Back Muscle Groups
Muscle Groups of the Back
Introduction
Introduction
The human body is a complex system of muscles, joints, and movement structures, each playing a crucial role in our daily functions. Among these structures, the back muscles are one of the most important muscle groups. They not only provide stability and balance to the body but also play a key role in the movements of the spine and upper limbs. These muscles range from the most superficial layers, which control major movements of the upper limbs, to the deep muscles that contribute to the stabilization and strength of the spine.
In this page, we examine the anatomy of the back muscles based on scientific standards and inspired by Gray’s Anatomy. This book, one of the most reputable and recognized sources in the field of anatomy, provides a detailed description of the back muscles and highlights their vital role in body movements and spinal stability. We will present a precise classification of these muscles and analyze their functions, anatomical significance, and applications in sports activities and daily life.
🔹 In this review, key points include:
✅ The location and function of each muscle in body movements
✅ The connection of back muscles with other musculoskeletal components
✅ The role of these muscles in sports and injury prevention
This article serves as a comprehensive guide for athletes, coaches, and anatomy enthusiasts who seek a deeper understanding of the function of back muscles and their relationship with body movements.
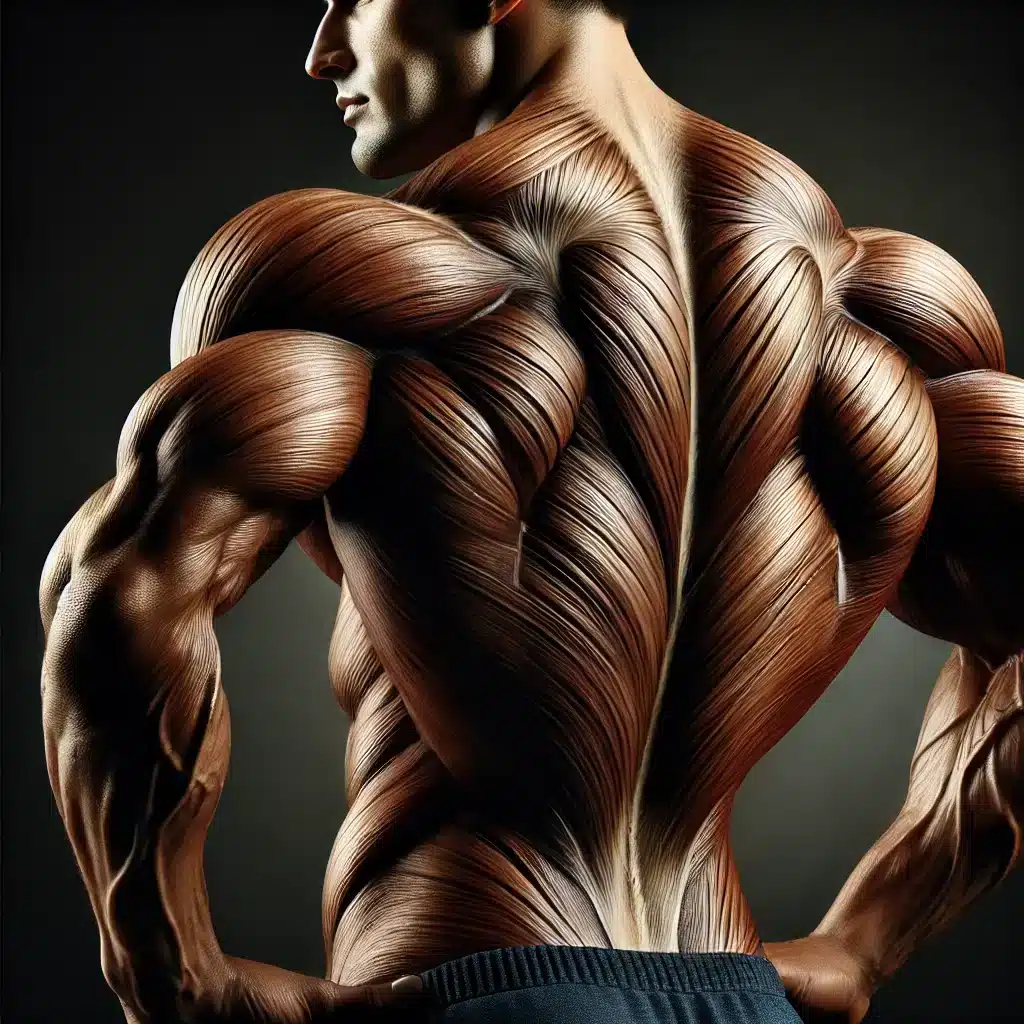

1. Superficial back muscles
Superficial Muscles of the Back
Trapezius muscle
Trapezius Muscle
The trapezius muscle is one of the most important superficial back muscles, extending from the occipital region to the middle of the back. It plays a key role in shoulder movements, scapular stabilization, and neck motions. Strengthening this muscle improves shoulder endurance, reduces neck pain, and enhances overall posture.
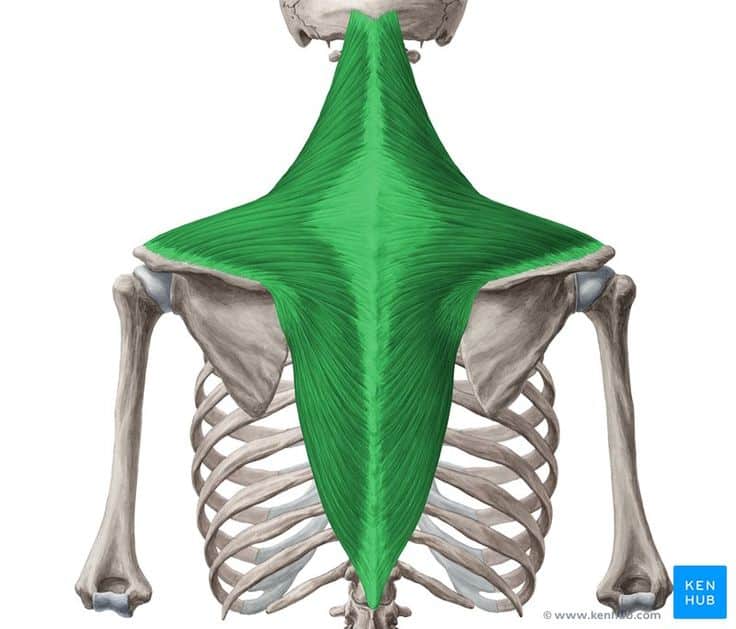
✅ Persian Name: ذوزنقهای
✅ Latin Name: Trapezius
✅ Common Name: Trapezius muscle
✅ Location:
🟡 A superficial muscle extending from the base of the skull to the twelfth thoracic vertebra (T12).
🟡 Positioned as a broad, diamond-shaped muscle on both sides of the spine.
🟡 Responsible for shoulder movements, scapular stabilization, and assisting neck motions.
✅ 🦾 Origin
✔ Occipital bone
✔ Cervical ligamentum nuchae
✔ Cervical and thoracic vertebrae (C7-T12)
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ Clavicle (lateral third)
✔ Acromion process of the scapula
✔ Spine of the scapula
✅ 📌 Division and Function | Muscle Roles
🔹 The trapezius muscle consists of three main parts, each with different functions:
1️⃣ Upper (Superior) part
✔ Elevates the scapula (like shrugging the shoulders)
✔ Assists in head rotation and neck flexion
2️⃣ Middle part
✔ Retracts the scapula (drawing the shoulder blades closer together)
3️⃣ Lower (Inferior) part
✔ Depresses the scapula (pressing the shoulders downward)
✔ Assists in upward-to-downward rotation of the scapula
✅ Main Functions:
✔ Stabilization and movement of the scapula
✔ Assistance in head and neck movements
✔ Providing stability during shoulder and arm motions
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Types
✔ A combination of slow-twitch fibers (Type 1) for endurance and fast-twitch fibers (Type 2) for rapid movements.
✔ The lower part contains more slow-twitch fibers, aiding in endurance maintenance.
✔ The upper part has a higher proportion of fast-twitch fibers, suited for explosive and quick movements.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Motor and Sports Performance
✔ Plays a key role in weightlifting, bodybuilding, swimming, gymnastics, and wrestling.
✔ Active during overhead press, pull-ups, deadlifts, and rowing movements.
✔ Strengthening this muscle increases neck endurance and reduces injuries caused by spinal stress.
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ This muscle is engaged in all overhead and shoulder movements.
✔ Weakness in this muscle leads to reduced endurance in strength training and increases the risk of shoulder and neck pain.
🧠 Innervation | Neural Control
✔ Accessory nerve (Cranial Nerve XI)
✔ Branches of cervical nerves (C3-C4)
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Transverse cervical artery
✔ Suprascapular artery
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Important in sports such as bodybuilding, weightlifting, swimming, wrestling, and boxing.
✔ Vital for head and neck stability in American football, rugby, and martial arts.
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Relationship with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Works alongside the rhomboid muscles, levator scapulae, and latissimus dorsi in scapular movement and stabilization.
✔ Weakness in this muscle leads to poor posture, neck pain, and limited shoulder mobility.
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ Spasms and tightness in this muscle are common and often cause pain in the neck and upper shoulder area.
✔ Weakness or lack of strengthening can lead to shoulder drooping and reduced power in overhead movements.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Key Exercises to Strengthen the Trapezius Muscle
1️⃣ Dumbbell or Barbell Shrugs – Increase size and strength of the upper trapezius
2️⃣ Wide-Grip Pull-Ups – Engage the middle and lower parts of the muscle
3️⃣ Deadlifts – Strengthen the entire trapezius muscle
4️⃣ Bent-Over Rows with Barbell or Dumbbells – Target the middle portion of the muscle
5️⃣ Face Pulls with Cable – Enhance strength and endurance of the middle and lower trapezius
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery Exercises
✔ Neck Stretch – Reduces tension in the upper trapezius
✔ Trapezius Stretch – Increases flexibility and reduces spasms
✔ Shoulder Stretch – Improves range of motion
✅ Interesting Fact:
✔ The trapezius muscle plays a crucial role not only in shoulder and neck movements but also in stabilizing the spine and controlling upper body motions.
✅ Practical Tip:
✔ Combining strength exercises (such as deadlifts) with stretching movements (like neck stretches) is highly effective for improving performance and preventing muscle injuries.
🔴 Name and Location: A superficial muscle on both sides of the spine from the neck to mid-back
🟠 Anatomy: Three parts (upper, middle, lower) with distinct functions
🟡 Function: Stabilizes and moves the scapula; assists head and neck movements
🟢 Physiology: Combination of slow- and fast-twitch fibers for endurance and strength
🔵 Innervation: Accessory nerve and cervical nerves (C3-C4)
🟣 Importance: Active in bodybuilding, weightlifting, swimming, and martial arts
🟤 Exercises: Shrugs, deadlifts, pull-ups, rows, neck stretches
⚫ Interesting Fact: The most important muscle for overhead movements and shoulder stabilization
Latissimus dorsi muscle
Latissimus Dorsi Muscle
The latissimus dorsi is one of the strongest and widest superficial back muscles, playing a crucial role in pulling movements, backward bending, and internal rotation of the arm. It extends from the lower spine to the humerus and is responsible for generating pulling force in exercises like pull-ups, swimming, and rowing. Strengthening this muscle enhances pulling power, improves body posture, and reduces the risk of lower back and shoulder injuries.
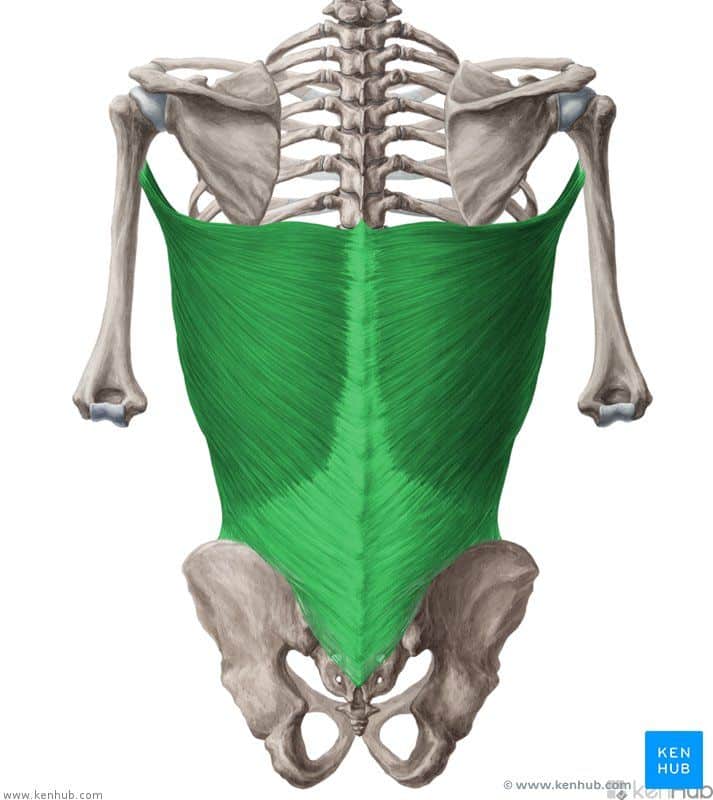
✅ Persian Name: پشتی بزرگ
✅ Latin Name: Latissimus Dorsi
✅ Common Name: Lat
✅ Location:
🟡 A superficial muscle that connects from the lower spine, ribs, and pelvis to the humerus (upper arm bone).
🟡 A large, broad muscle located on both sides of the back, covering most of the lumbar and dorsal regions.
🟡 Responsible for pulling movements, arm adduction, and internal rotation of the arm.
✅ 🦾 Origin
✔ Lower six thoracic vertebrae (T7-T12)
✔ Lumbar vertebrae (L1-L5)
✔ Sacrum
✔ Iliac crest
✔ Lower ribs (9th to 12th)
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ Humerus (intertubercular groove)
✅ 📌 Function and Roles
🔹 The latissimus dorsi plays a role in various movements, including pulling, arm adduction, and internal rotation of the shoulder:
1️⃣ Pulling the arm down and back (Adduction)
✔ Like pulling the bar down during a lat pulldown exercise.
2️⃣ Internal rotation of the arm
✔ Like moving the arm inward during swimming and ball throwing.
3️⃣ Extension of the arm backward
✔ Like pulling the arm backward during pull-ups and rowing exercises.
✅ Main Functions:
✔ Lowering the arm and generating pulling force
✔ Assisting in shoulder stabilization during sports movements
✔ Increasing muscular endurance in strength exercises
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Types
✔ A combination of slow-twitch fibers (Type 1) for endurance and fast-twitch fibers (Type 2) for power movements.
✔ The middle section contains more slow-twitch fibers and is active during sustained pulling movements.
✔ The lower section has fast-twitch fibers used in explosive power movements.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Motor and Sports Performance
✔ The most important muscle in pulling movements such as pull-ups, swimming, and weightlifting.
✔ Plays a significant role in rowing, swimming, wrestling, and gymnastics.
