Abdominal Muscle Groups
Abdominal Muscle Groups
Introduction
Introduction
The abdominal muscles not only contribute to a well-defined appearance and athletic physique but are also functionally one of the most important muscle groups in the body. According to Gray’s Anatomy, these muscles have roles beyond merely flexing and extending the trunk; as a power center, they play a crucial role in maintaining balance, stabilizing the spine, and transmitting force during daily and athletic movements.
The abdominal muscles are divided into three main groups:
- The anterior abdominal muscles include the Rectus Abdominis, which is effective in trunk flexion and controlling intra-abdominal pressure.
- The lateral abdominal muscles include the external and internal obliques, which play roles in rotational and lateral movements of the body.
- The posterior abdominal muscles, such as the Quadratus Lumborum, are effective in stabilizing the spine and maintaining overall body balance.
From bodybuilding exercises and martial arts to everyday movements like standing, walking, and twisting, the abdominal muscles are involved in all body motions. Weakness in this muscle group can lead to lower back pain, reduced endurance, and poor performance in strength and endurance training.
🔹 In this comprehensive review, based on Gray’s Anatomy, we will analyze the structure, function, and importance of the abdominal muscles, as well as explore methods to strengthen them and prevent injuries.

1. Anterior Abdominal Muscles
Anterior Abdominal Muscles
Rectus Abdominis (Six-Pack Muscle)
Rectus Abdominis Muscle
The rectus abdominis is one of the most important muscles in the anterior abdominal wall, located vertically on both sides of the linea alba. This muscle is responsible for flexing the trunk, stabilizing the spine, and compressing the abdominal viscera.
The “six-pack” appearance seen in athletes results from the presence of tendinous intersections on this muscle. Strengthening the rectus abdominis through bodybuilding, gymnastics, and martial arts exercises significantly improves overall body performance.
✅ Effective exercises for this muscle include crunches, leg raises, planks, and ab wheel rollouts, which help strengthen its power and endurance.
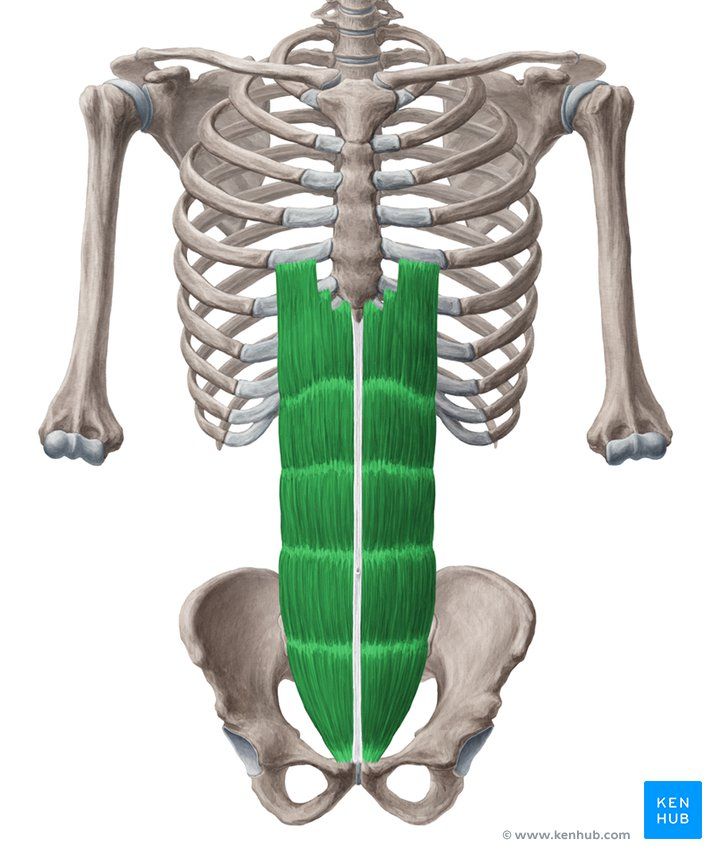
✅ Persian Name: Azole Raaste Shakami
✅ Latin Name: Rectus Abdominis | Six-Pack
✅ Common Name: Abs
✅ Location:
🟡 This muscle is located on the front of the abdomen, on both sides of the Linea Alba.
🟡 It originates from the lower ribs and extends to the pelvis.
🟡 It has horizontal tendinous bands that create the six-pack appearance.
✅ 🦾 Origin
✔ Costal cartilage of ribs 5, 6, and 7
✔ Xiphoid process of the sternum
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ Pubic crest of the pelvic bone
✔ Pubic symphysis
✅ 📌 Classification and Function
✔ Flexion of the trunk – such as during a crunch
✔ Compression of abdominal contents – aids in exhalation and increases intra-abdominal pressure
✔ Maintaining the strength of the abdominal wall and spinal balance
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Type
✔ Mostly composed of slow-twitch (Type I) fibers to maintain body endurance.
✔ Contains fast-twitch (Type II) fibers for rapid and powerful movements, such as explosive crunches.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Motor and Athletic Performance
✔ Plays a key role in all abdominal and core exercises, such as crunches, leg raises, and planks.
✔ Responsible for maintaining body balance and preventing lower back injuries.
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ One of the most important muscles for body stability, especially in endurance sports.
✔ Weakness in this muscle can lead to lower back pain and decreased body balance.
