- No Comments
- زمان مطالعه : 7 دقیقه
Description
Neck Flexion Stretch:
This exercise is designed to reduce tension and pain in the neck and shoulder area. By gently bending the head forward and creating a stretch in the back of the neck, it can increase neck muscle flexibility and help improve posture. It is suitable for relieving fatigue caused by prolonged desk work or frequent use of mobile phones.
How to perform the exercise

Preparation
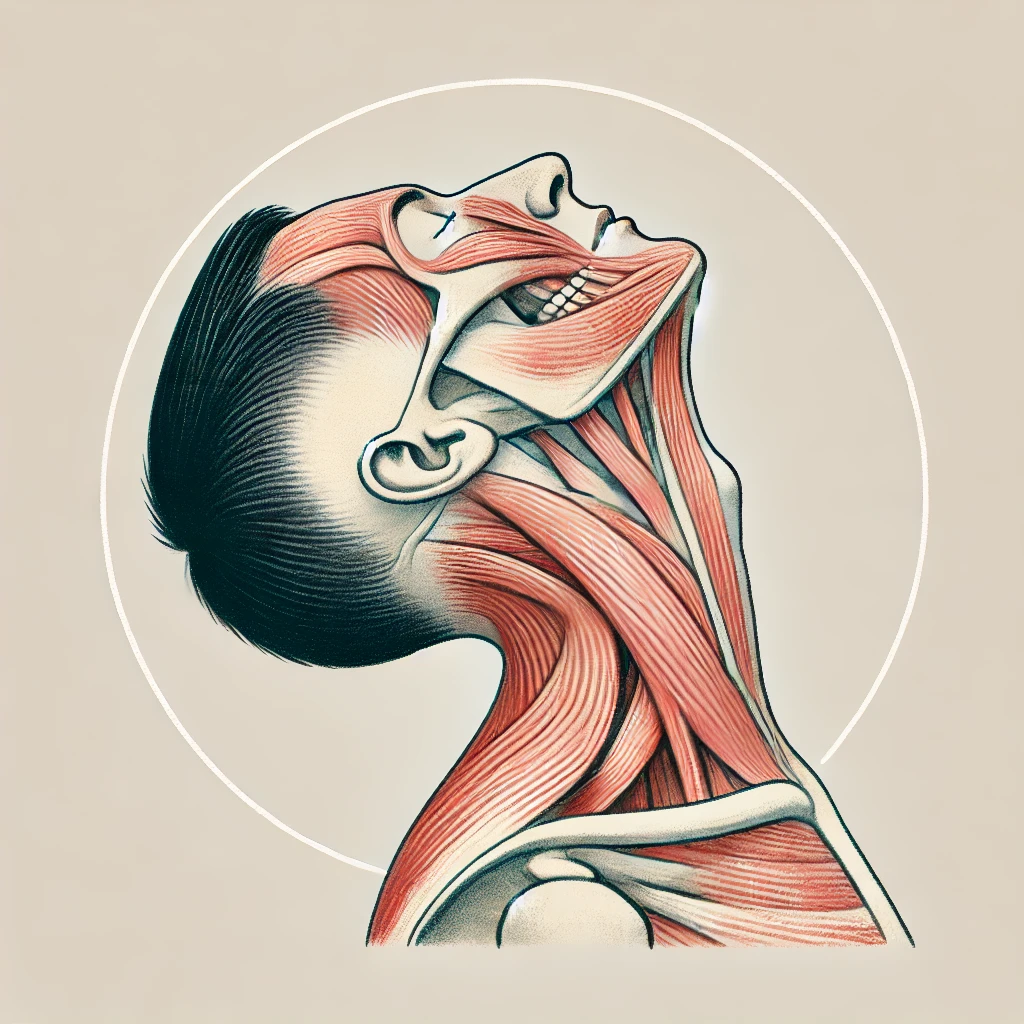
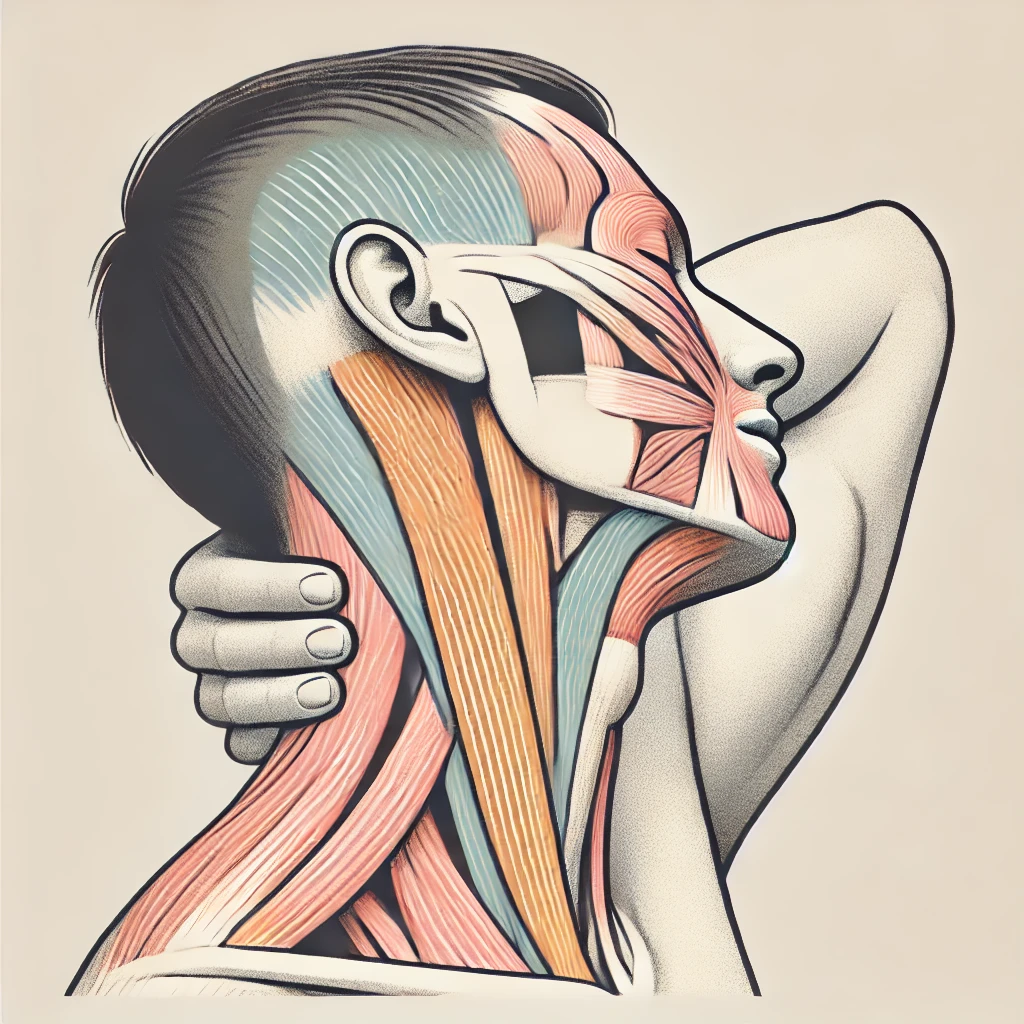
Sit in the position shown in the image and get ready to perform the exercise.
Execution method
- Gently bend your head forward, bringing your chin toward your chest. Allow the weight of your head to create a gentle stretch in the back of your neck.
- Hold this position gently for 5 to 10 seconds.
- Then return to the starting position.
Repetitions
Repeat this exercise 3 to 5 times.
Coaching tips and recommendations
- It is important to avoid applying excessive pressure or making forced movements.
- Avoid holding your breath.
- If you feel any pain during the neck stretch, stop immediately and consult a healthcare professional.
Benefits of the exercise

Neck stretches are also used in physiotherapy with the goal of rehabilitating the muscles, joints, and bones of the neck.