✔ Strengthening this muscle increases pulling power, improves endurance, and reduces lower back injuries.
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ This muscle plays a key role in all pulling and strengthening movements of the upper body.
✔ Weakness in this muscle reduces endurance and increases stress on the lumbar and cervical vertebrae.
🧠 Innervation | Neural Control
✔ Thoracodorsal nerve (C6, C7, C8)
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Thoracodorsal artery
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Vital in sports such as bodybuilding, swimming, wrestling, rock climbing, and gymnastics.
✔ Plays a key role in shot put, cable pulling, weightlifting, and swimming.
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Relationship with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Interacts with the deltoid muscle, rotator cuff muscles, and teres major muscle.
✔ Weakness in this muscle leads to reduced pulling strength and pain in the lower back and shoulders.
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ Strain or weakness in this muscle can lead to lower back problems and pain in the upper back and shoulders.
✔ Weakness increases stress on the lumbar and cervical vertebrae.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Key Exercises to Strengthen the Latissimus Dorsi
1️⃣ Pull-Ups – The most effective exercise for full lat engagement
2️⃣ Lat Pulldown – Increases arm pulling strength
3️⃣ Bent-Over Barbell Rows – Builds size and strength in the back
4️⃣ One-Arm Dumbbell Rows – Strengthens the lateral and upper sections of the muscle
5️⃣ Deadlifts – Enhances endurance and strengthens the entire posterior chain
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery Exercises
✔ Overhead Lat Stretch – Improves range of motion and reduces muscle tension
✔ Wall Lat Stretch – Increases flexibility during pulling movements
✅ Interesting Fact:
✔ The latissimus dorsi is one of the broadest muscles in the human body and plays a role in numerous daily and sports movements.
✅ Practical Tip:
✔ To better strengthen this muscle, combine compound exercises like deadlifts and pull-ups with isolation movements such as lat pulldowns.
🔴 Name and Location: A broad back muscle extending from the lower spine to the arm
🟠 Anatomy: Originates from lumbar and thoracic vertebrae and ribs, attaching to the humerus
🟡 Function: Pulling, lowering, and internal rotation of the arm
🟢 Physiology: A mix of slow- and fast-twitch fibers for endurance and strength
🔵 Innervation: Thoracodorsal nerve (C6, C7, C8)
🟣 Importance: Active in bodybuilding, swimming, wrestling, weightlifting, and rock climbing
🟤 Exercises: Pull-ups, lat pulldown, rowing, deadlifts, arm stretches
⚫ Interesting Facts: One of the broadest muscles in the body and the key muscle in pulling movements
Levator scapulae muscle
Levator Scapulae Muscle
The levator scapulae muscle is one of the superficial back muscles that plays a role in elevating the scapula, stabilizing the neck, and maintaining shoulder stability. It extends from the cervical spine to the medial border of the scapula and is active in movements such as shoulder shrugging, neck rotation, and maintaining balance during upper body motions. Strengthening this muscle improves neck strength, reduces shoulder pain, and enhances posture.
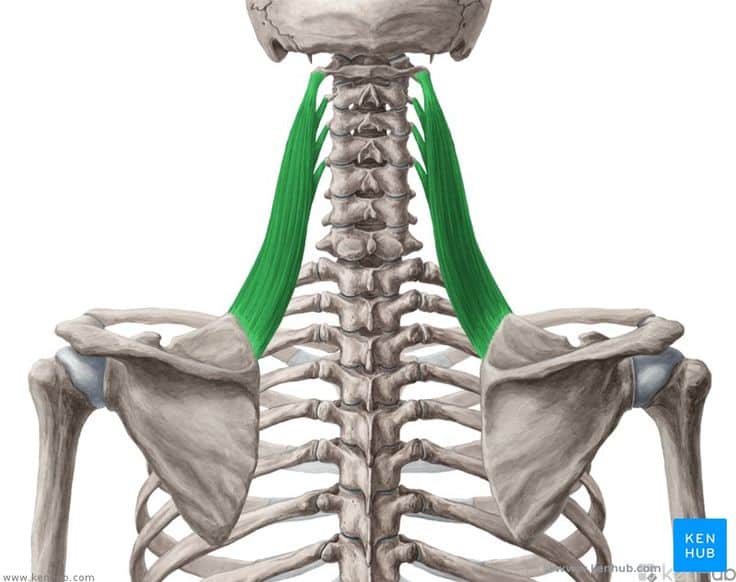
✅ Persian Name: گوشهای کتف
✅ Latin Name: Levator Scapulae
✅ Common Name: Levator Scapulae Muscle
✅ Location:
🟡 A narrow, elongated muscle extending from the cervical vertebrae to the upper part of the scapula.
🟡 Located on both sides of the neck and upper back, working alongside the rhomboid and trapezius muscles.
🟡 Its main function is to elevate the scapula and assist in lateral neck movements.
✅ 🦾 Origin
✔ Cervical vertebrae C1 to C4
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ Medial border of the scapula (upper part)
✅ 📌 Function and Roles
🔹 The levator scapulae muscle is responsible for the following functions:
1️⃣ Scapular elevation
✔ Like shrugging the shoulders during indifference or lifting the shoulders toward the ears.
2️⃣ Downward rotation of the scapula
✔ Assists in internal rotation of the scapula, involved in movements like pulling the arm downward.
3️⃣ Neck stability and movement
✔ Assists with lateral bending and flexion of the neck to one side.
✅ Main Functions:
✔ Elevating the scapula and assisting lateral neck movements
✔ Stabilizing shoulder position during various movements
✔ Supporting proper posture and reducing neck strain
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Types
✔ Contains a mix of slow-twitch fibers (Type 1) for endurance and stability, and fast-twitch fibers (Type 2) for sudden neck and shoulder movements.
✔ Slow-twitch fibers help maintain balance and proper posture.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Motor and Sports Performance
✔ Plays an important role in swimming, weightlifting, bodybuilding, boxing, and gymnastics.
✔ Influences overhead movements and neck stabilization during intense activities.
✔ Strengthening this muscle helps reduce neck pain and pressure caused by prolonged sitting.
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ The strength of this muscle is crucial for neck stability, reducing fatigue, and preventing shoulder and neck injuries.
✔ Weakness may lead to chronic neck pain and reduced shoulder range of motion.
🧠 Innervation | Neural Control
✔ Dorsal scapular nerve (C3, C4, C5)
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Transverse cervical artery
✔ Dorsal scapular artery
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Highly effective in sports such as boxing, weightlifting, wrestling, and bodybuilding.
✔ Plays a key role in neck and shoulder stretching movements.
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Relationship with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Works alongside the rhomboids, trapezius, and latissimus dorsi to stabilize the shoulder and neck.
✔ Weakness in this muscle increases pressure on the neck and leads to chronic muscular pain.
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ Tightness or spasms in this muscle can cause pain in the neck and shoulder area.
✔ Weakness increases strain on neck muscles and reduces shoulder mobility.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Key Exercises to Strengthen the Levator Scapulae
1️⃣ Dumbbell Shrugs – Increase muscle strength and endurance
2️⃣ Close-Grip Pull-Ups – Engage cervical and back muscles
3️⃣ Overhead Shoulder Press with Dumbbells – Enhance muscle stabilization strength
4️⃣ Narrow-Grip Lat Pulldown – Strengthen and increase muscle size
5️⃣ Cable Rows – Stabilize shoulder positioning
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery Exercises
✔ Lateral Neck Stretch – Reduces tension and increases range of motion
✔ Trapezius & Levator Scapulae Stretch – Improves flexibility
✅ Interesting Fact:
✔ This muscle often tightens and becomes painful due to daily stress and tension, making regular stretching highly recommended.
✅ Practical Tip:
✔ To reduce tightness in this muscle, perform neck and shoulder stretches for a few minutes daily.
🔴 Name and Location: A long, narrow muscle extending from the cervical vertebrae to the scapula
🟠 Anatomy: Originates from cervical vertebrae (C1-C4) and attaches to the superior border of the scapula
🟡 Function: Elevates the scapula, performs internal scapular rotation, and stabilizes the neck
🟢 Physiology: A mix of slow- and fast-twitch fibers for endurance and quick movements
🔵 Innervation: Dorsal scapular nerve (C3, C4, C5)
🟣 Importance: Active in strength sports, wrestling, boxing, and bodybuilding
🟤 Exercises: Shrugs, close-grip pull-ups, shoulder press, lateral neck stretches
⚫ Interesting Facts: This muscle often tightens due to stress and prolonged sitting
Rhomboid Major Muscle
Rhomboid Major Muscle
The rhomboid major is one of the superficial muscles of the back, located between the spine and the scapula. It lies adjacent to the rhomboid minor muscle and is responsible for retracting the scapula towards the spine, stabilizing the shoulder, and assisting with scapular movements. Strengthening this muscle helps improve posture, prevent shoulder drooping, and reduce pain in the area between the shoulder blades.
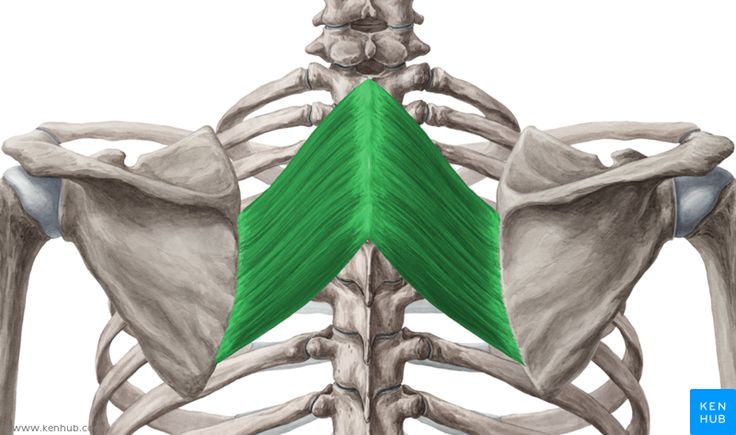
✅ Persian Name: Rhomboid Major
✅ Latin Name: Rhomboid Major
✅ Common Name: Large Rhomboid Muscle
✅ Location:
🟡 A relatively deep muscle located between the thoracic vertebrae and the scapula.
🟡 It lies beneath the trapezius muscle and works in conjunction with the rhomboid minor muscle.
🟡 It plays a key role in scapular retraction and stabilizing the position of the shoulders.
✅ 🦾 Origin
✔ Thoracic vertebrae T2 to T5
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ Medial border of the scapula (from the scapular spine to the inferior angle)
✅ 📌 Function and Responsibilities of the Muscle
🔹 The rhomboid major performs the following functions:
1️⃣ Scapular Retraction
✔ Similar to bringing the shoulder blades closer together during a rowing motion.
2️⃣ Shoulder Stability
✔ Helps maintain the scapula in the proper position to prevent shoulder drooping.
3️⃣ Downward Rotation of the Scapula
✔ Assists in rotating the scapula when lowering the arm.
✅ Main Functions:
✔ Retracting the scapula towards the spine
✔ Stabilizing the scapula for arm movements
✔ Assisting in improving posture and reducing neck strain
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Type
✔ Predominantly composed of slow-twitch fibers (Type 1) for endurance and stability.
✔ Contains fast-twitch fibers (Type 2) for quicker movements, such as sudden shoulder reactions.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Movement and Sports Performance
✔ Plays a key role in rowing, weightlifting, swimming, and martial arts.
✔ Strengthening this muscle enhances shoulder retraction strength and upper body stability.
✔ Weakness in this muscle can lead to shoulder drooping and reduced strength in pulling movements.
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ The strength of this muscle is crucial for shoulder stability and preventing injuries caused by scapular imbalances.
✔ Weakness in this muscle may lead to pain between the shoulder blades and reduced arm range of motion.
🧠 Innervation | Neural Control
✔ Dorsal Scapular Nerve (C4, C5)
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Dorsal Scapular Artery
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Effective in sports such as bodybuilding, swimming, rowing, weightlifting, and boxing.
✔ Active in upper body pulling and endurance movements like pull-ups and rowing.
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Connection with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Works with the trapezius, rhomboid minor, and scapular muscles to stabilize and move the shoulder.
✔ Weakness in this muscle increases pressure on the neck muscles and reduces shoulder stability.
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ Weakness in this muscle can lead to chronic pain in the area between the shoulder blades.
✔ Failure to strengthen this muscle can cause shoulder drooping and increased pressure on the neck.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Main Exercises for Strengthening the Rhomboid Major Muscle
1️⃣ Bent-Over Rows – The strongest exercise for this muscle
2️⃣ Wide-Grip Pull-Ups – Strengthens the back and rhomboids
3️⃣ Face Pulls – Enhances shoulder strength and stability
4️⃣ One-Arm Dumbbell Row – Deep activation of muscles between the shoulder blades
5️⃣ Narrow-Grip Lat Pulldown – Improves shoulder and scapular muscle strength
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery
✔ Scapular Stretch – Reduces tension and increases flexibility
✔ Upper Back Stretch – Improves range of motion and reduces stiffness
✅ Interesting Fact:
✔ The rhomboid major muscle is often weakened due to poor posture and slouching, which is why corrective exercises for it are highly recommended.
✅ Practical Tip:
✔ To prevent pain between the shoulder blades, combining strength exercises (like rowing) with stretching exercises (such as upper back and shoulder stretches) is very effective.
🔴 Name and Location: A muscle between the spine and scapula, located beneath the trapezius muscle.
🟠 Anatomy: Originates from the thoracic vertebrae (T2-T5) and attaches to the medial border of the scapula.
🟡 Function: Scapular retraction, stabilizing the shoulder position, downward rotation of the scapula.
🟢 Physiology: Contains slow-twitch fibers for endurance and stability.
🔵 Innervation: Dorsal scapular nerve (C4, C5).
🟣 Importance: Active in bodybuilding, rowing, weightlifting, swimming.
🟤 Exercises: Bent-over rows, pull-ups, face pulls, lat pulldown.
⚫ Interesting Fact: Plays an important role in posture and preventing shoulder drooping.
Rhomboid Minor Muscle
Rhomboid Minor Muscle
The rhomboid minor is a superficial, rhomboid-shaped muscle in the upper back, located above the rhomboid major. This muscle is responsible for retracting the scapula towards the spine, stabilizing the shoulder position, and assisting with scapular movements. Strengthening this muscle helps improve posture, reduce pain between the shoulder blades, and increase shoulder stability.
