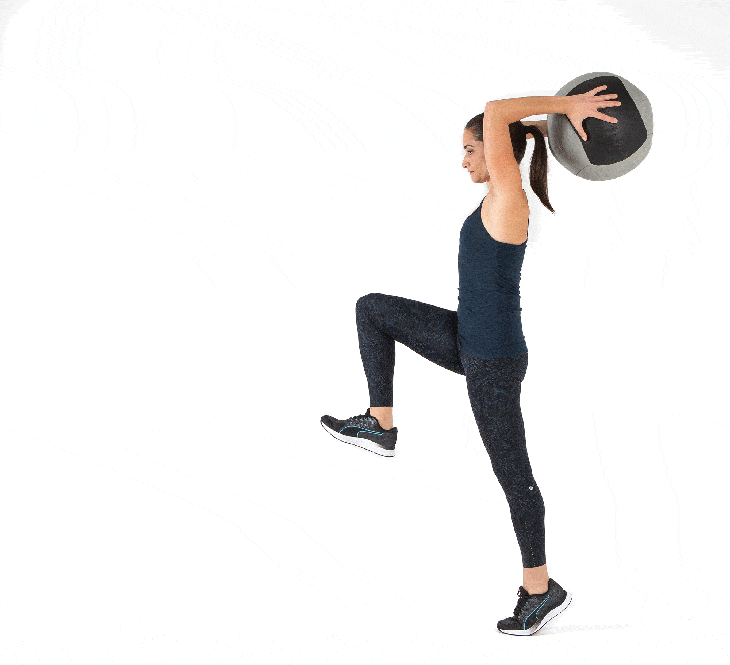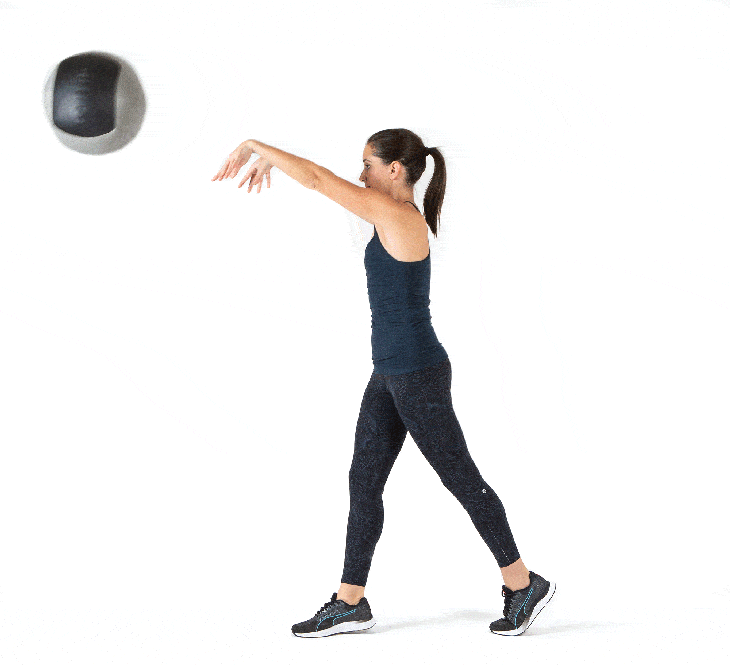
💠 How to perform the exercise

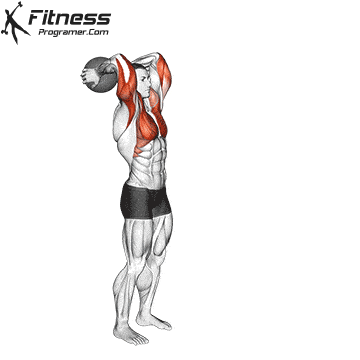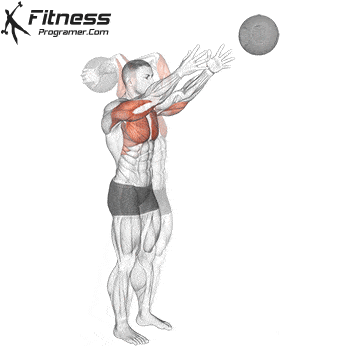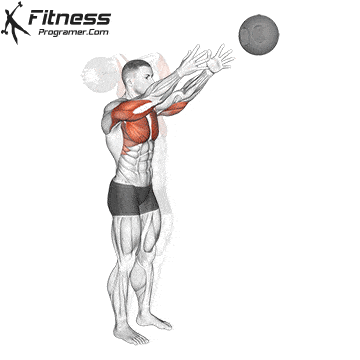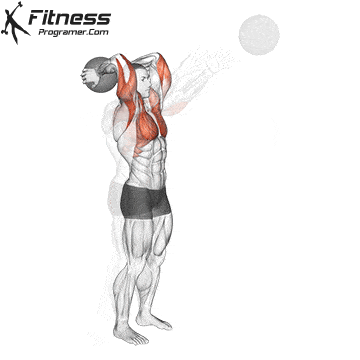
Preparation
✅ Stand tall and hold the medicine ball overhead with both hands
✅ Feet hip-width apart, knees slightly bent
✅ Core engaged, eyes forward, elbows close to the ears
Execution method
✅ Forcefully throw the ball down toward the ground or forward in one powerful motion
✅ At the moment of release, engage the shoulders, chest, and core muscles
✅ Allow the entire body to contribute to the transfer of force, then pick up the ball and repeat
Coaching tips and recommendations
✔ Keep the elbows from flaring out too much to reduce shoulder strain
✔ Exhale during the throw to enhance core performance
✔ Use a non-bouncing (dead) ball for greater safety
✔ Keep the torso and back straight and strong; avoid excessive forward bending
Benefits of the exercise
🔹 Shoulder strengthening with an explosive movement:
The anterior deltoid plays the primary role in the throwing motion, and this exercise enhances shoulder throwing performance in combat and team sports.
🔹 Functional engagement of the chest and triceps:
Alongside the shoulders, the chest and triceps are activated during the throw, enhancing the performance of the pressing muscles.
🔹 Increased core strength:
Engaging the abdominals and torso, especially during force transfer, improves midsection control and helps prevent lower back injuries.
🔹 Application in fat-burning and HIIT workouts:
The explosive nature of the movement and the involvement of multiple muscle groups make this exercise an excellent option for increasing workout intensity.
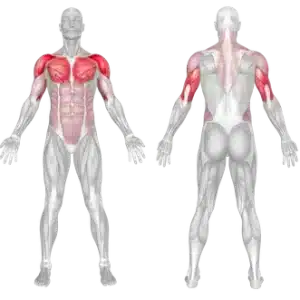
💠 Muscles engaged in the movement
In this exercise, the explosive overhead throwing motion engages multiple muscle groups simultaneously. The anterior deltoid acts as the primary mover, the chest and triceps provide support, and the core muscles stabilize the midsection. This combination enables efficient force transfer and improves overall body power.
Main muscles
Synergistic muscles
Stabilizers
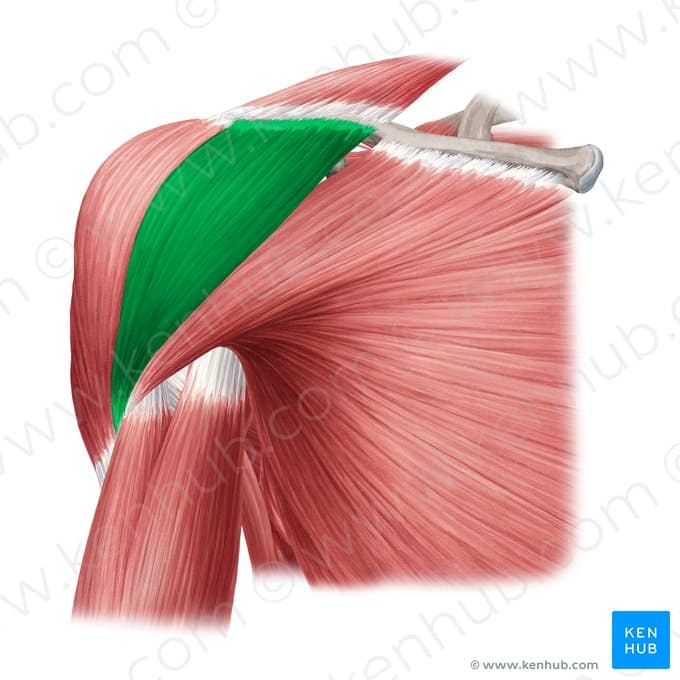
Anterior Deltoid muscle
Anterior Deltoid Muscle
🔹 The anterior deltoid is one of the three parts of the deltoid muscle. Its primary functions are moving the arm forward (flexion), internal rotation, and assisting in horizontal shoulder movements. This muscle plays a key role in many upper-body exercises, especially strength training movements like bench press, front raises, and throwing actions.