Neck flexion stretches are performed to increase the strength, tone, and flexibility of the neck muscles. They also help make the ligaments of the neck joints more flexible and able to withstand greater pressure.
When poor posture causes the head and shoulders to lean forward, some chest and neck muscles may shorten and gradually become tight. This condition can worsen improper posture that leads to neck pain. Neck stretching exercises can help relax the muscles associated with posture and potentially reduce neck pain.
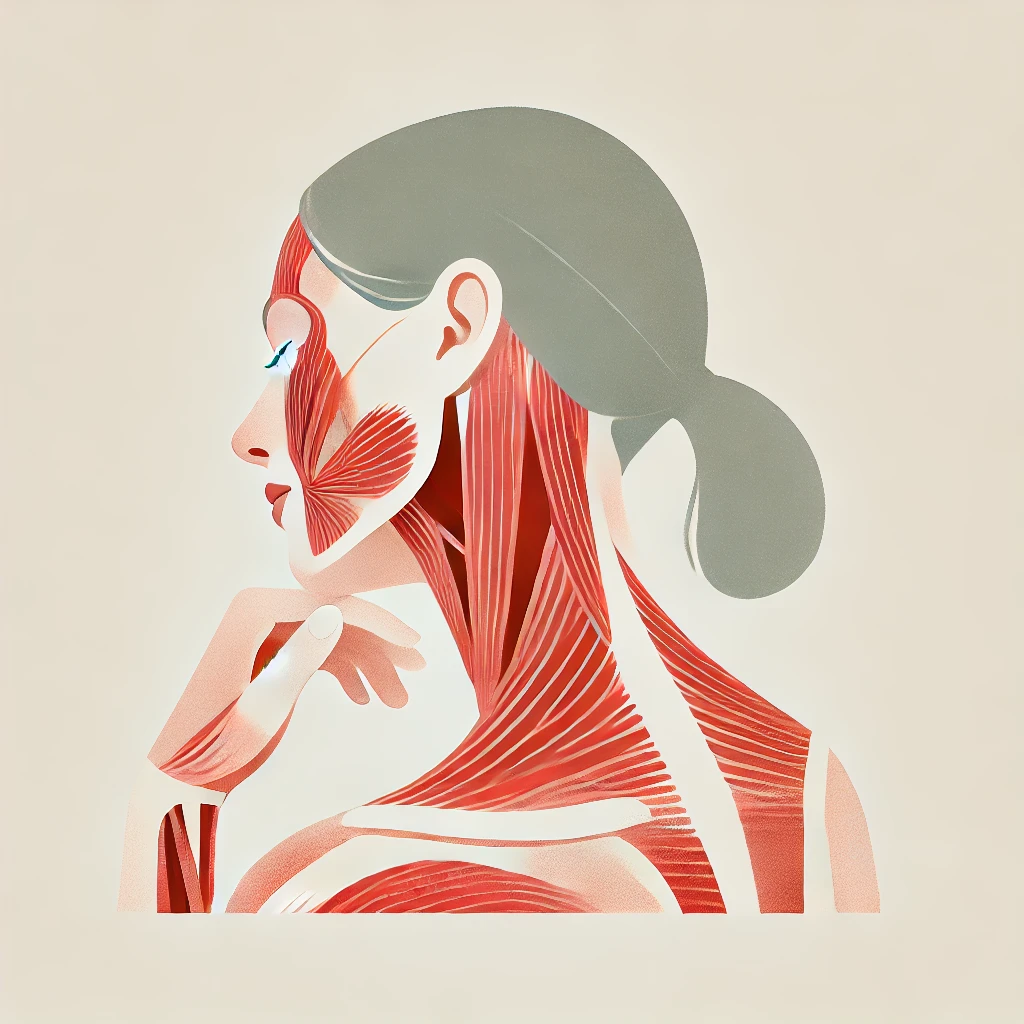
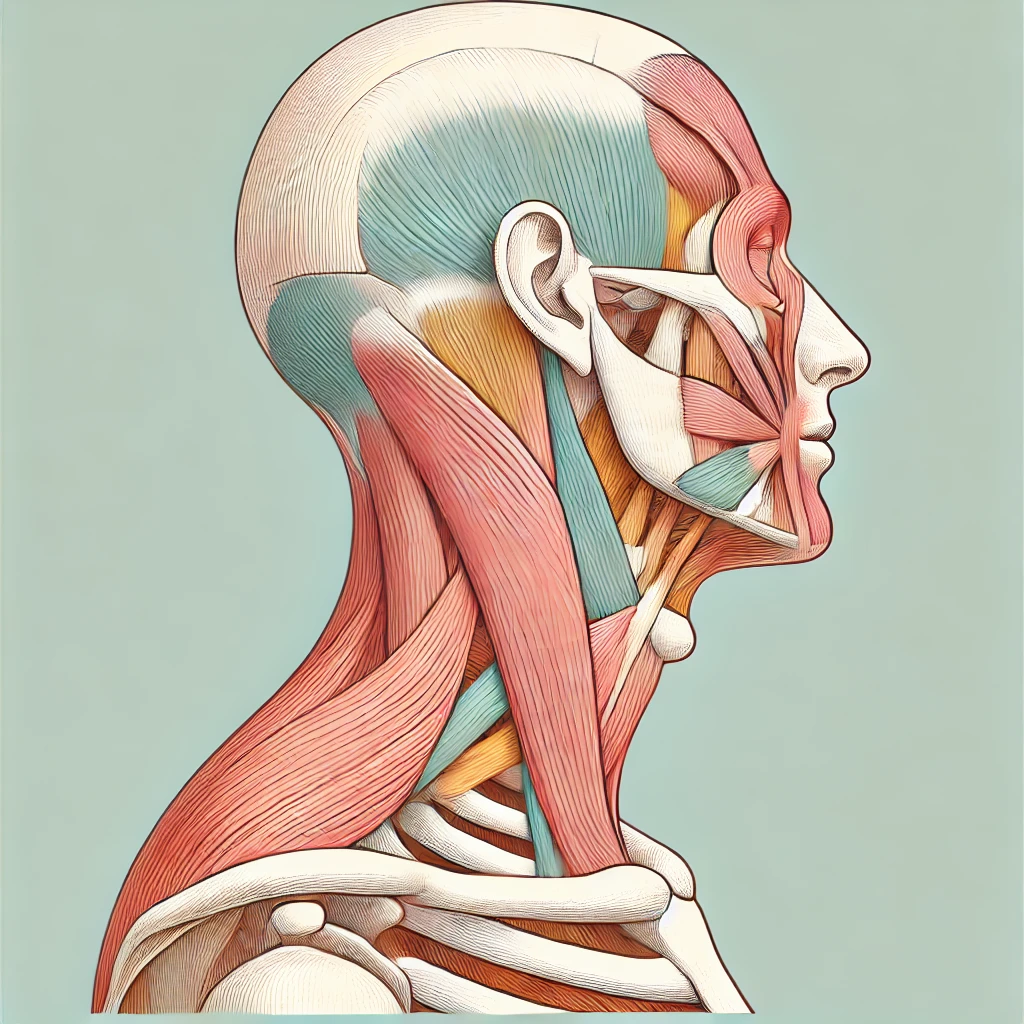
Muscles involved in the exercise
List of muscles involved
Instruction on the involved muscles
1. Semispinalis Capitis
The semispinalis capitis is a deep, long muscle located in the neck and back of the head. It connects to the upper cervical and upper thoracic vertebrae and attaches to the bones of the skull, particularly the occipital and temporal regions.
The primary functions of the semispinalis capitis include extending the head backward and rotating it to the sides. In addition, this muscle helps stabilize the neck and maintain spinal alignment. It also plays a role in twisting movements of the neck and head during activities such as looking around or turning the head.
