Introduction
Introduction
The forearm muscles are among the most complex and important parts of the body when it comes to everyday movements and sports activities. These muscles play a key role in all actions that require gripping, lifting, rotating, and stabilizing the hand. Whether it’s holding a weight at the gym or performing delicate tasks like writing or playing music, all of these depend on the strength, flexibility, and endurance of the forearm muscles.
In this section, we aim to examine the forearm muscles using a precise and standardized checklist. This checklist includes basic information, anatomy, physiology, innervation, significance in sports, strengthening exercises, and scientific insights. The goal is to gain a deep understanding of these muscles and learn how to strengthen them for improved performance in sports and daily activities.
🔍 Scientific Basis of the Review
The analyses in this series are based on reputable scientific sources, especially Gray’s Anatomy. Recognized as one of the most authoritative references in human anatomy, this book provides detailed information on the structure, function, and connections of the muscles.
1. Flexor Group (Anterior)
Flexor Compartment (Anterior Compartment)
Pronator Teres Muscle
Pronator Teres Muscle
The pronator teres is one of the superficial muscles of the forearm, with its main function being to rotate the forearm inward (pronation) and assist in elbow flexion. Acting as a pivotal muscle, it plays a vital role in many daily and athletic activities. From turning a door handle to performing boxing techniques or weightlifting movements, the pronator teres is key to optimal forearm function. Weakness or injury to this muscle can lead to reduced range of motion and decreased wrist and forearm strength. Below, we provide a comprehensive review of this muscle based on a standardized checklist. ✅
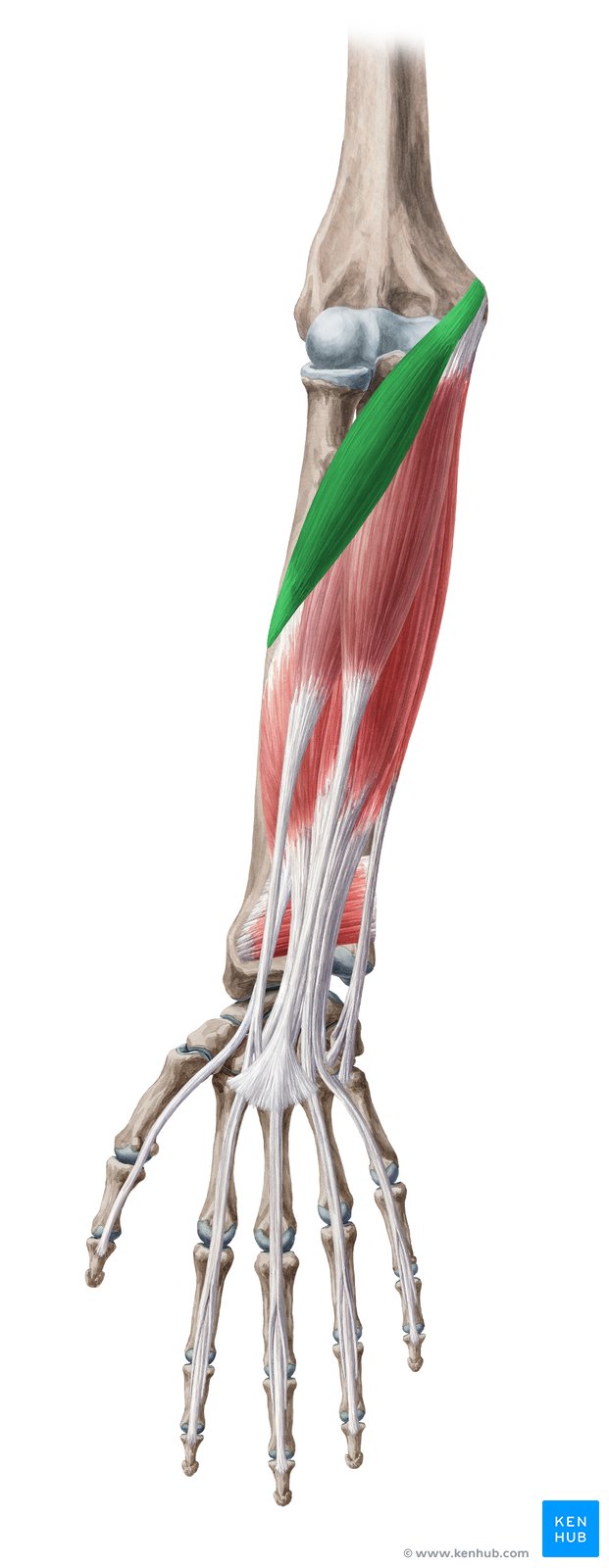
✅ Persian Name: Pronator Teres
✅ Latin Name: Pronator Teres
✅ Common Name: Forearm Pronator Muscle
✅ Location:
🟡 Situated on the anterior side of the forearm, originating from the humerus and the ulna, and attaching to the radius.
🟡 Located in the superficial layer of the flexor compartment.
🟡 Responsible for forearm pronation (inward rotation) and assists in elbow flexion.
✅ 🦾 Origin
✔ Humeral Head: Medial epicondyle of the humerus
✔ Ulnar Head: Coronoid process of the ulna
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ Lateral surface of the middle part of the radius
✅ 📌 Function
✔ Pronation: Rotates the forearm inward (turns the palm downward).
✔ Elbow Flexion: Assists in bending the elbow.
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Type
✔ A combination of slow-twitch fibers (Type I) for endurance and fast-twitch fibers (Type II) for rapid, powerful movements.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Movement and Sports Performance
✔ Plays a key role in sports that require wrist and forearm rotation, such as boxing, weightlifting, tennis, and basketball.
✔ Highly active in movements like javelin throwing and ball throwing.
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ Plays an important role in stabilizing forearm movements and reducing stress on the wrist.
✔ Weakness in this muscle can lead to reduced forearm rotation and limited wrist movement.
🧠 Innervation
✔ Median nerve (C6, C7), which controls pronation movements.
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Radial artery
✔ Ulnar artery
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Boxing: Essential for rapid wrist rotation when delivering powerful punches.
✔ Weightlifting: Helps stabilize the forearm when gripping weights.
✔ Tennis and Basketball: Contributes to ball control and quick passes.
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Relationship with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Works closely with the flexor carpi radialis and brachioradialis muscles for forearm movements.
✔ Plays a supportive role in stabilizing the elbow joint during combined arm and forearm movements.
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ Median nerve compression, which can lead to reduced rotational strength and pain in the forearm area.
✔ Pronator teres syndrome: Causes numbness and weakness in finger and wrist movements.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Key Exercises to Strengthen the Pronator Teres
1️⃣ Dumbbell Pronation – Rotating the wrist with a light dumbbell
2️⃣ Resisted Pronation – Using a resistance band to strengthen wrist rotation
3️⃣ Barbell Wrist Twists – Enhancing forearm rotational strength and control
4️⃣ Seated Wrist Pronation & Supination – Focusing on pronation and supination movements with the forearm supported on a bench or table
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery
✔ Forearm stretch with a flexed wrist – Improves flexibility and reduces muscle tension
✔ Forearm massage – Prevents cramps and enhances blood circulation
✅ 🔍 Fun Fact
✔ The pronator teres muscle is highly active in everyday activities such as turning a doorknob, using a screwdriver, and typing.
✅ 💡 Practical Tip
✔ If you want to improve your wrist rotation strength and forearm endurance, be sure to include pronator teres resistance exercises in your training routine.
🔴 Name & Location: A superficial anterior forearm muscle located between the humerus and the radius.
🟠 Anatomy: Originates from the humerus and ulna, inserts into the radius.
🟡 Function: Rotates the forearm inward (pronation) and assists in elbow flexion.
🟢 Physiology: Contains a mix of slow-twitch and fast-twitch fibers for both endurance and power.
🔵 Innervation: Median nerve (C6, C7).
🟣 Importance: Active in boxing, weightlifting, tennis, and daily movements.
🟤 Exercises: Dumbbell pronation, resistance exercises, stretching, and recovery.
⚫ Fun Facts: A key muscle for turning the hand and stabilizing the forearm during various activities.
Flexor Carpi Radialis Muscle
Pronator Teres Muscle
The Radial Wrist Flexor is one of the superficial muscles of the forearm in the flexor group. Its primary function is to flex the wrist and deviate it laterally (radially). This muscle plays a key role during gripping, throwing, and repetitive wrist movements. From typing on the keyboard to performing sports movements like weightlifting and tennis, this muscle is constantly engaged. Weakness in this muscle can lead to reduced wrist strength and increased pressure on the wrist joint. Next, we’ll provide a comprehensive overview of this muscle following the standard checklist. ✅
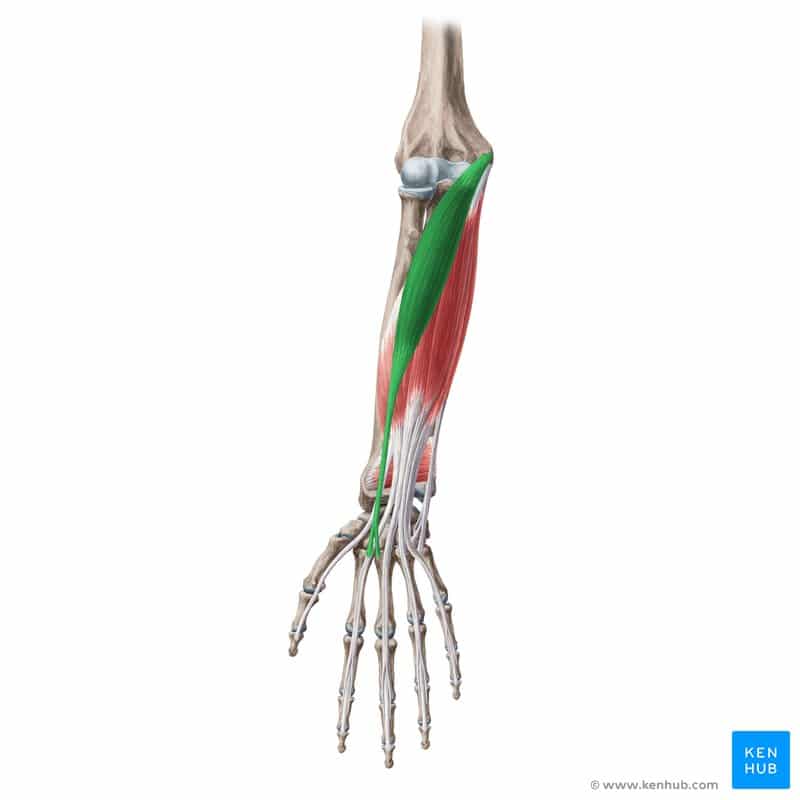
✅ Persian Name: Kham Konande-ye Moch-e Dast Radiyal
✅ Latin Name: Flexor Carpi Radialis
✅ Common Name: Flexor Carpi Radialis
✅ Location:
🟡 Located on the anterior side of the forearm, originating from the humerus and attaching to the wrist bones.
🟡 Part of the superficial flexor muscle group of the forearm.
🟡 Responsible for flexing the wrist and abducting it toward the radial (thumb) side.
✅ 🦾 Origin
✔ Medial epicondyle of the humerus
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ Base of the second and third metacarpal bones
✅ 📌 Function
✔ Wrist flexion
✔ Radial deviation (moving the wrist toward the thumb side)
✔ Stabilizes the wrist during gripping and throwing movements
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Type
✔ A combination of slow-twitch fibers (Type I) for endurance and fast-twitch fibers (Type II) for quick and powerful movements.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Movement and Sports Performance
✔ Plays a key role in sports such as weightlifting, tennis, basketball, and bodybuilding.
✔ Actively involved in gripping and throwing movements.
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ Plays an important role in grip strength and wrist stability.
✔ Weakness in this muscle can lead to reduced control and pain in the wrist.
🧠 Innervation
✔ Median nerve (C6, C7)
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Radial artery
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Tennis and badminton: Important for racket control and effective shots.
✔ Weightlifting: Essential for gripping and stabilizing the weight.
✔ Basketball and volleyball: Involved in passing and ball control.
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Relationship with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Interacts with other flexor muscles of the wrist and forearm for precise and coordinated movements.
✔ Works together with extensor muscles to maintain balance during wrist actions.
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ Flexor tendinitis, which causes pain on the inner side of the wrist.
✔ Weakness in this muscle can lead to reduced grip strength and decreased control of wrist movements.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Key Exercises to Strengthen the Flexor Carpi Radialis
1️⃣ Wrist curls with dumbbells – Strengthen the wrist flexor muscles
2️⃣ Resistance band wrist flexion – Improve muscle endurance
3️⃣ Finger roll dumbbell curls – Enhance motor control and wrist stability
4️⃣ Grip strength exercises – Boost gripping power
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery
✔ Wrist extension stretch – Reduces tension and improves flexibility
✔ Forearm and wrist massage – Prevents cramps and enhances blood circulation
✅ 🔍 Fun Fact
✔ The flexor carpi radialis muscle plays a key role in everyday activities such as driving, typing, and writing.
✅ 💡 Practical Tip
✔ To improve grip strength and reduce wrist strain, make sure to include strengthening exercises for this muscle in your workout routine.
🔴 Name & Location: A superficial anterior forearm muscle that extends from the humerus to the metacarpal bones of the wrist.
🟠 Anatomy: Originates from the medial epicondyle of the humerus and inserts into the base of the second and third metacarpal bones.
🟡 Function: Flexes the wrist, abducts the wrist (radial deviation), and stabilizes the wrist.
🟢 Physiology: Contains a combination of slow-twitch and fast-twitch fibers for endurance and powerful movements.
🔵 Innervation: Median nerve (C6, C7).
🟣 Importance: Active in weightlifting, tennis, basketball, and everyday activities.
🟤 Exercises: Wrist curls with dumbbells, resistance band exercises, grip strength training.
⚫ Fun Facts: A key muscle for both fine and powerful wrist movements.
