Introduction
Introduction
The human body is a complex and coordinated structure in which each muscle plays a vital role in movement, breathing, and structural integrity. The pectoral muscles are among the most important muscle groups in the body. They not only contribute to upper body movements and shoulder stability but also play a role in respiration, protect vital organs, and assist in both pushing and pulling actions.
These muscles include superficial muscles such as the pectoralis major and minor, deep muscles like the intercostals, and the diaphragm, which is the body’s primary respiratory muscle. Each of these muscles has its own unique structure, function, and significance. Understanding them is essential not only for athletes, coaches, and physiotherapists but also for anyone who values their physical health.
In this review, we have conducted a detailed analysis of the chest muscles using the renowned reference “Gray’s Anatomy,” one of the most authoritative anatomy books in the world. This analysis covers the names, structures, functions, innervation, strengthening exercises, and common injuries of the thoracic muscles. Gaining this knowledge provides a deeper understanding of the body’s movement mechanisms and can be used to enhance athletic performance, increase strength, and prevent injuries.

1. Superficial muscles of the chest
Superficial Thoracic Muscles
Pectoralis major muscle
Pectoralis major Muscle
The pectoralis major is one of the most important muscles of the chest, located at the front of the thorax. It is responsible for various shoulder movements such as adduction, rotation, and elevation of the arm. This muscle plays a key role in pushing exercises like the bench press and push-ups. Strengthening the pectoralis major enhances upper body power, improves chest aesthetics, and increases stability during strength training.
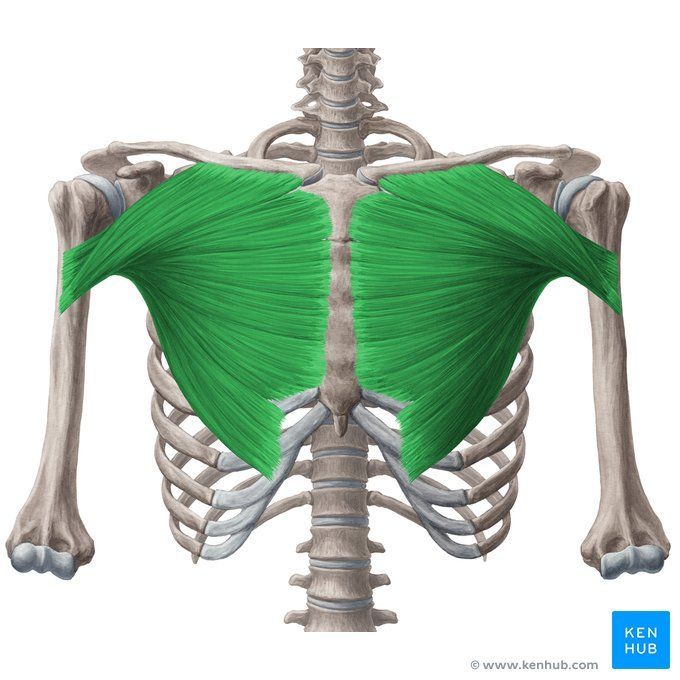
✅ Persian Name: Sine-ye Bozorg | Pectoralis Major
✅ Latin Name: Pectoralis Major
✅ Common Name: Chest Muscle | Pecs
✅ Location:
🟡 Positioned at the front of the chest, lying over the pectoralis minor muscle.
🟡 Originates from the clavicle, sternum, and ribs, and inserts into the humerus.
🟡 Plays a key role in pushing movements such as bench presses and push-ups.
✅ 🦾 Origin
✔ Inner part of the clavicle (Clavicular Head)
✔ Sternum (Sternal Head)
✔ Ribs 1 to 6 (Costal Cartilage)
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ Intertubercular groove of the humerus (bicipital groove)
✅ 📌 Function
The pectoralis major consists of two main parts:
1️⃣ Clavicular Head
✔ Responsible for lifting the arm and moving it forward
✔ Activated in movements such as incline bench press
2️⃣ Sternal Head
✔ Responsible for adducting the arm inward and downward
✔ Activated in movements such as flat bench press and push-ups
✅ Main Functions:
✔ Flexing the arm at the shoulder joint
✔ Adducting the arm toward the body
✔ Medial rotation of the arm
✔ Assisting in pushing movements such as bench press and push-ups
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Type
✔ A combination of fast-twitch fibers (Type II) for explosive power generation
✔ A small amount of slow-twitch fibers (Type I) for maintaining muscular endurance
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Movement and Athletic Performance
✔ Primary muscle involved in bench press, parallel bar dips, push-ups, and cable flys
✔ Enhances upper body strength in bodybuilding, CrossFit, and boxing
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ A large and powerful muscle responsible for explosive upper body movements
✔ Strengthening it improves performance in all pushing exercises and helps prevent shoulder injuries
🧠 Innervation
✔ Medial and lateral pectoral nerves
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Lateral thoracic artery
✔ Internal thoracic artery
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Bodybuilding: bench press, parallel bar dips, cable crossover
✔ Boxing & MMA: delivering powerful punches and maintaining a defensive guard
✔ Push-based sports: push-ups, dips, and upper body strength training
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Interaction with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Works in coordination with the anterior deltoid, triceps brachii, and pectoralis minor during pushing movements
✔ Strengthening it helps reduce stress on the shoulder joint and prevents injuries
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ Weakness in the muscle can lead to reduced upper body strength and poor posture
✔ Overstretching may result in tendon inflammation or partial tears
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Key Exercises to Strengthen the Pectoralis Major
1️⃣ Barbell Bench Press – The best exercise for increasing chest strength and size
2️⃣ Incline Bench Press – Targets the clavicular head of the chest muscle
3️⃣ Parallel Bar Dips – Builds mass and strength in the pectoralis major
4️⃣ Cable Crossover – Focuses on contraction and squeezing of the chest
5️⃣ Dumbbell Flyes – Stretches and strengthens the chest muscles
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery Movements
✔ Chest Stretch on Wall – Improves chest flexibility
✔ Standing Chest Stretch – Enhances range of motion in the shoulders and chest
✅ Fun Fact
✔ The pectoralis major is one of the strongest upper body muscles and plays a vital role in all strength-based sports.
✅ Practical Tip
✔ To build a well-developed and symmetrical chest, combine pushing exercises with stretching movements and focus on all areas of the muscle.
🔴 Name & Location: A large, superficial muscle located at the front of the chest
🟠 Anatomy: Consists of two heads (clavicular and sternocostal) with distinct functions
🟡 Function: Arm adduction, internal rotation, and assistance in pushing movements
🟢 Physiology: A mix of fast- and slow-twitch fibers for both power and endurance
🔵 Innervation: Medial and lateral pectoral nerves
🟣 Importance: Crucial in bodybuilding, boxing, swimming, and push-based movements
🟤 Exercises: Bench press, dips, cable crossover, dumbbell flyes
⚫ Fun Fact: The most important muscle for upper body power and an aesthetically shaped chest
Sections of the Pectoralis Major Muscle
Parts of the Pectoralis Major Muscle
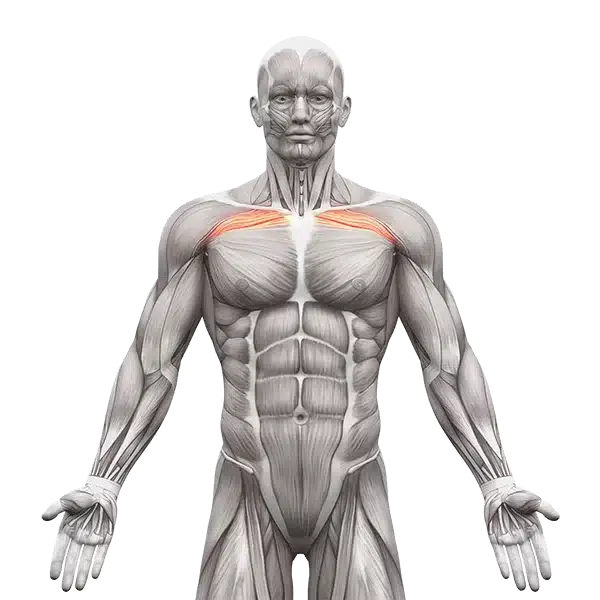
Upper Chest | Clavicular Part
Upper Chest Muscles (Clavicular Head)
The clavicular part of the pectoralis major is located in the upper region of the chest and originates from the inner surface of the clavicle. It extends downward and inward, inserting onto the humerus.
🔹 Function:
- Its primary role is in shoulder flexion—raising the arm from a low position upward and forward.
- It also assists in adduction movements, bringing the arm toward the center of the body.
- It also contributes to internal rotation of the arm.
💪 Effective Exercises:
- Incline bench press with barbell or dumbbells
- Incline fly
- Incline bench press with Smith machine
⚡ Special Feature: This section typically has less muscle mass compared to other parts of the chest in most individuals, and it often requires targeted exercises for proper development.