Image of the Splenius Capitis Muscles

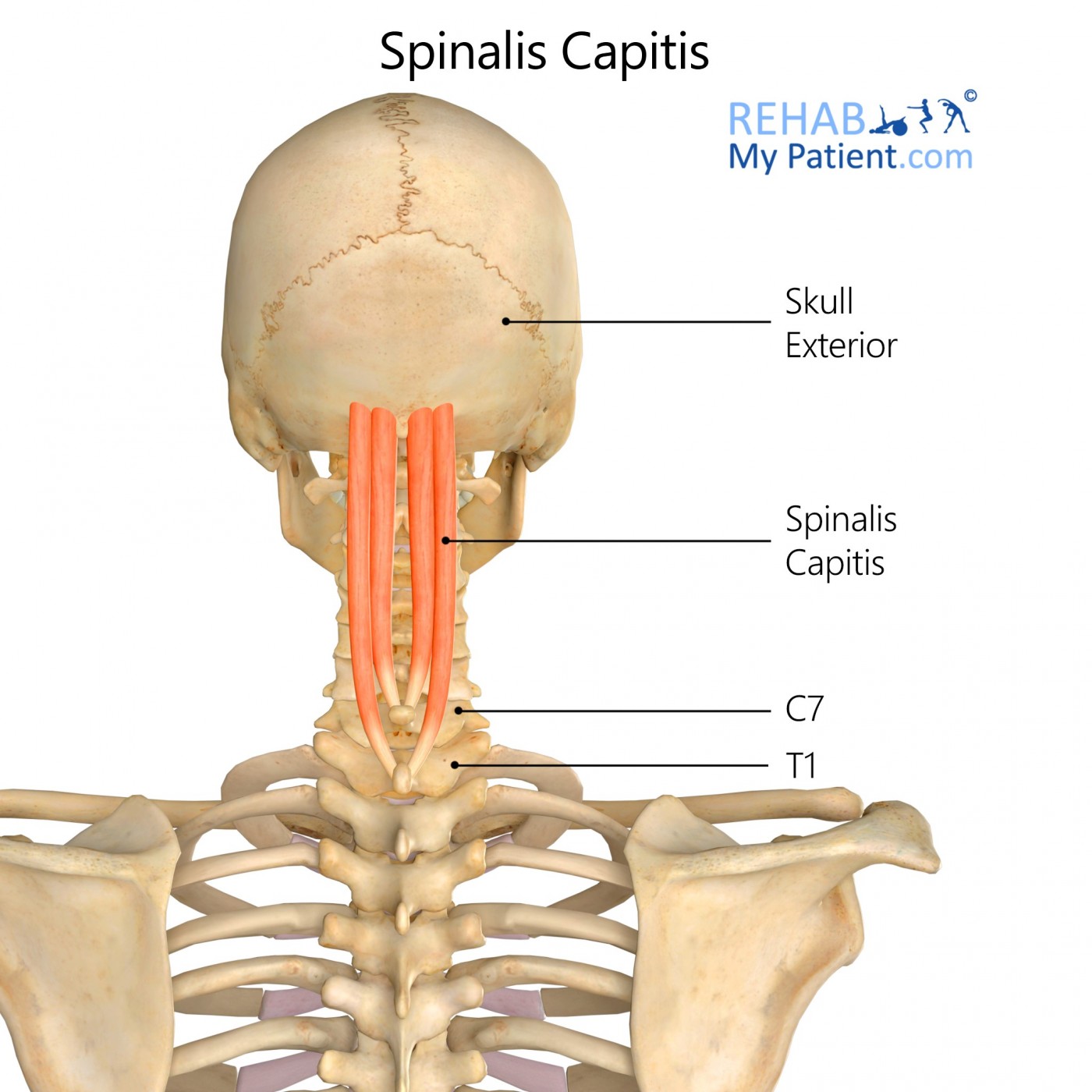
2. Spinalis Capitis
The spinalis capitis is a muscle that is part of the erector spinae group and is located in the head region. It originates from the upper cervical and thoracic vertebrae and attaches to the skull bones, particularly the occipital bone. The spinalis capitis is responsible for extending the head and assisting in maintaining the stability and support of the cervical spine and head.