Palmaris Longus Muscle
Palmaris Longus Muscle
The palmaris longus is one of the anterior forearm muscles, primarily responsible for assisting in wrist flexion and tightening the palmar aponeurosis. Interestingly, this muscle is absent in about 10 to 15 percent of the population due to a congenital variation. However, when present, it contributes to actions such as gripping objects, enhancing wrist strength, and throwing movements. Below, we provide a comprehensive overview of this muscle based on a standardized checklist. ✅
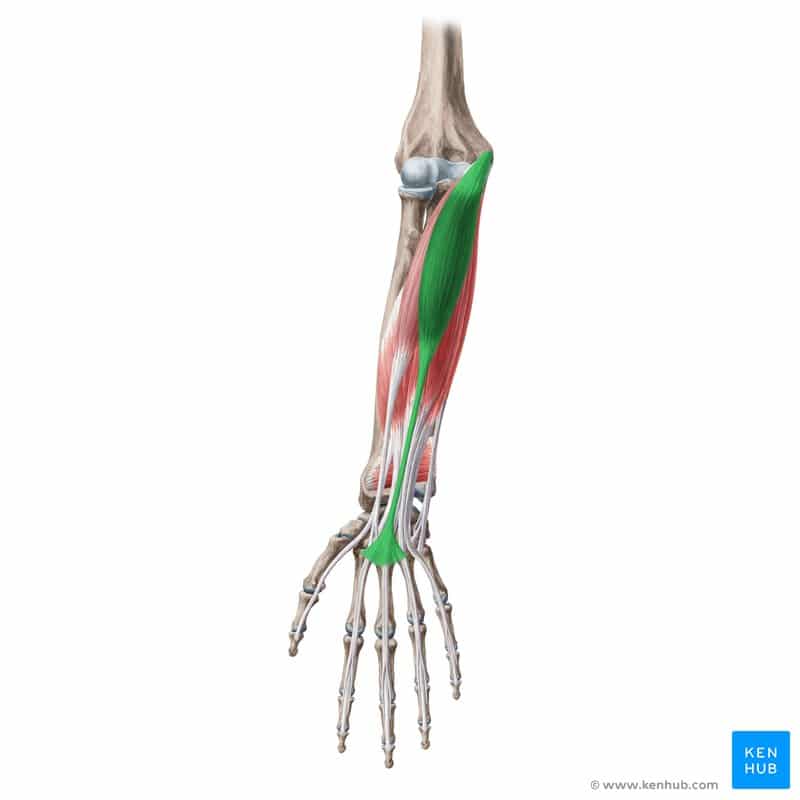
✅ Persian Name:Kaf-Dasti Boland
✅ Latin Name: Palmaris Longus
✅ Common Name: Palmaris Longus
✅ Location:
🟡 Located superficially on the anterior side of the forearm, originating from the humerus and inserting into the palmar aponeurosis.
🟡 Part of the superficial flexor muscle group of the forearm.
🟡 This muscle is congenitally absent in some individuals!
✅ 🦾 Origin
✔ Medial epicondyle of the humerus
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ Palmar aponeurosis
✅ 📌 Function
✔ Assists in wrist flexion
✔ Tenses the palmar aponeurosis
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Type
✔ Primarily slow-twitch fibers (Type I) for endurance and maintaining tension in the palmar aponeurosis.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Movement and Sports Performance
✔ Provides support in sports such as boxing, weightlifting, basketball, and gymnastics.
✔ Contributes to gripping objects and strengthening the palm.
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ Plays an important role in stabilizing the palm and the palmar aponeurosis.
✔ In individuals without this muscle, its function is compensated by other wrist flexor muscles.
🧠 Innervation
✔ Median nerve (C7, C8)
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Radial artery
✔ Ulnar artery
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Boxing: Helps stabilize and control the fist during punches.
✔ Weightlifting: Enhances grip strength for lifting weights.
✔ Gymnastics: Assists in controlling palm movements during acrobatic exercises.
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Relationship with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Works in coordination with the flexor carpi radialis and flexor carpi ulnaris for synchronized wrist movements.
✔ If absent, its functions are taken over by other wrist flexor muscles.
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ Palmar fasciitis, which can cause stiffness and reduced flexibility of the palmar aponeurosis.
✔ In plastic surgery and tendon graft procedures, this muscle is often used as a donor for tendon replacement!
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Key Exercises to Strengthen the Palmaris Longus
1️⃣ Dumbbell wrist flexion – Increases wrist and palmar aponeurosis strength
2️⃣ Grip strength exercises – Improves gripping ability
3️⃣ Palmar aponeurosis stretching with a resistance band – Enhances hand motor control
4️⃣ Medicine ball throws – Boosts palm strength and power
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery
✔ Wrist flexion and extension stretches – Reduce muscle tension and improve flexibility
✔ Palm and forearm massage – Prevents cramps and enhances blood circulation
✅ 🔍 Fun Fact
✔ The palmaris longus muscle is congenitally absent in 10 to 15 percent of people!
✅ 💡 Practical Tip
✔ Plastic and orthopedic surgeons often use this muscle for grafting and replacing damaged tendons in the hand and arm.
🔴 Name & Location: A superficial anterior forearm muscle that extends from the humerus to the palmar aponeurosis.
🟠 Anatomy: Originates from the medial epicondyle of the humerus and inserts into the palmar aponeurosis.
🟡 Function: Assists in wrist flexion and stabilizes the palmar aponeurosis.
🟢 Physiology: Contains slow-twitch fibers to help maintain palm stability.
🔵 Innervation: Median nerve (C7, C8).
🟣 Importance: Active in boxing, weightlifting, gymnastics, and palm movements.
🟤 Exercises: Dumbbell wrist flexion, grip strength training, palmar aponeurosis stretching.
⚫ Fun Facts: This muscle is congenitally absent in many individuals.
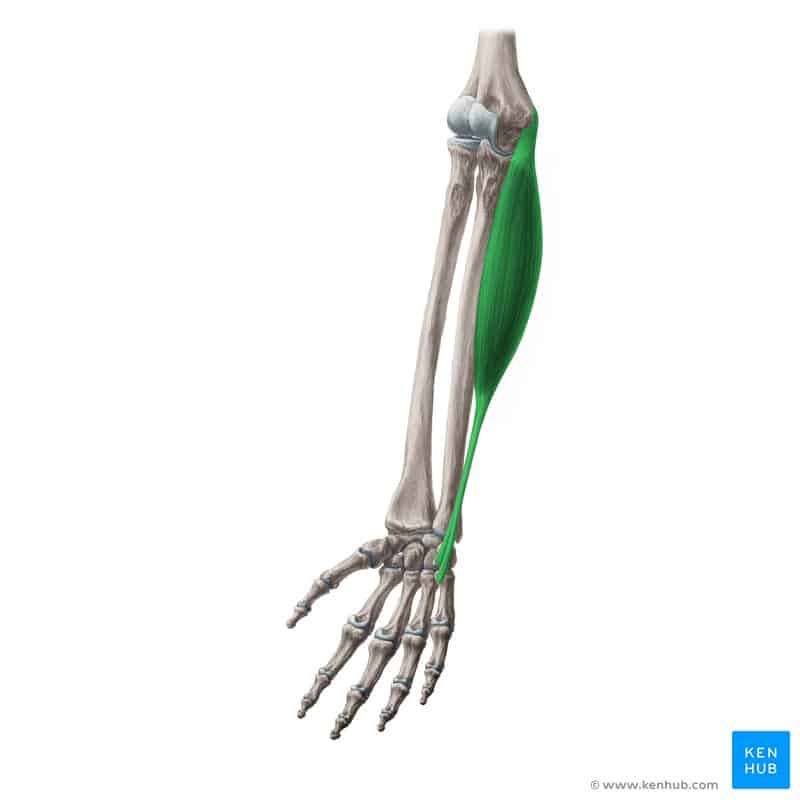
Flexor Carpi Ulnaris Muscle
Flexor Carpi Ulnaris Muscle
The flexor carpi ulnaris is a superficial muscle of the forearm primarily responsible for flexing the wrist and bending it inward toward the ulnar (little finger) side. This muscle plays a key role in gripping objects, lifting weights, and stabilizing the wrist during both pushing and pulling movements. It is highly active during activities like weightlifting, gymnastics, and rock climbing. Weakness in this muscle can lead to decreased wrist control and a higher risk of forearm injuries. Next, we’ll provide a comprehensive overview of this muscle following the standard checklist. ✅
✅ Persian Name: Kham Konande-ye Moch-e Dast Olnari
✅ Latin Name: Flexor Carpi Ulnaris
✅ Common Name: Flexor Carpi Ulnaris
✅ Location:
🟡 Located on the anterior side of the forearm, originating from the humerus and ulna, and attaching to the wrist bones.
🟡 Part of the superficial flexor muscle group of the forearm.
🟡 Responsible for flexing the wrist and deviating it inward (ulnar deviation).
✅ 🦾 Origin
✔ Medial epicondyle of the humerus
✔ Olecranon of the ulna
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ Pisiform bone
✔ Hook of hamate
✔ Base of the fifth metacarpal
✅ 📌 Function
✔ Wrist flexion
✔ Ulnar deviation (moving the wrist toward the ulnar side/little finger)
✔ Assists in gripping objects and stabilizing pushing movements
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Type
✔ A combination of slow-twitch fibers (Type I) for endurance and fast-twitch fibers (Type II) for quick, powerful movements.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Movement and Sports Performance
✔ Plays a key role in sports such as weightlifting, gymnastics, wrestling, and rock climbing.
✔ Highly active during wrist flexion and when gripping heavy objects.
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ Plays an important role in wrist stability and grip strength.
✔ Weakness in this muscle leads to reduced control and stability during resistance movements.
🧠 Innervation
✔ Ulnar nerve (C7, C8, T1)
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Ulnar artery
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Weightlifting: Enhances grip strength and wrist stability when lifting weights.
✔ Gymnastics: Helps control the wrist during hanging and pressing movements.
✔ Rock climbing: Increases the ability to grip rocks and bear loads on the fingers.
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Relationship with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Works in coordination with the flexor carpi radialis for balanced wrist movements.
✔ Collaborates with the flexor digitorum superficialis to enhance grip strength.
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ Flexor carpi ulnaris (FCU) tendinitis, which causes pain on the inner side of the wrist.
✔ Ulnar nerve compression, which can result in weakness and numbness in the ring and little fingers.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Key Exercises to Strengthen the Flexor Carpi Ulnaris
1️⃣ Dumbbell wrist flexion (ulnar side) – Focuses on strengthening inward wrist movement
2️⃣ Resistance band wrist flexion – Increases wrist stability
3️⃣ Fat grip training – Enhances grip strength
4️⃣ Ulnar deviation stretch – Reduces muscle tension and improves flexibility
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery
✔ Wrist stretches inward and outward – Help reduce tension and improve flexibility.
✔ Forearm massage and compression – Prevent muscle cramps.
✅ 🔍 Fun Fact
✔ The flexor carpi ulnaris is the only forearm flexor muscle innervated by the ulnar nerve.
✅ 💡 Practical Tip
✔ To increase wrist strength and prevent injuries, make sure to include strengthening exercises for this muscle in your workout routine.
🔴 Name & Location: A superficial anterior forearm muscle that extends from the humerus and ulna to the wrist.
🟠 Anatomy: Originates from the medial epicondyle of the humerus and the olecranon process, and inserts into the pisiform bone and the base of the fifth metacarpal.
🟡 Function: Flexes the wrist, deviates the wrist inward (ulnar deviation), and assists in gripping objects.
🟢 Physiology: Contains a combination of slow-twitch and fast-twitch fibers for endurance and powerful movements.
🔵 Innervation: Ulnar nerve (C7, C8, T1).
🟣 Importance: Active in weightlifting, gymnastics, rock climbing, and wrestling.
🟤 Exercises: Dumbbell wrist flexion, resistance exercises, grip strengthening.
⚫ Fun Fact: The only forearm flexor muscle innervated by the ulnar nerve.