🧠 Innervation
✔ Thoracoabdominal nerves – T7 to T12
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Superior and inferior epigastric arteries
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Bodybuilding – Active in all abdominal exercises such as crunches, planks, and V-ups.
✔ Martial arts – Helps increase endurance and abdominal resilience.
✔ Gymnastics and CrossFit – Plays a key role in movements such as toe-bar, leg lifts, and V-sit.
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Connection with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Works in coordination with the internal and external oblique muscles to create rotational movements of the trunk.
✔ Collaborates with the erector spinae and gluteal muscles to stabilize the spine and pelvis.
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ Weakness in this muscle leads to core instability and lower back pain.
✔ Strain and muscle tightness due to heavy training or improper execution of abdominal exercises.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Main exercises to strengthen the rectus abdominis muscle:
1️⃣ Standard Crunches – The most effective exercise for strengthening the middle of the abdomen
2️⃣ Leg Raises – Focuses on the lower part of the rectus abdominis
3️⃣ Plank – Improves core endurance and stability
4️⃣ Ab Wheel Rollout – A challenging exercise for deep abdominal muscle engagement
5️⃣ V-Sit Hold – Strengthens the abdominal muscles and enhances core control
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery Movements
✔ Cobra Stretch – Opens up and aids in the recovery of the abdominal muscles
✔ Cat-Cow Stretch – Increases core flexibility
✅ Interesting Fact
✔ The rectus abdominis is one of the strongest endurance muscles in the body, capable of staying active for long periods, even in static movements like the plank!
✅ Practical Tip
✔ To fully strengthen the six-pack, exercises should include both endurance (like planks) and strength (like crunches and leg raises) training.
🔴 Name and Location: Located on the front of the abdomen, from the lower ribs to the pelvis.
🟠 Anatomy: It has tendinous bands that divide it into several sections.
🟡 Function: Trunk flexion, abdominal compression, and core stabilization.
🟢 Physiology: A combination of slow-twitch and fast-twitch fibers for endurance and strength.
🔵 Innervation: Thoracoabdominal nerves T7-T12
🟣 Importance: Key role in bodybuilding, CrossFit, martial arts, and gymnastics
🟤 Exercises: Crunches, leg raises, planks, ab wheel rollouts, V-sits
⚫ Interesting Fact: A resilient muscle with high endurance capacity in static exercises.
The Pyramidalis Muscle
Pyramidalis Muscle
The Pyramidalis Muscle is a small, triangular-shaped muscle located in the lower abdomen, in front of the rectus abdominis muscle.
This muscle may be naturally absent in 20 to 25 percent of individuals and plays a limited role in the function of the abdominal muscles.
Its primary function is to tension and stabilize the linea alba, which connects the central part of the rectus abdominis muscles.
✅ Although this muscle plays a minor role in abdominal movements, it is used as an anatomical landmark in some abdominal surgeries.
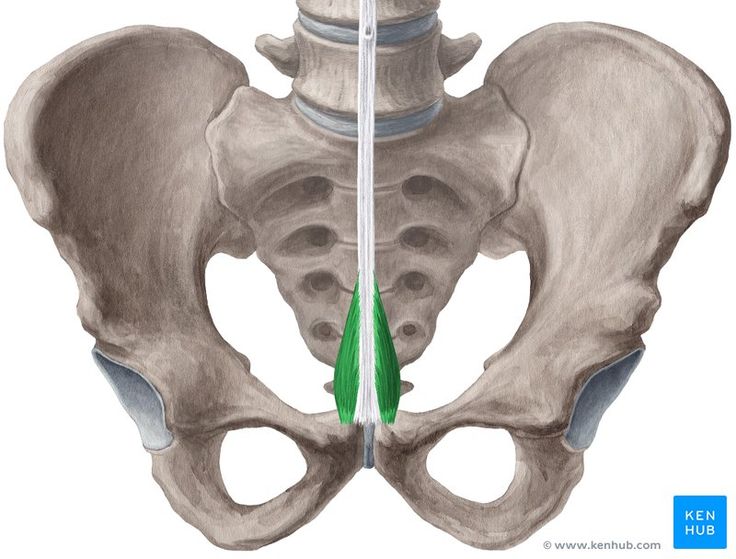
✅ Persian Name: Azole Herami
✅ Latin Name: Pyramidalis
✅ Common Name: Pyramid Muscle
✅ Location:
🟡 Located in the lower abdomen, in front of the rectus abdominis muscle and close to the pelvis.
🟡 It originates from the pubic bone and extends towards the linea alba.
🟡 It is naturally absent in 20-25% of individuals.
✅ 🦾 Origin
✔ Pubic Crest
✔ Pubic Symphysis
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ Linea Alba – A fibrous connective tissue band that connects the abdominal muscles at the center.
✅ 📌 Classification and Function
✔ Tensing the Linea Alba
✔ Minor role in abdominal compression and movements of the rectus abdominis muscle
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Type
✔ Primarily composed of slow-twitch fibers (Type I) for endurance maintenance.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Motor and Athletic Performance
✔ It does not have a direct impact on abdominal exercises, but it helps maintain symmetry and strengthen the Linea Alba.
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ It is weak and small, and unlike the rectus abdominis, it does not play a significant role in strength movements.
🧠 Innervation
✔ Subcostal Nerve – T12
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Inferior Epigastric Artery
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ It does not have a direct impact on abdominal exercises, but it plays a role in trunk stability and abdominal surgeries.
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Connection with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Interacts with the rectus abdominis and Linea Alba for abdominal stabilization and tension.