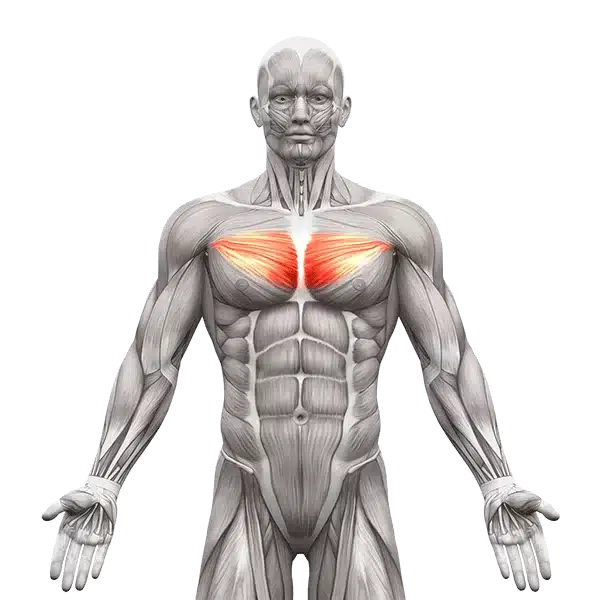
Middle Chest | Sternocostal Part
Middle Chest Muscles (Sternocostal Head)
This is the largest and most voluminous part of the pectoralis major. It originates from the anterior surface of the sternum and the cartilage of ribs 1 to 6. The muscle fibers run horizontally and insert into the humerus.
🔹 Function:
- Adducting the arm toward the body (such as when bringing the arms forward from the sides).
- Generating power in pressing movements such as the bench press.
- Assisting in internal rotation of the arm and stabilizing the shoulder.
💪 Effective Exercises:
- Flat bench press with barbell or dumbbells
- Flat dumbbell fly
- Push-ups
⚡ Special Feature: This section shows the most muscle growth in bodybuilding routines, as it bears the greatest load during most compound movements like the bench press.
Lower Chest | Abdominal Part
Lower Chest Muscles (Abdominal Head)
This part originates from the anterior rectus sheath or the lower portion of the sternum and the cartilage of the lower ribs (ribs 6 to 7). Its fibers run upward and outward, inserting into the humerus.
🔹 Function:
- Lowering the arm (shoulder extension from a flexed position), such as when bringing the arm down from an overhead position.
- Adducting the arm toward the midline of the body, especially during movements where the arm is brought downward and inward.
- It plays a key role in pressing movements and decline (negative angle) exercises.
💪 Effective Exercises:
- Decline bench press with barbell or dumbbells
- Parallel bar dips
- Low to high cable crossover
⚡ Special Feature: This section often shows less development in individuals who don’t train the chest comprehensively, which can result in a flat or unfinished appearance in the lower chest area.
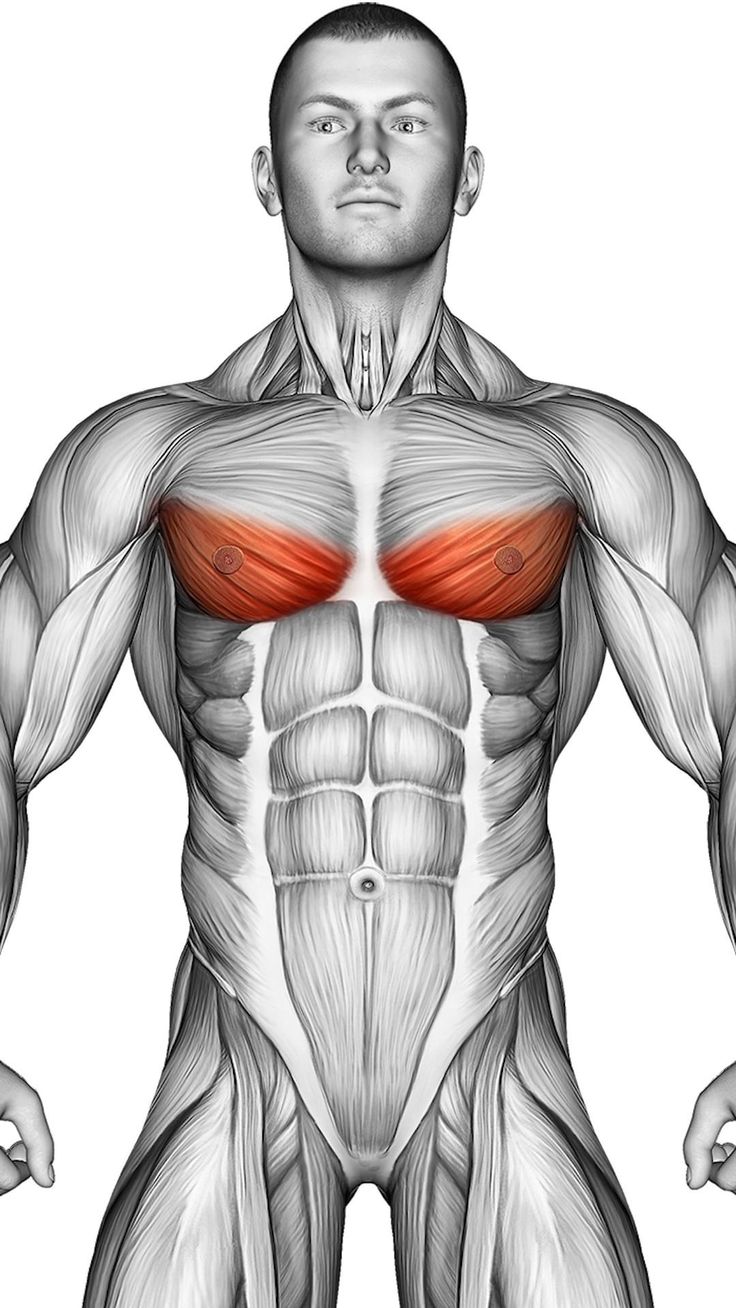
Pectoralis Minor Muscle
Pectoralis Minor Muscle
The pectoralis minor is a small but important muscle located beneath the pectoralis major. It plays a key role in the movement and stabilization of the scapula, assisting in upper body motions such as pulling and shoulder rotation. Its primary function is to draw the shoulder downward and stabilize the scapula during both athletic movements and daily activities. Weakness in this muscle can lead to movement dysfunctions in the shoulder and chest.
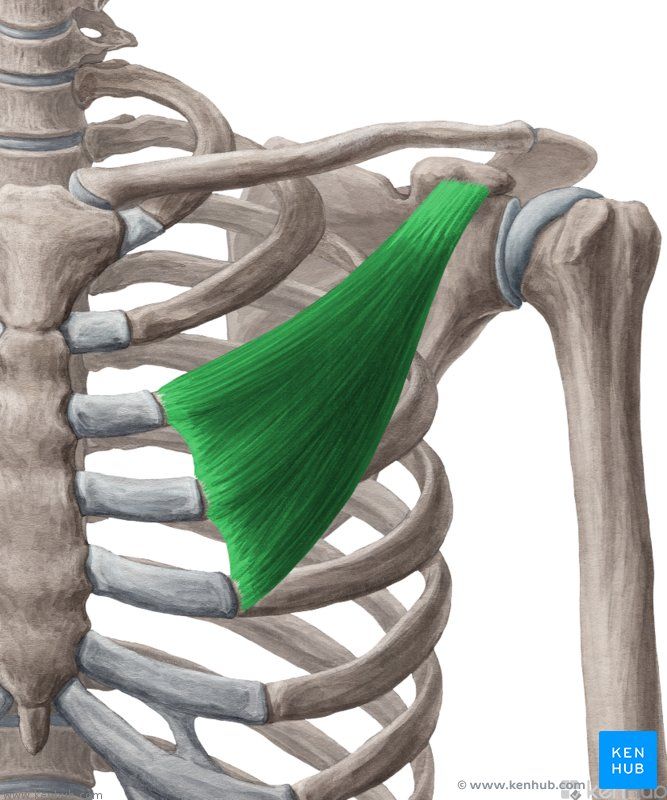
✅ Persian Name: Sine-ye Kuchak
✅ Latin Name: Pectoralis Minor
✅ Common Name: Minor Pec
✅ Location:
🟡 A deep muscle located beneath the pectoralis major
🟡 Originates from the upper ribs and inserts into the scapula
🟡 Plays an important role in the movement and stabilization of the scapula
✅ 🦾 Origin
✔ Ribs 3 to 5
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ Coracoid process of the scapula
✅ 📌 Function
✔ Depresses and stabilizes the scapula
✔ Assists in respiratory movements by elevating the ribs
✔ Involved in shoulder rotation and protraction movements
✔ Ribs 3–5
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ Coracoid process of the scapula
✅ 📌 Function
✔ Depresses and stabilizes the scapula
✔ Assists with breathing by elevating the ribs
✔ Participates in shoulder rotation and protraction movements
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Type
✔ A mix of slow-twitch fibers (Type I) for maintaining muscular endurance
✔ Fast-twitch fibers (Type II) for quick and sudden shoulder movements
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Movement and Athletic Performance
✔ Crucial for scapular stabilization during bench press and push-ups
✔ Plays a key role in sports that involve throwing motions (basketball, boxing, shot put)
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ A small but important muscle for shoulder stabilization and injury prevention
✔ Weakness in this muscle can lead to scapular and shoulder movement imbalances
🧠 Innervation
✔ Medial pectoral nerve
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Lateral thoracic artery
✔ Internal thoracic artery
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Bodybuilding: stabilizes the scapula during bench press and push-ups
✔ Boxing and throwing sports: assists in throwing and striking motions
✔ Gymnastics and CrossFit: helps prevent shoulder injuries
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Interaction with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Works in coordination with the pectoralis major, deltoid, and trapezius muscles during upper body movements
✔ Strengthening it enhances shoulder stability and reduces strain on the trapezius and neck muscles
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ Weakness in this muscle can lead to shoulder pain and instability
✔ Spasms or tightness may contribute to Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Key Exercises to Strengthen the Pectoralis Minor
1️⃣ Dips – Strengthens and stabilizes the muscle during pushing movements
2️⃣ Push-ups – Activates the supporting role of the pectoralis minor
3️⃣ Dumbbell Bench Press – Enhances stabilization and muscle engagement
4️⃣ Seated Row – Strengthens the connection between the scapula and back muscles
5️⃣ Scapular Stretch – Prevents muscle tightness and cramping
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery Movements
✔ Wall chest stretch – increases flexibility and improves shoulder mobility
✔ Seated shoulder stretch – enhances range of motion
✅ Fun Fact
✔ The pectoralis minor assists in breathing and becomes more active during increased oxygen demand, such as in aerobic exercises.