2. Deep Anterior Muscles
Flexor Compartment - Deep Layer
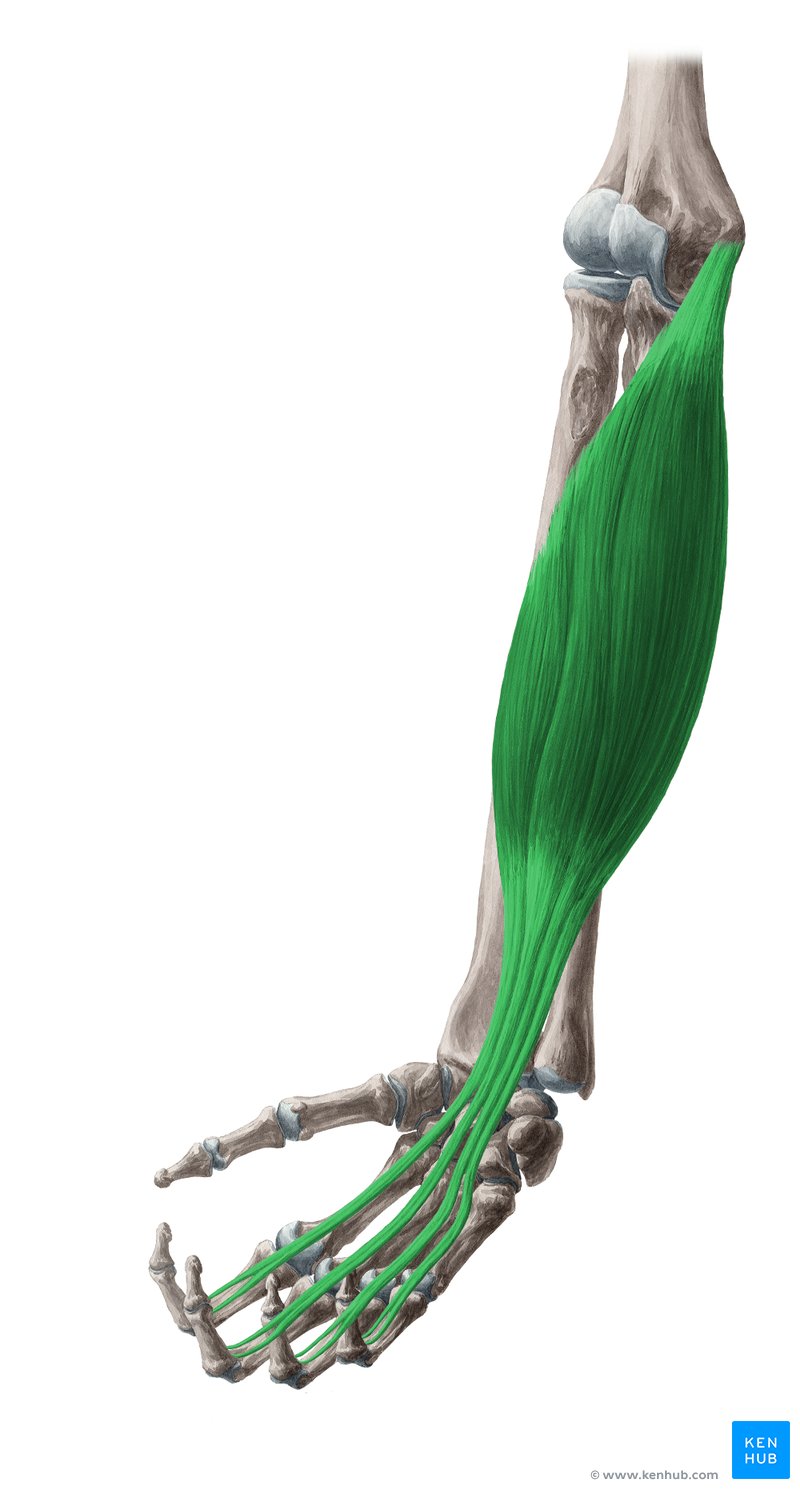
Flexor Digitorum Superficialis Muscle
Flexor Digitorum Superficialis Muscle
The Flexor Digitorum Superficialis is an important muscle in the anterior forearm, primarily responsible for flexing the joints of the second to fifth fingers (excluding the thumb) and assisting in wrist flexion. This muscle plays a crucial role in gripping objects, writing, playing music, and engaging in sports activities. Weakness or injury to this muscle can lead to reduced finger control and difficulties in performing daily tasks. Next, we’ll provide a comprehensive overview of this muscle following the standard checklist. ✅

✅ Persian Name: Kham Konande-ye Sathi-ye Angoshtan
✅ Latin Name: Flexor Digitorum Superficialis
✅ Common Name: Flexor Digitorum Superficialis
✅ Location:
🟡 Situated in the anterior and deep part of the forearm, originating from the humerus, radius, and ulna, and attaching to the second through fifth fingers.
🟡 Part of the deep flexor muscle group of the forearm.
🟡 Responsible for flexing the middle joints of the fingers and assisting in wrist flexion.
✅ 🦾 Origin
✔ Medial epicondyle of the humerus
✔ Coronoid process of the ulna
✔ Anterior surface of the radius
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ Sides of the middle phalanges of the second to fifth fingers
✅ 📌 Function
✔ Flexes the proximal interphalangeal (PIP) joints of the second to fifth fingers
✔ Assists in wrist flexion
✔ Enhances hand grip strength and control
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Type
✔ A combination of slow-twitch fibers (Type I) for endurance and fast-twitch fibers (Type II) for quick finger movements.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Movement and Sports Performance
✔ Plays a key role in sports such as weightlifting, rock climbing, gymnastics, tennis, and playing musical instruments.
✔ Active in all gripping actions, typing, playing instruments, and fine manual tasks.
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ Plays an important role in grip strength, finger movement control, and wrist stability.
✔ Weakness in this muscle reduces the ability to grasp objects and limits precision in fine movements.
🧠 Innervation
✔ Median nerve (C7, C8, T1)
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Radial artery
✔ Ulnar artery
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Weightlifting and powerlifting: Enhances grip strength and the ability to hold weights.
✔ Gymnastics and rock climbing: Improves control on various surfaces and finger endurance.
✔ Music (piano, guitar, violin): Helps with dexterity and agility in finger movements.
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Relationship with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Works together with the flexor digitorum profundus and wrist flexors for precise and coordinated movements.
✔ Interacts with the finger extensors to balance hand movements.
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ Carpal tunnel syndrome: Compression of the median nerve can cause weakness and numbness in the fingers.
✔ Tendon strain or inflammation: Can occur due to overuse, such as excessive typing or intensive finger exercises.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Key Exercises to Strengthen the Flexor Digitorum Superficialis
1️⃣ Grip strength training – Improves grip power and finger control
2️⃣ Finger resistance band exercises – Increases strength and flexibility
3️⃣ Hand gripper exercises – Strengthens the fingers and forearm
4️⃣ Finger and wrist flexor stretches – Reduces muscle tension and increases flexibility
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery
✔ Stretching the fingers and wrist backward – Reduces muscle tension and improves flexibility.
✔ Hand and forearm massage – Helps improve blood flow and speeds up recovery.
✅ 🔍 Fun Fact
✔ The flexor digitorum superficialis is the strongest muscle for finger flexion, and without it, gripping objects becomes much more difficult.
✅ 💡 Practical Tip
✔ To improve finger control and prevent early fatigue, include grip exercises and finger stretches in your training routine.
🔴 Name & Location: A deep anterior forearm muscle that extends from the arm and forearm to the second through fifth fingers.
🟠 Anatomy: Originates from the medial epicondyle of the humerus and the radius, and inserts into the middle phalanges of the second to fifth fingers.
🟡 Function: Flexes the middle joints of the fingers and assists in wrist flexion.
🟢 Physiology: Contains a combination of slow-twitch and fast-twitch fibers for precise finger movement control.
🔵 Innervation: Median nerve (C7, C8, T1).
🟣 Importance: Active in weightlifting, gymnastics, rock climbing, music, and fine manual tasks.
🟤 Exercises: Grip training, resistance band exercises, hand gripper squeezing.
⚫ Fun Fact: The strongest finger flexor muscle, playing a role in all hand movements.
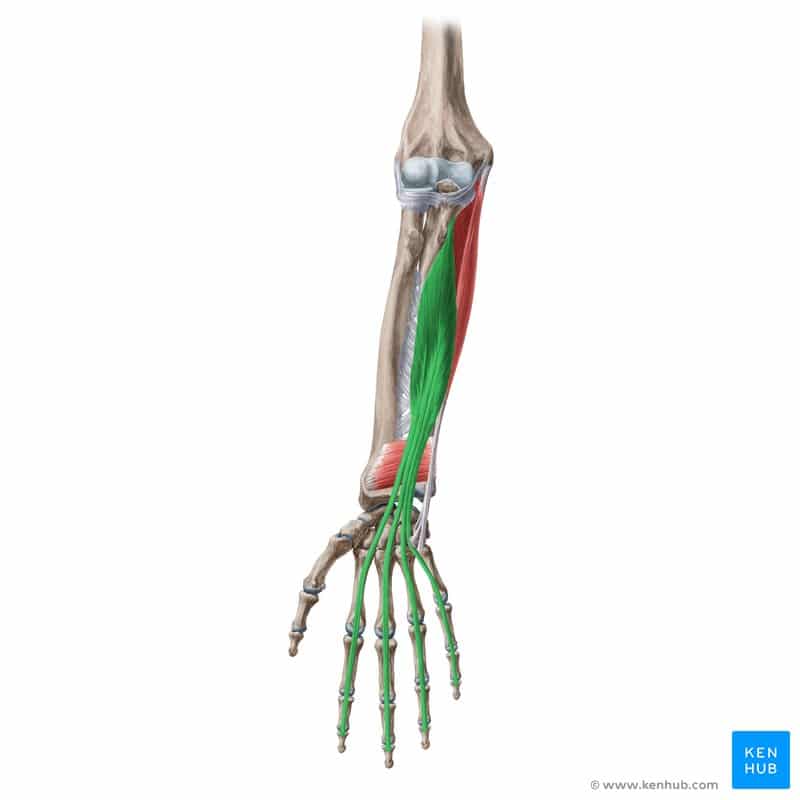
Flexor Digitorum Profundus Muscle
Flexor Digitorum Profundus Muscle
The flexor digitorum profundus is one of the key muscles located in the anterior compartment of the forearm. Its primary role is to flex the distal joints of the second to fifth fingers and assist in wrist flexion. This muscle plays a crucial part in activities that involve gripping heavy objects, rock climbing, playing musical instruments, racquet sports, and strength training exercises. Weakness or injury in this muscle can lead to reduced finger control, decreased grip strength, and quicker hand fatigue.
Below, you’ll find a comprehensive overview of this muscle based on the standard checklist. ✅
✅ Persian Name: Kham Konande Amqi Angoshtan
✅ Latin Name: Flexor Digitorum Profundus
✅ Common Name: Deep Finger Flexor
✅ Location:
🟡 This muscle is situated in the deep anterior compartment of the forearm. It originates from the ulna (the inner bone of the forearm) and extends all the way to the tips of the second to fifth fingers.
🟡 It belongs to the group of deep flexor muscles of the forearm.
🟡 Its main function is to flex the distal joints of the fingers and assist with wrist flexion.
✅ 🦾 Origin
✔ Anterior and medial surface of the ulna
✔ Interosseous membrane of the forearm
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ Distal phalanges of the second to fifth fingers (fingers 2–5)
✅ 📌 Function
✔ Flexes the distal interphalangeal (DIP) joints of the second to fifth fingers
✔ Assists in wrist flexion
✔ Increases grip strength and enhances finger movement control
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Type
✔ Contains a mix of slow-twitch fibers (Type I) for endurance and fast-twitch fibers (Type II) for powerful and rapid movements.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Movement and Sports Performance
✔ Plays a key role in weightlifting, rock climbing, gymnastics, playing musical instruments, and racquet sports.
✔ It is actively engaged in all gripping movements, strong grasping of objects, and fine motor control of the fingers.
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ This muscle is essential for improving grip strength, precise finger control, and wrist stability.
✔ Weakness in this muscle can lead to a reduced ability to hold objects and a weaker grip overall.
🧠 Innervation
✔ Lateral half (fingers 2 and 3): Median nerve (C8, T1)
✔ Medial half (fingers 4 and 5): Ulnar nerve (C8, T1)
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Radial artery
✔ Anterior interosseous artery
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Weightlifting & Powerlifting: Enhances grip strength and wrist stability.
✔ Rock Climbing & Gymnastics: Improves finger control and endurance for holding onto different surfaces.
✔ Tennis, Badminton, & Basketball: Boosts finger strength for better control of rackets and balls.
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Interaction with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Works together with the superficial finger flexors and wrist flexors to coordinate finger and wrist movements.
✔ Cooperates with the finger extensor muscles to maintain balance and control in hand movements.
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Can lead to weakness and numbness in the fingers.
✔ Flexor Digitorum Profundus Tendonitis: May develop due to intense training or repetitive finger movements.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Key Exercises to Strengthen the Flexor Digitorum Profundus
1️⃣ Grip Strength Training: Increases your ability to hold and grip objects firmly.
2️⃣ Finger Resistance Bands: Enhances finger control and flexibility.
3️⃣ Hand Gripper Exercises: Improves finger and forearm strength.
4️⃣ Towel Grip and Plate Pinch: Boosts finger endurance and agility by gripping towels or pinching weight plates.
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery Movements
✔ Stretching the fingers and wrist backward — helps reduce tension and improve flexibility.
✔ Hand and forearm massage — boosts blood circulation and speeds up recovery.
✅ 🔍 Fun Fact
✔ The flexor digitorum profundus is the only muscle that flexes all the joints of the second to fifth fingers.
✅ 💡 Practical Tip
✔ To boost finger control and endurance, include resistance and grip exercises in your workout routine.
🔴 Name & Location:
A deep anterior forearm muscle that runs from the ulna all the way to the tips of the second to fifth fingers.
🟠 Anatomy: Originates from the anterior surface of the ulna and inserts into the distal phalanges of the second to fifth fingers.
🟡 Function: Flexes the distal joints of the fingers and assists with wrist flexion.
🟢 Physiology: Contains both slow-twitch and fast-twitch fibers, allowing for endurance and precise control of finger movements.
🔵 Innervation: Median nerve (C8, T1) and ulnar nerve (C8, T1).
🟣 Significance: Active in weightlifting, rock climbing, gymnastics, racquet sports, and tasks that require fine manual skills.
🟤 Exercises: Grip strength exercises, finger resistance bands, gripping drills, and finger stretching movements.
⚫ Fun Fact: It’s the only muscle that flexes all the joints of the second to fifth fingers.