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ Due to its small size and limited role, it is less prone to injury.
✔ It is used as an anatomical landmark in abdominal surgeries.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Main exercises to strengthen the Pyramidalis muscle
✔ This muscle is not strengthened independently, and there are no specific exercises for it.
✔ It is indirectly engaged in abdominal exercises like crunches and planks.
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery Movements
✔ General abdominal stretches, such as the Cobra Stretch, can help maintain the flexibility of this muscle.
✅ Interesting Fact
✔ The Pyramidalis muscle may be absent in 20 to 25 percent of the population, but its absence does not affect the function of the abdominal muscles! 😮
✅ Practical Tip
✔ This muscle is used as a landmark for the location of the Linea Alba in abdominal surgeries.
🔴 Name and Location: A small muscle located in the lower abdomen, in front of the rectus abdominis.
🟠 Anatomy: Originates from the pubic bone, attaches to the Linea Alba
🟡 Function: Tension and stabilization of the Linea Alba
🟢 Physiology: Primarily composed of slow-twitch fibers
🔵 Innervation: Subcostal Nerve (T12)
🟣 Importance: Does not have a direct impact on abdominal exercises but is important in abdominal surgeries
🟤 Exercises: It does not have independent exercises, but general abdominal exercises activate it.
⚫ Interesting Fact: It may be absent in one-quarter of individuals! 😮
2. Lateral Abdominal Muscles (Oblique Muscles)
Lateral Abdominal Muscles
External Oblique Muscle
External Oblique Muscle
The external oblique muscle is one of the most important lateral abdominal muscles, located on both sides of the torso. This muscle performs essential functions such as trunk rotation and lateral flexion, abdominal compression, and assists in breathing.
✅ The external oblique muscle is the largest and most superficial lateral abdominal muscle, and due to the direction of its fibers, it slopes downward and forward (similar to the motion of putting your hand in your pocket).
✅ This muscle is highly activated in exercises such as twisting crunches, bicycle crunches, side planks, and Russian twists, playing a key role in core stability and rotational movements.
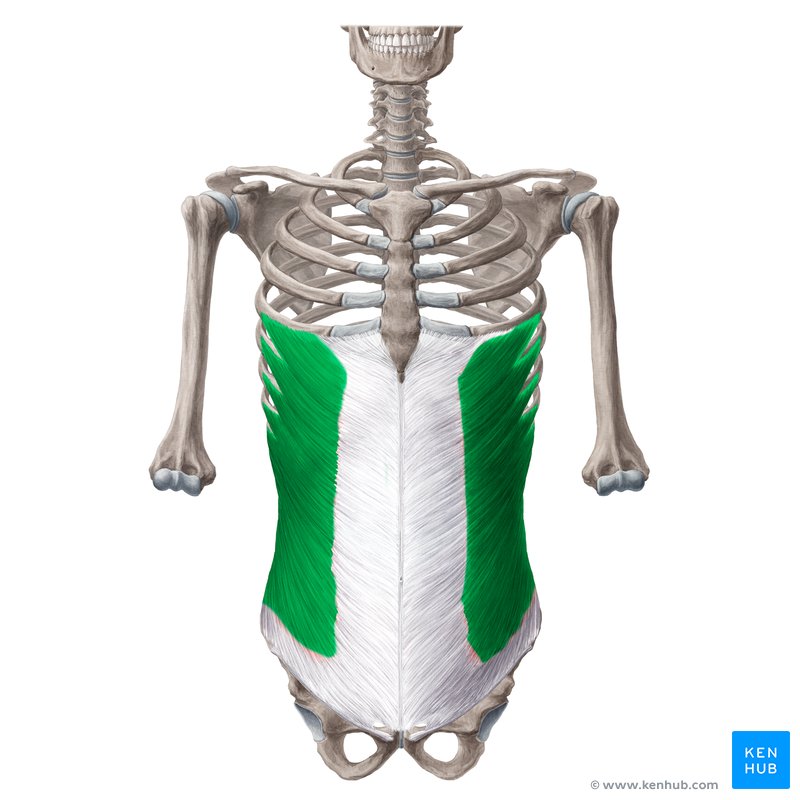
✅ Persian Name: Azole Mayel Khareji
✅ Latin Name: External Oblique
✅ Common Name: Side Abs | External Obliques
✅ Location:
🟡 This muscle extends on both sides of the abdomen, from the lower ribs to the pelvic bone.
🟡 It is the largest and most superficial lateral abdominal muscle.
🟡 It has fibers that run diagonally from top to bottom and from back to front.
✅ 🦾 Origin
✔ Ribs 5-12 – The origin of this muscle begins from the outer surface of these ribs.
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ Linea Alba – A fibrous connective tissue structure located at the center of the abdomen.
✔ Iliac Crest – The upper portion of the pelvic bone.
✔ Inguinal Ligament – A band that runs between the pelvis and the groin area.
✅ 📌 Classification and Function
✔ Trunk Rotation – For rotating the abdomen and sides, such as in bicycle crunches.
✔ Lateral Flexion – In bending to the side, like in side planks.
✔ Compression of Abdominal Contents – Helps increase intra-abdominal pressure, such as during a strong exhalation.
✔ Maintaining trunk stability and assisting in strength movements like deadlifts and squats.
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Type
✔ It has a combination of ✔ A combination of slow-twitch fibers (Type I) and fast-twitch fibers (Type II). ✔ For maintaining balance and power movements.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Motor and Athletic Performance
✔ It is active in all twisting and lateral exercises, such as Russian twists and twisting crunches.