Image of the Spinalis Capitis Muscles
3. Spinalis Cervicis
The spinalis cervicis is a muscle that is part of the erector spinae group and is located in the neck region. It originates from the upper thoracic vertebrae (T2–T4) and attaches to the upper cervical vertebrae (C2). The spinalis cervicis is responsible for extending the neck and maintaining the upright position of the cervical spine. This muscle plays a role in strengthening and stabilizing the cervical spine and contributes to improved head and neck movements.
Image of the Splenius Cervicis Muscles

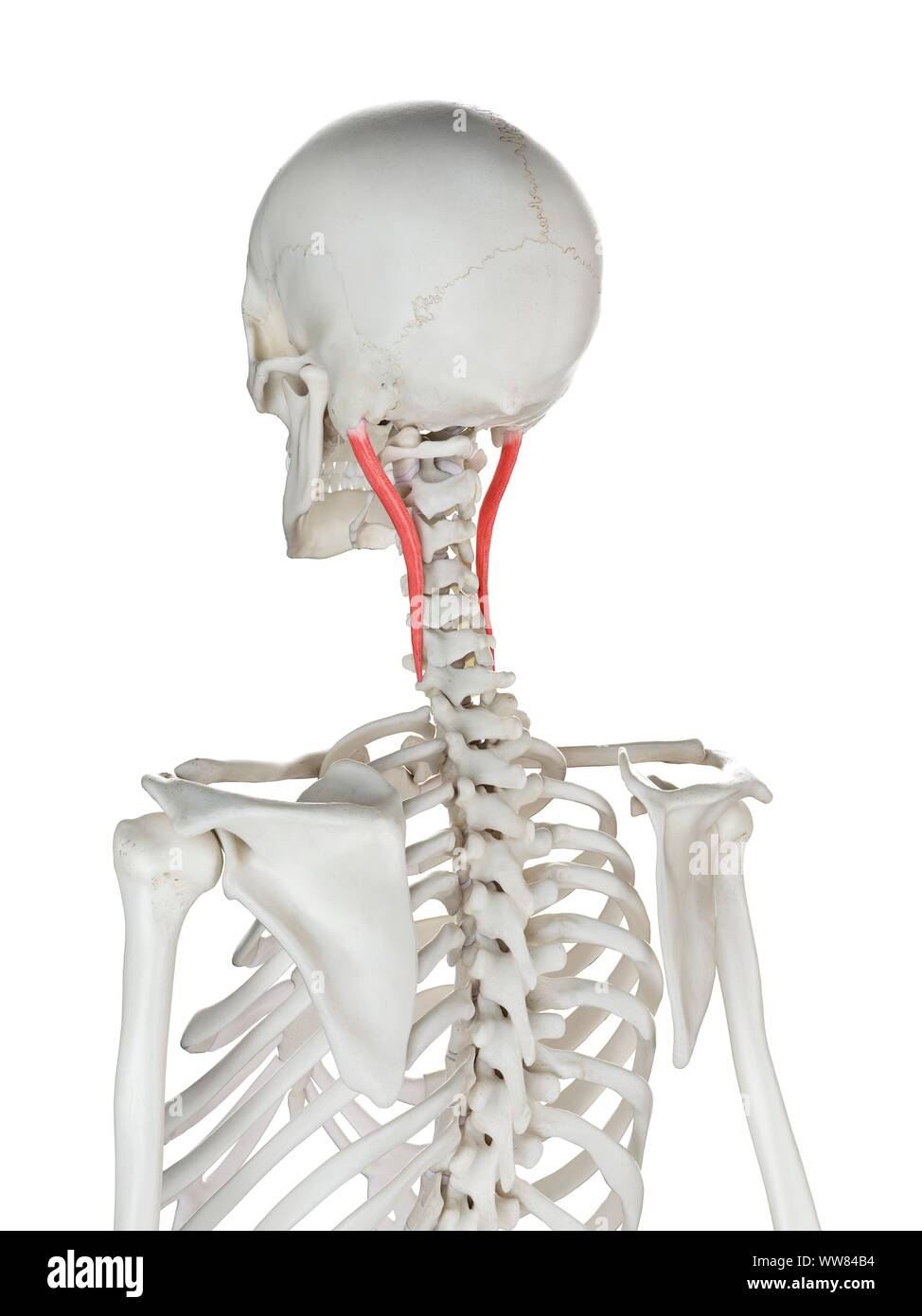
4. Longissimus Capitis
This muscle is a part of the longissimus, which belongs to the erector spinae muscle group. The longissimus capitis is located in the neck and head region and particularly assists in head rotation and extension. It originates from the upper neck and lower spine and attaches to the bones at the back of the head.