🔹 The anterior deltoid is one of the most important muscles involved in pressing and pushing movements. Due to its engagement in many strength exercises, it is often well-developed among athletes and bodybuilders. However, overusing this muscle without strengthening the posterior shoulder muscles (posterior deltoid and rotator cuff) can lead to muscular imbalances and increase the risk of shoulder injuries.
✅ Persian Name: Deltoid Ghodami
✅ Latin Name: Anterior Deltoid
✅ Common Names: Front part of the deltoid muscle | Anterior head of the shoulder
✅ Location:
🟡 Located at the front of the shoulder, forming the anterior part of the deltoid muscle.
🟡 Originates from the clavicle and lies over the upper part of the humerus.
🟡 Alongside the middle and posterior parts of the deltoid, it acts as part of the shoulder cap and assists in arm movements.
✅ 🔹 Origin
✔ Anterior surface of the lateral third of the clavicle (Clavicle – Anterior Surface of Lateral Third)
✅ 🔹 Insertion
✔ Deltoid tuberosity on the humerus bone (Deltoid Tuberosity, Humerus)
✅ 🔹 Function
📌 Primary functions of the anterior deltoid:
✔ Arm flexion – moving the arm forward (like raising the hand in front of the body)
✔ Internal rotation of the arm – rotating the arm inward toward the body
✔ Assisting in horizontal adduction – moving the arm inward on a horizontal plane (such as during a chest fly)
✔ Helping stabilize the shoulder joint during upper-body movements
📌 Movements that activate the anterior deltoid:
✔ Raising the arm forward (such as front raises)
✔ Throwing movements (ball throws, javelin throws)
✔ Moving weights in pressing and fly exercises
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Types
✔ A combination of fast-twitch fibers (Type II) and slow-twitch fibers (Type I)
✔ Predominantly composed of fast-twitch fibers for rapid and powerful movements
✔ This characteristic makes the anterior deltoid highly active in explosive and strength exercises like weightlifting and throwing
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Active in all pressing, throwing, and forward arm-raising exercises
✔ Plays a key role in strength sports, bodybuilding, weightlifting, boxing, and discus throwing
✔ An important muscle in daily activities such as lifting objects and carrying items
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Strength and Endurance
✔ Requires high strength for pressing exercises and overhead movements
✔ Overdevelopment can lead to muscular imbalances and increase the risk of shoulder injuries
✅ 🧠 Innervation
✔ Axillary nerve (C5, C6), which controls the movements of this muscle.
✅ 🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Posterior Circumflex Humeral Artery
✔ Thoracoacromial Artery
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ One of the key muscles for pushing and pressing movements in bodybuilding and weightlifting
✔ Active in throwing sports, swimming, boxing, gymnastics, and pulling movements
✔ Weakness can reduce pressing strength and increase the risk of shoulder injury
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Interaction with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Closely connected with the middle deltoid, pectoralis major, rotator cuff muscles, and triceps brachii
✔ Weakness in this muscle can lead to excessive strain on the shoulder joint and reduced upper body strength
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ One of the muscles prone to inflammation and strain due to high activity in upper-body training
✔ Weakness can cause excessive strain on the pectoral and shoulder muscles, leading to shoulder injuries
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Strength Training Exercises for the Anterior Deltoid
1️⃣ Front Raise with Dumbbells – the most important exercise for strengthening the anterior deltoid
2️⃣ Overhead Shoulder Press with Dumbbells or Barbell – high engagement of the anterior deltoid
3️⃣ Arnold Press – simultaneous strengthening of all deltoid parts with emphasis on the anterior head
4️⃣ Incline Bench Press – combined strengthening of the anterior deltoid and pectoralis major
5️⃣ Close-Grip Push-ups – bodyweight exercise targeting this muscle
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery
✔ Stretching the arm forward and across the body to improve flexibility and prevent muscle tightness
✔ Using a foam roller to reduce muscle tension and enhance blood flow
✅ Fun Fact
✔ The anterior deltoid is most engaged in throwing movements, which is why athletes in discus, javelin, and boxing typically have a very strong anterior deltoid.