✔ Responsible for core stability during weightlifting and stretching movements.
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ This muscle has high endurance due to its activity in all daily and athletic movements.
✔ Its weakness can lead to trunk imbalance and reduced spinal stability.
🧠 Innervation
✔ Intercostal Nerves T7-T11
✔ Subcostal Nerve – T12
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Posterior Intercostal Arteries
✔ Superior & Inferior Epigastric Arteries
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Bodybuilding and Fitness: Plays a crucial role in rotational and lateral abdominal movements such as Russian twists and side planks.
✔ Martial Arts: This muscle plays an important role in rotation and body stability during punching, kickboxing, wrestling, and MMA.
✔ Yoga and Pilates: Helps improve flexibility and body balance.
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Connection with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Interacts with the internal oblique muscles, rectus abdominis, and lumbar muscles to create lateral and rotational movements of the torso.
✔ Works together with the gluteal muscles and erector spinae in trunk stability and spinal balance.
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ Weakness of this muscle leads to trunk weakness, sagging sides, and spinal imbalance.
✔ Muscle strain may occur due to intense abdominal exercises or excessive twisting movements.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Main exercises to strengthen the external oblique muscle:
1️⃣ Russian Twists – The most effective movement for strengthening trunk rotation
2️⃣ Bicycle Crunches – Builds power and endurance in the sides
3️⃣ Side Plank – Increases trunk stability and balance
4️⃣ Oblique Crunches – Enhances size and definition of the sides
5️⃣ Dumbbell Side Bends – Increases strength in lateral movements
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery Movements
✔ Cobra Stretch – Enhances flexibility and aids in abdominal muscle recovery
✔ Side Stretch – Reduces tension and improves the range of motion in the sides
✅ Interesting Fact
✔ The external oblique muscle is one of the most important rotational and stabilizing muscles of the body, and it is automatically activated in all daily movements!
✅ Practical Tip
✔ If you want to strengthen and shape your sides, a combination of resistance exercises and endurance movements (such as side planks) is the best option!
🔴 Name and Location: Superficial lateral abdominal muscle, from the lower ribs to the pelvis
🟠 Anatomy: Has diagonal fibers running from top to bottom and forward
🟡 Function: Rotation, lateral flexion, abdominal compression
🟢 Physiology: A combination of slow-twitch and fast-twitch fibers
🔵 Innervation: Intercostal nerves T7-T11 and T12
🟣 Importance: Plays a key role in abdominal exercises, martial arts, bodybuilding, and yoga
🟤 Exercises: Russian Twists, Side Planks, Bicycle Crunches, Dumbbell Side Bends
⚫ Interesting Fact: A muscle that is active in all daily and athletic movements.
Internal Oblique Muscle
Internal Oblique Muscle
🔹 The internal oblique muscle is one of the deep lateral abdominal muscles located beneath the external oblique muscle.
🔹 This muscle plays a crucial role in trunk rotation, lateral flexion, abdominal compression, and maintaining trunk stability.
🔹 The direction of its fibers is opposite to that of the external oblique, extending upward and forward.
✅ The internal oblique muscle is highly active in exercises such as twisting crunches, bicycle crunches, side planks, and Russian twists, playing a key role in core stability and rotational movements.
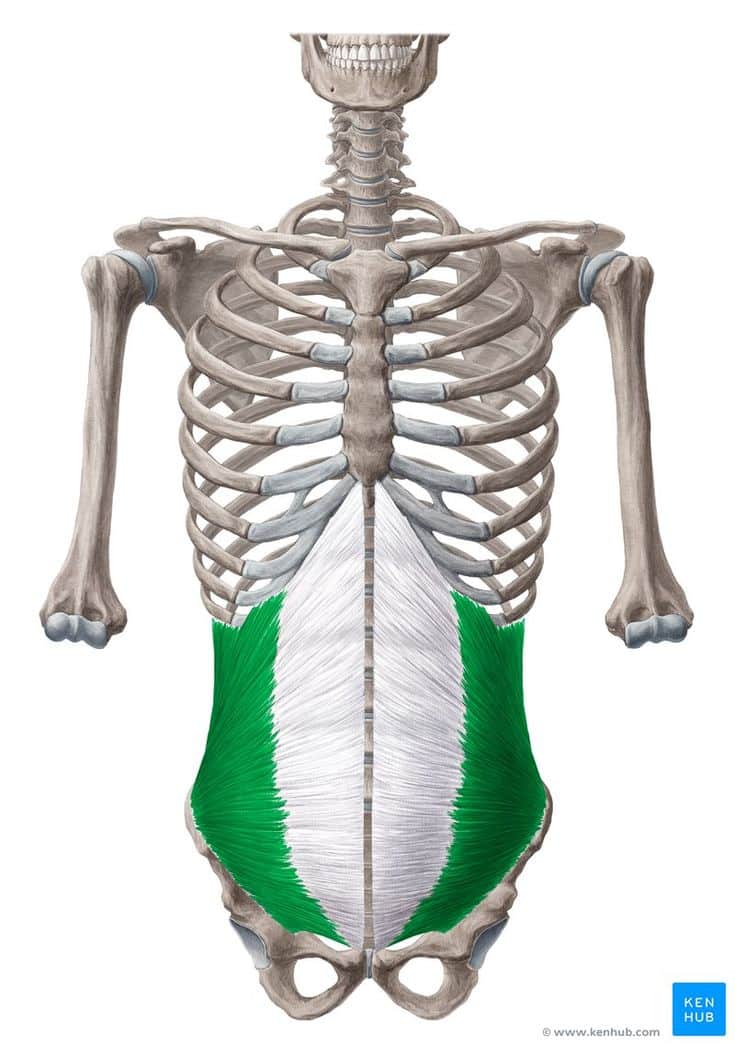
✅ Persian Name: Azole Mayel Dakheli
✅ Latin Name: Internal Oblique
✅ Common Name: Deep Side Abs | Internal Obliques
✅ Location:
🟡 This muscle lies beneath the external oblique, extending from the lower ribs to the pelvis and the Linea Alba.