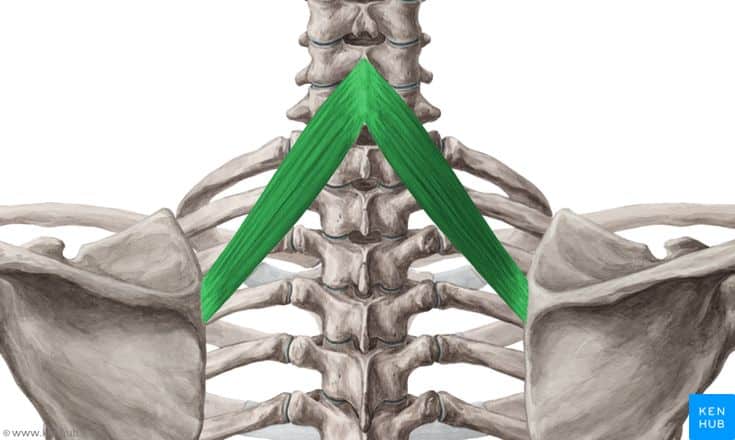
✅ Persian Name: متوازیالاضلاع کوچک
✅ Latin Name: Rhomboid Minor
✅ Common Name: Small Rhomboid Muscle
✅ Location:
🟡 A narrow, elongated muscle located between the cervical vertebrae and the scapula.
🟡 Situated beneath the trapezius muscle and above the rhomboid major.
🟡 Its main function is to retract the scapula inward and stabilize the shoulder position.
✅ 🦾 Origin
✔ Cervical vertebrae C7 and T1
✔ Nuchal Ligament
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ Medial border of the scapula (in the upper part, near the scapular spine)
✅ 📌 Function and Responsibilities of the Muscle
🔹 The rhomboid minor performs the following functions:
1️⃣ Scapular Retraction
✔ Similar to bringing the shoulder blades closer together during a rowing motion.
2️⃣ Scapular Stability
✔ Helps keep the scapula in the correct position to prevent shoulder drooping.
3️⃣ Downward Rotation of the Scapula
✔ Assists in lowering the arm and maintaining scapular balance.
✅ Main Functions:
✔ Retracting the scapula towards the spine
✔ Stabilizing the shoulder position during various movements
✔ Improving posture and reducing neck strain
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Type
✔ Contains slow-twitch fibers (Type 1) for endurance and scapular stabilization
✔ Contains fast-twitch fibers (Type 2) for rapid reactions in shoulder movements
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Movement and Sports Performance
✔ Plays a key role in bodybuilding, weightlifting, rowing, swimming, and boxing.
✔ Strengthening this muscle increases endurance in shoulder movements and enhances strength in pulling exercises.
✔ Weakness in this muscle can lead to pain between the shoulder blades and reduced shoulder stability.
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ This muscle is crucial for stabilizing and correcting shoulder movements.
✔ Weakness in this muscle increases pressure on the neck and spine.
🧠 Innervation | Neural Control
✔ Dorsal Scapular Nerve (C4, C5)
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Dorsal Scapular Artery
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Plays a key role in sports such as bodybuilding, swimming, weightlifting, rowing, and wrestling.
✔ Essential for shoulder stabilization and improving posture.
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Connection with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ This muscle works alongside the rhomboid major, trapezius, and scapular muscles.
✔ Weakness in this muscle can lead to imbalance in shoulder movements and pain between the shoulder blades.
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ Weakness in this muscle can lead to shoulder drooping and muscle pain in the upper back.
✔ Failure to strengthen this muscle increases pressure on the cervical spine.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Main Exercises for Strengthening the Rhomboid Minor Muscle
1️⃣ Bent-Over Rows – The most important exercise for strengthening this muscle
2️⃣ Wide-Grip Pull-Ups – Engages the back and rhomboid muscles
3️⃣ Narrow-Grip Lat Pulldown – Increases shoulder strength
4️⃣ Face Pulls – Strengthens scapular stabilizers
5️⃣ Seated Cable Rows – Strengthens the muscles between the shoulder blades
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery
✔ Scapular Stretch – Increases flexibility and reduces muscle tension
✔ Neck & Shoulder Stretch – Reduces stiffness and improves range of motion
✅ Interesting Fact:
✔ The rhomboid minor muscle is often weak because it is used less in daily activities, making targeted exercises necessary for its strengthening.
✅ Practical Tip:
✔ To prevent shoulder drooping, make sure to include this muscle in your training routine!
🔴 Name and Location: A rhomboid-shaped muscle in the upper back located between the cervical vertebrae and the scapula.
🟠 Anatomy: Originates from the cervical vertebrae (C7-T1) and attaches to the medial border of the scapula.
🟡 Function: Scapular retraction, stabilizing the shoulder position, downward rotation of the scapula.
🟢 Physiology: Contains slow-twitch fibers for endurance and scapular stabilization.
🔵 Innervation: Dorsal Scapular Nerve (C4, C5).
🟣 Importance: Active in bodybuilding, swimming, weightlifting, rowing, and wrestling.
🟤 Exercises: Bent-over rows, pull-ups, lat pulldown, face pulls, stretching exercises.
⚫ Interesting Fact: This muscle is usually weak and requires targeted exercises to strengthen it.
2. Intermediate Muscles of the Back
Intermediate Muscles of the Back
Superior Posterior Serratus Muscle
Serratus Posterior Superior Muscle
The superior posterior serratus is one of the middle back muscles, primarily responsible for assisting with rib movements and facilitating respiration. Located in the upper back, beneath the trapezius muscle, it lifts the ribs during inhalation. Strengthening this muscle improves respiratory function, reduces neck strain, and enhances posture.
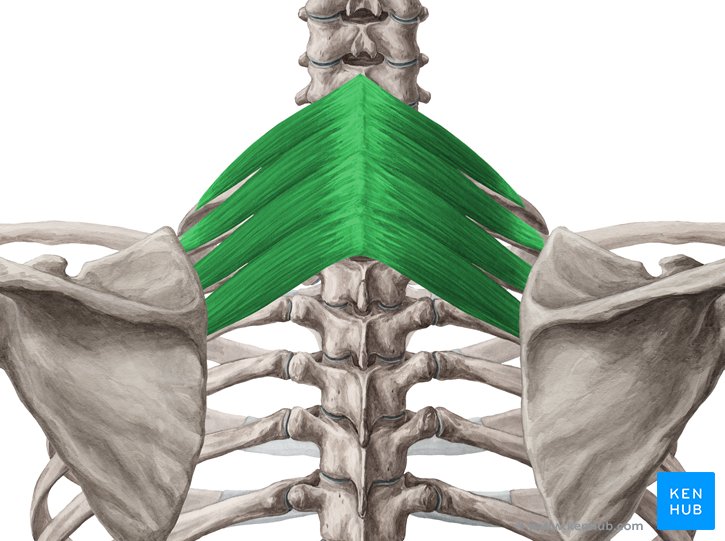
✅ Persian Name: دندهای خلفی فوقانی
✅ Latin Name: Serratus Posterior Superior
✅ Common Name: Upper Respiratory Helper Muscle
✅ Location:
🟡 A relatively small muscle located in the upper back, beneath the trapezius and above the erector spinae muscles.
🟡 Extends from the cervical and thoracic vertebrae to the upper ribs.
🟡 Its primary function is to lift the ribs during inhalation (the act of breathing).
✅ 🦾 Origin
✔ Vertebrae C7 to T3
✔ Nuchal Ligament
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ Ribs 2 to 5 (upper border of the ribs)
✅ 📌 Function and Responsibilities of the Muscle
🔹 The superior posterior serratus performs the following functions:
1️⃣ Elevation of Ribs
✔ This muscle helps expand the rib cage during inhalation.
2️⃣ Postural Support
✔ This muscle, in coordination with other back muscles, helps stabilize the rib cage and shoulders.
✅ Main Functions:
✔ Elevating the ribs during inhalation
✔ Assisting in expanding the chest and facilitating breathing
✔ Stabilizing the upper back in the correct posture
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Type
✔ Contains slow-twitch fibers (Type 1) for endurance and stability to assist with continuous breathing.
✔ Also contains some fast-twitch fibers (Type 2) to help with faster rib movements during endurance sports.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Movement and Sports Performance
✔ Plays a role in sports requiring deep breathing, such as running, swimming, yoga, and breathing exercises.
✔ In stretching movements, it helps maintain the proper posture of the chest and prevents neck and shoulder muscle stiffness.
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ The strength of this muscle plays a crucial role in stabilizing the rib cage and improving respiratory function.
✔ Weakness in this muscle may lead to reduced breathing capacity and fatigue during deep breaths.
🧠 Innervation | Neural Control
✔ Intercostal Nerves (T2 to T5)
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Posterior Intercostal Arteries
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Plays an important role in sports such as running, swimming, weightlifting, yoga, and breathing exercises.
✔ In endurance sports requiring deep and regular breathing, this muscle helps improve performance.
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Connection with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ This muscle works alongside the inferior posterior serratus, erector spinae muscles, and trapezius in stabilizing the shoulder and rib cage.
✔ Weakness in this muscle can lead to pressure and pain in the upper back and reduced breathing efficiency.
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ Weakness in this muscle can lead to respiratory issues, pain between the shoulder blades, and reduced lung capacity.
✔ Tightness or spasms in this muscle can cause stiffness in the upper back and neck area.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Main Exercises for Strengthening the Superior Posterior Serratus Muscle
1️⃣ Diaphragmatic Breathing – Enhances the muscle’s performance in the breathing process
2️⃣ Dumbbell Shoulder Shrugs – Engages the muscle in upper back movements
3️⃣ Cat-Cow Stretch – Improves flexibility and reduces muscle tightness
4️⃣ Dynamic Plank – Increases the strength of respiratory muscles and back stabilizers
5️⃣ Yoga Chest Opener – Helps open the chest and improve breathing posture
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery
✔ Chest Expansion Stretch – Increases range of motion and improves respiratory function
✔ Thoracic Spine Stretch – Reduces pressure on the upper back muscles
✅ Interesting Fact:
✔ This muscle plays a crucial role in the breathing process and often experiences tightness in individuals with poor posture.
✅ Practical Tip:
✔ To improve the performance of this muscle, a combination of breathing exercises and stretching movements is highly recommended!
🔴 Name and Location: A muscle in the upper back, located beneath the trapezius muscle
🟠 Anatomy: Originates from the cervical vertebrae (C7-T3) and attaches to ribs 2 to 5
🟡 Function: Elevates the ribs during inhalation, helps expand the chest, and stabilizes the shoulders
🟢 Physiology: Contains slow-twitch fibers for endurance and assisting in respiratory function
🔵 Innervation: Intercostal Nerves (T2-T5)
🟣 Importance: Active in breathing, endurance sports, running, swimming, and yoga
🟤 Exercises: Diaphragmatic breathing, dynamic plank, thoracic spine stretch, yoga
⚫ Interesting Fact: This muscle is vital in the breathing process and often becomes tight due to poor posture.
Inferior Posterior Serratus Muscle
Serratus Posterior Inferior Muscle
The inferior posterior serratus is one of the middle back muscles responsible for pulling the ribs downward during exhalation and stabilizing the rib cage. Located at the lower part of the back, beneath the latissimus dorsi, this muscle plays a role in exhalation, unlike the superior posterior serratus, which assists during inhalation. Strengthening this muscle improves respiratory function, stabilizes the rib cage, and reduces pressure on the lumbar spine.
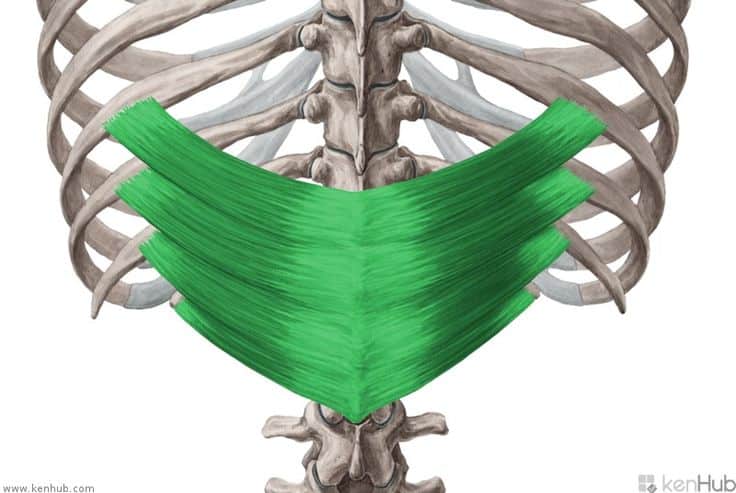
✅ Persian Name: دندهای خلفی تحتانی
✅ Latin Name: Serratus Posterior Inferior
✅ Common Name: Lower Exhalation Helper Muscle
✅ Location:
🟡 A broad and narrow muscle located in the lower back, beneath the latissimus dorsi.
🟡 Extends from the lumbar and thoracic vertebrae to the lower ribs.
🟡 Its primary function is to lower the ribs during exhalation and assist in stabilizing the rib cage.
✅ 🦾 Origin
✔ Vertebrae T11 to L2 (lower thoracic and upper lumbar vertebrae)
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ Ribs 9 to 12 (lower border of the ribs)
✅ 📌 Function and Responsibilities of the Muscle
🔹 The inferior posterior serratus performs the following functions:
1️⃣ Depression of Ribs
✔ Assists in expelling air from the lungs and enhancing the efficiency of respiratory muscles.
2️⃣ Thoracic Stability
✔ Helps maintain the balance of the ribs and prevents unstable movements in the chest and abdomen.
3️⃣ Lumbar Spine Support
✔ Assists in stabilizing the lumbar spine and reduces pressure on the lower back.
✅ Main Functions:
✔ Depressing the ribs during exhalation
✔ Stabilizing the position of the ribs and rib cage
✔ Helping reduce pressure on the lumbar spine
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Type
✔ Contains slow-twitch fibers (Type 1) for endurance in continuous breathing.
✔ Also contains some fast-twitch fibers (Type 2) to assist with faster exhalation during intense activities.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Movement and Sports Performance
✔ Plays a role in sports requiring breath control, such as running, swimming, yoga, and endurance exercises.
✔ Assists in stabilizing the rib cage during strength movements like deadlifts and squats.
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ The strength of this muscle is important for maintaining rib balance, reducing pressure on the spine, and improving respiratory function.
✔ Weakness in this muscle may lead to reduced breath control and increased pressure on the lumbar vertebrae.
🧠 Innervation | Neural Control
✔ Intercostal Nerves (T9 to T12)
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Posterior Intercostal Arteries
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Plays a role in sports such as running, swimming, weightlifting, yoga, and breathing exercises.
✔ Active in strength sports that require rib cage stabilization, such as deadlifts and squats.
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Connection with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ This muscle works alongside the superior posterior serratus, erector spinae muscles, and latissimus dorsi to stabilize the shoulder and rib cage.
✔ Weakness in this muscle can lead to lower back pain and reduced breathing efficiency.
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ Weakness in this muscle can lead to respiratory issues, lower back pain, and reduced performance in heavy movements.
✔ Tightness or spasms in this muscle can cause stiffness in the lower back and abdomen.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Main Exercises for Strengthening the Inferior Posterior Serratus Muscle
1️⃣ Diaphragmatic Breathing – Enhances the muscle’s function during exhalation
2️⃣ Deadlift – Increases strength in the lower back stabilizing muscles
3️⃣ Weighted Squats – Engages the muscle in trunk stabilization
4️⃣ Glute Bridge – Strengthens the back and abdominal stabilizers
5️⃣ Cat-Cow Stretch – Improves flexibility and reduces muscle tightness
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery
✔ Chest & Abdominal Stretch – Increases range of motion and improves exhalation function
✔ Lumbar Spine Stretch – Reduces pressure on the lower back muscles
✅ Interesting Fact:
✔ This muscle plays a crucial role in the exhalation process and is particularly active in strength and endurance exercises for stabilizing the rib cage.