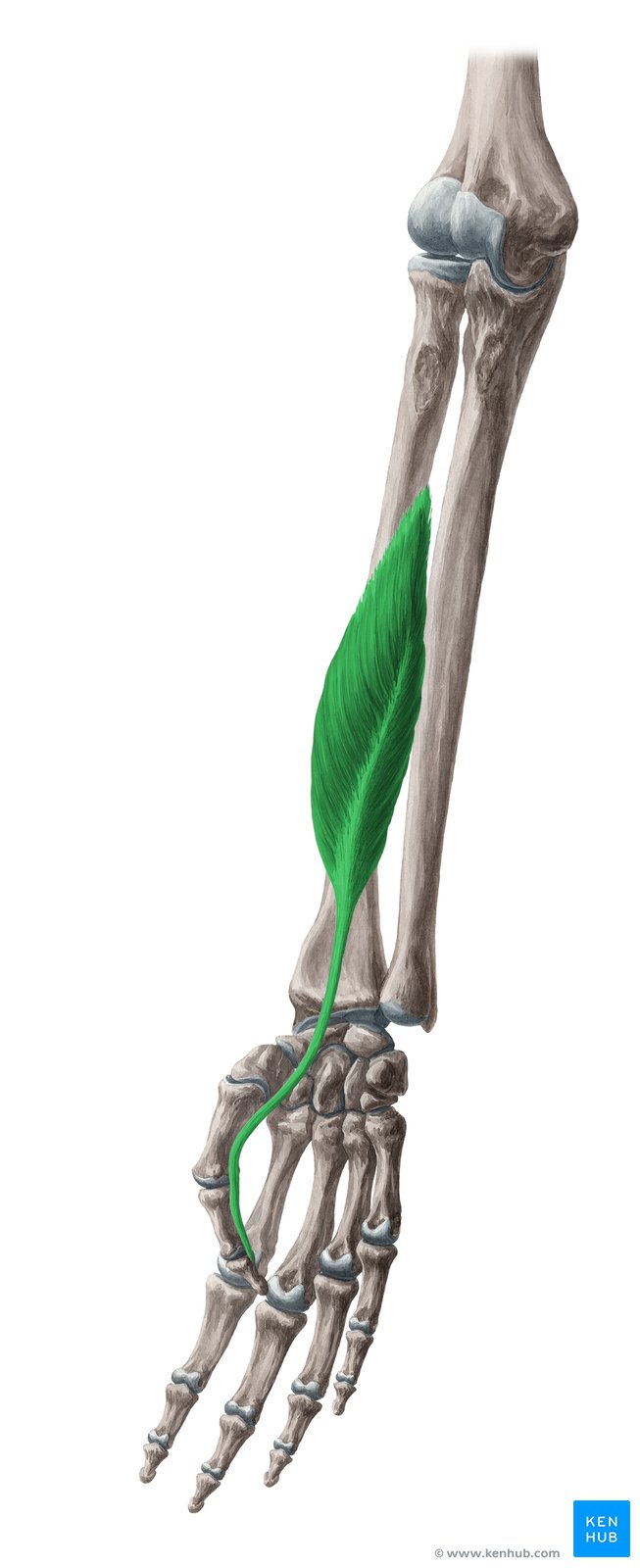
Flexor Pollicis Longus
Flexor Pollicis Longus Muscle
The flexor pollicis longus is a deep muscle in the anterior compartment of the forearm. Its main job is to flex the tip of the thumb (the distal joint) and assist with wrist flexion. This muscle is essential for delicate tasks that require fine thumb movement, such as writing, gripping objects, playing musical instruments, and any activity demanding precision from the thumb. It’s also highly active in sports like tennis, strength training, and rock climbing, where thumb control and stability are critical. Weakness or injury in this muscle can lead to reduced grip strength and limited thumb mobility.
Below, you’ll find a thorough review of this muscle based on the standard checklist. ✅
✅ Persian Name: Kham-konande Boland Shast
✅ Latin Name: Flexor Pollicis Longus
✅ Common Name: Flexor Pollicis Longus
✅ Location:
🟡 Located deep in the anterior compartment of the forearm, it originates from the radius (the lateral forearm bone) and inserts into the distal phalanx of the thumb.
🟡 It is part of the deep flexor muscle group of the forearm.
🟡 Its main function is to flex the joints of the thumb and assist in wrist flexion.
✅ 🦾 Origin
✔ Anterior surface of the radius
✔ Interosseous membrane of the forearm
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ Distal phalanx of the thumb
✅ 📌 Function
✔ Flexes the joints of the thumb (both MCP and IP joints)
✔ Assists with wrist flexion
✔ Enhances grip strength and precision of thumb movements
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Type
✔ Contains a mix of slow-twitch fibers (Type I) for endurance and fast-twitch fibers (Type II) for quick and powerful movements.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Movement and Sports Performance
✔ Plays a key role in sports such as tennis, badminton, weightlifting, and rock climbing.
✔ Actively engaged in all gripping actions, precise thumb control, and pressing objects.
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ This muscle is essential for grip strength, endurance, and precise control of fine thumb movements.
✔ Weakness in this muscle can decrease your ability to grasp objects and reduce the accuracy of thumb movements.
🧠 Innervation
✔ Anterior interosseous nerve (a branch of the median nerve – C8, T1)
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Anterior interosseous artery
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Tennis & Badminton: Improves thumb control for holding and maneuvering the racket.
✔ Weightlifting: Increases grip strength and finger stability during pressing movements.
✔ Rock Climbing: Enhances thumb control and grip on various surfaces.
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Interaction with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Works together with the wrist flexors and the short flexor of the thumb to coordinate thumb movements.
✔ Cooperates with the thumb extensors to maintain balance and control in thumb actions.
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Compression of the anterior interosseous nerve can lead to weakness in thumb movements.
✔ Flexor Pollicis Longus Tendinitis: Overuse from repetitive activities like typing, playing instruments, or strength sports can cause inflammation of the thumb flexor tendon.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Key Exercises to Strengthen the Flexor Pollicis Longus
1️⃣ Thumb Squeeze with a Stress Ball: Boosts grip strength and improves thumb control.
2️⃣ Thumb Resistance Band Exercises: Enhances thumb flexibility and control.
3️⃣ Dumbbell Pinch Grip Hold: Strengthens the thumb and wrist.
4️⃣ Towel Grip and Pinch Strength Training: Increases thumb stability and agility by gripping and pinching various surfaces.
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery Movements
✔ Stretching the thumb and wrist backward — helps relieve tension and improve flexibility.
✔ Massaging the thumb and palm — boosts blood circulation and speeds up recovery.
✅ 🔍 Fun Fact
✔ The flexor pollicis longus is one of the few muscles dedicated to controlling just a single finger—the thumb!
✅ 💡 Practical Tip
✔ To improve thumb strength and precision, make sure to include resistance and grip exercises in your workout routine.
🔴 Name & Location:
A deep anterior forearm muscle that runs from the radius to the distal phalanx of the thumb.
🟠 Anatomy:
Originates from the anterior surface of the radius and inserts into the distal phalanx of the thumb.
🟡 Function:
Flexes the thumb joints and assists with wrist flexion.
🟢 Physiology:
Contains both slow- and fast-twitch fibers for precise thumb control.
🔵 Innervation:
Anterior interosseous nerve (C8, T1).
🟣 Significance:
Active in weightlifting, tennis, rock climbing, and tasks requiring fine manual skills.
🟤 Exercises:
Thumb squeeze with a ball, resistance band exercises, and dumbbell pinch grip holds.
⚫ Fun Fact:
It’s the only muscle that exclusively flexes the thumb.
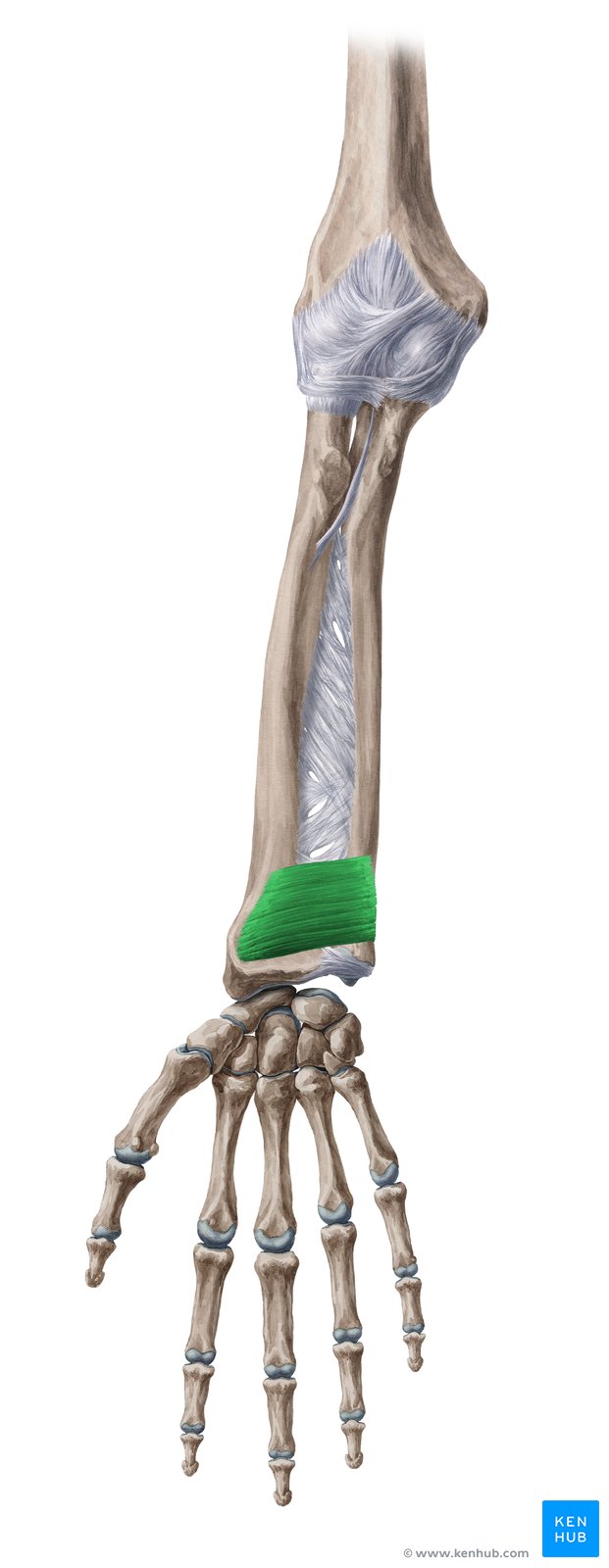
Pronator Quadratus Muscle
Pronator Quadratus Muscle
The pronator quadratus is one of the smallest yet most important deep muscles of the forearm. Its primary function is to pronate the forearm, turning the palm downward. Located at the lower end of the forearm, this muscle is responsible for rotating the radius and ulna against each other. Every time you turn your palm down, the pronator quadratus is activated. It plays a vital role in wrist and forearm movements such as twisting a screwdriver, typing, throwing objects, and playing racquet sports. Weakness or injury of this muscle can reduce the forearm’s range of motion and decrease the strength of wrist rotation.
Below, you’ll find a comprehensive overview of this muscle based on the standard checklist. ✅
✅ Persian Name: Pronator Chahar-Goosh
✅ Latin Name: Pronator Quadratus
✅ Common Name: Pronator Quadratus
✅ Location:
🟡 Situated deep in the anterior forearm, between the radius and ulna bones.
🟡 It is part of the deep flexor muscle group of the forearm.
🟡 Responsible for pronating (rotating inward) the forearm and stabilizing the wrist joint.
✅ 🦾 Origin
✔ Anterior distal surface of the ulna
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ Anterior distal surface of the radius
✅ 📌 Function
✔ Rotates the forearm inward (pronation)
✔ Helps stabilize the wrist and forearm joints
✔ Works with the pronator teres muscle to enhance pronation
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Type
✔ Contains mainly slow-twitch fibers (Type I) for stability and endurance during wrist rotation.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Movement and Sports Performance
✔ Plays a key role in sports such as boxing, tennis, basketball, and weightlifting.
✔ Actively involved in twisting movements of the wrist and forearm, such as using a screwdriver, throwing a ball, and gripping tools.
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ Plays an important role in forearm stability and precise wrist rotation.
✔ Weakness in this muscle can reduce range of motion and limit wrist rotation.
🧠 Innervation
✔ Anterior interosseous nerve (a branch of the median nerve, C8, T1)
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Anterior interosseous artery
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Boxing & Racquet Sports: Improves wrist control when striking.
✔ Weightlifting: Stabilizes the wrist and forearm while lifting weights.
✔ Martial Arts & Self-Defense: Enables quick, precise forearm rotation during defensive and offensive moves.
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Interaction with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Works with the pronator teres to produce forearm rotation.
✔ Cooperates with the wrist flexor and extensor muscles for precise forearm movement control.
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Compression of the anterior interosseous nerve can weaken rotational movements.
✔ Muscle strain or inflammation: Can occur with frequent twisting motions of the wrist and forearm.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Key Exercises to Strengthen the Pronator Quadratus
1️⃣ Dumbbell Pronation: Improves wrist and forearm rotation.
2️⃣ Resistance Band Pronation: Increases control over rotational movements.
3️⃣ Seated Wrist Pronation & Supination: Strengthens precise wrist rotation with your forearm supported on a table.
4️⃣ Twisting Rope Exercise: Boosts endurance and rotational strength of the wrist.
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery Movements
✔ Forearm stretch with a flexed wrist — reduces tension and improves flexibility.
✔ Forearm and wrist massage — helps prevent muscle tightness and boosts blood circulation.
✅ 🔍 Fun Fact
✔ The pronator quadratus is always involved in turning the wrist inward and plays the main role in forearm pronation!
✅ 💡 Practical Tip
✔ To improve forearm rotation and endurance, include resistance exercises for this muscle in your workout routine.
🔴 Name & Location:
A deep anterior forearm muscle located between the radius and ulna.
🟠 Anatomy:
Originates from the anterior surface of the ulna and inserts into the anterior surface of the radius.
🟡 Function:
Rotates the forearm inward (pronation) and stabilizes the forearm and wrist joints.
🟢 Physiology:
Composed mainly of slow-twitch fibers for endurance and controlled wrist rotation.
🔵 Innervation:
Anterior interosseous nerve (C8, T1).
🟣 Significance:
Active in boxing, tennis, weightlifting, martial arts, and everyday tasks.
🟤 Exercises:
Dumbbell pronation, resistance band exercises, and wrist rotation drills on a table.
⚫ Fun Fact:
A key muscle in wrist rotational movements that is always active during pronation.