🟡 It is deeper than the external oblique, but in some areas, it lies on top of the transverse abdominis muscle.
🟡 Its fibers run diagonally from bottom to top, opposite to the external oblique.
✅ 🦾 Origin
✔ Iliac Crest – The upper portion of the pelvic bone.
✔ Thoracolumbar Fascia – A strong connective tissue in the lumbar region.
✔ Inguinal Ligament – A band running between the pelvis and the groin.
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ Ribs 10-12
✔ Linea Alba – Located at the center of the abdomen and connected to the rectus abdominis muscle.
✅ 📌 Classification and Function
✔ Trunk Rotation – Works with the opposite external oblique muscle to create abdominal rotation (such as in Russian twists).
✔ Lateral Flexion – Assists in bending the sides, like in side planks.
✔ Compression of Abdominal Contents – Plays a role in strong exhalation and increasing intra-abdominal pressure.
✔ Maintaining trunk stability and supporting the spine during heavy movements such as deadlifts and squats.
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Type
✔ A combination of ✔ A combination of slow-twitch fibers (Type I) and fast-twitch fibers (Type II). For maintaining endurance and power movements.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Motor and Athletic Performance
✔ Active in all rotational and lateral movements such as bicycle crunches and Russian twists.
✔ Plays a key role in stabilizing the body’s core during weightlifting and athletic movements.
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ It has high endurance and plays a vital role in maintaining spinal and trunk stability.
✔ Weakness in this muscle can lead to trunk imbalance and reduced spinal stability.
🧠 Innervation
✔ Intercostal Nerves T8-T12
✔ Iliohypogastric & Ilioinguinal Nerves
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Posterior Intercostal Arteries
✔ Inferior Epigastric Artery
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Bodybuilding and Fitness: Plays an important role in rotational and lateral movements such as Russian twists and side planks.
✔ Martial Arts: This muscle plays a key role in rotation and body stability during boxing, kickboxing, wrestling, and MMA.
✔ Yoga and Pilates: Helps in stretching movements and improving body balance.
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Connection with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Interacts with the external oblique muscles, rectus abdominis, and transverse abdominis to create rotational and lateral trunk movements.
✔ Works together with the gluteal muscles and erector spinae in trunk stability and spinal balance.
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ Weakness in this muscle can lead to reduced body balance and increased risk of lower back pain.
✔ Muscle strain may occur due to sudden rotational movements or intense exercises.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Main exercises to strengthen the internal oblique muscle:
1️⃣ Russian Twists – Enhance rotational power of the torso
2️⃣ Bicycle Crunches – Combine rotation and endurance
3️⃣ Side Plank – Improve core stability and side strength
4️⃣ Oblique Crunches – Increase size and strength in the sides
5️⃣ Dumbbell Side Bends – Build strength in lateral movements
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery Movements
✔ Cobra Stretch – Enhances torso flexibility
✔ Side Stretch – Reduces tension and improves range of motion
✅ Interesting Fact
✔ The internal oblique muscle works in conjunction with the opposite external oblique; that is, the right internal oblique coordinates with the left external oblique in trunk rotation!
✅ Practical Tip
✔ To have strong and firm sides, combine rotational and lateral exercises with weights for better muscle growth!
🔴 Name and Location: Deep lateral abdominal muscle, located beneath the external oblique
🟠 Anatomy: Fibers run opposite to the external oblique, extending upward and inward
🟡 Function: Rotation, lateral flexion, abdominal compression
🟢 Physiology: A combination of slow-twitch and fast-twitch fibers
🔵 Innervation: Intercostal nerves T8-T12 and lumbar nerves
🟣 Importance: Plays a key role in martial arts, bodybuilding, and yoga
🟤 Exercises: Russian Twists, Side Planks, Bicycle Crunches, Dumbbell Side Bends
⚫ Interesting Fact: Works with the opposite external oblique for trunk rotation.
Transverse Abdominis Muscle
Transversus Abdominis Muscle
🔹 The Transverse Abdominis (TVA) is the deepest abdominal muscle, encircling the torso like a muscular belt.
🔹 This muscle is responsible for increasing intra-abdominal pressure, stabilizing the spine, and maintaining trunk strength.
🔹 Unlike other abdominal muscles, it is not directly involved in rotational or bending movements of the torso, but it plays a vital role in all strength and endurance exercises.
✅ The TVA muscle is known as the body’s core stabilizer and plays a key role in sports such as bodybuilding, yoga, Pilates, and weightlifting.