✅ Practical Tip:
✔ To improve the performance of this muscle, a combination of breathing exercises, deadlifts, and stretching movements is recommended!
🔴 Name and Location: A muscle in the lower back, located beneath the latissimus dorsi
🟠 Anatomy: Originates from the lower thoracic vertebrae (T11-L2) and attaches to ribs 9 to 12
🟡 Function: Depresses the ribs during exhalation, stabilizes the rib cage, reduces pressure on the lower back
🟢 Physiology: Contains slow-twitch fibers for endurance and assisting in respiratory function
🔵 Innervation: Intercostal Nerves (T9-T12)
🟣 Importance: Active in breathing, weightlifting, running, swimming, and yoga
🟤 Exercises: Deadlifts, squats, diaphragmatic breathing, thoracic spine stretch
⚫ Interesting Fact: This muscle is vital in the exhalation process and plays an important role in trunk stabilization.
3. Deep (Intrinsic) Back Muscles
Deep (Intrinsic) Muscles of the Back
🔹 The deep back muscles, also known as the intrinsic muscles of the spine, play a key role in the stability, strength, and fine movements of the spine. These muscles are organized into three layers: superficial, intermediate, and deep, and are involved in rotational movements, bending, and extending the spine.
🔶 Superficial Layer of Deep Back Muscles
Superficial Layer of Deep Muscles
Erector Spinae Muscles
Erector Spinae Muscles
🔹 The erector spinae muscles are a group of deep, long muscles located on both sides of the spine, extending from the lower back to the base of the skull. These muscles are responsible for maintaining spinal integrity, flexing and extending the back, and stabilizing the body’s posture.
✅ These muscles are one of the most important muscle groups for maintaining body stability and performing daily movements, as well as strength and endurance exercises.
📌 The erector spinae muscles consist of three main sections:
1️⃣ Iliocostalis – The most lateral part of this group
2️⃣ Longissimus – Located in the center, and the longest muscle in this group
3️⃣ Spinalis – The closest part to the spine
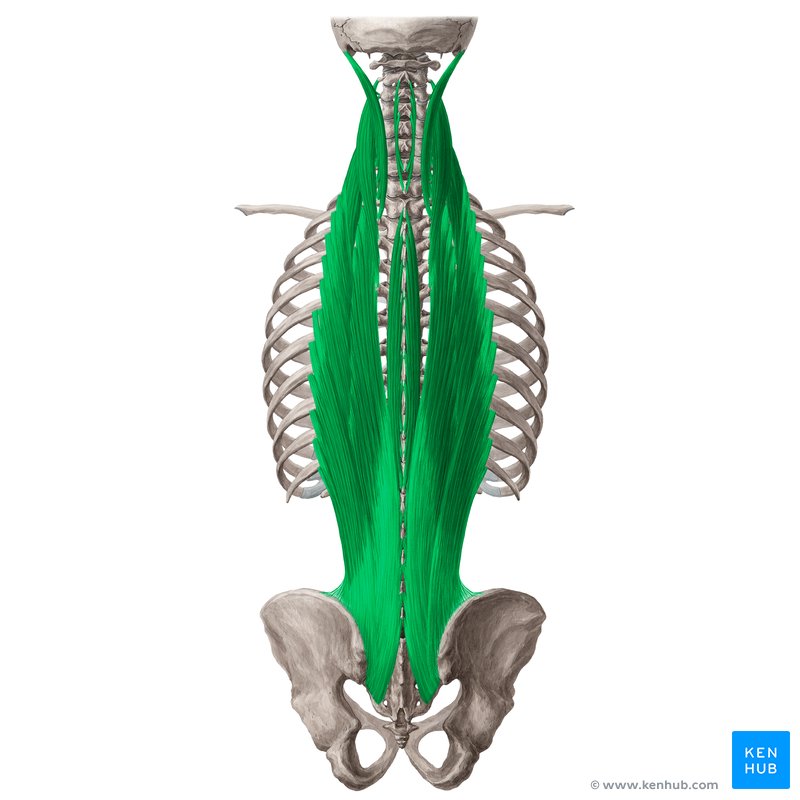
✅ Persian Name: عضلات راستکننده ستون فقرات
✅ Latin Name: Erector Spinae Muscles
✅ Common Name: Lumbar and Dorsal Stabilizing Muscles
✅ Location:
🟡 A group of deep, long muscles extending along the spine, from the sacrum to the skull.
🟡 They are positioned bilaterally along the vertebrae and are responsible for maintaining the body’s balance and stability.
✅ 🦾 Origin
✔ Sacrum
✔ Iliac Crest
✔ Lumbar vertebrae and ribs
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ Cervical and thoracic vertebrae
✔ Ribs
✔ Occipital Bone in the skull
✅ 📌 Classification and Function | Erector Spinae Muscle Duties
🔹 These muscles are divided into three main categories, each with specific functions:
1️⃣ Iliocostalis
✔ Responsible for lateral flexion of the lower back and stabilizing the spine
2️⃣ Longissimus
✔ Helps keep the back upright and assists in moving the head and neck
3️⃣ Spinalis
✔ Brings the vertebrae of the spine closer together and stabilizes the body
✅ Main Functions:
✔ Maintain body balance in an upright position
✔ Assist in the flexion and extension of the spine
✔ Stabilize the vertebrae and prevent spinal injuries
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Types
✔ This group primarily consists of slow-twitch fibers (Type 1) for body endurance.
✔ It also contains some fast-twitch fibers (Type 2) to assist with powerful movements like deadlifts and weightlifting.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Movement and Sports Performance
✔ Plays a key role in fundamental movements such as squats, deadlifts, heavy lifting, and stretching exercises.
✔ Responsible for the muscular endurance of the spine in endurance and strength sports.
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ These muscles are among the most important for body stability and preventing lower back injuries.
✔ Weakness in these muscles leads to lower back pain, decreased endurance, and an increased risk of injury during heavy training.
🧠 Innervation | Neural Control
✔ The lumbar, thoracic, and cervical spinal nerves (Spinal Nerves – C1 to L5) control the movements of these muscles.
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Posterior Intercostal Arteries
✔ Lumbar Arteries
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ These muscles play a stabilizing role in movements like deadlifts, squats, pull-ups, and shoulder presses.
✔ They are vital for maintaining balance in endurance sports and explosive movements like weightlifting and CrossFit.
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Connection with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Works in conjunction with the gluteal muscles, hamstrings, and abdominal muscles to stabilize the spine.
✔ Strengthening these muscles helps reduce pressure on the intervertebral discs and prevents lower back issues.
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ Weakness in these muscles can lead to lower back pain, lumbar lordosis, and spinal injuries.
✔ Strain or spasms in these muscles can cause chronic pain in the lower back and reduce the range of motion.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Main Exercises to Strengthen These Muscles
1️⃣ Deadlift – The most important exercise for strengthening the lower back and erector spinae muscles.
2️⃣ Hip Thrusts – Increases strength in the lower back and gluteal muscles.
3️⃣ Glute Bridge – Activates the posterior muscles and enhances lower back stability.
4️⃣ Superman Pose – Endurance exercise to strengthen these muscles.
5️⃣ Weighted Squats – Helps stabilize the spine and strengthen deep muscles.
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery
✔ Cat-Cow Stretch – Increases spinal flexibility.
✔ Lumbar Stretch – Reduces muscle tension in the lower back.
✅ Interesting Fact:
✔ These muscles are among the primary muscles for body balance and play a vital role in all standing and strength movements.
✅ Practical Tip:
✔ To prevent lower back pain and improve the performance of these muscles, combining strength exercises (such as deadlifts) with stretching movements (like yoga) is highly effective.
🔴 Name and Location: A group of deep muscles that extend along the spine from the lower back to the neck.
🟠 Anatomy: Consists of three parts (Iliocostalis, Longissimus, Spinalis) with different functions.
🟡 Function: Stabilize the spine, assist in bending and extending the body, maintain balance.
🟢 Physiology: It has slow-twitch fibers for endurance and fast-twitch fibers for powerful movements.
🔵 Innervation: The lumbar, thoracic, and cervical spinal nerves (C1 to L5).
🟣 Importance: Active in bodybuilding, weightlifting, yoga, and stretching movements.
🟤 Exercises: Deadlift, Hip Thrust, Glute Bridge, Squat, Superman.
⚫ Interesting Facts: The most important muscle group for maintaining body balance and preventing lower back injuries.
Erector Spinae Muscles Review
Review of Erector Spinae Muscles
Iliocostalis Muscle
Iliocostalis Muscle
🔹 The iliocostalis muscle is the outermost part of the erector spinae group and extends from the lower back to the neck. This muscle plays a key role in maintaining body endurance, stabilizing the spine, and facilitating lateral bending of the lower back. Strengthening this muscle enhances power in stretching movements, reduces the risk of lower back pain, and improves body balance.
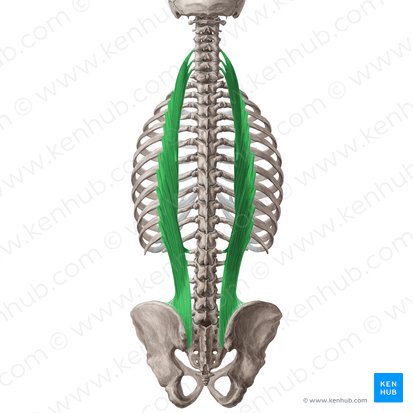
✅ Persian Name: خاصرهایدندهای
✅ Latin Name: Iliocostalis
✅ Common Name: عضله جانبی راستکننده ستون فقرات
✅ Location:
🟡 This muscle is the outermost part of the erector spinae group, extending from the lower back to the neck.
🟡 It is positioned as a narrow, long band on both sides of the spine, running along the ribs.
🟡 Its primary function is to stabilize the spine, facilitate lateral flexion of the body, and assist in straightening the lower back.
✅ 🦾 Origin | Starting Point
✔ Sacrum
✔ Iliac Crest
✔ Lower ribs and lumbar vertebrae
✅ 🦿 Insertion | Attachment Point
✔ Middle and upper ribs
✔ Cervical vertebrae
✅ 📌 Function and Duties of the Muscle
🔹 The iliocostalis muscle is responsible for the following tasks:
1️⃣ Lateral Flexion of Spine
✔ This muscle is activated when bending to the sides.
2️⃣ Extension of Spine
✔ Activated during movements like rising from a bent position or standing upright after bending.
3️⃣ Spinal Stabilization
✔ Prevents unstable movements and helps distribute forces evenly across the spine.
✅ Main Functions:
✔ Lateral flexion of the body
✔ Extension of the spine
✔ Assisting in body balance and stability
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Types
✔ Contains slow-twitch fibers (Type 1) for endurance and supporting the spine.
✔ Contains fast-twitch fibers (Type 2) for faster movements and enhancing power in dynamic actions.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Movement and Sports Performance
✔ Active in endurance sports such as running, swimming, and bodybuilding.
✔ Plays a key role in lower back movements like deadlifts, squats, glute bridges, and stretching exercises.
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ The strength of this muscle is crucial for maintaining body balance and preventing lower back injuries.
✔ Weakness in this muscle can lead to lower back pain, reduced spinal stability, and an increased risk of injury during heavy training.
🧠 Innervation | Neural Control
✔ The lumbar, thoracic, and cervical spinal nerves (Spinal Nerves – C4 to L3).
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Posterior Intercostal Arteries
✔ Lumbar Arteries
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Involved in sports like weightlifting, yoga, CrossFit, and stretching exercises.
✔ Responsible for maintaining stability in endurance sports and bodybuilding.
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Connection with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Works alongside the erector spinae, gluteal muscles, and hamstrings to maintain body balance.
✔ Weakness in this muscle can lead to increased pressure on the lower back and decreased endurance during prolonged activities.
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ Weakness in this muscle can lead to chronic lower back pain and increased pressure on the intervertebral discs.
✔ Failure to strengthen this muscle results in decreased balance in strength and endurance movements.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Main Exercises to Strengthen These Muscles
1️⃣ Deadlift – The most important exercise for strengthening the lower back and erector spinae muscles.
2️⃣ Hip Thrusts – Increases strength in the lower back and gluteal muscles.
3️⃣ Glute Bridge – Activates the posterior muscles and enhances lower back stability.
4️⃣ Superman Pose – Endurance exercise to strengthen these muscles.
5️⃣ Weighted Squats – Helps stabilize the spine and strengthen deep muscles.
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery
✔ Cat-Cow Stretch – Increases spinal flexibility.
✔ Lumbar Stretch – Reduces muscle tension in the lower back.
✅ Interesting Fact:
✔ This muscle is one of the most important stabilizing muscles in sports movements and is active in many endurance and strength exercises.
✅ Practical Tip:
✔ Combining stretching exercises and resistance training is the best way to improve the performance of this muscle and prevent lower back injuries!
🔴 Name and Location: A lateral muscle that extends from the lower back to the neck.
🟠 Anatomy: Originates from the iliac bone and lumbar vertebrae, attaching to the ribs and cervical vertebrae.
🟡 Function: Stabilizes the spine, facilitates lateral flexion of the body, and assists in straightening the lower back.
🟢 Physiology: Contains slow-twitch fibers for endurance and fast-twitch fibers for strength.
🔵 Innervation: The lumbar, thoracic, and cervical spinal nerves (C4 to L3).
🟣 Importance: Active in bodybuilding, yoga, weightlifting, and endurance movements.
🟤 Exercises: Romanian Deadlifts, Superman, Glute Bridge, Side Twists, Good Mornings.
⚫ Interesting Facts: One of the main muscles for maintaining body balance and preventing lower back injuries.
Longissimus Muscle
Longissimus Muscle
🔹 The longissimus is the longest and central muscle in the erector spinae group, extending from the lower back to the neck and head. This muscle plays a role in maintaining body endurance, keeping the spine upright, lateral movements, and neck and head rotation. Strengthening this muscle improves spinal stability, reduces lower back pain, and enhances upper body strength.