3. Extensor Muscle Group (Posterior Compartment)
Extensor Compartment (Posterior Compartment)
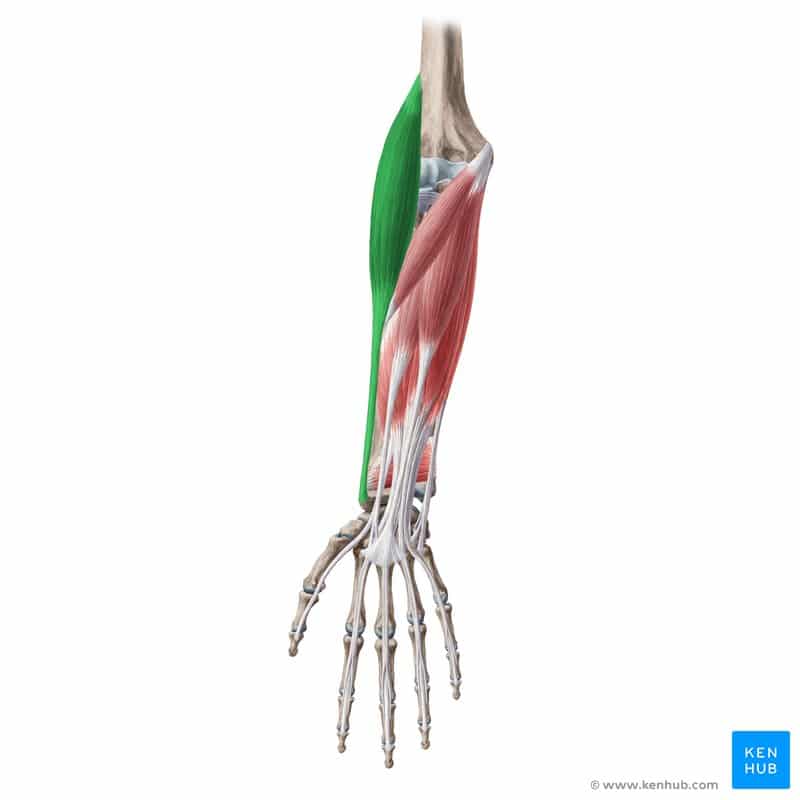
Brachioradialis Muscle
Brachioradialis Muscle
The brachioradialis is a superficial muscle located on the posterior (back) side of the forearm. Unlike many muscles in this region, it functions primarily as an elbow flexor. This muscle is highly active during movements like lifting weights, gripping objects, and performing hammering actions with the forearm. Unlike other flexors, the brachioradialis is most engaged when the elbow is flexed in a mid-rotation position—like holding a hammer. In sports such as bodybuilding, wrestling, boxing, and rock climbing, the brachioradialis plays a key role in maintaining arm and forearm strength and stability. Weakness in this muscle can lead to reduced grip strength and quicker forearm fatigue.
Below, you’ll find a comprehensive review of this muscle based on the standard checklist. ✅
✅ Persian Name: Brakyoradialis
✅ Latin Name: Brachioradialis
✅ Common Name: Brachioradialis
✅ Location:
🟡 Located superficially on the posterior forearm, originating from the humerus and inserting into the radius (specifically the styloid process of the radius).
🟡 Part of the superficial extensor muscle group of the forearm.
🟡 Responsible for flexing the elbow when the forearm is in a neutral (hammer) position and assisting in elbow joint stabilization.
✅ 🦾 Origin
✔ Lateral supracondylar ridge of the humerus
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ Lateral distal radius (styloid process)
✅ 📌 Function
✔ Flexes the elbow, especially when the forearm is in a neutral (hammer) position
✔ Assists in stabilizing the elbow during pushing and pulling movements
✔ Resists excessive stretching of the forearm and arm muscles
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Type
✔ Contains a mix of slow-twitch fibers (Type I) for endurance and fast-twitch fibers (Type II) for powerful movements.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Movement and Sports Performance
✔ Plays a key role in weightlifting, wrestling, boxing, rock climbing, and bodybuilding.
✔ Actively involved in gripping objects, lifting weights, and pushing and pulling movements of the elbow.
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ Plays a crucial role in grip strength, elbow stabilization, and handling heavy loads.
✔ Weakness in this muscle can reduce hammering power and decrease endurance in gripping tasks.
🧠 Innervation
✔ Radial nerve (C5, C6, C7)
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Radial artery
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Wrestling & Boxing: Enhances elbow stability when gripping opponents and throwing punches.
✔ Weightlifting: Boosts grip strength and stabilizes the elbow during lifts.
✔ Rock Climbing & Gymnastics: Improves forearm control and increases the ability to hold the body on bars or ropes.
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Interaction with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Works alongside the biceps brachii and brachialis muscles to flex the elbow.
✔ Cooperates with the forearm extensor muscles to stabilize wrist and elbow movements.
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ Brachioradialis tendinitis caused by repetitive heavy training.
✔ Weakness in this muscle can lead to forearm pain and decreased grip strength.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Key Exercises to Strengthen the Brachioradialis
1️⃣ Hammer Curls: Increase strength and endurance of the brachioradialis.
2️⃣ Fat Grip Training: Strengthen forearm and wrist muscles.
3️⃣ Neutral Grip Pull-ups: Enhance control over the arm and forearm.
4️⃣ Farmer’s Walks: Improve grip strength and endurance.
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery Movements
✔ Wrist and forearm stretches by bending them backward — helps reduce muscle tension and increase flexibility.
✔ Forearm and wrist massage — prevents stiffness and improves blood circulation.
✅ 🔍 Fun Fact
✔ The brachioradialis is the only elbow flexor muscle controlled by the radial nerve!
✅ 💡 Practical Tip
✔ To boost endurance in martial arts and weightlifting, include resistance exercises targeting the brachioradialis in your training routine.
🔴 Name & Location:
A superficial posterior forearm muscle that extends from the humerus to the radius.
🟠 Anatomy:
Originates from the lateral part of the humerus and inserts into the distal radius.
🟡 Function:
Elbow flexion, elbow joint stabilization, and assistance in gripping objects.
🟢 Physiology:
Contains both slow- and fast-twitch fibers for endurance and strength.
🔵 Innervation:
Radial nerve (C5, C6, C7).
🟣 Significance:
Active in wrestling, boxing, weightlifting, rock climbing, and bodybuilding.
🟤 Exercises:
Hammer curls, fat grip training, and elbow resistance exercises.
⚫ Fun Fact:
The only elbow flexor muscle controlled by the radial nerve.
Extensor Carpi Radialis Longus
Extensor Carpi Radialis Longus Muscle
The Extensor Carpi Radialis Longus is one of the superficial posterior muscles of the forearm. Its primary function is to extend the wrist and deviate it laterally (radially). This muscle plays an important role in throwing movements, gripping objects, and controlling wrist motions in sports such as tennis, basketball, weightlifting, and rock climbing. Weakness in this muscle can lead to decreased wrist stability and reduced hand movement control. Next, we’ll provide a comprehensive overview of this muscle following the standard checklist. ✅
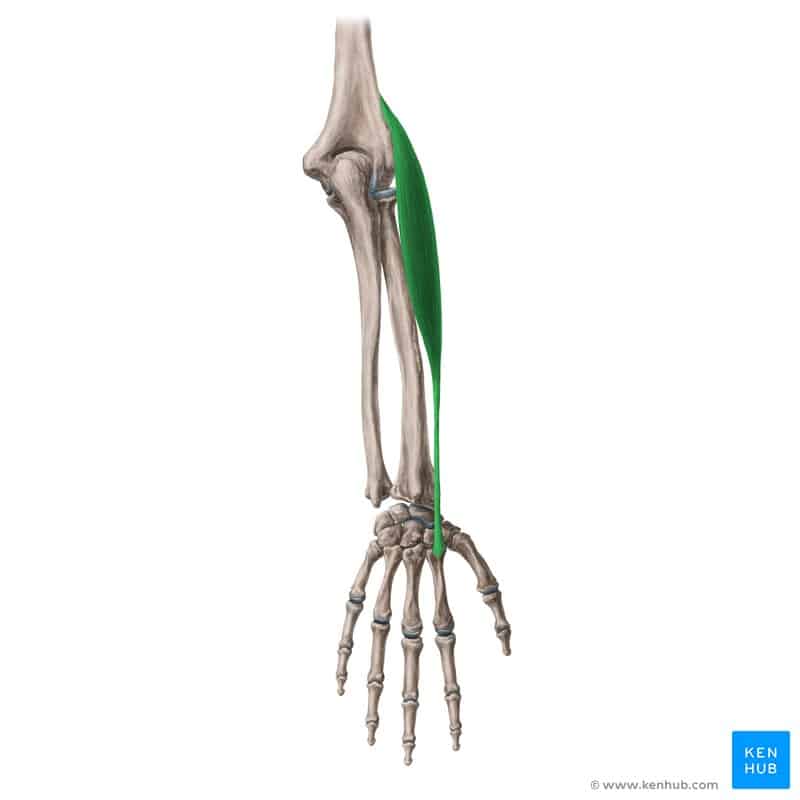
✅ Persian Name: Bazkonandeh Moch Dast Radial Boland
✅ Latin Name: Extensor Carpi Radialis Longus
✅ Common Name: Extensor Carpi Radialis Longus
✅ Location:
🟡 Located superficially on the posterior forearm, originating from the humerus and inserting into the metacarpal bones.
🟡 Part of the superficial extensor muscle group of the forearm.
🟡 Responsible for wrist extension and radial (outward) deviation.
✅ 🦾 Origin
✔ Lateral supracondylar ridge of the humerus
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ Base of the second metacarpal bone
✅ 📌 Function
✔ Extends the wrist
✔ Abducts the wrist toward the radial (thumb) side
✔ Assists in stabilizing wrist movements and gripping objects
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Type
✔ A combination of slow-twitch fibers (Type I) for endurance and fast-twitch fibers (Type II) for quick, powerful movements.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Movement and Sports Performance
✔ Plays a key role in sports like tennis, badminton, weightlifting, basketball, and rock climbing.
✔ Actively involved in gripping, wrist extension, and controlling throwing movements.
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ Plays an important role in grip strength, wrist stabilization, and handling heavy loads.
✔ Weakness in this muscle can reduce wrist control and overall hand stability.
🧠 Innervation
✔ Radial nerve (C6, C7)
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Radial artery
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Tennis & Badminton: Controls the racket and enables quick wrist movements.
✔ Weightlifting: Stabilizes the wrist during lifts.
✔ Basketball & Volleyball: Enhances accuracy in throwing and ball control.
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Interaction with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Works together with the extensor carpi radialis brevis to stabilize wrist movements.
✔ Collaborates with wrist flexor muscles to ensure precise control of wrist actions.
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ Extensor tendinitis caused by repetitive and excessive wrist movements.
✔ Lateral elbow pain (Tennis Elbow) resulting from overuse and strain on this muscle.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Key Exercises to Strengthen the Extensor Carpi Radialis Longus
1️⃣ Wrist Extensions with Dumbbell: Builds strength in wrist extensors.
2️⃣ Wrist Twisting with Resistance Band: Enhances wrist endurance and agility.
3️⃣ Static Grip Holds (holding a racket or dumbbell): Improves wrist control and stability.
4️⃣ Plate Pinch Hold: Increases forearm muscle endurance and finger agility.
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery Movements
✔ Wrist stretches by bending it downward — helps reduce tension and improve flexibility.
✔ Forearm and wrist massage — prevents stiffness and boosts blood circulation.
✅ 🔍 Fun Fact
✔ This muscle is one of the most important for controlling wrist movements in tennis and other racquet sports!
✅ 💡 Practical Tip
✔ If you experience pain on the outside of your elbow (Tennis Elbow), strengthening this muscle can help reduce the strain on your elbow.
🔴 Name & Location:
A superficial posterior forearm muscle that extends from the humerus to the base of the second metacarpal.
🟠 Anatomy:
Originates from the lateral part of the humerus and inserts at the base of the second metacarpal.
🟡 Function:
Extends the wrist, abducts the wrist outward, and assists in gripping objects.
🟢 Physiology:
Contains both slow- and fast-twitch fibers for endurance and powerful movements.
🔵 Innervation:
Radial nerve (C6, C7).
🟣 Significance:
Active in tennis, badminton, weightlifting, basketball, and throwing motions.
🟤 Exercises:
Wrist dumbbell exercises, resistance training, and weighted grip exercises.
⚫ Fun Fact:
Plays a key role in reducing elbow strain and preventing Tennis Elbow.
Extensor Carpi Radialis Brevis
Extensor Carpi Radialis Brevis Muscle
The extensor carpi radialis brevis is a superficial muscle on the posterior side of the forearm. Its main function is to extend the wrist and assist with its radial (outward) deviation. Compared to the extensor carpi radialis longus, this muscle is shorter and thicker, playing a greater role in stabilizing wrist movements and gripping objects. It is highly active in sports like tennis, badminton, weightlifting, and other activities requiring precise wrist control. Weakness or overuse of this muscle can lead to pain and inflammation on the outer elbow, commonly known as Tennis Elbow.
Below, you’ll find a comprehensive overview of this muscle based on the standard checklist. ✅
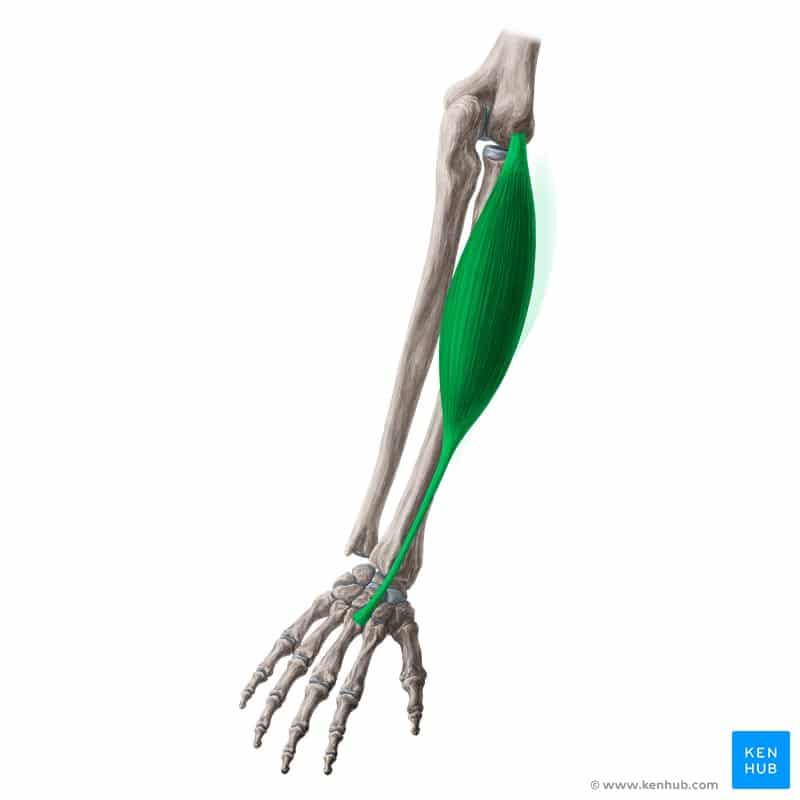
✅ Persian Name: Bazkonandeh Moch Dast Radial Kootah
✅ Latin Name: Extensor Carpi Radialis Brevis
✅ Common Name: Extensor Carpi Radialis Brevis
✅ Location:
🟡 Located superficially on the posterior forearm, originating from the humerus and inserting into the metacarpal bones.