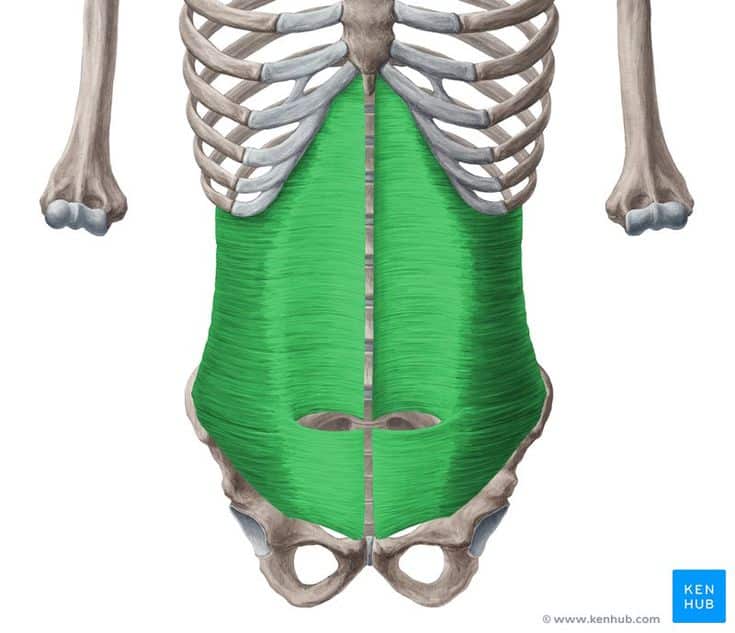
✅ Persian Name: Azole Arzi Shekam
✅ Latin Name: Transversus Abdominis
✅ Common Name: TVA | Deep Core Muscle
✅ Location:
🟡 The deepest abdominal muscle, located beneath the internal oblique muscle.
🟡 Its fibers run horizontally from the spine to the Linea Alba.
🟡 Its main role is to provide stability to the torso and increase intra-abdominal pressure.
✅ 🦾 Origin
✔ Thoracolumbar Fascia – The lumbar region of the back
✔ Inner Surface of Ribs 7-12
✔ Iliac Crest – The upper portion of the pelvic bone
✔ Inguinal Ligament – A band running between the pelvis and the groin
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ Linea Alba – The center of the abdomen, connected to the rectus abdominis muscle
✔ Pubic Symphysis
✅ 📌 Classification and Function
✔ Intra-Abdominal Pressure – Similar to holding the breath during heavy movements like deadlifts and squats.
✔ Core Stabilization – Prevents lower back injuries and improves balance.
✔ Assists in exhalation and abdominal compression – In respiratory exercises and endurance sports.
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Type
✔ Primarily composed of slow-twitch fibers (Type I) that play a role in maintaining trunk endurance.
✔ Contains some fast-twitch fibers (Type II) to assist in sudden and powerful activities.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Motor and Athletic Performance
✔ Active in all endurance and stabilizing movements such as planks, squats, and deadlifts.
✔ Plays a key role in sports requiring balance and body control, such as yoga, Pilates, and gymnastics.
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ Weakness in this muscle leads to trunk imbalance, sagging abdomen, and lower back pain.
✔ Its strength helps improve athletic performance and prevent lower back injuries.
🧠 Innervation
✔ Intercostal Nerves T7-T12
✔ Iliohypogastric & Ilioinguinal Nerves
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Posterior Intercostal Arteries
✔ Inferior Epigastric Artery
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Bodybuilding and Weightlifting: Helps maintain intra-abdominal pressure in movements like squats, deadlifts, and presses.
✔ Yoga and Pilates: Crucial for controlling balance and improving core stability.
✔ Running and Martial Arts: This muscle prevents lower back injuries and enhances overall body efficiency.
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Connection with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Interacts with the rectus abdominis, internal oblique, and external oblique muscles to create trunk stability and control.
✔ Works with the erector spinae and gluteal muscles to maintain spinal stability.
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ Weakness in this muscle increases the risk of lower back pain, reduces balance, and causes abdominal sagging.
✔ Improper exercise or lifting heavy weights without engaging the TVA can lead to lumbar disc injuries.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Main exercises to strengthen the transverse abdominis muscle:
1️⃣ Plank – The best exercise for core endurance
2️⃣ Diaphragmatic Breathing – Increases TVA control
3️⃣ V-Sit Hold – Strengthens deep abdominal muscles
4️⃣ Dead Bug Exercise – Improves coordination and core stability
5️⃣ Hip Thrusts – Strengthens TVA muscles in combination with glutes
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery Movements
✔ Cobra Stretch – Helps open up the TVA muscles
✔ Yoga stretching and breathing exercises – Enhance TVA muscle control
✅ Interesting Fact
✔ The transverse abdominis muscle acts like a muscular belt, playing a crucial role in stabilizing the trunk and reducing pressure on the spine.
✅ Practical Tip
✔ If you want a strong and stable core, incorporate TVA exercises like planks and dead bugs into your routine!
🔴 Name and Location: The deepest abdominal muscle, located beneath the internal oblique muscles.
🟠 Anatomy: Its fibers run transversely, encircling the abdomen.
🟡 Function: Increases intra-abdominal pressure, stabilizes the trunk, and assists with breathing.
🟢 Physiology: Primarily composed of slow-twitch fibers for endurance.
🔵 Innervation: Intercostal nerves T7-T12 and lumbar nerves.
🟣 Importance: Plays a key role in strength training, yoga, and fitness.
🟤 Exercises: Plank, Dead Bug, V-Sit Hold, Hip Thrusts, Breathing Exercises.