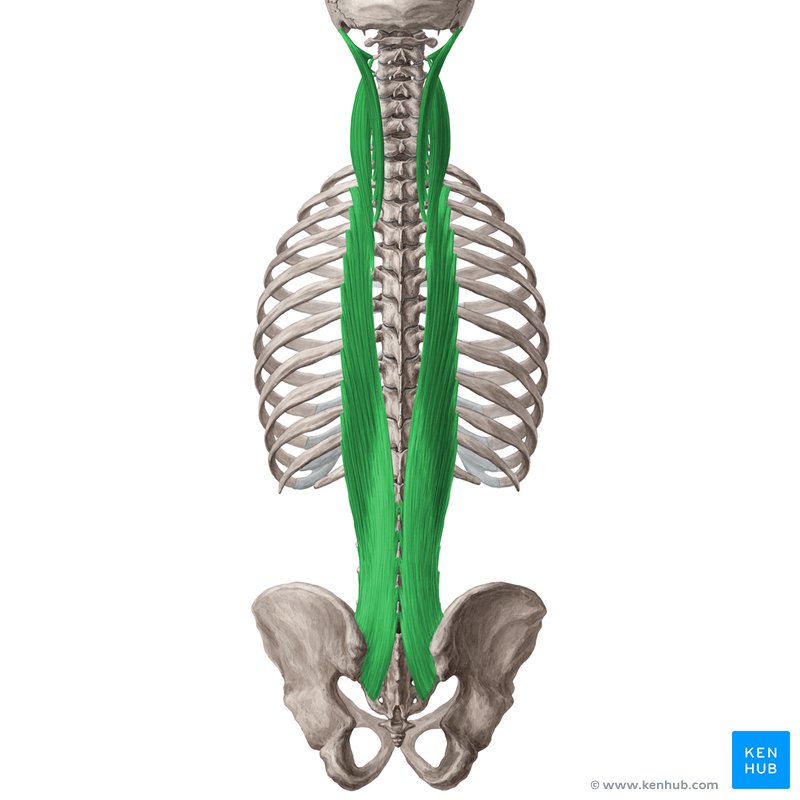
✅ Persian Name: طویل
✅ Latin Name: Longissimus
✅ Common Name: عضله طولانی راستکننده ستون فقرات
✅ Location:
🟡 This is the central and longest muscle of the erector spinae group, extending from the lower back to the neck and the back of the skull.
🟡 It is positioned as a strong muscle column along the spine, between the iliocostalis and spinalis muscles.
🟡 Its main function is to maintain stability, assist in lateral movements, and keep the spine and head upright.
✅ 🦾 Origin | Starting Point
✔ Sacrum
✔ Iliac Crest
✔ Lower ribs and lumbar vertebrae
✅ 🦿 Insertion | Attachment Point
✔ Middle and upper ribs
✔ Cervical vertebrae
✅ 📌 Function and Duties of the Muscle
🔹 The iliocostalis muscle is responsible for the following tasks:
1️⃣ Lateral Flexion of Spine
✔ This muscle is activated when bending to the sides.
2️⃣ Extension of Spine
✔ Activated during movements like rising from a bent position or standing upright after bending.
3️⃣ Spinal Stabilization
✔ Prevents unstable movements and helps distribute forces evenly across the spine.
✅ Main Functions:
✔ Lateral flexion of the body
✔ Extension of the spine
✔ Assisting in body balance and stability
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Types
✔ Contains slow-twitch fibers (Type 1) for endurance and spinal stability.
✔ Contains fast-twitch fibers (Type 2) for rapid movements and controlling neck and head movements.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Movement and Sports Performance
✔ Plays a key role in strength sports such as weightlifting, bodybuilding, and CrossFit.
✔ This muscle is highly active in daily movements like standing, walking, and running.
✔ It is active in exercises such as pull-ups, deadlifts, squats, and balance training.
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ The strength of this muscle is crucial for spinal stability, preventing lower back pain, and maintaining balance during sports movements.
✔ Weakness in this muscle may lead to reduced movement control, pain in the lower back and neck, and instability in standing movements.
🧠 Innervation | Neural Control
✔ The lumbar, thoracic, and cervical spinal nerves (Spinal Nerves – C3 to L5).
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Posterior Intercostal Arteries
✔ Lumbar Arteries
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Plays an important role in sports like bodybuilding, weightlifting, swimming, CrossFit, and stretching exercises.
✔ One of the key muscles for body balance and endurance during strength movements.
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Connection with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ This muscle works with the erector spinae muscles, gluteal muscles, and cervical muscles to maintain body balance.
✔ Weakness in this muscle increases pressure on the cervical and lumbar vertebrae and reduces endurance during prolonged activities.
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ Weakness in this muscle can lead to lower back pain, neck pain, and decreased endurance in physical activities.
✔ Muscle tightness or strain may cause limited movement in the lower back and neck.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Main Exercises to Strengthen This Muscle:
1️⃣ Deadlift – Increases strength and endurance of the spine
2️⃣ Weighted Squats – Strengthens the erector spinae muscles
3️⃣ Superman Pose – Enhances stability and balance of the lower back muscles
4️⃣ Side Bends – Increases flexibility and power in lateral movements
5️⃣ Good Morning Exercise – Strengthens the entire erector spinae muscle group
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery:
✔ Cat-Cow Stretch – Improves spinal flexibility
✔ Lumbar Stretch – Reduces muscle tension in the lower back and neck
✅ Interesting Fact:
✔ This muscle is one of the longest muscles in the body and covers nearly the entire length of the spine!
✅ Practical Tip:
✔ To prevent lower back pain and increase body strength, combining strengthening and stretching exercises is essential!
🔴 Name and Location: The longest erector spinae muscle that extends from the lower back to the neck and head.
🟠 Anatomy: Originates from the lumbar and thoracic vertebrae and attaches to the cervical vertebrae and the occipital bone.
🟡 Function: Stabilizing and extending the spine, lateral movements, and rotation of the head and neck.
🟢 Physiology: Contains both slow-twitch and fast-twitch fibers for endurance and controlled movements.
🔵 Innervation: The lumbar, thoracic, and cervical spinal nerves (C3 to L5).
🟣 Importance: Active in bodybuilding, weightlifting, CrossFit, and endurance sports.
🟤 Exercises: Deadlift, Squat, Superman, Good Morning, Cat-Cow Stretch.
⚫ Interesting Facts: It is one of the longest muscles in the body and plays a key role in maintaining balance.
Spinalis Muscle
Spinalis Muscle
🔹 The spinalis muscle is the innermost and closest muscle to the spine in the erector spinae group. It runs along the midline of the spine, extending from the lumbar vertebrae to the neck. Its primary function is to stabilize and keep the spine upright. This muscle is shorter than the other two muscles in the erector spinae group (iliocostalis and longissimus), but it plays a key role in spinal stability and proper function.
✅ Strengthening this muscle helps reduce the risk of lower back and neck injuries, improves body balance, and increases endurance in daily and sports movements.
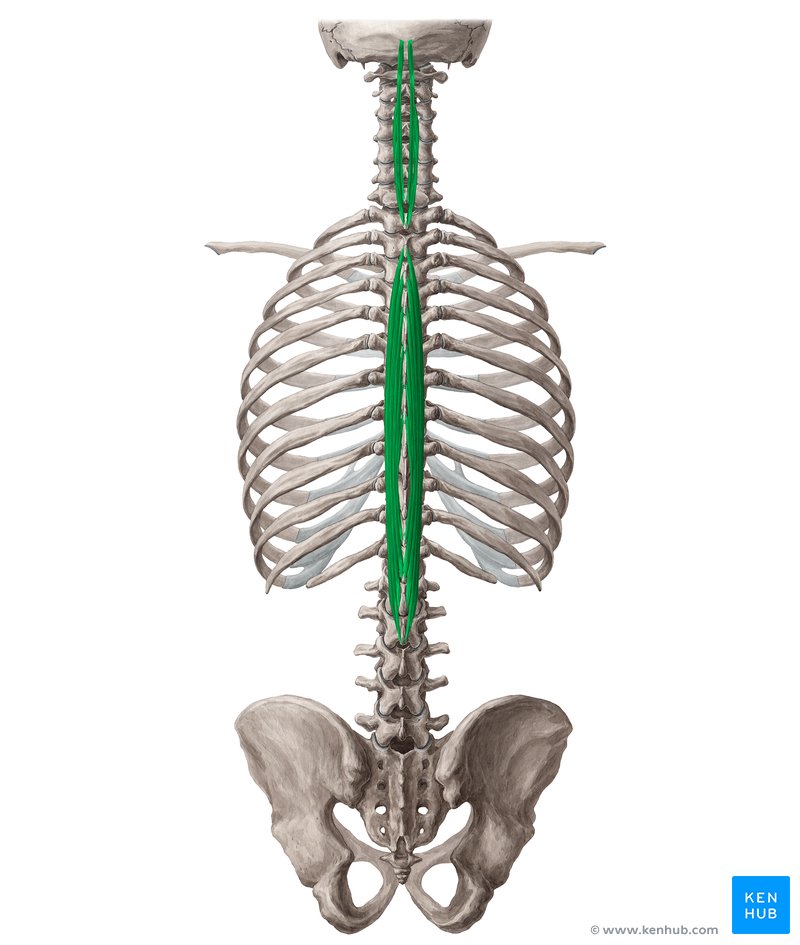
✅ Persian Name: خاری
✅ Latin Name: Spinalis
✅ Common Name: Central Erector Spinae Muscle
✅ Location:
🟡 This muscle is the closest to the spine and runs along the vertebrae.
🟡 It extends along the spine from the lumbar region to the cervical region.
🟡 Its main function is to maintain stability, assist in extending the spine, and stabilize the body’s position.
✅ 🦾 Origin | Starting Point
✔ Lumbar and thoracic vertebrae (L2-T11)
✔ Spinal ligaments
✅ 🦿 Insertion | Attachment Point
✔ Thoracic and cervical vertebrae (T2-C4)
✔ Occipital Bone
✅ 📌 Function and Duties of the Muscle
🔹 The spinalis muscle is responsible for the following tasks:
1️⃣ Spinal Extension
✔ This muscle is activated when standing up and returning to an upright position.
2️⃣ Spinal Stability
✔ Helps prevent unstable movements and maintains the alignment of the spine.
3️⃣ Micro Movements of Spine
✔ Plays a role in controlled and subtle movements of the neck and lower back.
✅ Main Functions:
✔ Spinal extension
✔ Stabilizing and maintaining balance during body movements
✔ Preventing lower back and neck injuries
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Types
✔ Contains slow-twitch fibers (Type 1) for endurance and spinal stability.
✔ Contains fast-twitch fibers (Type 2) for assisting in faster movements and controlling neck movements.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Movement and Sports Performance
✔ Active in strength sports like weightlifting, bodybuilding, and CrossFit.
✔ This muscle is used in balance, standing, and stretching movements like deadlifts, squats, and planks.
✔ Plays an important role in sports that require spinal movement control, such as yoga and Pilates.
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ The strength of this muscle is crucial for spinal stability, preventing lower back pain, and maintaining body balance.
✔ Weakness in this muscle may lead to reduced spinal endurance, lower back pain, and limited mobility.
🧠 Innervation | Neural Control
✔ The lumbar, thoracic, and cervical spinal nerves (Spinal Nerves – C3 to L5).
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Posterior Intercostal Arteries
✔ Lumbar Arteries
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Plays a key role in sports like bodybuilding, weightlifting, swimming, CrossFit, and yoga.
✔ This muscle is vital for spinal stability in strength movements like deadlifts and squats.
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Connection with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ This muscle works alongside other erector spinae muscles and lumbar and cervical stabilizing muscles to maintain body balance.
✔ Weakness in this muscle increases pressure on the lumbar and cervical vertebrae, raising the risk of injury during prolonged activities.
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ Weakness in this muscle can lead to lower back pain and reduced spinal stability.
✔ Tightness or strain in this muscle may cause limited movement and pain in the middle and upper back.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Main Exercises to Strengthen This Muscle:
1️⃣ Deadlift – The most important exercise for strengthening the erector spinae muscles.
2️⃣ Weighted Squats – Helps stabilize and increase spinal strength.
3️⃣ Superman Pose – Improves strength and reinforces the back muscles.
4️⃣ Good Morning Exercise – Increases strength in the erector spinae and stabilizers.
5️⃣ Plank Hold – Helps stabilize the spine and improve muscle balance.
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery:
✔ Cat-Cow Stretch – Improves spinal flexibility
✔ Lumbar Stretch – Reduces pressure on the back muscles
✅ Interesting Fact:
✔ This muscle is one of the shortest muscles in the erector spinae group, but it has the greatest impact on stabilizing the vertebrae!
✅ Practical Tip:
✔ Resistance and endurance exercises like deadlifts and planks are the best way to strengthen this muscle and prevent lower back injuries.
🔴 Name and Location: The closest erector spinae muscle to the spine, extending from the lumbar vertebrae to the neck.
🟠 Anatomy: Originates from the lumbar and thoracic vertebrae and attaches to the cervical vertebrae and the occipital bone.
🟡 Function: Stabilizing and extending the spine, controlling movements of the neck and lower back.
🟢 Physiology: Contains both slow-twitch and fast-twitch fibers for endurance and controlling subtle movements.
🔵 Innervation: The lumbar, thoracic, and cervical spinal nerves (C3 to L5).
🟣 Importance: Active in bodybuilding, weightlifting, CrossFit, and yoga.
🟤 Exercises: Deadlift, Squat, Superman, Good Morning, Plank.
⚫ Interesting Facts: One of the shortest yet most stable muscles in maintaining spinal balance.
🔶 The Middle Layer of Deep Muscles
Intermediate Layer of Deep Muscles
🔹 The muscles of the middle layer of the back are positioned deeper than the erector spinae muscles and play a crucial role in stabilizing, controlling fine spinal movements, and small vertebral rotations. These muscles are particularly involved in bending movements, subtle spinal rotations, and controlling neck and lower back movements.
Semispinalis Muscle
Semispinalis Capitis, Cervicis, Thoracis Muscle
🔹 The semispinalis muscle is one of the deep middle layer muscles of the back, extending from the thoracic and cervical vertebrae to the skull. This muscle assists in rotational movements and bending of the neck and upper spine, playing a crucial role in stabilizing body posture and controlling fine spinal movements. Strengthening this muscle improves neck stability, reduces pressure on the cervical vertebrae, and increases strength in rotational movements of the head and lower back.
✅ The semispinalis muscle is divided into three parts:
1️⃣ Semispinalis Capitis – The upper portion, controls head movements.
2️⃣ Semispinalis Cervicis – Located in the cervical region, controls movements of the cervical vertebrae.
3️⃣ Semispinalis Thoracis – Located in the thoracic region, assists in spinal stability and movement.