✅ Practical Tip
✔ Strengthening this muscle alongside the pectoralis major enhances upper body stability and performance while helping to prevent shoulder injuries.
🔴 Name & Location: A deep muscle located beneath the pectoralis major
🟠 Anatomy: Connects ribs 3 to 5 to the coracoid process of the scapula
🟡 Function: Stabilizes and moves the scapula; assists in breathing
🟢 Physiology: Composed of both slow- and fast-twitch muscle fibers
🔵 Innervation: Medial pectoral nerve
🟣 Importance: Key for shoulder stabilization and pushing movements
🟤 Exercises: Dips, push-ups, bench press, rowing
⚫ Fun Fact: An important muscle for throwing and striking movements
Subclavius Muscle
Subclavius Muscle
The subclavius is a small, spindle-shaped muscle located beneath the clavicle. It helps stabilize and move the clavicle, playing an important role in protecting the vital blood vessels and nerves beneath it. Additionally, it reduces stress on the shoulder joint. Weakness or tightness in this muscle can lead to restricted shoulder movement and pain in the clavicle area.

✅ Persian Name: Aozle Zir-Targhovei
✅ Latin Name: Subclavius
✅ Common Name: Clavicle Stabilizer Muscle
✅ Location:
🟡 Situated beneath the clavicle
🟡 Extends between the first rib and the clavicle
🟡 Responsible for clavicle stability and assisting shoulder movements
✅ 🦾 Origin
✔ Superior surface of the first rib and its costal cartilage
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ Inferior surface of the clavicle
✅ 📌 Function
✔ Stabilizes the clavicle to prevent excessive movement
✔ Depresses the clavicle during overhead movements
✔ Protects the nerves and vessels beneath the clavicle from compression
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Type
✔ Predominantly composed of slow-twitch fibers (Type I) for long-term stability and endurance
✔ Contains a mix of fast-twitch fibers (Type II) for quick reactions in shoulder stabilization
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Movement and Athletic Performance
✔ Stabilizes the clavicle during shoulder and arm movements
✔ Helps prevent injuries to the clavicle and shoulder joint
✔ Provides support in sports such as boxing, gymnastics, and discus throwing
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ A small but essential muscle for shoulder and neck stability
✔ Weakness can cause excessive strain on other shoulder and neck muscles
🧠 Innervation
✔ Subclavian nerve (branch of the brachial plexus)
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Suprascapular artery
✔ Clavicular branch of the thoracoacromial artery
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Bodybuilding: assists shoulder stability during bench press, push-ups, and overhead movements
✔ Boxing and martial arts: protects the clavicle during punching
✔ Gymnastics and throwing sports: aids stability and reduces stress on the shoulder joint
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Interaction with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Works in coordination with the deltoid, pectoralis major, and trapezius muscles to maintain shoulder stability
✔ Poor function of this muscle can lead to asymmetrical shoulder movement and clavicle pain
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ Muscle weakness can lead to clavicle instability and shoulder problems
✔ Tightness or spasms in this muscle may cause pain and limited upper body mobility
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Key Exercises to Strengthen the Subclavius Muscle
1️⃣ Dumbbell Shrugs – activates the muscle during clavicle stabilization
2️⃣ Overhead Dumbbell Press – strengthens the muscle during overhead movements
3️⃣ Low-to-High Cable Pulls – resistance training for clavicle stability
4️⃣ Push-ups – helps strengthen the muscle during upper body pressing
5️⃣ Shoulder Control with Resistance Bands – improves muscle balance and endurance
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery Movements
✔ Neck & Shoulder Stretch – releases tension in the subclavius muscle
✔ Wall Chest Stretch – increases muscle flexibility and prevents stiffness
✅ Fun Fact
✔ The subclavius is one of the first muscles to have evolved in humans and plays a fundamental role in stabilizing the clavicle during daily activities.
✅ Practical Tip
✔ Strengthening this muscle improves upper body exercise performance and reduces the risk of shoulder joint injuries.
🔴 Name & Location: A small muscle located beneath the clavicle
🟠 Anatomy: Connects the first rib to the underside of the clavicle
🟡 Function: Stabilizes the clavicle and assists shoulder movements
🟢 Physiology: A combination of slow- and fast-twitch muscle fibers
🔵 Innervation: Subclavian nerve
🟣 Importance: Key in clavicle stabilization, upper body movements, and preventing shoulder injuries
🟤 Exercises: Shoulder shrugs, overhead press, low-to-high cable pulls, push-ups
⚫ Fun Fact: One of the key muscles involved in protecting the nerves and vessels beneath the clavicle
Serratus Anterior Muscle
Serratus Anterior Muscle
The serratus anterior is one of the most important muscles for scapular stabilization and movement. Named for its saw-toothed shape as it attaches to the ribs, this muscle plays a key role in maintaining scapular balance and stability. It is highly active during forward pushing movements such as throwing, punching, and push-ups. Strengthening the serratus anterior improves shoulder range of motion, increases endurance in athletic activities, and helps prevent shoulder pain and instability.