⚫ Interesting Fact: It functions like a muscular belt to maintain body stability.
3. Posterior Abdominal Muscles
Posterior Abdominal Muscles
Quadratus Lumborum Muscle
Quadratus Lumborum Muscle
🔹 The quadratus lumborum muscle is one of the most important posterior abdominal muscles, located on both sides of the spine, between the 12th rib and the pelvic bone.
🔹 This muscle is responsible for stabilizing the spine, lateral trunk flexion, and assisting with breathing.
🔹 Due to its unique position, this muscle is recognized as one of the key muscles in preventing lower back pain and maintaining body balance.
✅ The quadratus lumborum is active in exercises such as side planks, deadlifts, dumbbell side bends, and stretching exercises, playing a crucial role in trunk stability.
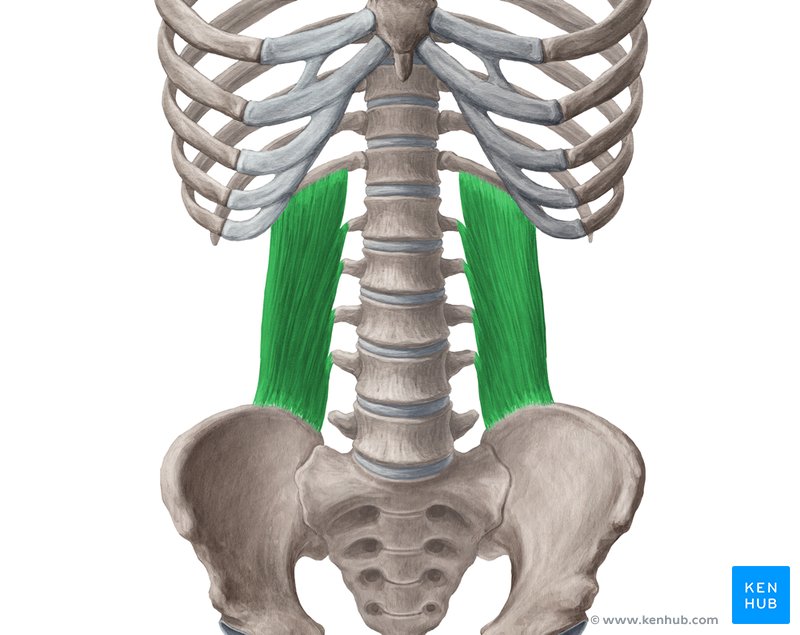
✅ Persian Name: Azole Morabae Kamari
✅ Latin Name: Quadratus Lumborum (QL)
✅ Common Name: Lower Back Muscle | QL
✅ Location:
🟡 Located on both sides of the spine, between the 12th rib and the pelvic bone.
🟡 Positioned behind the abdominal muscles and alongside the erector spinae muscles.
🟡 Its main function is to stabilize the spine and assist with lateral flexion.
✅ 🦾 Origin
✔ Iliac Crest – The upper portion of the pelvic bone
✔ Iliolumbar Ligament – A ligament that connects the spine to the pelvis
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ 12th Rib – The last rib
✔ Transverse Processes of L1-L4 – The transverse processes of the first to fourth lumbar vertebrae
✅ 📌 Classification and Function
✔ Lateral Flexion of the Trunk – Like the dumbbell side bend movement
✔ Core & Spinal Stability – In movements such as squats, deadlifts, and other strength exercises
✔ Respiration Support – During deep exhalation
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Type
✔ A combination of Slow-twitch fibers (Type I) for endurance and fast-twitch fibers (Type II) for power movements.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Motor and Athletic Performance
✔ It is active in all core stabilization movements such as side planks, deadlifts, and squats.
✔ Plays a key role in balance and preventing lower back injuries.
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ Weakness in this muscle leads to spinal imbalance and lower back pain.
✔ Strengthening it helps improve athletic performance and prevent spinal injuries.
🧠 Innervation
✔ Subcostal Nerve – T12
✔ Lumbar Spinal Nerves – L1-L4
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Lumbar Arteries
✔ Subcostal Artery
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Bodybuilding and Weightlifting: Helps stabilize the spine in movements like squats, deadlifts, and other strength exercises.
✔ Yoga and Pilates: Plays an important role in spinal balance and stretching.
✔ Martial Arts and CrossFit: Highly effective in building strength and improving trunk control.
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Connection with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Works with the erector spinae muscles, internal and external obliques, and glutes to stabilize the spine and control lateral movements.
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ Weakness in this muscle increases the risk of lower back pain and spinal issues.
✔ Over-tightness of the QL muscle can lead to lower back pain.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Main exercises to strengthen the quadratus lumborum muscle:
1️⃣ Side Plank – The best exercise for strengthening and building endurance in the QL
2️⃣ Deadlift – A powerful exercise for strengthening all lumbar and back muscles
3️⃣ Dumbbell Side Bends – An effective exercise for increasing side strength
4️⃣ Standing Side Stretch with Band – Helps improve endurance and flexibility of the QL muscle
5️⃣ Superman Exercise – Enhances strength in the lower back and core muscles
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery Movements
✔ Side Stretch – Reduces tension and stiffness in the QL muscle
✔ Cat-Cow Stretch – Improves flexibility of the spine
✅ Interesting Fact
✔ The quadratus lumborum is a key muscle in preventing lower back pain and is involved in nearly all daily body movements.