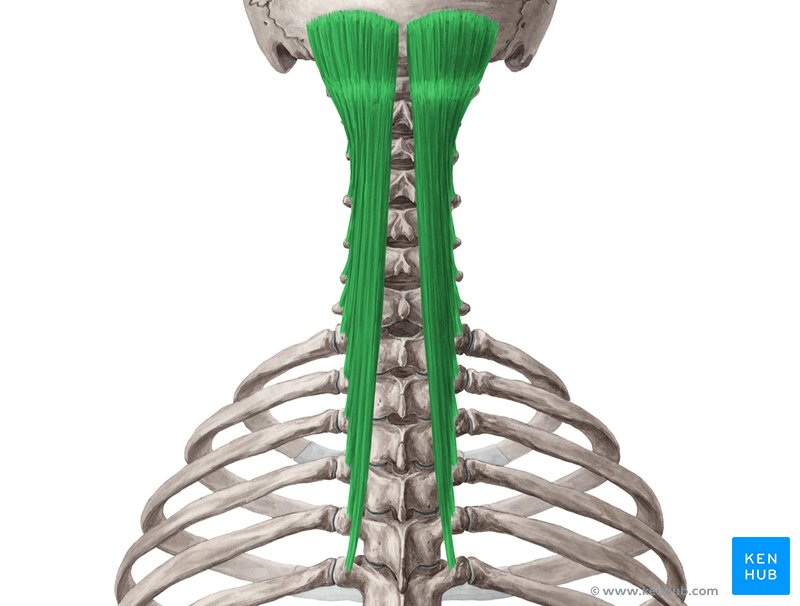

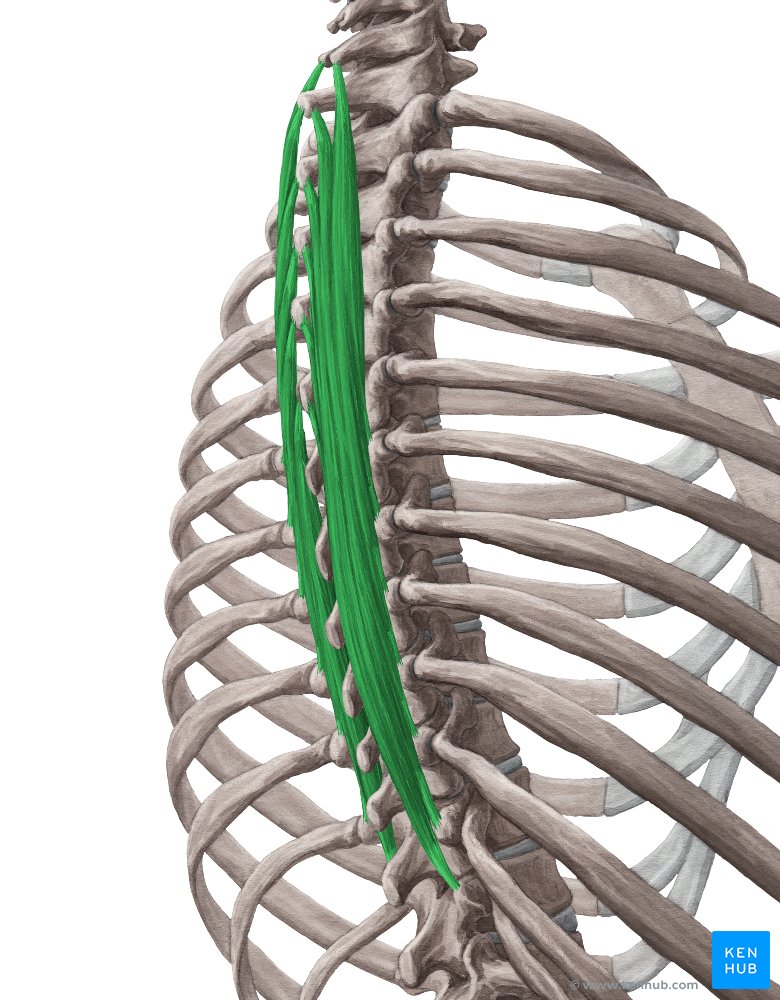
✅ Persian Name: نیمهخاری
✅ Latin Name: Semispinalis
✅ Common Name: Neck and Upper Body Stabilizing Muscle
✅ Location:
🟡 This muscle is located in the deep layer of the back muscles, running along the spine from the chest to the skull.
🟡 It lies beneath the more superficial muscles, such as the trapezius and erector spinae.
🟡 It is responsible for rotational movements, flexion, and stabilization of the neck and spine.
✅ 🦾 Origin | Starting Point
✔ Thoracic vertebrae (T6 to T10) – for the semispinalis thoracis section
✔ Cervical vertebrae (C4 to C7) – for the semispinalis cervicis section
✔ Upper cervical vertebrae (C1 to C3) – for the semispinalis capitis section
✅ 🦿 Insertion | Attachment Point
✔ Cervical and thoracic vertebrae, above the origin point
✔ Occipital bone in the skull
✅ 📌 Function and Duties of the Muscle
🔹 The semispinalis muscle is responsible for the following tasks:
1️⃣ Spinal Extension & Stability
✔ Helps maintain the alignment of the neck and chest in both standing and sitting positions.
2️⃣ Lateral Flexion & Rotation of Neck
✔ Assists in rotating the head to one side and laterally flexing the neck.
3️⃣ Segmental Control of Spine
✔ Prevents unstable movements in the cervical and thoracic vertebrae.
✅ Main Functions:
✔ Stabilizing the position of the neck and upper back
✔ Assisting in the rotation and flexion of the neck
✔ Controlling subtle movements of the cervical and thoracic vertebrae
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Types
✔ Contains slow-twitch fibers (Type 1) for endurance and stabilizing the neck and chest position.
✔ Contains fast-twitch fibers (Type 2) for controlled neck movements and rapid rotations.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Movement and Sports Performance
✔ Active in head and neck movements in sports like boxing, gymnastics, weightlifting, and bodybuilding.
✔ Plays a crucial role in stretching exercises, neck control movements, and chest stabilization.
✔ Used in sports that require neck and head stability, such as swimming, cycling, and yoga.
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ The strength of this muscle is crucial for neck stability, preventing vertebral injuries, and maintaining upper body balance.
✔ Weakness in this muscle can lead to neck pain, muscle weakness-induced headaches, and reduced range of motion in the head and neck.
🧠 Innervation | Neural Control
✔ Cervical and thoracic spinal nerves (Spinal Nerves – C2 to T6).
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Vertebral Artery
✔ Occipital Artery
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Plays an important role in sports like bodybuilding, boxing, swimming, yoga, and CrossFit.
✔ Essential for neck stability in sports that require balance and head control.
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Connection with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ This muscle works alongside the trapezius, erector spinae muscles, and deeper cervical muscles to maintain neck and chest balance.
✔ Weakness in this muscle can lead to imbalance in neck movements and increased tension in the cervical and lumbar vertebrae.
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ Weakness in this muscle can lead to neck pain, headaches, and reduced control of head movements.
✔ Muscle spasms or strain may cause limited neck range of motion and vertebral pain.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Main Exercises to Strengthen This Muscle:
1️⃣ Neck Rotations – Improve neck strength and flexibility
2️⃣ Neck Lifts – Increase neck muscle stability
3️⃣ Neck & Head Plank Holds – Stabilize and enhance cervical vertebrae stability
4️⃣ Neck Stretching Exercises – Improve flexibility and reduce muscle tension
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery:
✔ Lateral Neck Stretch – Increases range of motion and reduces tension
✔ Occipital Stretch – Improves neck movement function and reduces vertebral pressure
✅ Interesting Fact:
✔ This muscle is one of the most important muscles controlling the head and neck, and its weakness can lead to muscular headaches.
✅ Practical Tip:
✔ Strengthening and stretching exercises for this muscle can help reduce neck pain and improve range of motion.
🔴 Name and Location: A muscle that extends from the thoracic and cervical vertebrae to the head.
🟠 Anatomy: Consists of three parts (Semispinalis Capitis, Semispinalis Cervicis, Semispinalis Thoracis), originating from the thoracic and cervical vertebrae and attaching to higher vertebrae and the occipital bone.
🟡 Function: Stabilizing and extending the spine, controlling rotational and lateral movements of the neck and head.
🟢 Physiology: Contains both slow-twitch and fast-twitch fibers for endurance and controlling subtle movements of the neck and spine.
🔵 Innervation: Cervical and thoracic spinal nerves (C2 to T6).
🟣 Importance: Active in bodybuilding, yoga, boxing, CrossFit, and balance sports.
🟤 Exercises: Neck Rotations, Neck & Head Plank Holds, Neck Lifts, Lateral Neck Stretch.
⚫ Interesting Fact: This muscle is one of the most important muscles controlling the head and neck, and its weakness can lead to muscular headaches.
Multifidus Muscle
Multifidus Muscle
🔹 The multifidus muscle is one of the deepest and most important spinal stabilizing muscles, extending along the length of the spine from the sacral vertebrae (sacrum) to the cervical vertebrae. This muscle is responsible for maintaining vertebral balance, stabilizing body posture, preventing unnecessary spinal movements, and improving lumbar stability. Strengthening this muscle enhances spinal strength, prevents lower back injuries, and increases power in both sports and everyday movements.
✅ This muscle plays a crucial role in the stability of the lumbar spine (lower back), and its weakness is a major cause of many chronic lower back pains.
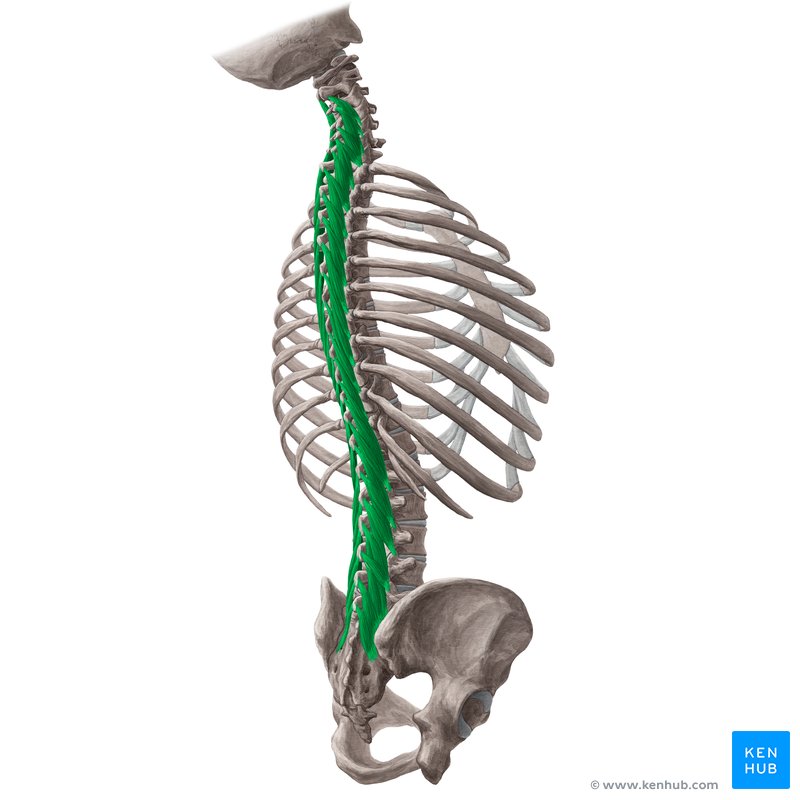
✅ Persian Name: عضله چندپاره
✅ Latin Name: Multifidus
✅ Common Name: Lumbar and Spinal Stabilizing Muscle
✅ Location:
🟡 A long, multi-layered muscle that runs along both sides of the spine, from the sacrum to the cervical vertebrae.
🟡 Located beneath the erector spinae muscles and alongside the rotatores muscles of the spine.
🟡 Its primary function is to stabilize the vertebrae of the spine, prevent unnecessary movements, and assist in maintaining body stability.
✅ 🦾 Origin | Starting Point
✔ Sacrum
✔ Lumbar, thoracic, and cervical vertebrae (L5 to C2)
✅ 🦿 Insertion | Attachment Point
✔ Spinous processes of higher vertebrae
✅ 📌 Function and Duties of the Muscle
🔹 The multifidus muscle is responsible for the following tasks:
1️⃣ Spinal Stabilization
✔ This muscle, through its contraction, prevents unstable and unnecessary movements of the spine.
2️⃣ Segmental Control of Spine
✔ Helps control and limit excessive movements between vertebrae.
3️⃣ Spinal Rotation & Flexion
✔ This muscle plays a role in the fine rotational movements and flexion of the spine.
✅ Main Functions:
✔ Stabilization of the lumbar and thoracic vertebrae
✔ Helping prevent spinal injuries
✔ Supporting the lumbar vertebrae and reducing pressure on intervertebral discs
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Types
✔ Contains slow-twitch fibers (Type 1) for endurance and spinal stabilization.
✔ Contains fast-twitch fibers (Type 2) for rapid movements and controlling small movements between vertebrae.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Movement and Athletic Functions
✔ This muscle plays a key role in all physical activities that require balance and spinal stability, such as weightlifting, bodybuilding, yoga, and CrossFit.
✔ It is crucial in preventing lower back pain and enhancing performance in movements like running, squats, and balance exercises.
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ The strength of this muscle is crucial for spinal stability, preventing lower back pain, and improving posture.
✔ Weakness in this muscle is one of the primary causes of chronic lower back pain and increased pressure on intervertebral discs.
🧠 Innervation | Neural Control
✔ The lumbar, thoracic, and cervical spinal nerves (Spinal Nerves – C3 to L5).
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Lumbar Arteries
✔ Posterior Intercostal Arteries
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Plays a key role in sports such as bodybuilding, weightlifting, CrossFit, gymnastics, yoga, and Pilates.
✔ Vital for maintaining body balance and preventing lower back injuries during heavy exercises like deadlifts and squats.
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Connection with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Works alongside other spinal stabilizing muscles, such as the erector spinae and abdominal muscles.
✔ Weakness in this muscle increases the risk of back injury and reduces the control of spinal movement.
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ Weakness in this muscle is one of the main causes of chronic lower back pain and decreased spinal stability.
✔ Tightness or improper functioning of this muscle may lead to lower back pain and reduced balance during athletic movements.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Key Exercises to Strengthen This Muscle:
1️⃣ Plank Holds – The most important exercise for strengthening this muscle and stabilizing the spine.
2️⃣ Deadlift – Helps strengthen the lumbar stabilizing muscles.
3️⃣ Bird-Dog Exercise – Enhances balance and control of stabilizing muscles.
4️⃣ Glute Bridge – Improves the strength and power of the lumbar muscles.
5️⃣ Controlled Spine Rotation – Enhances rotational and stabilizing movement strength.
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery Moves:
✔ Lumbar Stretch – Reduces pressure on the lumbar spine.
✔ Seated Spinal Stretch – Improves spinal flexibility.
✅ Interesting Fact:
✔ The multifidus muscle is one of the first muscles to become inactive in cases of lower back pain, and there are specific exercises designed to activate it!
✅ Practical Tip:
✔ Strengthening exercises like planks and deadlifts can help improve the performance of this muscle and reduce lower back pain.
🔴 Name and Location: A deep muscle that extends from the lumbar to the cervical vertebrae and is the closest muscle to the vertebrae of the spine.
🟠 Anatomy: Originates from the sacrum and the lumbar, thoracic, and cervical vertebrae, and attaches to the higher vertebrae.
🟡 Function: Stabilizes the vertebrae of the spine, prevents unstable movements, assists in subtle rotations, and helps prevent lower back injuries.
🟢 Physiology: Contains both slow-twitch and fast-twitch fibers for strength and controlling subtle movements of the spine.
🔵 Innervation: The lumbar, thoracic, and cervical spinal nerves (C3 to L5).