Image of the Longissimus Capitis Muscles
5. Levator scapulae
The levator scapulae is a long, slender muscle located in the neck and shoulder region, considered part of the deep neck muscles. It originates from the transverse processes of the cervical vertebrae (C1 to C4) and attaches to the medial border of the scapula near the superior angle.
Image of the levator scapulae muscles

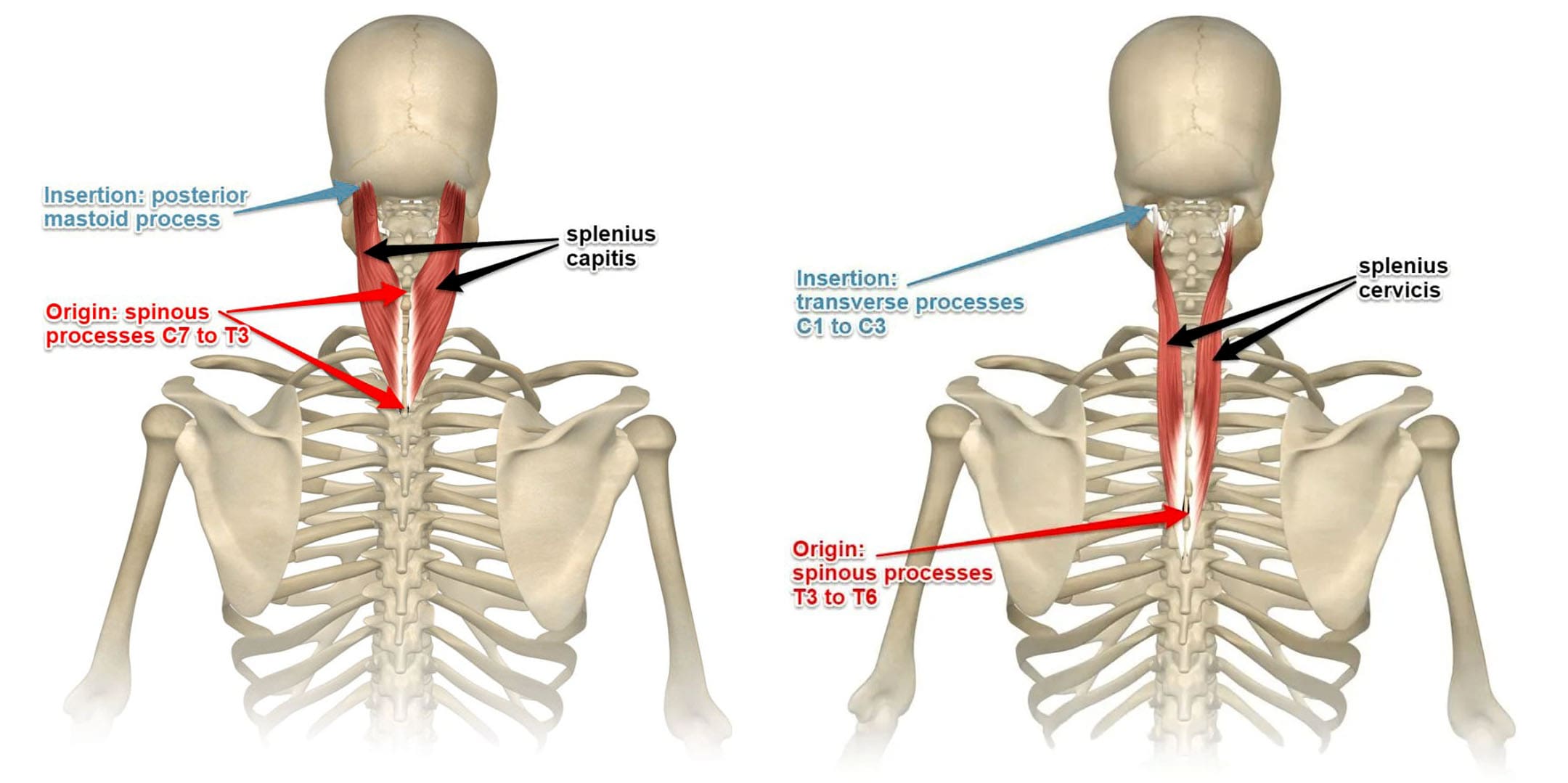
6. Splenius Capitis
Image of the Splenius Capitis Muscles

7. Splenius Cervitis
A muscle that plays a role in neck rotation, movement, and stabilization.