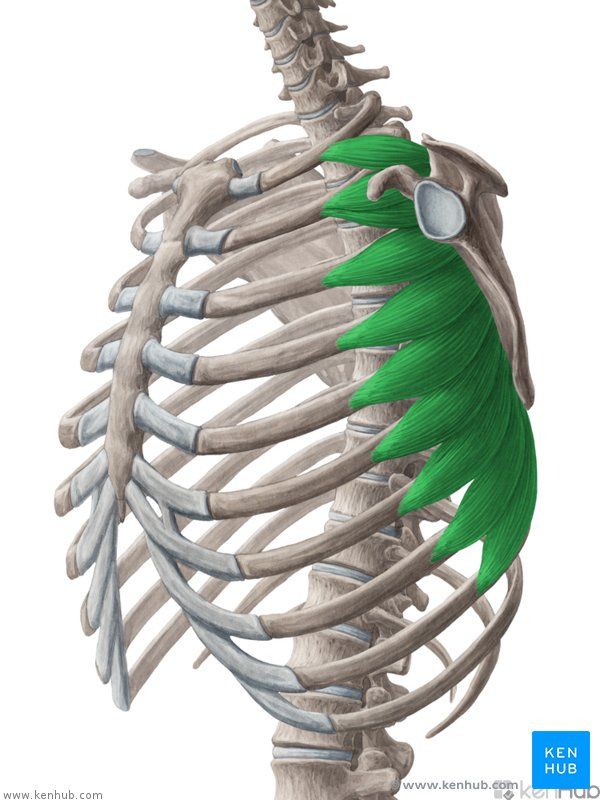
✅ Persian Name: Dandane-ye Ghodami
✅ Latin Name: Serratus Anterior
✅ Common Name: Boxer’s Muscle
✅ Location:
🟡 Located on the lateral aspect of the chest, over the upper ribs
🟡 Originates from the upper ribs and attaches to the medial border of the scapula
🟡 Its primary role is scapular stabilization and protraction (moving the scapula forward)
✅ 🦾 Origin
✔ Ribs 1 to 8 or 9
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ Medial border of the scapula
✅ 📌 Function
✔ Scapular protraction – assists movements such as punching and throwing
✔ Stabilizes the scapula against the rib cage – prevents instability and scapular winging
✔ Upward rotation of the scapula – during arm elevation above the head
✔ Supports pushing movements like push-ups and bench press
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Type
✔ A combination of slow-twitch fibers (Type I) for endurance and fast-twitch fibers (Type II) for rapid movements
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Movement and Athletic Performance
✔ Active in all throwing and punching movements, such as in boxing
✔ Primary scapular stabilizer during exercises like push-ups and bench press
✔ Assists scapular rotation when lifting objects overhead (e.g., weightlifting and discus throwing)
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ A key muscle for shoulder stability and joint injury prevention
✔ Weakness can cause scapular winging, leading to limited upper body movement
🧠 Innervation
✔ Long thoracic nerve
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Thoracodorsal artery
✔ Posterior intercostal arteries
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Boxing and MMA: responsible for powerful and rapid punching motions
✔ Weightlifting: aids proper scapular rotation during heavy lifts
✔ Bodybuilding and fitness: active in pushing exercises such as push-ups, dips, and bench press
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Interaction with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Works in coordination with the trapezius, deltoid, and pectoralis major muscles for proper shoulder stabilization and movement
✔ Poor scapular stabilization due to weakness in this muscle can lead to shoulder pain and decreased athletic performance
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ Weakness in this muscle can cause “scapular winging,” reducing shoulder range of motion
✔ Spasms or weakness may lead to interscapular pain and decreased shoulder stability
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Key Exercises to Strengthen the Serratus Anterior
1️⃣ Scapular push-ups – directly activate and strengthen the muscle
2️⃣ Resistance band punches – simulate punching motions to build strength
3️⃣ Wall slides with resistance band – aid in scapular strengthening and stabilization
4️⃣ Push-ups plus (push-ups with added scapular protraction) – increase muscle endurance
5️⃣ Scapular control exercises with bands – enhance muscle stability
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery Movements
✔ Chest & scapular stretch – improves flexibility and prevents muscle tightness
✔ Scapular mobility drills – enhance control and strengthen the shoulder joint
✅ Fun Fact
✔ The serratus anterior is highly developed in boxers and throwing athletes, which is why it is often called the “boxer’s muscle.”
✅ Practical Tip
✔ If you experience pain or imbalance in the shoulder when raising your arm, this muscle is likely weak. Strengthening and mobility exercises can help improve its function.
🔴 Name & Location: A superficial muscle over the ribs, attached to the scapula
🟠 Anatomy: Originates from ribs 1 to 8 and inserts into the medial border of the scapula
🟡 Function: Stabilizes and moves the scapula, assisting in throwing and pushing movements
🟢 Physiology: Composed of both slow- and fast-twitch muscle fibers
🔵 Innervation: Long thoracic nerve
🟣 Importance: Essential in boxing, bodybuilding, and overhead activities
🟤 Exercises: Scapular push-ups, resistance band punches, scapular control with bands
⚫ Fun Fact: A vital muscle for throwing and combat athletes
2. Deep muscles of the chest
Deep chest muscles
External intercostal muscles
External Intercostals Muscle
The external intercostal muscles are a group of thin, flat muscles located between adjacent ribs. They play a crucial role in the process of inhalation. When these muscles contract, they elevate the ribs and increase the volume of the thoracic cavity, facilitating the entry of air into the lungs.
These muscles also play an important role in stabilizing the chest structure and assisting upper body movements, especially in sports that require deep breathing and thoracic stability.
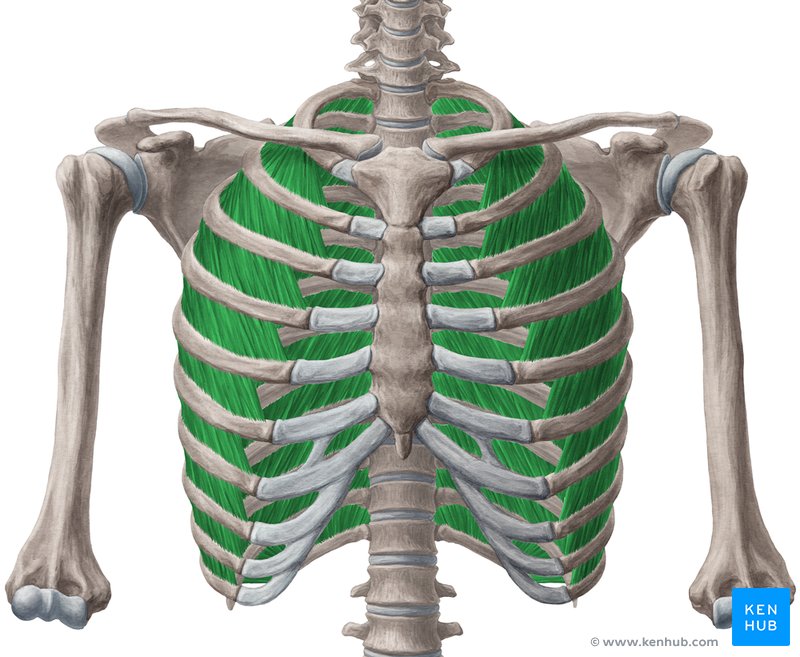
✅ Persian Name: Azolat-e Beyne-dandehi Khareji
✅ Latin Name: External Intercostals
✅ Common Name: Intercostal Respiratory Muscles
✅ Location:
🟡 Located between ribs 1 to 11, extending from the back near the spine to the costal cartilages at the front of the chest
🟡 Positioned in the outer layer of intercostal muscles, lying over the internal intercostal muscles
🟡 Fibers run obliquely from top to bottom and from back to front
✅ 🦾 Origin
✔ Inferior border of the upper ribs
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ Superior border of the lower ribs
✅ 📌 Function
✔ Assists inhalation by elevating the ribs and increasing chest volume
✔ Stabilizes the chest during weight bearing, upper body movements, and physical activities
✔ Contributes to overall chest stability and protects the lungs and heart
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Type
✔ Primarily slow-twitch fibers (Type I) for endurance and sustained respiratory stability
✔ A mix of fast-twitch fibers (Type II) for sudden movements and increased oxygen demand during exercise
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Movement and Athletic Performance
✔ Key muscles in endurance sports such as running, swimming, and climbing
✔ Assist deep inhalation during weightlifting and strength training
✔ Important during core exercises like planks and crunches
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ Since these muscles are continuously engaged in the breathing process, they possess high endurance.
✔ Weakness in these muscles can lead to reduced respiratory capacity and early fatigue during aerobic activities.
🧠 Innervation
✔ Intercostal nerves (T1–T11) originating from the thoracic spinal cord.
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Anterior and posterior intercostal arteries
✔ Internal thoracic artery
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Endurance sports (running, swimming, cycling): strengthening these muscles helps increase lung capacity and improve respiratory performance.
✔ Strength sports (weightlifting, CrossFit): aids in maintaining chest stability and enhances endurance of the lumbar and core muscles.
✔ Combat sports (boxing, wrestling): provides greater oxygen supply and prevents early fatigue.
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Relationship with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Interacts with the diaphragm, abdominal muscles, and lumbar muscles to create proper breathing patterns and maintain upper body stability.
✔ Strengthening these muscles helps improve diaphragm function and optimize oxygen delivery throughout the body.
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ Weakness in these muscles can cause chest tightness and reduced ability to breathe deeply during exercise.
✔ In severe cases, intercostal muscle spasms or strains can lead to intense pain while breathing (Intercostal Strain).
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Key Exercises to Strengthen External Intercostal Muscles
1️⃣ Diaphragmatic Breathing Exercises – enhance strength and flexibility of respiratory muscles
2️⃣ Controlled Inhalation and Exhalation with Weights (Weighted Breathing) – simulates intense exercise conditions
3️⃣ Chest Expansion Stretches – improve rib mobility and range of motion
4️⃣ Planks with Deep Breathing – strengthen core and intercostal muscles
5️⃣ High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) – increase respiratory capacity and muscle endurance
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery Exercises
✔ Side Chest Stretch – helps open the ribs and improve flexibility
✔ Yoga Breathing Techniques – optimize the function of the intercostal muscles
✅ Interesting Fact
✔ External intercostal muscles are significantly stronger in people living at high altitudes, as their bodies rely on these muscles to optimize oxygen intake.