🟡 Part of the superficial extensor muscle group of the forearm.
🟡 Responsible for wrist extension and assisting radial (outward) deviation.
✅ 🦾 Origin
✔ Lateral epicondyle of the humerus
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ Base of the third metacarpal bone
✅ 📌 Function
✔ Extends the wrist
✔ Abducts the wrist toward the radial (thumb) side
✔ Assists in stabilizing wrist movements and controlling grip actions
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Type
✔ Contains a mix of slow-twitch fibers (Type I) for endurance and fast-twitch fibers (Type II) for powerful movements.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Movement and Sports Performance
✔ Plays a key role in sports like tennis, badminton, weightlifting, basketball, and rock climbing.
✔ Actively involved in gripping, wrist extension, and controlling throwing movements.
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ Plays a key role in wrist stability and strength during gripping actions.
✔ Weakness in this muscle reduces wrist control and increases the risk of elbow and wrist injuries.
🧠 Innervation
✔ Deep branch of the radial nerve (C7, C8)
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Radial artery
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Tennis and Badminton: Precise control of racket movements.
✔ Weightlifting: Stabilizes the wrist when holding heavy weights.
✔ Basketball and Volleyball: Enhances accuracy in ball throwing.
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Interaction with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Works together with the extensor carpi radialis longus to stabilize wrist movements.
✔ Collaborates with wrist flexor muscles to control various wrist motions.
✅ 💉 Vulnerabilities and Common Issues
✔ Extensor tendinitis causing pain and limited wrist movement.
✔ Lateral elbow pain (Tennis Elbow), often resulting from overuse of this muscle.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Key Exercises to Strengthen the Extensor Carpi Radialis Brevis
1️⃣ Wrist Extensions with Dumbbell – boosts the strength of wrist extensors.
2️⃣ Wrist Twisting with Resistance Band – enhances endurance and control of wrist movements.
3️⃣ Static Grip Holds – improves wrist stability and control.
4️⃣ Medicine Ball Rotations – strengthens throwing and rotational motions.
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery
✔ Wrist stretches bending downward – relieve tension and improve flexibility.
✔ Forearm and wrist massage – prevent stiffness and boost blood circulation.
✅ 🔍 Interesting Fact
✔ This muscle is highly active during precise wrist movements such as playing musical instruments, typing, and painting.
✅ 💡 Practical Tip
✔ To prevent tennis elbow pain, regularly strengthen and stretch this muscle.
🔴 Name and Location:
A superficial posterior forearm muscle that extends from the humerus to the base of the third metacarpal bone.
🟠 Anatomy:
Originates from the lateral epicondyle of the humerus and inserts at the base of the third metacarpal.
🟡 Function:
Wrist extension, wrist radial deviation (movement toward the thumb side), and stabilization of wrist movements.
🟢 Physiology:
Contains both slow- and fast-twitch muscle fibers, providing endurance and strength for powerful movements.
🔵 Innervation:
Deep branch of the radial nerve (C7, C8).
🟣 Importance:
Active in tennis, badminton, weightlifting, basketball, and throwing motions.
🟤 Exercises:
Wrist exercises with dumbbells, resistance training, and weight-grip exercises.
⚫ Interesting Fact:
This muscle plays a crucial role in controlling fine and precise wrist movements.
Extensor Digitorum Muscle
Extensor Digitorum Muscle
The extensor digitorum is an important muscle located on the posterior side of the forearm. Its main function is to extend the joints of the second to fifth fingers and assist in wrist extension. This muscle plays a key role in any activity that requires opening the fingers and controlling wrist movement, such as typing, playing musical instruments, throwing objects, and power sports like weightlifting and rock climbing. Weakness or injury to this muscle can reduce finger control and weaken grip strength.
Below, you’ll find a comprehensive review of this muscle following the standard checklist. ✅
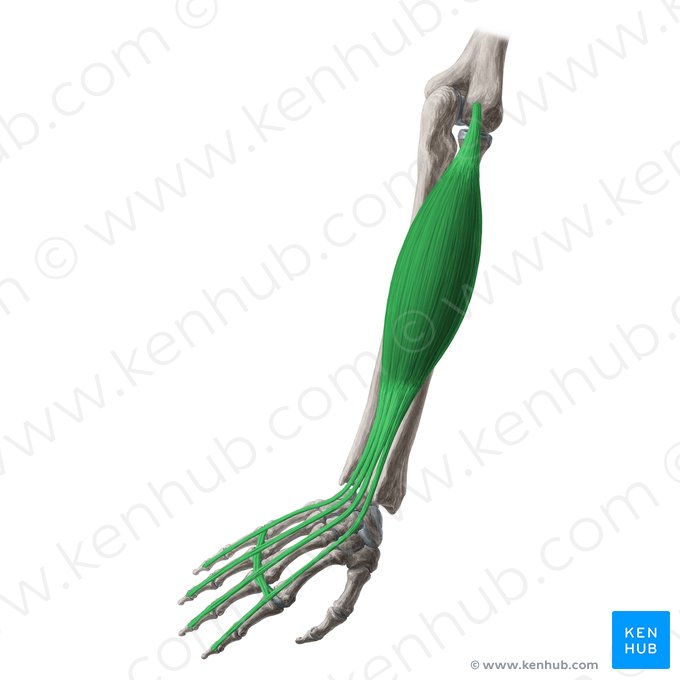
✅ Persian Name: Bazkonandeh Angoshtan
✅ Latin Name: Extensor Digitorum
✅ Common Name: Extensor Digitorum
✅ Location:
🟡 Located superficially on the posterior forearm, originating from the humerus and inserting into the phalanges of the second to fifth fingers.
🟡 Part of the superficial extensor muscle group of the forearm.
🟡 Responsible for extending the joints of the second to fifth fingers and assisting in wrist extension.
✅ 🦾 Origin
✔ Lateral epicondyle of the humerus
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ Middle and distal phalanges of the second to fifth fingers
✅ 📌 Function
✔ Extends the second to fifth fingers
✔ Assists in wrist extension
✔ Stabilizes wrist and finger movements during gripping and object control
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Type
✔ A combination of slow-twitch fibers (Type I) for endurance and fast-twitch fibers (Type II) for quick, powerful movements.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Movement and Sports Performance
✔ Plays a key role in typing, playing musical instruments, throwing, gripping objects, and power sports.
✔ Actively involved in fine finger control and wrist stabilization during activities like rock climbing and weightlifting.
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ Plays a vital role in finger extension strength and wrist stabilization during gripping.
✔ Weakness in this muscle can lead to reduced finger control, quicker hand fatigue, and decreased grip strength.
🧠 Innervation
✔ Posterior interosseous nerve (a branch of the radial nerve, C7, C8)
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Posterior interosseous artery
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Typing and playing musical instruments: Controls fine finger movements.
✔ Weightlifting and rock climbing: Stabilizes and maintains strength in gripping and finger control.
✔ Basketball, volleyball, and tennis: Manages throwing motions and ball handling.
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Interaction with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Works alongside other finger and wrist extensors to stabilize movements.
✔ Collaborates with finger flexor muscles to balance finger control.
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ Extensor tendinitis causing pain and reduced range of motion.
✔ Extensor compartment syndrome in the forearm, often due to overuse and repetitive strain.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Key Exercises to Strengthen the Extensor Digitorum
1️⃣ Finger Extensions with Resistance Band: Increases the strength of finger extensors.
2️⃣ Wrist Extensions with Dumbbell: Builds strength in the forearm extensors.
3️⃣ Finger Spread with Stress Ball: Improves finger strength and agility.
4️⃣ Grip and Twist Exercises: Enhances endurance and finger control.
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery Movements
✔ Stretch fingers and wrist forward and backward — reduces tension and improves flexibility.
✔ Hand and forearm massage — prevents stiffness and boosts blood circulation.
✅ 🔍 Interesting Fact
✔ This muscle is responsible for extending all the fingers except the thumb. Without it, fully straightening your fingers would be impossible!
✅ 💡 Practical Tip
✔ To improve finger strength and prevent fatigue during long tasks, make sure to include strengthening exercises for this muscle in your routine.
🔴 Name & Location:
A superficial muscle located on the back of the forearm, extending from the upper arm down to the second through fifth fingers.
🟠 Anatomy:
Originates from the lateral epicondyle of the humerus and inserts into the middle and distal phalanges of the second to fifth fingers.
🟡 Function:
Extends the fingers, assists in wrist extension, and helps stabilize hand movements.
🟢 Physiology: Contains both slow-twitch and fast-twitch fibers, allowing for endurance and precise control of finger movements.
🔵 Innervation:
Posterior interosseous nerve (C7, C8).
🟣 Importance:
This muscle plays a key role in activities like typing, playing musical instruments, weightlifting, rock climbing, tennis, and basketball.
🟤 Exercises:
Finger extension drills, resistance band exercises, and wrist extensions using dumbbells.
⚫ Fun Fact:
This muscle is responsible for extending all the fingers except the thumb.
Extensor Digiti Minimi Muscle
Extensor Digiti Minimi Muscle
The Extensor Digiti Minimi is one of the superficial posterior muscles of the forearm. Its primary function is to extend the little finger (fifth finger) and assist in wrist extension. This muscle plays a crucial role in precise movements of the little finger, grip control, and stabilizing wrist movements in sports such as tennis, weightlifting, and rock climbing. Weakness in this muscle can lead to reduced control of the little finger and limitations in fine hand movements. Next, we’ll provide a comprehensive overview of this muscle following the standard checklist. ✅
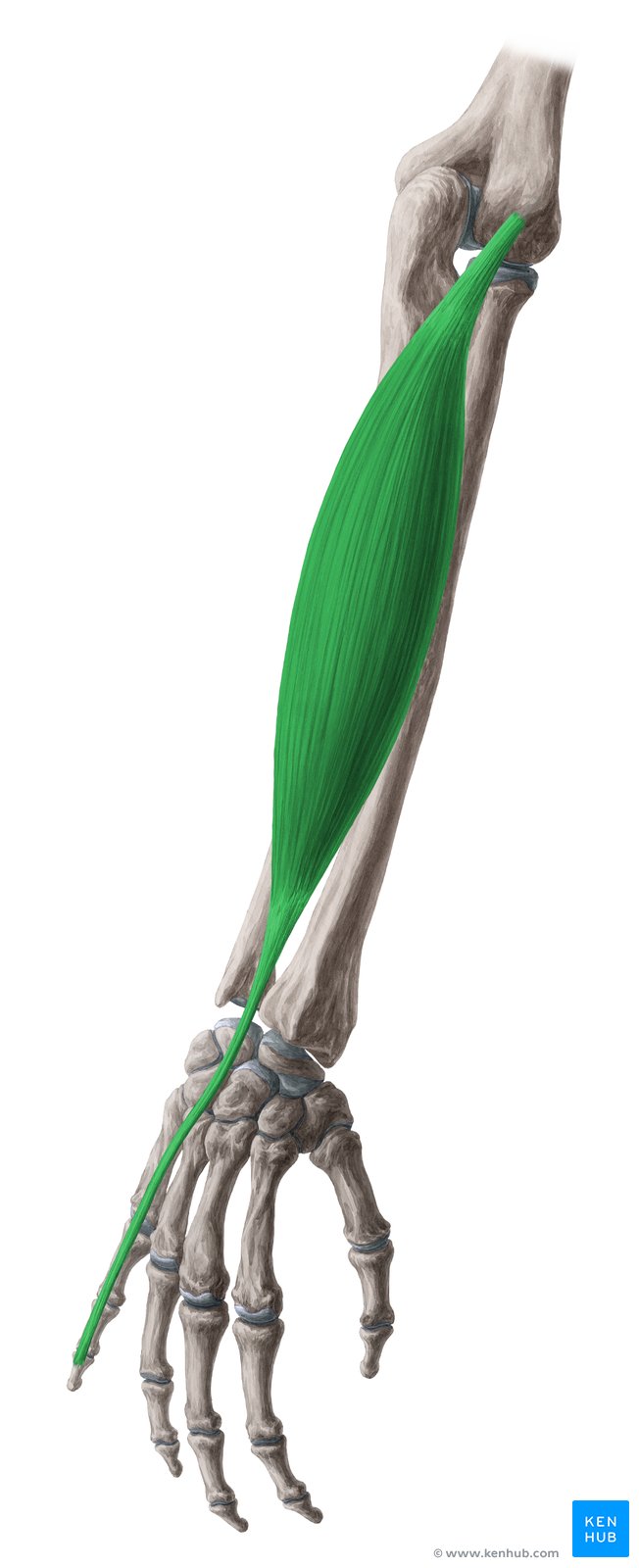
✅ Persian Name: Bazkoneh-ye Angosht-e Kuchak
✅ Latin Name: Extensor Digiti Minimi
✅ Common Name: Extensor Digiti Minimi
✅ Location:
🟡 Located on the posterior (back) and superficial part of the forearm, originating from the humerus (upper arm bone) and attaching to the little finger.
🟡 It belongs to the group of superficial extensor muscles of the forearm.
🟡 Its main function is to extend the little finger joint and assist in wrist extension.
✅ 🦾 Origin
✔ Lateral epicondyle of the humerus
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ Middle and distal phalanges of the little finger via the extensor expansion (Extensor Expansion of the Fifth Finger)
✅ 📌 Function
✔ Extension of the little finger (Fifth Finger)
✔ Assisting in wrist extension
✔ Assisting in ulnar deviation of the wrist (movement of the wrist toward the pinky side)
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Type
✔ Contains a mix of slow-twitch fibers (Type I) for endurance and fast-twitch fibers (Type II) for quick and powerful movements.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Motor Functions and Sports
✔ Plays a key role in fine movements of the little finger, wrist stabilization, and grip strength control.
✔ Actively involved in sports such as tennis, weightlifting, rock climbing, and basketball.
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ Plays an important role in enhancing control of the little finger and strengthening grip.