✅ Practical Tip
✔ Overdeveloping the anterior deltoid without balancing it with the posterior deltoid can lead to muscular imbalances and increased stress on the shoulder joint.
🔴 Name and Location: A superficial muscle located at the front of the shoulder joint, originating from the clavicle.
🟠 Anatomy: Part of the deltoid muscle that, along with the middle and posterior deltoids, surrounds the shoulder and attaches to the humerus.
🟡 Function:
✔ Arm flexion – moving the hand forward
✔ Internal rotation of the arm – rotating the hand inward
✔ Horizontal adduction – assisting in bringing the arm inward on a horizontal plane
🟢 Physiology: Composed mainly of fast-twitch fibers, which provide power and speed in pressing movements.
🔵 Innervation: Axillary nerve, which controls the movements of this muscle.
🟣 Importance: Plays a vital role in pressing exercises, throwing, bodybuilding, boxing, and strength sports.
🟤 Exercises:
✔ Front raise
✔ Shoulder press
✔ Arnold press
✔ Incline bench press
✔ Close-grip push-ups
⚫ Fun Fact: One of the most utilized muscles in throwing and pressing movements, which, if overdeveloped, can lead to muscular imbalances and shoulder injuries.
Pectoralis major muscle
Pectoralis major Muscle
The pectoralis major is one of the most important muscles of the chest, located at the front of the thorax. It is responsible for various shoulder movements such as adduction, rotation, and elevation of the arm. This muscle plays a key role in pushing exercises like the bench press and push-ups. Strengthening the pectoralis major enhances upper body power, improves chest aesthetics, and increases stability during strength training.
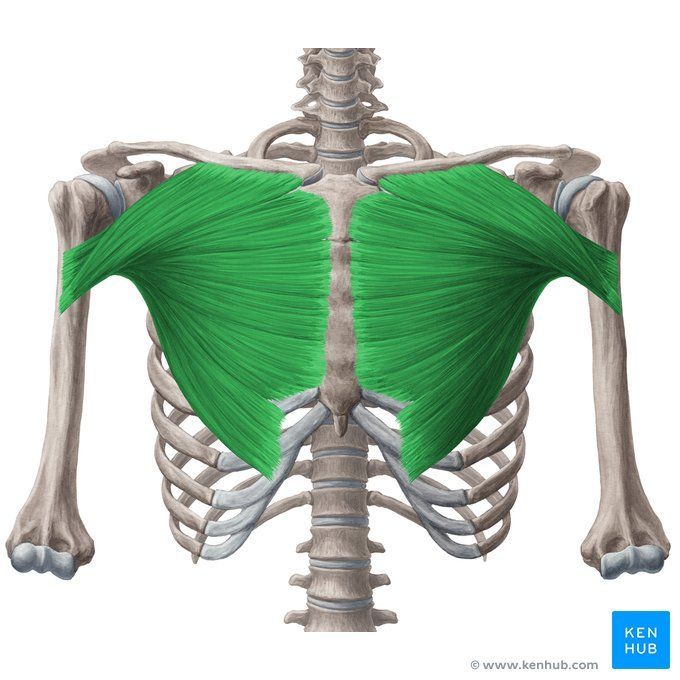
✅ Persian Name: Sine-ye Bozorg | Pectoralis Major
✅ Latin Name: Pectoralis Major
✅ Common Name: Chest Muscle | Pecs
✅ Location:
🟡 Positioned at the front of the chest, lying over the pectoralis minor muscle.