✅ Practical Tip
✔ Improving breathing technique and strengthening these muscles increases lung capacity and enhances athletic performance across all sports.
🔴 Name and Location: Between ribs 1 to 11, on the outer surface of the chest
🟠 Anatomy: Attachment from the inferior border of the upper ribs to the superior border of the lower ribs
🟡 Function: Assists breathing by elevating the ribs and increasing lung capacity
🟢 Physiology: Combination of slow- and fast-twitch fibers for endurance and strength
🔵 Innervation: Intercostal nerves (T1–T11)
🟣 Importance: Key in endurance, strength, and combat sports
🟤 Exercises: Diaphragmatic breathing, planks, interval training, chest stretches
⚫ Interesting Facts: Strengthened at high altitudes and contribute to improved respiratory performance
Internal Intercostal Muscles
Internal Intercostal Muscles
The internal intercostal muscles are a group of thin, flat muscles located beneath the external intercostal muscles and play a crucial role in active exhalation. During deep exhalation, these muscles pull the ribs downward, helping to decrease the volume of the chest cavity.
They also play a key role in maintaining chest stability, protecting internal organs, and assisting upper body movements—especially in sports that require breath control and core strength.
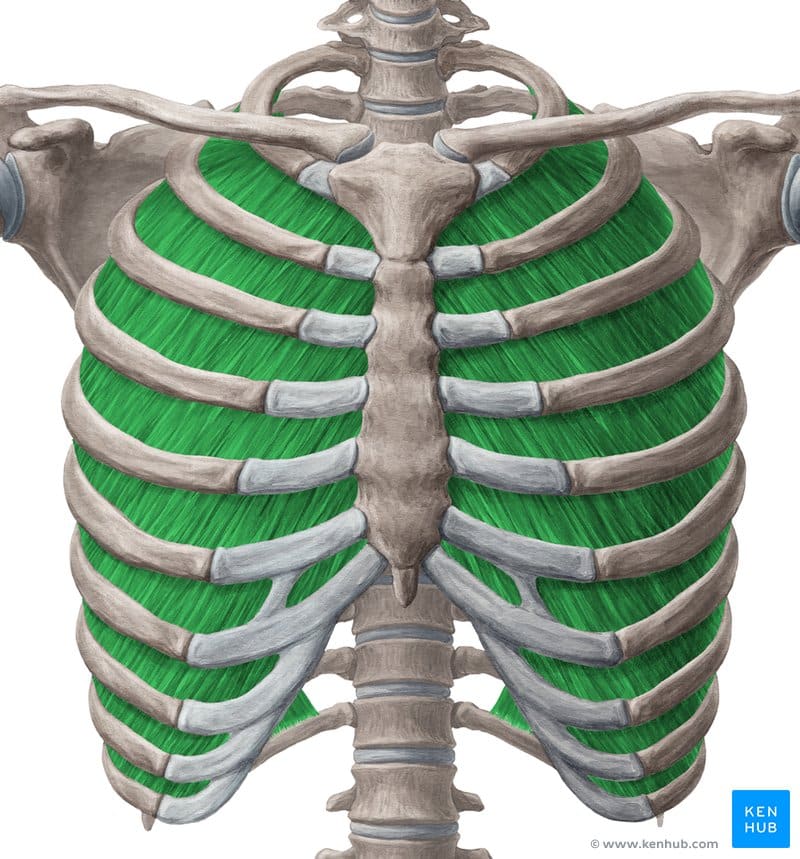
✅ Persian Name: Azolate Beyne Dandei Khareji
✅ Latin Name: Internal Intercostals
✅ Common Name: Expiratory Intercostal Muscles
✅ Location:
🟡 Extend between ribs 1 to 11, on the inner surface of the chest
🟡 Located beneath the external intercostal muscles and function in the opposite direction
🟡 Muscle fibers run obliquely from bottom to top and front to back
✅ 🦾 Origin
✔ Superior border of the lower ribs
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ Inferior border of the upper ribs
✅ 📌 Function
✔ Assists exhalation by lowering the ribs and decreasing chest volume
✔ Stabilizes the chest during strength and endurance sports
✔ Helps maintain pressure balance within the chest cavity
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Type
✔ Primarily slow-twitch fibers (Type I) for respiratory endurance and sustained stability
✔ A combination of fast-twitch fibers (Type II) to support forceful exhalation during intense exercise
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Movement and Athletic Performance
✔ Facilitates forceful exhalation in sports like running, swimming, and interval training
✔ Primary stabilizer of the chest during weightlifting and explosive movements
✔ Crucial for breath control and increasing lung capacity in bodybuilding and endurance training
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ These muscles are constantly engaged in the breathing process, so they possess high endurance.
✔ Weakness in these muscles can reduce exhalation efficiency and decrease oxygen delivery during exercise.
🧠 Innervation
✔ Intercostal nerves (T1–T11) originating from the thoracic spinal cord.
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Anterior and posterior intercostal arteries
✔ Internal thoracic artery
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Endurance sports (running, swimming, cycling): aids in improving exhalation and preventing early fatigue
✔ Strength sports (weightlifting, CrossFit): stabilizes the chest during heavy loads
✔ Combat sports (boxing, wrestling): enhances respiratory endurance and improves diaphragm control
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Relationship with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Interacts with the diaphragm, abdominal muscles, and external intercostals to balance breathing patterns
✔ Strengthening these muscles aids in improving respiratory function and optimizing lung capacity
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ Weakness in these muscles can reduce exhalation strength and increase fatigue during intense exercise.
✔ Spasms or strains of the internal intercostal muscles may cause pain during exhalation or chest tightness.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Key Exercises to Strengthen Internal Intercostal Muscles
1️⃣ Resistance Breathing Exercises – enhance exhalation strength
2️⃣ Controlled Inhalation and Exhalation with Weights (Weighted Breathing) – improve respiratory endurance
3️⃣ Chest Expansion Stretches – increase chest flexibility
4️⃣ High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) – boost lung capacity
5️⃣ Planks with Controlled Breathing – stabilize intercostal and core muscles
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery Exercises
✔ Side Chest Stretch – improves rib mobility
✔ Yoga Techniques for Exhalation – optimizes intercostal muscle function
✅ Interesting Fact
✔ Internal intercostal muscles are significantly stronger in professionals like divers and endurance runners, as they require deeper and more controlled exhalation.
✅ Practical Tip
✔ Improving exhalation technique and strengthening these muscles reduces fatigue and enhances athletic performance.
🔴 Name and Location: Between ribs 1 to 11, on the inner surface of the chest
🟠 Anatomy: Attachment from the superior border of the lower ribs to the inferior border of the upper ribs
🟡 Function: Assists exhalation by lowering the ribs and stabilizing the chest
🟢 Physiology: Combination of slow- and fast-twitch fibers for endurance and strength
🔵 Innervation: Intercostal nerves (T1–T11)
🟣 Importance: Key in endurance, strength, and combat sports
🟤 Exercises: Resistance breathing, planks, HIIT, chest stretches
⚫ Interesting Facts: Stronger in divers and endurance athletes
Innermost Intercostal Muscles
Innermost Intercostal Muscles
The innermost intercostal muscles are the deepest layer of the intercostal muscles, located on the inner surface of the chest wall. They play a role in active exhalation and, together with the internal intercostal muscles, help lower the ribs and decrease the volume of the chest cavity.
Due to their deep position, these muscles receive less attention than the external and internal intercostals, but they are crucial for maintaining chest wall stability and enhancing respiratory function.