✔ Weakness in this muscle can lead to reduced endurance of the little finger and increased fatigue during fine hand movements.
🧠 Innervation
✔ Posterior interosseous nerve (a branch of the radial nerve, C7, C8)
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Posterior interosseous artery
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Tennis and Badminton: Helps stabilize the racket during powerful strokes.
✔ Weightlifting: Stabilizes the wrist while lifting heavy weights.
✔ Rock Climbing and Basketball: Enhances control of finger and wrist movements when gripping various surfaces.
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Interaction with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Works together with the finger extensors and the ulnar wrist extensor muscles to stabilize hand movements.
✔ Collaborates with the little finger flexor muscles to maintain balanced control over finger motions.
✅ 💉 Vulnerabilities and Common Issues
✔ Extensor tendinitis of the little finger tendon caused by repetitive or excessive movements.
✔ Pain in the outer forearm and wrist area (Extensor Compartment Syndrome), often resulting from intense training or heavy use.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Key Exercises to Strengthen the Extensor Digiti Minimi
1️⃣ Finger Extensions with Resistance Band – boosts the strength of the finger extensors.
2️⃣ Wrist Extensions with Dumbbell – strengthens the forearm extensor muscles.
3️⃣ Finger Spread with Stress Ball – improves the stability and endurance of the little finger.
4️⃣ Table Finger Extensions – enhances control and strength of the little finger by extending it against a flat surface.
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery Exercises
✔ Stretching the little finger and wrist downward to relieve tension and improve flexibility.
✔ Massaging the hand and forearm to prevent stiffness and promote better blood circulation.
✅ 🔍 Fun Fact
✔ The extensor digiti minimi is highly active in many everyday tasks like typing, gripping objects, and even playing musical instruments!
✅ 💡 Practical Tip
✔ To improve endurance and precision in little finger movements, incorporate resistance and stretching exercises into your training routine.
🔴 Name and Location: A superficial muscle on the back of the forearm that extends from the upper arm to the little finger.
🟠 Anatomy: Originates from the lateral epicondyle of the humerus and inserts into the middle and distal phalanges of the little finger.
🟡 Function: Extends the little finger, assists in wrist extension, and stabilizes movements of the wrist and fingers.
🟢 Physiology: Contains both slow-twitch and fast-twitch fibers, allowing for endurance and precise control of finger movements.
🔵 Innervation:
Posterior interosseous nerve (C7, C8).
🟣 Importance: Plays an active role in tennis, weightlifting, rock climbing, typing, and basketball.
🟤 Exercises: Little finger extension exercises, resistance band training, and finger control drills.
⚫ Interesting Facts: This muscle plays a vital role in nearly all everyday activities that involve movements of the little finger.
Extensor Carpi Ulnaris Muscle
Extensor Carpi Ulnaris Muscle
The extensor carpi ulnaris is one of the superficial muscles on the back of the forearm. Its primary function is to extend the wrist and move it inward toward the ulnar side (ulnar deviation). This muscle plays a crucial role in stabilizing the wrist during resistance and rotational movements, making it essential in activities like weightlifting, rock climbing, tennis, and basketball. Weakness or injury to this muscle can lead to reduced wrist control and a weaker grip. Below, we provide a comprehensive overview of this muscle following a standard checklist. ✅

✅ Persian Name: Bazkoneh-ye Moch-e Dast-e Ulnari
✅ Latin Name: Extensor Carpi Ulnaris
✅ Common Name: Extensor Carpi Ulnaris
✅ Location:
🟡 Located on the posterior (back) and superficial part of the forearm, originating from the humerus and the ulna, and attaching to the metacarpal bone.
🟡 Part of the superficial extensor muscle group of the forearm.
🟡 Responsible for extending the wrist and moving it inward toward the ulnar side (ulnar deviation).
✅ 🦾 Origin
✔ Lateral epicondyle of the humerus
✔ Posterior border of the ulna
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ Base of the fifth metacarpal bone
✅ 📌 Function
✔ Wrist extension
✔ Ulnar deviation (movement of the wrist toward the pinky side)
✔ Stabilizing the wrist during rotational and resistance movements
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Type
✔ A combination of slow-twitch fibers (Type I) for endurance and fast-twitch fibers (Type II) for quick, powerful movements.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Motor Functions and Sports
✔ Plays a key role in sports such as weightlifting, rock climbing, boxing, basketball, and racket sports.
✔ Actively stabilizes wrist movements during heavy gripping and rotational actions.
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ Plays a vital role in enhancing wrist endurance and improving grip strength.
✔ Weakness in this muscle can reduce wrist control and increase strain on other forearm muscles.
🧠 Innervation
✔ Posterior interosseous nerve (a branch of the radial nerve, C7, C8)
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Posterior interosseous artery
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Weightlifting: Helps stabilize the wrist when lifting heavy weights.
✔ Basketball and Tennis: Controls wrist movements and helps prevent injuries.
✔ Boxing and Martial Arts: Aids in precise control of punches and hand movements.
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Interaction with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Works in coordination with other wrist and finger extensors to stabilize hand movements.
✔ Collaborates with wrist flexor muscles to maintain balance and control during wrist motions.
✅ 💉 Vulnerabilities and Common Issues
✔ Extensor Carpi Ulnaris tendinitis, causing pain and reduced wrist mobility.
✔ Pain and inflammation in the back of the wrist (Extensor Compartment Syndrome), often resulting from overuse during intense training.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Key Exercises to Strengthen the Extensor Carpi Ulnaris
1️⃣ Wrist Extensions with Dumbbell – boosts the strength of wrist extensor muscles.
2️⃣ Ulnar Deviation with Resistance Band – improves wrist endurance and control.
3️⃣ Static Grip Holds – enhances endurance and stability of wrist movements.
4️⃣ Wrist Twisting with Dumbbell – increases forearm muscle strength and flexibility.
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery Exercises
✔ Wrist stretches directed downward to relieve tension and improve flexibility.
✔ Forearm and wrist massage to prevent stiffness and boost blood circulation.
✅ 🔍 Interesting Fact
✔ This muscle is highly active during all rotational movements and heavy gripping tasks, such as using a hammer or throwing a ball!
✅ 💡 Practical Tip
✔ To prevent weakness and loss of wrist endurance, be sure to include resistance exercises targeting this muscle in your training routine.
🔴 Name and Location: A superficial muscle on the back of the forearm that extends from the humerus and ulna to the fifth metacarpal bone.
🟠 Anatomy: Originates from the lateral epicondyle of the humerus and the posterior border of the ulna, inserting at the base of the fifth metacarpal.
🟡 Function: Extends the wrist, moves the wrist inward (ulnar deviation), and stabilizes rotational movements.
🟢 Physiology: Composed of both slow-twitch and fast-twitch muscle fibers to support endurance and powerful movements.
🔵 Innervation:
Posterior interosseous nerve (C7, C8).
🟣 Importance: Plays an active role in weightlifting, basketball, boxing, martial arts, and wrist movement control.
🟤 Exercises: Dumbbell wrist extensions, wrist ulnar deviation exercises, weight gripping, and wrist twisting movements.
⚫ Interesting Facts: This muscle plays a key role in all rotational wrist movements and gripping heavy objects.
4. Deep Posterior Muscle Group
Extensor Compartment - Deep Layer
Supinator Muscle
Supinator Muscle
The Supinator is one of the deep posterior muscles of the forearm. Its primary function is to rotate the forearm upward (supination), or turn the palm of the hand upward. Along with the Biceps Brachii, this muscle plays a key role in rotational movements of the forearm and is highly active in activities such as opening a bottle, using a screwdriver, lifting weights, and in sports like boxing and weightlifting. Weakness or injury to this muscle can reduce the ability to rotate the wrist and cause weakness in gripping objects. Next, we’ll provide a comprehensive overview of this muscle following the standard checklist. ✅
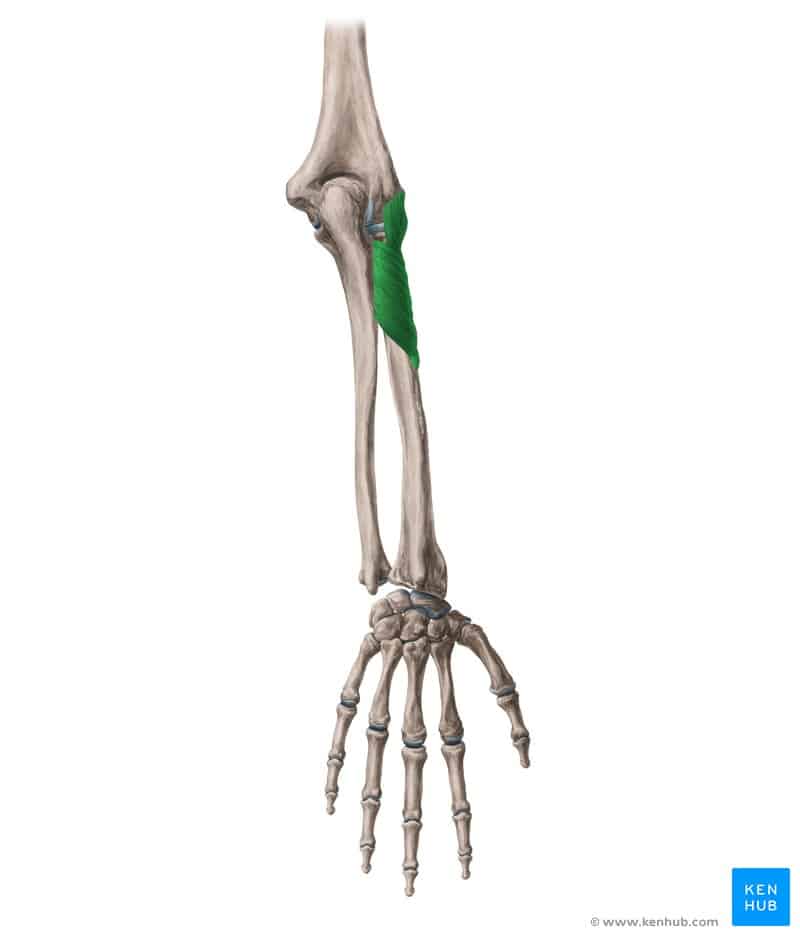
✅ Persian Name: Supinator
✅ Latin Name: Supinator
✅ Common Name: Supinator
✅ Location:
🟡 Located in the deep posterior part of the forearm, wrapping around the radius and originating from the ulna.
🟡 Part of the deep posterior forearm muscle group.
🟡 Responsible for rotating the forearm upward (supination).
✅ 🦾 Origin
✔ Lateral epicondyle of the humerus
✔ Posterior border of the ulna
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ Anterior and lateral surface of the radius
✅ 📌 Function
✔ Supination of the forearm (rotating the palm upward)
✔ Assists in stabilizing the elbow and forearm joints
✔ Works together with the biceps brachii in forearm rotational movements
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Type
✔ A combination of slow-twitch fibers (Type I) for endurance and fast-twitch fibers (Type II) for quick, powerful movements.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Motor Functions and Sports
✔ Plays a key role in sports like boxing, weightlifting, tennis, badminton, and basketball.
✔ Actively involved in movements such as using a screwdriver, opening bottles, and turning door handles.
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ Plays an important role in wrist rotation strength and forearm stability.
✔ Weakness in this muscle leads to reduced control over rotational movements and increased forearm fatigue.
🧠 Innervation
✔ Deep branch of the radial nerve (C5, C6)
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Posterior interosseous artery
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Boxing and martial arts: Controls forearm rotation during punches.
✔ Weightlifting: Stabilizes the forearm while lifting heavy weights.
✔ Tennis and badminton: Manages racket rotation during strokes.
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Interaction with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Works closely with the biceps brachii to rotate the forearm.
✔ Collaborates with forearm flexor and extensor muscles to stabilize wrist movements.
✅ 💉 Vulnerabilities and Common Issues
✔ Radial Tunnel Syndrome: compression of the radial nerve causing forearm pain.
✔ Weakness in forearm rotation and decreased grip strength.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Key Exercises to Strengthen the Supinator Muscle
1️⃣ Wrist Supination with Dumbbell – strengthens forearm rotational movements.
2️⃣ Twisting Screwdriver Motion with Weight – improves wrist endurance.
3️⃣ Resistance Band Supination – enhances forearm muscle strength and agility.
4️⃣ Medicine Ball Rotations – boosts control and stability of wrist and forearm movements.
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery Exercises
✔ Forearm and wrist stretches moving forward and backward to relieve tension and improve flexibility.
✔ Forearm and wrist massage to prevent stiffness and enhance blood circulation.
✅ 🔍 Interesting Fact
✔ This muscle is indirectly active in nearly all hand rotation movements—even during writing and typing!
✅ 💡 Practical Tip
✔ To prevent weakness in rotational movements and improve wrist control, include resistance exercises targeting this muscle in your training routine.
🔴 Name and Location: A deep posterior muscle of the forearm that connects the ulna to the radius.
🟠 Anatomy: Originates from the lateral epicondyle of the humerus and the posterior border of the ulna, inserting onto the anterior surface of the radius.
🟡 Function: Rotates the forearm upward (supination) and stabilizes rotational wrist movements.
🟢 Physiology: Composed of both slow-twitch and fast-twitch muscle fibers to support endurance and control during rotational movements.
🔵 Innervation: Deep branch of the radial nerve (C5, C6).
🟣 Importance: Active in boxing, weightlifting, tennis, badminton, and tasks like using a screwdriver.
🟤 Exercises: Wrist rotations with weights, forearm resistance training, and weighted screwdriver-style twisting exercises.
⚫ Interesting Fact: This muscle is even indirectly active during writing and typing.