🟣 Importance: Vital for maintaining body balance, preventing lower back pain, stabilizing the spine, and active in bodybuilding, weightlifting, yoga, and CrossFit.
🟤 Exercises: Plank, Deadlift, Bird-Dog, Glute Bridge, Controlled Spine Rotation.
⚫ Interesting Fact: This muscle becomes inactive in many individuals due to lower back pain and requires specific exercises for activation.
Rotator muscles of the spine
Rotatores - Longus & Brevis Muscle
🔹 The rotator muscles of the spine are a group of deep, short muscles located between the vertebrae of the spine. These muscles play a key role in subtle spinal rotations, maintaining vertebral stability, and controlling intervertebral movements. The rotator muscles consist of two parts: the long (Longus) and short (Brevis) muscles, which work in conjunction with the multifidus muscle.
✅ These muscles are crucial for controlled movements of the vertebrae and preventing intervertebral instability. Weakness in these muscles can lead to spinal instability and increase the risk of lower back pain.
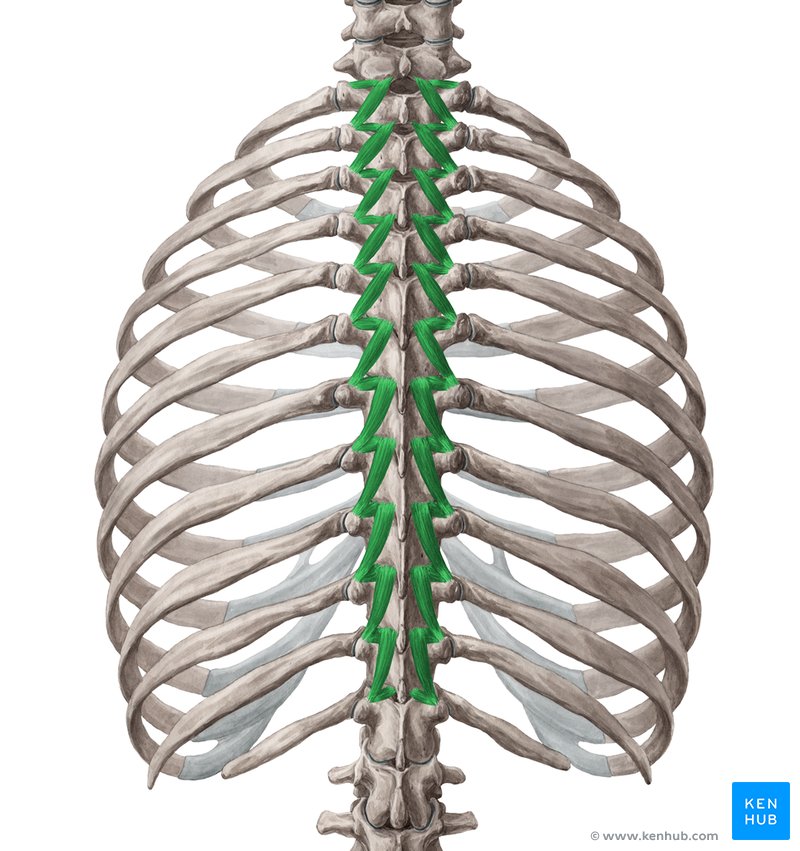
✅ Persian Name: عضلات چرخاننده ستون فقرات
✅ Latin Name: Rotatores
✅ Common Name: Intervertebral Rotator Muscles
✅ Location:
🟡 These muscles are located deep within the spine, between the transverse processes of adjacent vertebrae.
🟡 Each rotator muscle originates from one vertebra and attaches to the vertebra above.
🟡 Their primary function is to facilitate subtle rotational movements and stabilize the vertebrae of the spine.
✅ There are two types of rotator muscles:
1️⃣ Rotatores Longus – These connect two adjacent vertebrae.
2️⃣ Rotatores Brevis – These are located between adjacent vertebrae.
✅ 🦾 Origin (Starting Point)
✔ Transverse Processes of the lumbar, thoracic, and cervical vertebrae.
✅ 🦿 Insertion (Attachment Point)
✔ Spinous Processes of the higher vertebrae.
✅ 📌 Function and Responsibilities of the Muscle
🔹 The rotator muscles of the spine are responsible for the following tasks:
1️⃣ Segmental Rotation of Spine
✔ Assists in rotational and corrective movements of the spine, typically within a few degrees.
2️⃣ Segmental Stability of Spine
✔ Controls small movements between vertebrae and prevents spinal instability.
3️⃣ Fine-Tuning of Spinal Movements
✔ These muscles assist in the precise control of small movements between the vertebrae.
✅ Main Functions:
✔ Subtle rotation of the vertebrae
✔ Stabilizing the spine’s position
✔ Preventing unstable movements between vertebrae
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Types
✔ Contains slow-twitch fibers (Type 1) for endurance and maintaining balance between vertebrae.
✔ Contains fast-twitch fibers (Type 2) for controlling rapid movements and fine neural responses.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Movement and Athletic Functions
✔ Active in sports requiring control of rotational movements, such as golf, tennis, boxing, and gymnastics.
✔ This muscle is crucial in sports like CrossFit, bodybuilding, and balance exercises.
✔ Plays a key role in controlled rotations in yoga, Pilates, and flexibility training.
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ These muscles play a role in stabilizing the spine and reducing stress between vertebrae.
✔ Weakness in these muscles can lead to vertebral imbalance and increase the risk of lower back pain.
🧠 Innervation | Neural Control
✔ The lumbar, thoracic, and cervical spinal nerves (Spinal Nerves – C3 to L5).
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Posterior Intercostal Arteries
✔ Lumbar Arteries
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Plays a key role in sports such as boxing, golf, tennis, gymnastics, CrossFit, and bodybuilding.
✔ This muscle is essential for controlling subtle spinal rotations during both athletic movements and daily activities.
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Connection with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Works alongside other spinal stabilizing muscles, including the multifidus and erector spinae.
✔ Weakness in this muscle may increase the risk of instability during rotational movements of the spine.
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ Weakness in this muscle can lead to instability between vertebrae and rotational pain in the spine.
✔ Straining or injuring this muscle may result in decreased control over rotational body movements.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Key Exercises to Strengthen These Muscles:
1️⃣ Controlled Torso Rotation – Helps strengthen rotational movements.
2️⃣ Bird-Dog Exercise – Improves muscular control and vertebral balance.
3️⃣ Rotational Plank – Enhances the stability and flexibility of the vertebrae.
4️⃣ Seated Spinal Twist – Improves flexibility and strength of the rotator muscles.
5️⃣ Cable Rotations – An excellent exercise for strengthening spinal rotations.
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery Moves:
✔ Spinal Rotation Stretch – Increases flexibility and reduces vertebral tension.
✔ Side Stretch for Spine – Reduces pressure on the vertebrae and improves movement function.
✅ Interesting Fact:
✔ The rotator muscles of the spine are the smallest motor muscles of the spine, yet they are crucial for maintaining stability and balance in the body!
✅ Practical Tip:
✔ To prevent spinal injuries, it is recommended to perform controlled rotational exercises with light weights!
🔴 Name and Location: Small, deep muscles located between the vertebrae of the spine, responsible for controlling rotational movements and stabilizing the vertebrae.
🟠 Anatomy: Consists of two parts, Rotatores Longus and Rotatores Brevis, located between the transverse processes and spinous processes of the vertebrae in the spine.
🟡 Function: Assists in subtle rotations of the vertebrae, stabilizes the spine, and prevents unstable movements between vertebrae.
🟢 Physiology: Contains both slow-twitch and fast-twitch fibers for maintaining endurance and controlling subtle rotational movements.
🔵 Innervation: The lumbar, thoracic, and cervical spinal nerves (C3 to L5).
🟣 Importance: Active in strength, balance, and rotational sports such as boxing, golf, tennis, CrossFit, and yoga.
🟤 Exercises: Controlled Torso Rotation, Rotational Plank, Bird-Dog, Spinal Rotation Stretch.
⚫ Interesting Fact: These muscles are the smallest yet most important for controlling rotational movements of the spine, and weakness in them can lead to vertebral instability.
🔶 Deep Layer of Deep Muscles
Deep Layer of Deep Muscles
🔹 The deep layer muscles of the spine are the smallest and deepest muscles of the back, playing a role in controlling intervertebral movements, stabilizing the body, and assisting in subtle movements of the vertebrae. These muscles are positioned individually between the vertebrae and ribs, responsible for fine movements and spinal stability.
Interspinalis Muscle
Interspinales Muscle
The Interspinalis Muscle is a small, deep muscle located between the vertebrae of the spine. It plays a role in subtle movements and stabilizing the spine, helping to maintain balance between the vertebrae. The interspinalis muscles are primarily located in various sections of the spine, such as the cervical and lumbar regions, and assist in precise movements between the vertebrae.
✅ Persian Name: عضله بینخاری
✅ Latin Name: Interspinales
✅ Common Name: Intervertebral Muscle
✅ Location:
🟡 The interspinalis muscle is located in various regions of the spine, from the neck to the lumbar area.
🟡 This muscle is positioned between adjacent vertebrae, along the spinous processes.
🟡 Its primary function is to assist in the stability of the vertebrae and perform subtle movements in the spine.
✅ 🦾 Origin:
✔ From the spinous processes of various vertebrae in the cervical, thoracic, and lumbar regions.
✅ 🦿 Insertion:
✔ To the spinous processes of adjacent vertebrae in the upper or lower regions.
✅ 📌 Classification and Function:
🟡 As a deep muscle, it is primarily responsible for controlling subtle movements between the vertebrae.
🟡 Additionally, one of its main functions is to assist in the stability of the vertebrae in the spine.
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Types:
✔ Primarily composed of slow-twitch fibers (Type I) for maintaining endurance over time.
✔ Due to its function, this muscle requires slow-twitch fibers to perform stable and subtle movements.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Movement and Athletic Functions:
✔ This muscle plays a key role in stabilizing the spine during bending, straightening the body, and other fundamental movements.
✔ It is crucial in activities such as yoga and Pilates, which require precise control of spinal movements.
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance:
✔ This muscle has high endurance strength, helping to maintain spinal stability during prolonged activities.
✔ Weakness in this muscle can lead to issues such as lower back pain and neck pain.
✅ 🧠 Innervation:
✔ Spinal nerves from T1 to L5 are responsible for the movements and activities of this muscle.
✅ 🩸 Blood Supply:
✔ The Posterior Intercostal Arteries and Lumbar Arteries supply blood to this muscle.
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities:
✔ The interspinalis muscle is important in activities that require control and balance of the spine, such as dance, yoga, and Pilates.
✔ Strengthening this muscle helps maintain body endurance and prevents spinal injuries.
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Connection with Other Muscles and Joints:
✔ This muscle works in conjunction with other deep muscles, such as the multifidus and rotatores, to maintain spinal stability.
✔ Strengthening the interspinalis muscles helps prevent vertebral injuries and lower back issues.
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues:
✔ Weakness in this muscle can lead to lower back pain and damage to intervertebral discs.
✔ Strain or spasms in the muscle can cause pain and movement limitations in the lumbar or cervical regions.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Key Exercises to Strengthen the Interspinalis Muscle:
1️⃣ Spinal Stability Exercises: Such as planks and bridges (Crutches), which help stabilize the spine.
2️⃣ Spine Stretches: Exercises that increase flexibility and reduce pressure on the spine.
3️⃣ Yoga Stretches: Like the Cat-Cow Pose, which aids in strengthening and stretching this muscle.
✅ Interesting Fact:
✔ Despite its small size, the interspinalis muscle plays a crucial role in maintaining spinal stability and preventing sudden injuries in this area.
✅ Practical Tip:
✔ Compound exercises that include strengthening deep muscles and stretching movements can enhance the performance of this muscle and help prevent chronic spinal pain.
🔴 Name and Location: A deep muscle located between the vertebrae, from the neck to the lumbar region.
🟠 Anatomy: Originates from the spinous processes of the vertebrae and attaches to adjacent vertebrae.
🟡 Function: Stabilizes and controls subtle movements between the vertebrae.
🟢 Physiology: Slow-twitch fibers for maintaining endurance and stability.
🔵 Innervation: Spinal nerves from T1 to L5.
🟣 Importance: Crucial for maintaining balance and preventing spinal injuries.
🟤 Exercises: Stability exercises, spine stretches, yoga movements.
⚫ Interesting Fact: A small muscle, but very important for the stability and health of the spine.
Intertransversarii Muscle
Intertransversarii Muscle
The Intertransversarii muscles are a group of small, deep muscles located within the spine. These muscles are responsible for assisting with movement and stability of the spine, particularly in the cervical and lumbar regions. They are positioned between the transverse processes of the vertebrae and play a crucial role in fine, precise movements. In this review, all anatomical, physiological features, and applications of this muscle will be examined according to the checklist.
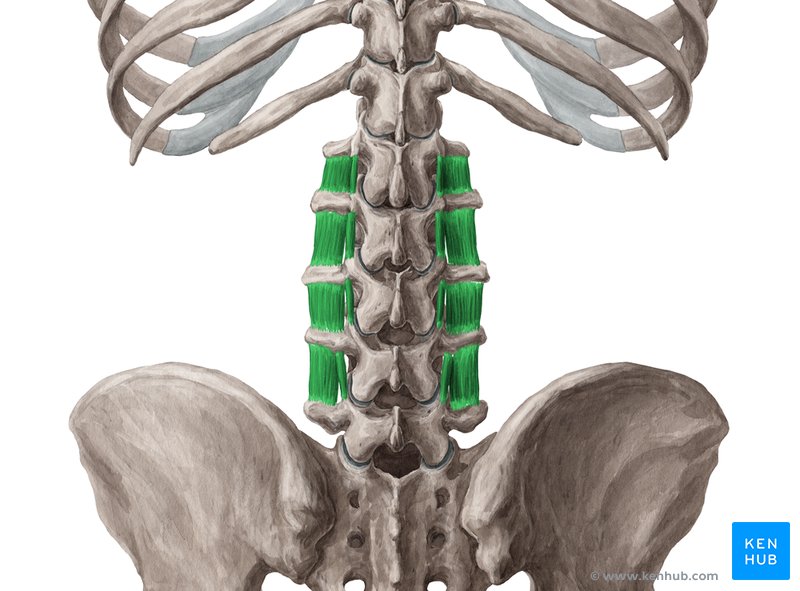
✅ Persian Name: عضله بینعرضی
✅ Latin Name: Intertransversarii
✅ Common Name: –
✅ Location:
🟡 This muscle is located in various regions of the spine, including the cervical, thoracic, and lumbar areas.
🟡 The intertransversarii muscles are positioned at the transverse processes of the vertebrae.
🟡 These muscles are placed on either side of the vertebrae and are interconnected, assisting in stabilization and movement on both sides of the spine.
✅ 🦾 Origin:
✔ The origin of these muscles is from the transverse processes of the vertebrae.