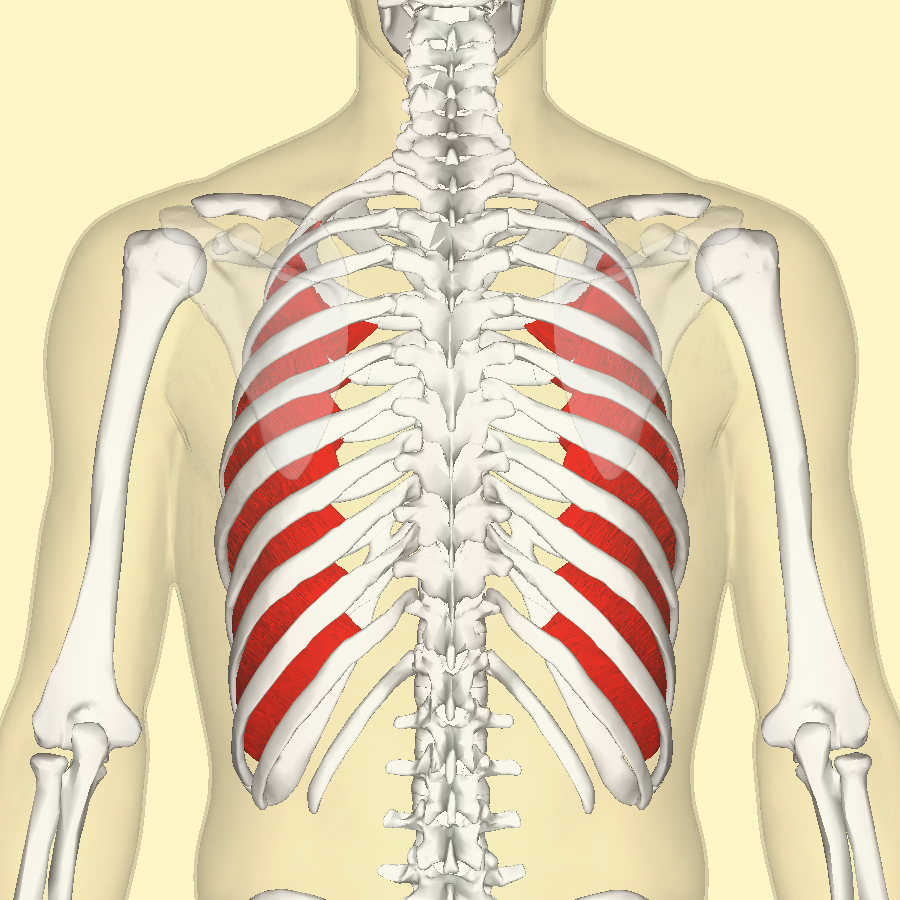
✅ Persian Name: Azole Beyne Dandei Dakhelitarin
✅ Latin Name: Innermost Intercostals
✅ Common Name: Deepest Intercostal Muscles
✅ Location:
🟡 Located deeper than the internal intercostal muscles, closer to the pleura
🟡 Span regionally between the ribs, attaching from the inner surface of the upper ribs to the inner surface of the lower ribs
🟡 Muscle fibers run vertically, similar to the internal intercostal muscles
✅ 🦾 Origin
✔ Inner surface of the upper ribs
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ Inner surface of the lower ribs
✅ 📌 Function
✔ Assists exhalation by lowering the ribs and decreasing chest volume
✔ Stabilizes the chest wall during breathing and upper body movements
✔ Supports the internal intercostal muscles in regulating intrathoracic pressure
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Type
✔ A mix of slow-twitch fibers (Type I) for endurance during continuous breathing
✔ Some fast-twitch fibers (Type II) to assist with forceful exhalation and lung pressure control
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Movement and Athletic Performance
✔ Active in controlling the breathing process during endurance sports such as running, swimming, and cycling
✔ Stabilize the chest during weightlifting and CrossFit workouts
✔ Enhance deep exhalation ability in yoga, meditation, and breathing exercises
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ A small but influential muscle in the active exhalation process.
✔ Weakness in these muscles can reduce respiratory efficiency and cause early fatigue in endurance sports.
🧠 Innervation
✔ Intercostal nerves (T1–T11) originating from the thoracic spinal cord.
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Anterior and posterior intercostal arteries
✔ Internal thoracic artery
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Endurance sports (running, swimming, climbing): better control of exhalation and optimized breathing
✔ Strength sports (weightlifting, CrossFit): stabilizes the chest during explosive movements
✔ Combat sports (boxing, wrestling): aids in improving respiratory endurance and proper breathing technique execution
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Relationship with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Works in coordination with the diaphragm, internal intercostal muscles, and abdominal muscles to regulate intrathoracic pressure
✔ Enhances chest stability during strength and aerobic exercises
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ Weakness in these muscles can reduce exhalation capacity and increase fatigue during physical activities.
✔ Tightness or spasms in these muscles may cause chest pain during deep breathing.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Key Exercises to Strengthen Innermost Intercostal Muscles
1️⃣ Resistance Breathing Exercises – improve exhalation performance
2️⃣ Controlled Breathing in Yoga (Pranayama) – strengthen respiratory muscle function
3️⃣ High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) – increase respiratory muscle strength and lung capacity
4️⃣ Planks with Controlled Breathing – stabilize intercostal and core muscles
5️⃣ Controlled Exhalation During Strength Training – optimize breathing in weightlifting
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery Exercises
✔ Side Chest Stretch – improves rib mobility
✔ Diaphragmatic Stretching Exercises – increases flexibility of the respiratory muscles
✅ Interesting Fact
✔ The innermost intercostal muscles become stronger and more flexible in individuals who practice breathing exercises, leading to increased respiratory capacity.
✅ Practical Tip
✔ Better control of exhalation and strengthening these muscles reduce fatigue and enhance athletic endurance.
🔴 Name and Location: Deepest intercostal layer in the chest wall
🟠 Anatomy: Attachments from the inner surface of the upper ribs to the inner surface of the lower ribs
🟡 Function: Assists exhalation by lowering the ribs and stabilizing the chest
🟢 Physiology: Combination of slow- and fast-twitch fibers for endurance and strength
🔵 Innervation: Intercostal nerves (T1–T11)
🟣 Importance: Key in respiratory control during endurance and strength sports
🟤 Exercises: Resistance breathing, yoga, HIIT, planks with controlled breathing
⚫ Interesting Facts: Breathing exercises enhance their strength and flexibility
Transversus Thoracis Muscle
Transversus Thoracis Muscle
The transversus thoracis muscle is a deep, thin muscle located on the inner wall of the chest cavity, attaching to the sternum. It plays a role in active exhalation by decreasing chest volume and lowering the ribs, thereby assisting in the expulsion of air from the lungs.
In addition to its role in respiration, this muscle helps strengthen the chest wall, stabilize the ribs, and support overall respiratory function during intense physical activities.

✅ Persian Name: Azole Arzi Ghafase Sine
✅ Latin Name: Transversus Thoracis
✅ Common Name: Sternum Stabilizer Muscle
✅ Location:
🟡 On the inner surface of the chest, attaching from the posterior part of the sternum to the upper ribs
🟡 Forms part of the inner chest wall and helps stabilize the chest structure
🟡 Assists in decreasing chest volume and facilitating air expulsion during exhalation
✅ 🦾 Origin
✔ Posterior surface of the sternum
✔ Costal cartilages of ribs 3 to 6
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ Inner border of ribs 2 to 6
✅ 📌 Function
✔ Assists exhalation by lowering the ribs and decreasing chest volume
✔ Stabilizes the chest during breathing and upper body movements
✔ Helps maintain the position and integrity of the sternum and ribs structure
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Type
✔ A mix of slow-twitch fibers (Type I) for endurance and maintaining respiratory structure
✔ Some fast-twitch fibers (Type II) to assist with rapid exhalation and chest pressure control
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Movement and Athletic Performance
✔ Plays a role in improving active exhalation during endurance sports such as running, swimming, and cycling
✔ Assists in decreasing chest volume and enhancing air expulsion from the lungs during intense physical activities
✔ Acts as a structural stabilizer in strength training exercises that require chest control, such as weightlifting and CrossFit
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ A small but important muscle involved in breathing and stabilizing the sternum structure.
✔ Weakness in this muscle can reduce exhalation control and increase strain on other respiratory muscles.
🧠 Innervation
✔ Intercostal nerves (T2–T6) originating from the thoracic spinal cord.
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Anterior intercostal arteries
✔ Internal thoracic artery
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Endurance sports (running, swimming, climbing): aids in improving exhalation and enhancing respiratory efficiency
✔ Strength sports (weightlifting, CrossFit): stabilizes the chest during heavy training sessions
✔ Combat sports (boxing, wrestling): helps increase respiratory endurance and better breath control during fights
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Relationship with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Interacts with the diaphragm, internal intercostal muscles, and abdominal muscles to regulate intrathoracic pressure
✔ Strengthening these muscles helps improve sternum stability and enhance chest wall strength
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ Weakness in these muscles can reduce exhalation ability and decrease lung capacity.
✔ Muscle tightness or spasms may cause chest pain and a feeling of restricted deep breathing.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Key Exercises to Strengthen the Transversus Thoracis Muscle
1️⃣ Resistance Breathing Exercises – improve exhalation performance
2️⃣ Controlled Breathing in Yoga (Pranayama) – strengthen respiratory muscle function
3️⃣ High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) – enhance exhalation muscle performance
4️⃣ Controlled Exhalation During Strength Training – improve breath control in weightlifting
5️⃣ Chest Expansion Stretching – increase mobility and reduce muscle tension in the chest
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery Exercises
✔ Side Chest Stretch – increases chest flexibility
✔ Diaphragmatic Stretching Exercises – improves exhalation function
✅ Interesting Fact
✔ The transversus thoracis muscle plays an important role in decreasing chest volume and aiding exhalation, yet it is often overlooked in training programs.
✅ Practical Tip
✔ Regular breathing exercises and strengthening this muscle improve respiratory efficiency and enhance lung performance in athletes.