Image of the Splenius Cervicis Muscles
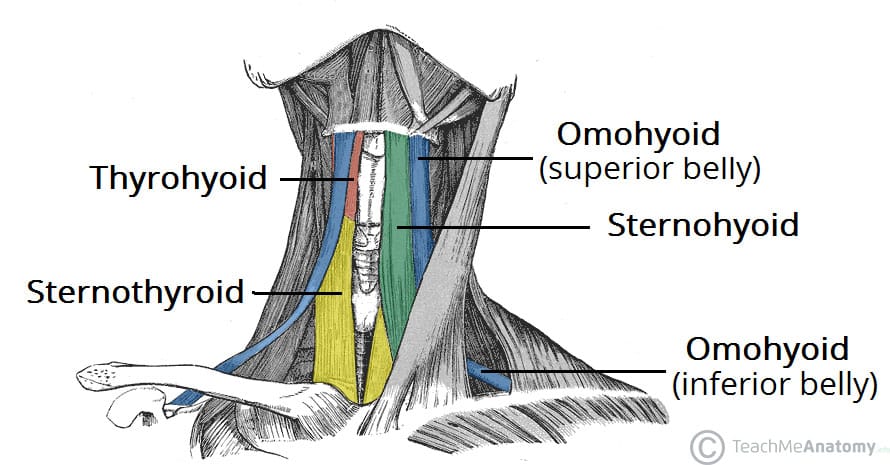
8. sternothyroid
One of the neck muscles that helps lower the thyroid cartilage and plays a role in the swallowing process.
Image of the Sternothyroid Muscles
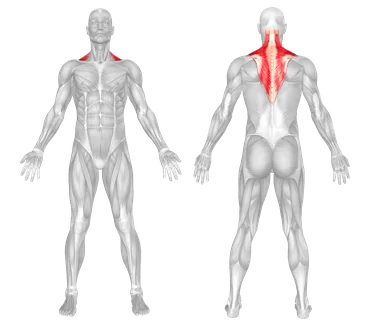
9. Trapezius
The trapezius is a large muscle in the back and neck region, shaped like a trapezoid, extending from the neck to the mid-back. It is composed of different parts and is divided into three main sections:
- Upper (Superior) Part: Responsible for elevating the shoulders and moving the head backward.
- Middle Part: Helps move the shoulders backward and maintain scapular stability.
- Lower (Inferior) Part: Responsible for lowering the shoulders.
The trapezius muscle plays a key role in various shoulder and neck movements, including elevating the shoulders, rotating the scapulae, and moving the head backward. It also contributes to maintaining and stabilizing the shoulder and neck region.
Image of the Trapezius Muscle

Founder of Pelank Platform (6+ years) | Founder & Manager of Galaxy Gym (11+ years) | M.Sc. Student in Exercise Physiology & Nutrition | Certified Fitness & Conditioning Coach | Official Member of the Bodybuilding & Physical Fitness Federation
- This author does not have any more posts.