🟡 Originates from the clavicle, sternum, and ribs, and inserts into the humerus.
🟡 Plays a key role in pushing movements such as bench presses and push-ups.
✅ 🦾 Origin
✔ Inner part of the clavicle (Clavicular Head)
✔ Sternum (Sternal Head)
✔ Ribs 1 to 6 (Costal Cartilage)
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ Intertubercular groove of the humerus (bicipital groove)
✅ 📌 Function
The pectoralis major consists of two main parts:
1️⃣ Clavicular Head
✔ Responsible for lifting the arm and moving it forward
✔ Activated in movements such as incline bench press
2️⃣ Sternal Head
✔ Responsible for adducting the arm inward and downward
✔ Activated in movements such as flat bench press and push-ups
✅ Main Functions:
✔ Flexing the arm at the shoulder joint
✔ Adducting the arm toward the body
✔ Medial rotation of the arm
✔ Assisting in pushing movements such as bench press and push-ups
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Type
✔ A combination of fast-twitch fibers (Type II) for explosive power generation
✔ A small amount of slow-twitch fibers (Type I) for maintaining muscular endurance
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Movement and Athletic Performance
✔ Primary muscle involved in bench press, parallel bar dips, push-ups, and cable flys
✔ Enhances upper body strength in bodybuilding, CrossFit, and boxing
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ A large and powerful muscle responsible for explosive upper body movements
✔ Strengthening it improves performance in all pushing exercises and helps prevent shoulder injuries
🧠 Innervation
✔ Medial and lateral pectoral nerves
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Lateral thoracic artery
✔ Internal thoracic artery
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Bodybuilding: bench press, parallel bar dips, cable crossover
✔ Boxing & MMA: delivering powerful punches and maintaining a defensive guard
✔ Push-based sports: push-ups, dips, and upper body strength training
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Interaction with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Works in coordination with the anterior deltoid, triceps brachii, and pectoralis minor during pushing movements
✔ Strengthening it helps reduce stress on the shoulder joint and prevents injuries
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ Weakness in the muscle can lead to reduced upper body strength and poor posture
✔ Overstretching may result in tendon inflammation or partial tears
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Key Exercises to Strengthen the Pectoralis Major
1️⃣ Barbell Bench Press – The best exercise for increasing chest strength and size
2️⃣ Incline Bench Press – Targets the clavicular head of the chest muscle
3️⃣ Parallel Bar Dips – Builds mass and strength in the pectoralis major
4️⃣ Cable Crossover – Focuses on contraction and squeezing of the chest
5️⃣ Dumbbell Flyes – Stretches and strengthens the chest muscles
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery Movements
✔ Chest Stretch on Wall – Improves chest flexibility
✔ Standing Chest Stretch – Enhances range of motion in the shoulders and chest
✅ Fun Fact
✔ The pectoralis major is one of the strongest upper body muscles and plays a vital role in all strength-based sports.
✅ Practical Tip
✔ To build a well-developed and symmetrical chest, combine pushing exercises with stretching movements and focus on all areas of the muscle.
🔴 Name & Location: A large, superficial muscle located at the front of the chest
🟠 Anatomy: Consists of two heads (clavicular and sternocostal) with distinct functions
🟡 Function: Arm adduction, internal rotation, and assistance in pushing movements
🟢 Physiology: A mix of fast- and slow-twitch fibers for both power and endurance
🔵 Innervation: Medial and lateral pectoral nerves
🟣 Importance: Crucial in bodybuilding, boxing, swimming, and push-based movements
🟤 Exercises: Bench press, dips, cable crossover, dumbbell flyes
⚫ Fun Fact: The most important muscle for upper body power and an aesthetically shaped chest
Triceps Brachii Muscle
Triceps Brachii Muscle
The triceps brachii is one of the strongest muscles at the back of the arm, primarily responsible for elbow extension and generating power in pushing movements. This three-headed muscle (long, medial, and lateral heads) is located on the back of the arm and attaches to the ulna bone in the forearm.