🔴 Name and Location: A deep muscle on the inner surface of the chest, attached to the sternum
🟠 Anatomy: Attaches from the inner surface of the sternum to ribs 2 through 6
🟡 Function: Assists exhalation, stabilizes the chest, and reduces lung volume
🟢 Physiology: Composed of both slow- and fast-twitch fibers for exhalation and structural support
🔵 Innervation: Intercostal nerves (T2–T6)
🟣 Importance: Key for breathing, chest wall stability, and endurance sports
🟤 Exercises: Resistance breathing, yoga, HIIT, breath control
⚫ Interesting Facts: Crucial for active exhalation and sternum stabilization
Subcostal Muscles
Subcostal Muscles
The subcostal muscles are a group of small, deep muscles located on the posterior chest wall, running along the ribs.
These muscles resemble the internal intercostal muscles but are typically found in the posterior part of the chest (behind the ribs). Their role is to assist with exhalation by decreasing chest volume, stabilizing the ribs, and supporting chest movements during respiration.
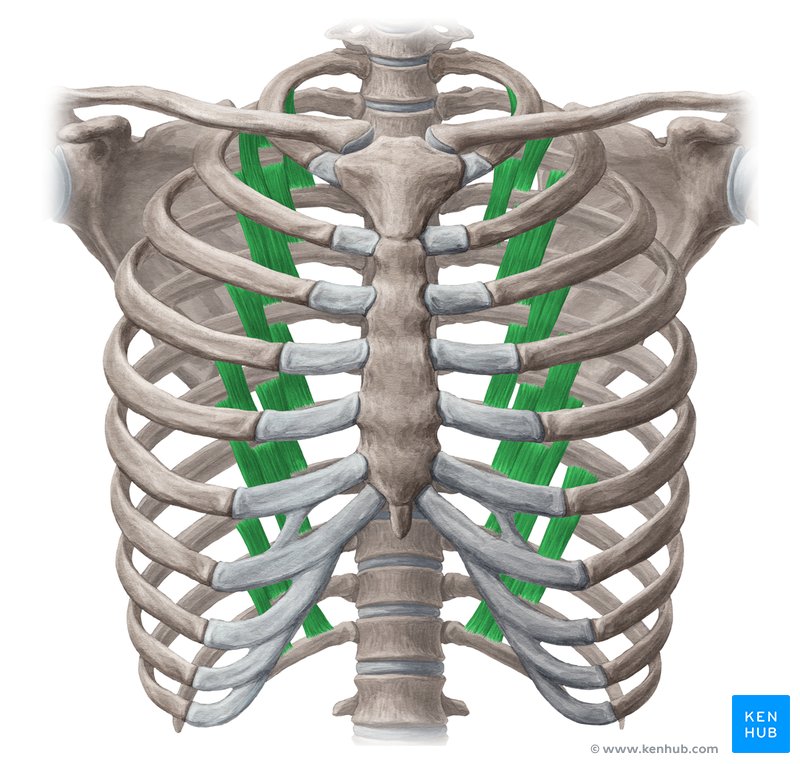
✅ Persian Name: Azolat Zir Dandei
✅ Latin Name: Subcostal Muscles
✅ Common Name: Posterior Chest Muscles
✅ Location:
🟡 Located on the posterior chest wall, between the ribs and near the pleura
🟡 Usually found in the lower chest region (ribs 10 to 12), but may also be present in upper areas
🟡 Function as accessory muscles controlling rib movements during respiration
✅ 🦾 Origin
✔ Inner surface of the upper ribs
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ Inner surface of the lower ribs, typically spanning over one rib below their origin
✅ 📌 Function
✔ Assists exhalation by lowering the ribs and decreasing chest volume
✔ Stabilizes the chest and prevents excessive rib movement
✔ Helps coordinate the function of the diaphragm and other respiratory muscles
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Type
✔ Slow-twitch fibers (Type I) for maintaining endurance during continuous breathing
✔ Some fast-twitch fibers (Type II) to assist active exhalation during intense exercise
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Movement and Athletic Performance
✔ Stabilizes the chest during strength sports (weightlifting, CrossFit)
✔ Assists deep exhalation in endurance sports (running, swimming, cycling)
✔ Provides structural stability of the chest in sports requiring core stability
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ A small but influential muscle in chest stability and the breathing process
✔ Weakness in these muscles can lead to reduced exhalation control and rib instability during intense movements
🧠 Innervation
✔ Intercostal nerves (T6–T12) originating from the thoracic spinal cord.
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Anterior and posterior intercostal arteries
✔ Internal thoracic artery
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Endurance sports (running, swimming, climbing): better control of exhalation and optimized breathing
✔ Strength sports (weightlifting, CrossFit): stabilizes the chest during heavy movements
✔ Combat sports (boxing, wrestling): enhances respiratory endurance and improves breathing techniques
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Relationship with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Works with the internal intercostal muscles and transversus thoracis muscle to coordinate exhalation
✔ Helps stabilize the lower ribs during intense and athletic activities
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ Weakness in these muscles can cause poor coordination in breathing and reduced exhalation performance.
✔ Tightness or spasms may lead to pain in the lower chest area and limit deep exhalation.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Key Exercises to Strengthen the Subcostal Muscles
1️⃣ Resistance Breathing Exercises – improve exhalation performance
2️⃣ Controlled Breathing in Yoga (Pranayama) – strengthen respiratory muscle function
3️⃣ High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) – enhance exhalation muscle strength
4️⃣ Chest Expansion Stretching – increase mobility and reduce muscle tension in the chest
5️⃣ Controlled Exhalation During Strength Training – optimize breathing during heavy workouts
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery Exercises
✔ Side Chest Stretch – increases chest flexibility
✔ Diaphragmatic Stretching Exercises – improves exhalation function
✅ Interesting Fact
✔ The subcostal muscles exhibit anatomical variation, with some individuals having more developed muscles while others have less pronounced ones.
✅ Practical Tip
✔ Regular breathing exercises and strengthening this muscle improve respiratory efficiency and enhance lung performance in athletes.
🔴 Name and Location: Small, deep muscles on the posterior chest wall, between the ribs
🟠 Anatomy: Attach from the inner surface of the upper ribs to the inner surface of the lower ribs
🟡 Function: Assist exhalation, stabilize the chest, and reduce lung volume
🟢 Physiology: Composed of both slow- and fast-twitch fibers for exhalation and structural support
🔵 Innervation: Intercostal nerves (T6–T12)
🟣 Importance: Key for breathing, chest wall stability, and endurance sports
🟤 Exercises: Resistance breathing, yoga, HIIT, breath control
⚫ Interesting Facts: May be more developed in some individuals
Diaphragm Muscle
Diaphragm Muscle
The diaphragm is a thin, dome-shaped muscle that separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominal cavity and is the primary muscle involved in the process of inhalation.
During inhalation, the diaphragm contracts and moves downward, increasing the volume of the chest cavity and allowing air to enter the lungs. During exhalation, the diaphragm relaxes and returns to its original position, aiding in the expulsion of air from the lungs. The diaphragm’s vital roles extend beyond breathing, including supporting the abdominal organs and assisting the circulatory and lymphatic systems.
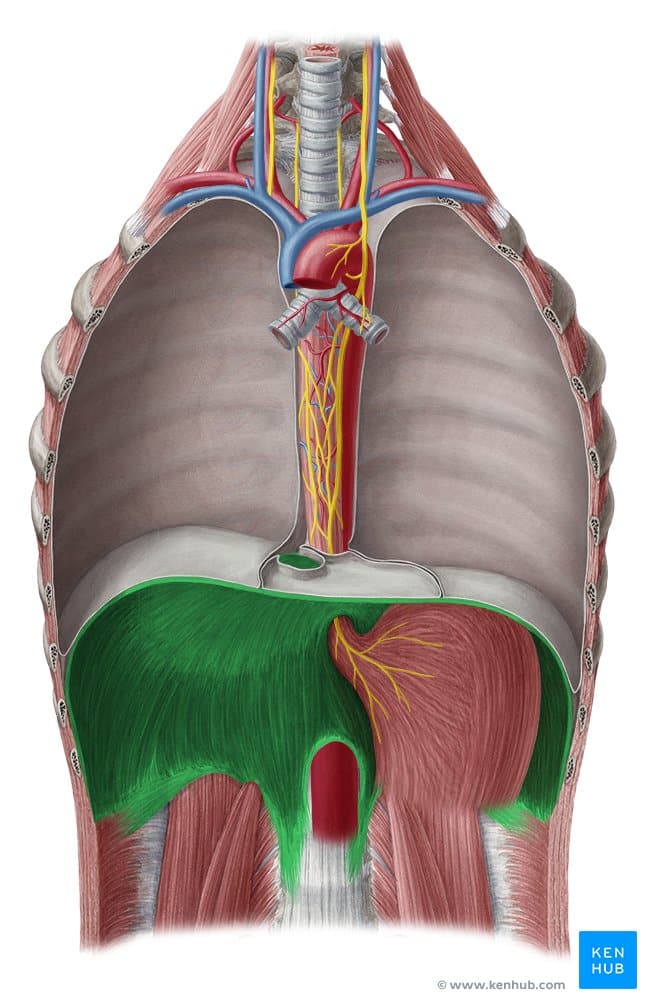
✅ Persian Name: Diafragm
✅ Latin Name: Diaphragm
✅ Common Name: Primary Respiratory Muscle
✅ Location:
🟡 Located at the base of the chest cavity and top of the abdomen, separating the thoracic and abdominal cavities
🟡 Contracts and moves downward during inhalation, relaxes and rises during exhalation
🟡 Connected to several vital organs including the lungs, heart, stomach, liver, and spleen
✅ 🦾 Origin
✔ Costal cartilages of ribs 7–12
✔ Lumbar vertebrae L1–L3
✔ Xiphoid process of the sternum
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ Central tendon of the diaphragm – a fibrous sheet located at the center of the diaphragm that allows it to contract and change shape.