✔ They originate from the transverse processes of the vertebrae in various regions of the spine (cervical, thoracic, and lumbar).
✅ 🦿 Insertion:
✔ These muscles attach to the transverse processes of adjacent vertebrae (in an upward and downward direction).
✅ 📌 Classification and Function:
🟡 These muscles are primarily responsible for small movements and changes in the angle and motion of the vertebrae in the spine.
🟡 Additionally, they play a role in stabilizing and precisely controlling spinal movements.
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Types:
✔ The intertransversarii muscle primarily uses slow-twitch fibers (Type I), which provide the muscle with the ability to maintain stability.
✔ These fibers are well-suited for long-duration activities and controlling subtle movements.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Movement and Athletic Functions:
✔ This muscle plays a role in rotational and lateral movements of the spine, helping with balance and coordination of body movements.
✔ It is essential for maintaining and adjusting the position of the vertebrae during twisting movements and subtle spinal flexions.
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance:
✔ Due to their anatomical and functional characteristics, these muscles have high endurance strength.
✔ Weakness in these muscles can lead to decreased balance and an increased risk of spinal injuries.
✅ 🧠 Innervation:
✔ Spinal nerves from various regions of the spine, particularly from the cervical, thoracic, and lumbar areas, are responsible for innervating the intertransversarii muscles.
✔ Intercostal nerves, especially in the thoracic region, innervate these muscles.
✅ 🩸 Blood Supply:
✔ Blood supply to these muscles is provided by the intercostal arteries and lumbar arteries.
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities:
✔ The intertransversarii muscle is important in sports that require rotational and lateral movement of the spine, such as gymnastics, Pilates, and light sports movements.
✔ Along with other small spinal muscles, this muscle helps prevent shoulder, back, and neck injuries.
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Connection with Other Muscles and Joints:
✔ These muscles, along with other deep spinal muscles such as the multifidus and rotatores, help maintain stability and control movements.
✔ Proper interaction of these muscles in the spine is essential for preventing twisting injuries and excessive pressure on the intervertebral discs.
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues:
✔ Weakness or injury to these muscles can lead to serious spine issues, including back pain, neck pain, and joint problems.
✔ Strain or spasms in these muscles can cause movement limitations in various areas of the body.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Key Exercises to Strengthen the Intertransversarii Muscle:
1️⃣ Spinal Rotations: These exercises help strengthen the intertransversarii muscles and improve flexibility.
2️⃣ Lateral Spine Movements: Such as side bending and stretching, which assist in stabilizing and strengthening this muscle.
3️⃣ Spinal Stability Exercises: Exercises like side planks that are highly effective in strengthening this muscle.
✅ Interesting Fact:
✔ The intertransversarii muscles are located on both sides of the spine and simultaneously assist in maintaining stability and balance of the spine.
✅ Practical Tip:
✔ Strengthening these muscles can enhance athletic performance and help prevent spinal injuries.
🔴 Name and Location: A deep muscle located at the transverse processes of the vertebrae.
🟠 Anatomy: Originates from the transverse processes of the vertebrae and attaches to adjacent vertebrae.
🟡 Function: Assists in movement and maintains spinal stability during lateral and rotational movements.
🟢 Physiology: Slow-twitch fibers for endurance and stability.
🔵 Innervation: Spinal nerves from the cervical, thoracic, and lumbar regions.
🟣 Importance: Strengthening and stabilizing the spine, especially during rotational and lateral movements.
🟤 Exercises: Rotational, lateral, and spinal stability exercises.
⚫ Interesting Fact: A small muscle with a key role in maintaining balance and stability of the spine.
Levator Costarum Muscles
Levatores Costarum Muscle
The Levatores Costarum muscles are small, deep muscles located in the thoracic region of the spine. These muscles play a significant role in the process of breathing and rib movement, acting as accessory muscles during inhalation and exhalation. They assist in lifting the ribs, helping expand the chest cavity during inhalation. A detailed examination of their anatomy, function, and importance will be conducted according to the checklist.
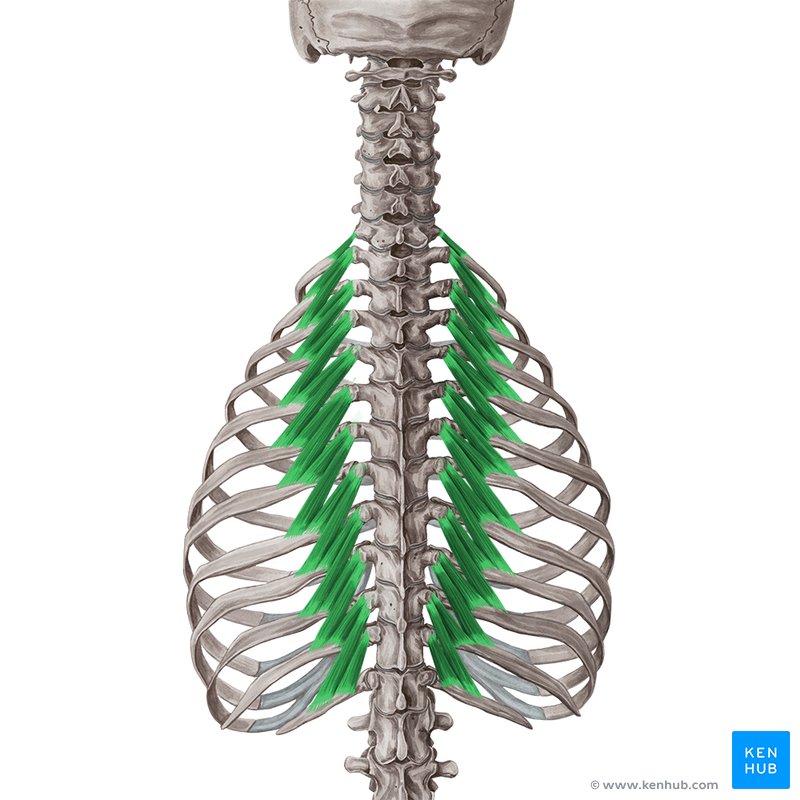
✅ Persian Name: عضلات بالابرنده دندهها
✅ Latin Name: Levatores Costarum
✅ Common Name: –
✅ Location:
🟡 These muscles are located in the thoracic region of the spine, specifically from the thoracic vertebrae T1 to T12.
🟡 Each muscle originates from the thoracic vertebrae and attaches to the adjacent ribs.
✅ 🦾 Origin:
✔ The Levatores Costarum muscles originate from the transverse processes of the thoracic vertebrae (T1 to T12).
✅ 🦿 Insertion:
✔ These muscles attach to the adjacent ribs (the rib located lower in position).
✔ Each muscle connects from one vertebra to the rib above, making these muscles function as crossover muscles.
✅ 📌 Classification and Function:
🟡 The Levatores Costarum muscles are primarily responsible for lifting the ribs during breathing.
🟡 These muscles play a role in both inhalation and exhalation processes, assisting in expanding the chest cavity.
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Types:
✔ The Levatores Costarum muscles primarily use slow-twitch fibers (Type I), which are suitable for long-duration performance.
✔ These fibers are more suited for support and sustained breathing rather than explosive strength.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Movement and Athletic Functions:
✔ These muscles are crucial in sports that require deep breathing, such as swimming and running.
✔ Additionally, these muscles help stabilize the spine and ribcage during physical activities.
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance:
✔ The Levatores Costarum muscles are specifically designed for endurance and optimal breathing.
✔ Weakness in these muscles can lead to respiratory issues and back pain, as they assist in the free movement of the ribs.
✅ 🧠 Innervation:
✔ These muscles are innervated by the intercostal nerves originating from the thoracic region.
✔ The intercostal nerves, especially from levels T1 to T12, are responsible for innervating the Levatores Costarum muscles.
✅ 🩸 Blood Supply:
✔ The blood supply to these muscles is provided by the intercostal arteries.
✔ The intercostal arteries, which originate from the aortic and subclavian arteries, supply blood to the Levatores Costarum muscles.
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities:
✔ The Levatores Costarum muscles are crucial in sports that require effective and deep breathing.
✔ These muscles also help increase lung capacity and improve respiratory performance in activities such as swimming, running, and wrestling.
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Connection with Other Muscles and Joints:
✔ These muscles are directly connected to the ribs and thoracic vertebrae, creating a close relationship with the respiratory muscles and diaphragm.
✔ Additionally, the intercostal muscles, along with other muscles, assist in stabilizing the ribcage and spine during sports and twisting movements.
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues:
✔ Weakness or injury to the Levatores Costarum muscles can lead to breathing difficulties and impaired rib movement.
✔ These muscles are prone to strain and spasms, especially in individuals with weak respiratory function or during intense physical activity.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Key Exercises to Strengthen the Levatores Costarum Muscles:
1️⃣ Breathing Exercises: Diaphragmatic breathing and deep breathing exercises that help strengthen these muscles and improve respiratory function.
2️⃣ Costal Stretching: Exercises designed to stretch the ribs and strengthen the Levatores Costarum muscles.
3️⃣ Respiratory Muscle Strengthening: Exercises like forced inhalation and exhalation that help strengthen these muscles.
✅ Interesting Fact:
✔ The Levatores Costarum muscles play a simultaneous role in both respiratory function and rib movement during deep breathing.
✅ Practical Tip:
✔ Strengthening these muscles can help improve respiratory function and increase lung capacity.
🔴 Name and Location: Small muscles that originate from the transverse processes of the thoracic vertebrae and attach to the ribs above.
🟠 Anatomy: Originates from the thoracic vertebrae T1 to T12 and attaches to the adjacent ribs.
🟡 Function: Lifting the ribs during the breathing process, especially during inhalation.
🟢 Physiology: Slow-twitch fibers for long-duration performance and supporting breathing.
🔵 Innervation: Intercostal nerves from the thoracic region.
🟣 Importance: Strengthening breathing, stability of the ribcage, and spine.
🟤 Exercises: Breathing and stretching exercises to strengthen these muscles.
⚫ Interesting Fact: A key role in breathing and improving lung capacity.
Interesting and Practical Facts
1.The muscles of the back are key to movement in the standing position.
The back muscles, especially the erector spinae, are crucial for maintaining an upright posture and body balance. Without these muscles, you wouldn't be able to effectively maintain your balance while standing. 💪
2.The back muscles protect the spine.
The back muscles, especially the multifidus and semispinalis, protect the spine from damage caused by incorrect movements or sudden pressure. These muscles help prevent injury to the intervertebral discs. 🛡️
3. The back muscles work in collaboration with the shoulders.
The trapezius muscles and rhomboids assist in the movement and stability of the shoulders, playing a key role in many sports such as swimming and weightlifting. 🏋️♂️
4. The back muscles assist in breathing.
Intercostal muscles, such as the serratus posterior superior, assist in breathing, especially in expanding the ribs during deep inhalation. 🌬️
5. The back muscles help in increasing height.
Strengthening the back muscles helps improve posture and increase height. By strengthening these muscles, the natural curve of the lower back is enhanced, allowing a person to appear taller and more upright. 📏
6. The back muscles are highly effective in preventing lower back pain.
Strengthening the erector spinae and other back muscles is particularly beneficial in reducing lower back pain and preventing chronic back issues. 🔴
7. The back muscles are the best companions for stretching exercises.
Many stretching exercises, such as the Cat-Cow Stretch and Lumbar Stretch, target the back muscles more than any other muscle. 🧘♂️
8. The back muscles are directly linked to the strength of the abdominal muscles.
The back muscles and abdominal muscles work directly together to maintain balance and perform strength movements such as deadlifts and squats. Strengthening both muscle groups enhances body stability. 🔄
9. The relationship between the back muscles and the neck region.
The back muscles, including the longissimus and semispinalis, are highly effective in strengthening the neck and preventing neck pain in individuals who spend long hours sitting. 🤕
10. The back muscles help in the growth of other muscles.
These muscles act as a "protective layer" for other muscles, such as the abdominal muscles, hamstrings, and glutes. When the back muscles are strengthened, other muscles experience less strain. 💥
11. Strengthening the back muscles improves stretching and flexibility.
With proper exercises, the back muscles gain more flexibility, which improves movement in stretching, yoga, and endurance sports. 🧘♀️
12. The back muscles may influence the simulation of other body positions.
Many movements in sports like gymnastics and yoga use the back muscles as the foundation for movement. For example, in the Superman Pose, the back muscles are engaged to stabilize the movement. 🦸♂️
13. The back muscles are vital in endurance sports.
Strengthening the back muscles is essential, especially in endurance sports like long-distance running, cycling, and swimming, which require body balance and endurance. 🚴♂️
14. The back muscles are key for strength movements.
The back muscles assist in stabilizing and strengthening the body in strength sports like deadlifts, squats, and hip thrusts, which require heavy and powerful movements. 🏋️♀️
15. Back exercises can help reduce pressure on the knees.
By strengthening the back muscles, the pressure on the knee joints is reduced. This is especially important for individuals with knee issues and athletes. 🦵
16. The back muscles have an impact on body psychology.
Exercises and strengthening of the back muscles, especially in sports like yoga, can help boost self-confidence and improve mental well-being. 🧠
17. The back muscles help protect the nervous system.
Strengthening the back muscles helps protect the nervous system and spinal cord, and can prevent pressure on the spinal nerves during improper movements. ⚡
18. The back muscles can impact digestive health.
Strengthening the back muscles improves posture, reduces pressure on the digestive system, and consequently enhances digestive function. 🍽️
19. The role of the back muscles in transforming body posture.
Strengthening the back muscles, especially in individuals with lower back curvature (lordosis), can help change posture and address long-standing issues. 💡
20. The back muscles and energy increase.
By strengthening the back muscles, the body can gain more energy for daily activities and more intense workouts. 🔋
Conclusion
Conclusion
In these reviews, we focused on a detailed analysis of the various muscles of the body, especially those related to the spine. Each muscle plays a specific role in maintaining balance, endurance, and optimal body movement. Strengthening these muscles through targeted exercises can help improve physical performance, prevent muscle injuries, and reduce chronic pain. Ultimately, understanding the anatomy and function of muscles allows us to perform more effective exercises for maintaining health and physical strength.

References
Resources
Anatomy and medical books :
Gray's Anatomy (one of the standard references in anatomy)
Netter's Atlas of Human Anatomy (a well-known illustrated atlas in anatomy)
Clinically Oriented Anatomy by Keith Moore
Medical databases :
PubMed (for scientific and research articles)
MedlinePlus (health and medical information)
WebMD (for practical and general health information)
Sports and training references :
Strength Training Anatomy by Frederic Delavier
Essentials of Strength Training and Conditioning by NSCA
Well-known articles and training programs by international coaches
Medical databases :
PubMed (for scientific and research articles)
MedlinePlus (health and medical information)
WebMD (for practical and general health information)
Specialized sports and health websites :
Images used:
(Kenhub) kenhub.com
Further Reading
Further reading
Pelank Life | Body Health Assessment
The Best Body Health Calculators Using Scientific Methods
Developed by Pelank Life ©