✅ Why is this muscle important?
✔ The sole muscle responsible for elbow extension and essential in strength movements.
✔ Stabilizes the elbow and shoulder joints during pressing exercises like the bench press.
✔ Directly impacts strength gains in bodybuilding, gymnastics, boxing, and weightlifting.
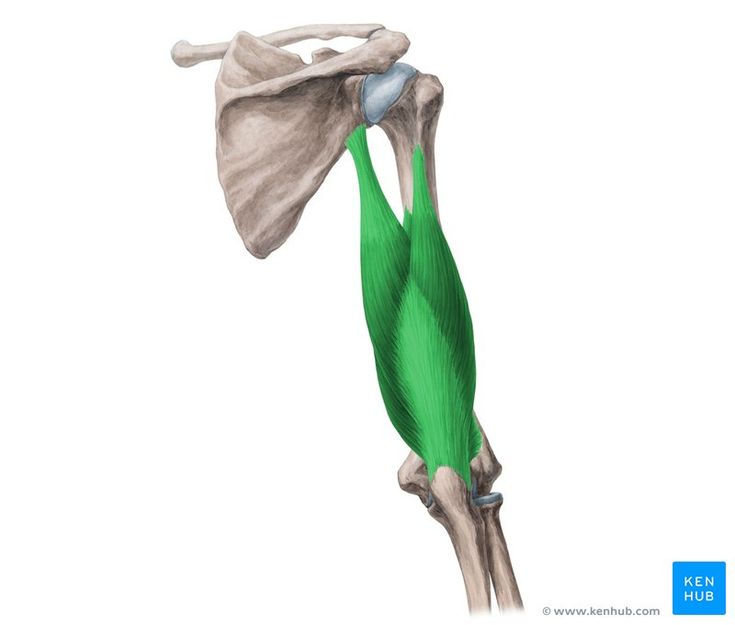
✅ Persian Name: Azole Se Sare Bazoei
✅ Latin Name: Triceps Brachii
✅ Common Name: Back of the Arm
✅ Location:
🟡 Located in the posterior (back) part of the arm, extending from the scapula to the forearm bone.
🟡 Composed of three heads: long, medial, and lateral.
🟡 Responsible for elbow extension and assists in shoulder stabilization.
✅ 🦾 Origin
✔ Long Head: originates from the infraglenoid tubercle of the scapula
✔ Medial Head: originates from the posterior surface of the humerus, below the lateral head
✔ Lateral Head: originates from the posterior surface of the humerus, above the medial head
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ Ulna bone – olecranon process
✅ 📌 Classification and Function
The three main heads of the triceps brachii muscle are:
1️⃣ Long Head
✔ The strongest head and the only one originating from the scapula.
✔ Besides extending the elbow, it plays a role in arm movements and shoulder stabilization.
✔ More active in movements that involve pulling weight behind the body, such as parallel dips.
2️⃣ Medial Head
✔ Located beneath the lateral head and more active during strength and endurance movements.
✔ Plays a greater role in light, repetitive exercises like cable triceps extensions.
3️⃣ Lateral Head
✔ Responsible for muscle mass and the V-shape appearance of the back of the arm.
✔ More active in heavy exercises such as close-grip bench press and lying barbell triceps extensions.
✅ Main Functions:
✔ Elbow extension – the primary muscle responsible for straightening the forearm.
✔ Stabilizes the elbow during pressing movements such as push-ups and bench press.
✔ Assists shoulder movements (long head of the muscle).
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Type
✔ A combination of fast-twitch fibers (Type II) and slow-twitch fibers (Type I) ✔ Fast-twitch fibers are activated during powerful and explosive movements such as bench press and dips.
✔ Slow-twitch fibers are important for endurance in continuous movements like push-ups and parallel bar exercises.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Motor and Athletic Performance
✔ Active in all pressing movements such as bench press, push-ups, dips, and parallel bar exercises.
✔ Plays a key role in sports like boxing, weightlifting, gymnastics, and basketball.
✔ Helps stabilize the shoulder joint during overhead movements like shoulder press and clean and jerk.