✅ 📌 Function
✔ The primary function of the diaphragm is respiration:
- Inhalation: When it contracts, it moves downward, increasing the chest cavity volume and allowing air to enter the lungs.
- Exhalation: When relaxed, it moves upward, decreasing chest cavity volume and expelling air from the lungs.
✔ Assists with intra-abdominal pressure for digestion, vomiting, hiccups, and childbirth.
✔ Plays a role in pumping blood and lymph from the abdomen to the chest during respiration.
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Type
✔ Composed mostly of slow-twitch fibers (Type I) to sustain lifelong continuous activity
✔ Contains fast-twitch fibers (Type II) to assist with rapid breathing during intense exercise or stress
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Movement and Athletic Performance
✔ Strengthening the diaphragm in endurance sports (running, swimming, cycling) enhances respiratory system efficiency.
✔ In strength training (weightlifting, CrossFit), it stabilizes the chest and improves breath control during heavy lifts.
✔ In combat sports (boxing, wrestling), strengthening it improves respiratory endurance and helps prevent fatigue.
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ One of the most resilient muscles in the body, functioning continuously throughout life without rest.
✔ Weakness in this muscle leads to respiratory issues, reduced athletic endurance, and impaired digestive function.
🧠 Innervation
✔ Phrenic nerve (C3–C5), originating from the cervical spinal cord, responsible for controlling diaphragm movement.
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Inferior phrenic artery
✔ Intercostal arteries
✔ Internal thoracic artery
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Endurance sports: enhances respiratory efficiency and oxygen uptake
✔ Strength training: improves breath control and endurance during intense workouts
✔ Yoga and meditation: aids in body relaxation and regulates the nervous system through deep breathing
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Relationship with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Works together with the abdominal and intercostal muscles to regulate intra-abdominal and intrathoracic pressure
✔ Stabilizes the spine during heavy lifting and sudden movements
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ Dysfunction of the diaphragm can lead to conditions such as diaphragmatic paralysis and respiratory disorders.
✔ Weakness or spasms in the diaphragm may cause chronic hiccups and breathing difficulties during sleep.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Key Exercises to Strengthen the Diaphragm
1️⃣ Diaphragmatic Breathing – enhances diaphragm strength
2️⃣ Resistance Breathing Exercises – improves lung capacity
3️⃣ Pranayama Yoga – regulates diaphragm function
4️⃣ HIIT Workouts – increases diaphragm power for intense sports
5️⃣ Chest Stretching Exercises – improves diaphragm flexibility
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery Exercises
✔ Side Chest Stretch – increases diaphragm flexibility
✔ Meditation and Deep Breathing Exercises – aid muscle recovery and improve function
✅ Interesting Fact
✔ The diaphragm is the only muscle in the body that works continuously throughout a person’s entire life, and survival is impossible without it.
✅ Practical Tip
✔ Individuals with a stronger diaphragm receive more oxygen and have greater endurance in intense sports.
🔴 Name and Location: Dome-shaped muscle separating the chest cavity from the abdomen
🟠 Anatomy: Attaches from the lower ribs, lumbar vertebrae, and sternum to the central tendon
🟡 Function: Primary respiratory muscle, assists exhalation, and stabilizes intra-abdominal pressure
🟢 Physiology: Mostly slow-twitch fibers for high endurance
🔵 Innervation: Phrenic nerve (C3–C5)
🟣 Importance: Essential for life, sports performance, and abdominal pressure control
🟤 Exercises: Diaphragmatic breathing, yoga, HIIT, chest stretching
⚫ Interesting Facts: The only muscle that works continuously throughout life without rest.
Interesting and Practical Facts
1️⃣ The pectoralis major muscle can generate up to 250 kilograms of force!
✔ In the strongest people in the world, this muscle can lift bench press weights up to 250 kilograms. However, without strength training, it may not even be able to handle 20 kilograms!
2️⃣ A tear in the pectoralis major muscle is one of the most painful sports injuries.
✔ When this muscle tears, it is often accompanied by a "pop" sound or muscle rupture, causing severe bruising, loss of strength, and even muscle deformity. This type of tear commonly occurs in bodybuilders who lift heavy weights during the bench press.
3️⃣ Women also have strong pectoralis major muscles, but they are hidden beneath a layer of fat tissue!
✔ The pectoralis major muscle is the same in both women and men, but in women it is less visible due to fat tissue and mammary glands. Therefore, chest exercises in women enhance the shape and natural lift of the breasts, rather than reducing their size!
4️⃣ The pectoralis major muscle contributes to 35% of daily movements!
✔ From opening doors, putting on clothes, swimming, and throwing a ball to combat movements, this muscle plays a role in most daily activities! So strengthening it isn’t just for aesthetics—it’s highly functional too.
5️⃣ Paralysis of the pectoralis minor muscle can cause impaired shoulder blade (scapular) movement.
✔ The pectoralis minor is a small muscle located beneath the pectoralis major. If this muscle is injured or weak, it can cause movement problems in the shoulder blade and shoulder, which may even affect overall body balance!
6️⃣ Up to 80% of the final shape of the chest muscles is determined by genetics!
✔ Even with the best training program, the shape and attachment of your chest muscle fibers depend largely on your genetics. That’s why some people have wider chests while others have rounder ones.
7️⃣ The pectoralis major muscle affects respiratory function.
✔ During deep breathing, especially in activities like running and swimming, the pectoral muscles help elevate the chest and increase lung capacity. So, if you have breathing difficulties, strengthening your chest muscles might help!
8️⃣ Increasing chest muscle strength also improves pulling power!
✔ Contrary to popular belief that chest muscles only play a role in pressing movements, they also assist the back muscles during pulling actions. That’s why people with strong chests often perform better in pull-ups!
9️⃣ Developing the upper part of the chest is more challenging than the middle and lower sections.
✔ The reason is that the clavicular head contains fewer muscle fibers and they are less frequently engaged. Therefore, to develop this area, you need to perform targeted exercises like incline bench presses.
🔟 Neglecting chest muscle training can lead to poor posture and a rounded, hunched back!
✔ If your back muscles are stronger than your chest muscles, your body tends to pull backward. Conversely, if your chest muscles are stronger than your back muscles, your body leans forward. This muscular imbalance can lead to neck, back, and shoulder pain.
Conclusion
Understanding the chest muscles and their functions not only enhances your grasp of upper body movements and breathing but also improves athletic performance, helps prevent injuries, and boosts overall quality of life.
An examination of these muscles based on Gray’s Anatomy reveals that each muscle plays a specific role in the respiratory system, chest stabilization, and strength movements. From superficial muscles like the pectoralis major to deep muscles such as the diaphragm and intercostals, they all work together in harmony to provide stability, movement, and respiration.
Understanding these structures and performing appropriate exercises is key to improving athletic performance and overall physical health.

References
Resources
Anatomy and medical books :
Gray's Anatomy (one of the standard references in anatomy)
Netter's Atlas of Human Anatomy (a well-known illustrated atlas in anatomy)
Clinically Oriented Anatomy by Keith Moore
Medical databases :
PubMed (for scientific and research articles)
MedlinePlus (health and medical information)
WebMD (for practical and general health information)
Sports and training references :
Strength Training Anatomy by Frederic Delavier
Essentials of Strength Training and Conditioning by NSCA
Well-known articles and training programs by international coaches
Medical databases :
PubMed (for scientific and research articles)
MedlinePlus (health and medical information)
WebMD (for practical and general health information)
Specialized sports and health websites :
Images used:
(Kenhub) kenhub.com
Further Reading
Further reading
Pelank Life | Body Health Assessment
The Best Body Health Calculators Using Scientific Methods
Developed by Pelank Life ©