✅ Practical Tip
✔ If you have lower back pain, be sure to focus on strengthening and stretching the quadratus lumborum muscle! Side planks and deadlifts are the best exercises to strengthen this muscle.
🔴 Name and Location: The posterior abdominal muscle, located between the pelvis and the 12th rib
🟠 Anatomy: Its fibers run vertically from the pelvis to the 12th rib
🟡 Function: Stabilizes the spine, assists with lateral trunk flexion, and helps with breathing
🟢 Physiology: A combination of slow-twitch and fast-twitch fibers for balance and strength
🔵 Innervation: Lumbar nerves L1-L4 and subcostal nerve T12
🟣 Importance: Plays a key role in strength training, yoga, and preventing lower back pain
🟤 Exercises: Side Plank, Deadlift, Dumbbell Side Bends, Side Stretch
⚫ Interesting Fact: It is one of the key muscles for preventing lower back pain and maintaining trunk stability.
Interesting and Practical Facts
- The Rectus Abdominis is Not Just for a Six-Pack!
✔ This muscle is responsible for bending the torso, maintaining core endurance, and even assisting in the breathing process! Without it, you wouldn’t be able to bend comfortably.
2. Without fat burning, your six-pack will remain hidden!
✔ Even if you have strong and well-developed abdominal muscles, if your body fat percentage is high, these muscles won't be visible.
3. Everyone has a six-pack, but it might be hidden.
✔ The rectus abdominis muscles are present in everyone, but the amount of fat covering them determines whether they are visible or not.
4. The number of tendons in the rectus abdominis muscle varies among individuals!
✔ Some people genetically have a 4, 6, or even 8-piece six-pack, depending on the number of tendinous strips between the different sections.
5. The transverse abdominal muscle acts like the body's natural belt!
✔ This muscle is located in the deepest layer of the abdomen and acts like a muscular belt, supporting the spine.
6. Plank exercises are more effective than crunches!
✔ Plank exercises, due to deeper engagement of the core muscles, are more effective than crunches in building abdominal endurance.
7. Ab exercises don't burn a lot of calories!
✔ Contrary to popular belief, abdominal exercises alone do not lead to spot fat loss. You need a proper diet plan and aerobic exercises to burn fat.
8. The oblique muscles play a role in stabilizing the lower back!
✔ The internal and external oblique muscles help prevent lower back injuries and increase core strength.
9. Sitting for long periods at a desk weakens the abdominal muscles!
✔ Prolonged sitting leads to the inactivity of core muscles and increases the risk of lower back pain.
10. Breathing exercises strengthen the abdominal muscles!
✔ Diaphragmatic breathing exercises activate the transverse abdominis muscle and help improve its function.
11. Abdominal muscles recover faster than other muscles!
✔ Due to the type of muscle fibers, abdominal muscles generally require less recovery time compared to other muscles.
12. 12. Most of your daily movements rely on your abdominal muscles!
✔ From getting out of bed to bending down to tie your shoes, your abdominal muscles are always engaged.
13. Back stretches can help improve abdominal performance!
✔ Flexibility in the lower back and back muscles helps improve the efficiency of the abdominal muscles.
14. 14. Overtraining the abdominal muscles can lead to weakness!
✔ Without proper recovery, intense abdominal exercises can have the opposite effect and weaken the muscles.
15. The oblique muscles are highly effective in rotational movements!
✔ In sports like boxing, golf, and baseball, the rotational power of the abdominal muscles plays a crucial role.
16. Stress can lead to fat storage in the abdominal area!
✔ The hormone cortisol, which is released during stress, can increase fat storage in the abdominal area.
17. Your core plays a key role in spinal stability!
✔ The abdominal and core muscles maintain spinal balance and endurance, preventing back injuries.
18. Nutrition is more important than exercise when it comes to revealing your six-pack!
✔ Without proper nutrition and calorie control, even the strongest abdominal muscles remain hidden under a layer of fat.
19. Weak abdominal muscles can affect the overall balance of your body!
✔ A weak core reduces body stability and leads to poor performance in various sports.
20. Abdominal muscles also play a role in pushing and pulling movements!
✔ Even in movements like push-ups, bench presses, and pull-ups, the abdominal muscles are active to maintain balance and body stability.
Conclusion
Conclusion
Abdominal muscles are more than just an attractive six-pack; they form the core of the body and play a vital role in stability, balance, strength, and injury prevention. Without strengthening these muscles, athletic performance and even daily activities can be compromised. A combination of diverse exercises, proper nutrition, and sufficient rest is the key to having a strong and resilient core. So remember, a strong core means a strong body! 💪🔥

References
Resources
Anatomy and medical books :
Gray's Anatomy (one of the standard references in anatomy)
Netter's Atlas of Human Anatomy (a well-known illustrated atlas in anatomy)
Clinically Oriented Anatomy by Keith Moore
Medical databases :
PubMed (for scientific and research articles)
MedlinePlus (health and medical information)
WebMD (for practical and general health information)
Sports and training references :
Strength Training Anatomy by Frederic Delavier
Essentials of Strength Training and Conditioning by NSCA
Well-known articles and training programs by international coaches
Medical databases :
PubMed (for scientific and research articles)
MedlinePlus (health and medical information)
WebMD (for practical and general health information)
Specialized sports and health websites :
Images used:
(Kenhub) kenhub.com
Further Reading
Further reading
Pelank Life | Body Health Assessment
The Best Body Health Calculators Using Scientific Methods
Developed by Pelank Life ©