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ A very strong and essential muscle for increasing upper body strength.
✔ Weakness in this muscle leads to reduced strength in pressing movements and increased strain on the elbow and shoulder.
🧠 Innervation
✔ The radial nerve (C6–C8) is responsible for controlling this muscle.
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Deep brachial artery
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Bodybuilding: Active in triceps exercises, bench press, dips, and lying barbell presses.
✔ Boxing and martial arts: Plays a key role in straight punches and increasing punching power.
✔ Weightlifting: Helps stabilize the elbow during shoulder presses and clean and jerk.
✔ Gymnastics and CrossFit: Vital in movements like parallel bars, pull-ups, and dips.
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Connection with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Works alongside the deltoid and pectoral muscles during pressing movements.
✔ Weakness in this muscle increases strain on the shoulder and elbow, raising the risk of joint injury.
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ Strain or inflammation of the triceps tendon (Triceps Tendinitis) causes pain at the back of the elbow.
✔ Weakness in this muscle may reduce pressing strength and increase strain on the shoulders.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Main Exercises to Strengthen the Triceps Brachii Muscle
1️⃣ Lying Barbell Triceps Extension (Skull Crushers) – targets all heads of the muscle
2️⃣ Parallel Dips – best for strength and endurance
3️⃣ Cable Triceps Pushdown – ideal for muscle isolation
4️⃣ Close-Grip Bench Press – combines triceps and chest muscles
5️⃣ Overhead Dumbbell Triceps Extension – emphasizes the long head more
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery Movements
✔ Triceps stretch to improve flexibility.
✔ Massage and foam rolling to reduce tension after exercise.
✅ 🔍 Interesting Fact
✔ 70% of the arm’s volume comes from the triceps brachii! If you want bigger arms, you need to focus on this muscle.
✅ 💡 Practical Tip
✔ For complete growth, perform exercises at different angles to engage all three heads of the muscle!
🔴 Name and Location: A three-headed muscle located at the back of the arm, extending from the shoulder to the elbow.
🟠 Anatomy: Originates from the scapula and humerus, and attaches to the ulna bone in the forearm.
🟡 Function: Elbow extension, shoulder stabilization, and assisting pressing movements.
🟢 Physiology: Contains both strength and endurance fibers, active in power and endurance arm movements.
🔵 Innervation: Radial nerve (C6–C8), which controls the function of this muscle.
🟣 Importance: Active in bodybuilding, boxing, weightlifting, swimming, CrossFit, and gymnastics.
🟤 Exercises: Parallel dips, close-grip bench press, lying barbell triceps extension, overhead dumbbell triceps extension, cable triceps pushdown.
⚫ Interesting Fact: It makes up 70% of the arm’s volume, so focusing on this muscle is essential for increasing arm size!
Muscle training
Pelank is a comprehensive encyclopedia of the body’s muscles, providing an accurate and scientific review of all muscles. Below, you can find muscle groups. By clicking on each muscle group, you will have access to complete information about it, including:
1️⃣ Basic information about the muscle
2️⃣ Muscle anatomy
3️⃣ Muscle physiology
4️⃣ Innervation and blood supply
5️⃣ Importance of the muscle in the body and sports
6️⃣ Strengthening exercises
7️⃣ Scientific and interesting facts
📌 At the end, a summary review of each muscle will be provided.
Body muscles training guide link
🔹 The muscle group engaged in this movement is highlighted in color.
References
Anatomy and medical books :
- Gray’s Anatomy (one of the standard references in anatomy).
- Netter’s Atlas of Human Anatomy (a famous visual atlas in anatomy).
- Clinically Oriented Anatomy by Keith Moore
Sports and training references :
- Strength Training Anatomy by Frederic Delavier
- Essentials of Strength Training and Conditioning by NSCA
- Well-known articles and training programs by international coaches
Medical databases :
- PubMed (for scientific and research articles)
- MedlinePlus (health and medical information)
- WebMD (for practical and general health information)
Pelank Life | Body Health Assessment
The Best Body Health Calculators Using Scientific Methods
Developed by Pelank Life ©
Comments