Abductor Pollicis Longus Muscle
Abductor Pollicis Longus Muscle
The abductor pollicis longus is one of the deep posterior muscles of the forearm. Its primary function is to abduct the thumb, moving it away from the other fingers. This muscle plays a vital role in activities that require independent thumb movement, gripping objects, throwing, and controlling handheld tools—such as weightlifting, playing musical instruments, and rock climbing. Weakness in this muscle can reduce the thumb’s range of motion and limit gripping ability. Below, we provide a comprehensive overview of this muscle following a standard checklist. ✅
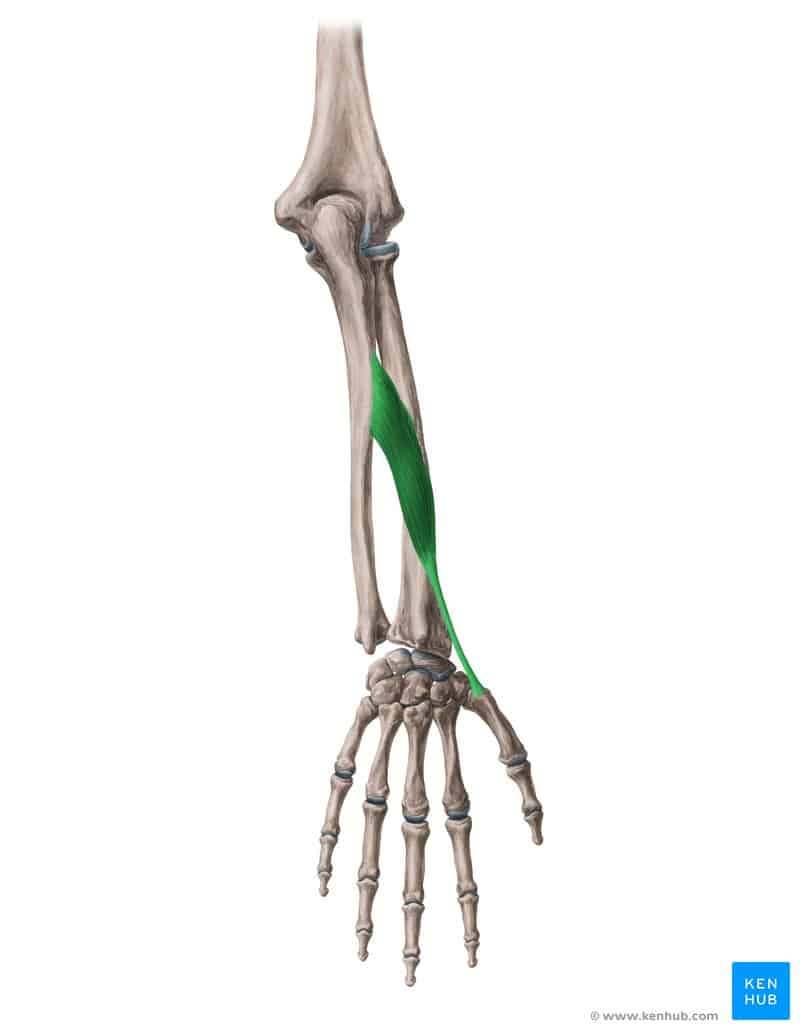
✅ Persian Name: Door-kondeh Boland-e Shast
✅ Latin Name: Abductor Pollicis Longus
✅ Common Name: Abductor Pollicis Longus
✅ Location:
🟡 Located in the deep posterior part of the forearm, originating from the radius and ulna bones and attaching to the thumb.
🟡 Part of the deep posterior forearm muscle group.
🟡 Responsible for abducting and moving the thumb away from the other fingers.
✅ 🦾 Origin
✔ Posterior surface of the radius and ulna
✔ Interosseous membrane of the forearm
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ Base of the first metacarpal bone (thumb)
✅ 📌 Function
✔ Thumb abduction (moving the thumb away from the palm)
✔ Assists in thumb extension
✔ Stabilizes thumb movements during gripping and rotational actions
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Type
✔ A combination of slow-twitch fibers (Type I) for endurance and fast-twitch fibers (Type II) for quick, powerful movements.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Motor Functions and Sports
✔ Plays a key role in controlling thumb movements in sports like weightlifting, rock climbing, tennis, and badminton.
✔ Active in gripping and manipulating small objects, as well as performing rotational movements with tools such as pens, screwdrivers, and rackets.
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ Plays a vital role in precise control of thumb movements and enhancing grip strength.
✔ Weakness in this muscle can reduce thumb range of motion and impair fine motor skills.
🧠 Innervation
✔ Posterior interosseous nerve (a branch of the radial nerve, C7, C8)
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Posterior interosseous artery
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Weightlifting: Stabilizes thumb movements during gripping of weights.
✔ Rock climbing and gymnastics: Helps improve grip control and holding strength.
✔ Tennis, badminton, and basketball: Enhances thumb control for catching and throwing the ball.
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Interaction with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Works alongside the abductor pollicis brevis and abductor pollicis longus to control thumb movements.
✔ Collaborates with the thumb flexor muscles to maintain balanced control of thumb actions.
✅ 💉 Vulnerabilities and Common Issues
✔ De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis: inflammation of the tendon sheath of this muscle causing pain at the base of the thumb.
✔ Reduced grip strength and limited thumb range of motion due to overuse or inactivity.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Key Exercises to Strengthen the Abductor Pollicis Longus
1️⃣ Thumb Abduction with Resistance Band – strengthens the thumb abductors.
2️⃣ Thumb Rotation with Dumbbell – improves control over thumb movements.
3️⃣ Grip Strength Training with Stress Ball – increases thumb and finger stability.
4️⃣ Thick Rope Twisting – enhances grip strength and control of rotational movements.
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery Exercises
✔ Stretching the thumb and wrist backward to relieve tension and improve flexibility.
✔ Massaging the thumb and forearm to enhance blood flow and speed up recovery.
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery Exercises
✔ Stretching the thumb and wrist backward to relieve tension and improve flexibility.
✔ Massaging the thumb and forearm to enhance blood flow and speed up recovery.
✅ 💡 Practical Tip
✔ To prevent wrist and thumb pain, make sure to include strengthening and stretching exercises for this muscle in your training routine.
🔴 Name and Location: A deep posterior muscle of the forearm that extends from the radius and ulna to the thumb’s metacarpal bone.
🟠 Anatomy: Originates from the radius, ulna, and interosseous membrane of the forearm, inserting at the base of the first metacarpal (thumb).
🟡 Function: Abducts and extends the thumb, stabilizing gripping and rotational movements.
🟢 Physiology: Contains both slow-twitch and fast-twitch muscle fibers to support endurance and precise control of thumb movements.
🔵 Innervation:
Posterior interosseous nerve (C7, C8).
🟣 Importance: Active in weightlifting, rock climbing, tennis, gymnastics, and precise thumb control.
🟤 Exercises: Thumb abduction with resistance bands, rotational exercises, and grip training using stress balls.
⚫ Interesting Fact: This muscle is key for independent thumb movements—a defining feature of human hand function.
Extensor Pollicis Brevis Muscle
Extensor Pollicis Brevis Muscle
The extensor pollicis brevis is one of the deep posterior muscles of the forearm. Its primary function is to extend the metacarpophalangeal (MCP) joint of the thumb and assist in overall thumb movements. This muscle plays an important role in gripping, thumb extension, and stabilization during activities like writing, typing, weightlifting, rock climbing, and racket sports. Weakness in this muscle can lead to reduced thumb control and decreased precision in fine motor tasks. Below, we provide a detailed overview of this muscle following a standard checklist. ✅
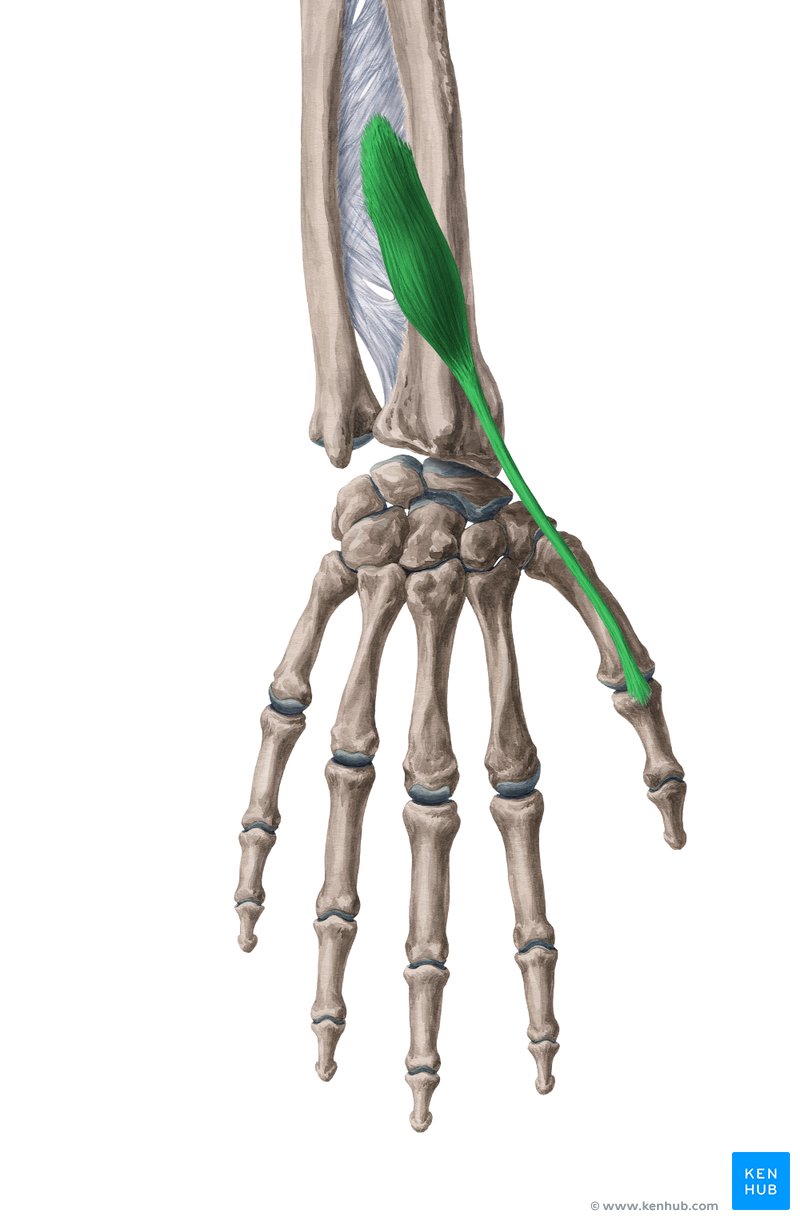
✅ Persian Name: Bazkondeh Kootah-e Shast
✅ Latin Name: Extensor Pollicis Brevis
✅ Common Name: Extensor Pollicis Brevis
✅ Location:
🟡 Located in the deep posterior forearm, originating from the radius and interosseous membrane, and attaching to the proximal phalanx of the thumb.
🟡 Part of the deep posterior forearm muscle group.
🟡 Responsible for extending the thumb’s MCP joint and assisting in stabilizing gripping and rotational movements.
✅ 🦾 Origin
✔ Posterior surface of the radius
✔ Interosseous membrane of the forearm
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ Base of the proximal phalanx of the thumb
✅ 📌 Function
✔ Extension of the thumb’s MCP joint (Thumb MCP Joint Extension)
✔ Assists in thumb extension and stabilization during gripping and fine motor control
✔ Works in coordination with the extensor pollicis longus and abductor pollicis muscles for controlled thumb movements
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Type
✔ Contains a mix of slow-twitch fibers (Type I) for endurance and fast-twitch fibers (Type II) for quick and powerful movements.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Motor Functions and Sports
✔ Plays a key role in sports requiring precise thumb control, such as tennis, badminton, weightlifting, basketball, and rock climbing.
✔ Active in fine hand movements like writing, painting, typing, and playing musical instruments.
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ Plays a crucial role in controlling precise thumb movements and enhancing grip strength.
✔ Weakness in this muscle leads to reduced thumb endurance and decreased accuracy in fine motor tasks.
🧠 Innervation
✔ Posterior interosseous nerve (a branch of the radial nerve, C7, C8)
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Posterior interosseous artery
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Tennis and Badminton: Assists in controlling the racket during strokes.
✔ Weightlifting: Stabilizes the thumb while gripping heavy weights.
✔ Basketball and Volleyball: Enhances accuracy in catching and throwing the ball.
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Interaction with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Works in coordination with the extensor pollicis longus and abductor pollicis longus to stabilize thumb movements.
✔ Collaborates with the thumb flexor muscles to maintain balanced control of precise thumb actions.
✅ 💉 Vulnerabilities and Common Issues
✔ De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis: inflammation of the extensor pollicis brevis tendon causing pain at the base of the thumb.
✔ Weakness in thumb extension leading to reduced precision in rotational movements and grip.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Key Exercises to Strengthen the Extensor Pollicis Brevis
1️⃣ Thumb Extension with Resistance Band – boosts strength of the thumb extensors.
2️⃣ Thumb Rotation with Dumbbell – improves control of rotational thumb movements.
3️⃣ Grip Strength Training with Stress Ball – enhances thumb strength and agility.
4️⃣ Pinch Grip Training – increases grip power and precision in fine motor tasks.
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery Exercises
✔ Stretching the thumb and wrist backward to relieve tension and improve flexibility.
✔ Massaging the thumb and forearm to enhance blood flow and speed up recovery.
✅ 🔍 Interesting Fact
✔ This muscle is highly active in all activities requiring thumb extension and stabilization, such as writing, painting, playing musical instruments, and racket sports!
✅ 💡 Practical Tip
✔ To prevent thumb pain and weakness, make sure to include strengthening and stretching exercises for this muscle in your training routine.
🔴 Name and Location: A deep posterior forearm muscle that originates from the radius and interosseous membrane and attaches to the proximal phalanx of the thumb.
🟠 Anatomy: Originates from the radius and the interosseous membrane of the forearm, inserting into the proximal phalanx of the thumb.
🟡 Function: Extends the thumb’s MCP joint, stabilizes gripping actions, and controls precise thumb movements.
🟢 Physiology: Composed of both slow-twitch and fast-twitch muscle fibers to support endurance and precise control of thumb movements.
🔵 Innervation:
Posterior interosseous nerve (C7, C8).
🟣 Importance: Active in racket sports, weightlifting, rock climbing, writing, and typing.
🟤 Exercises: Thumb extension with resistance bands, rotational exercises, and grip training using stress balls.
⚫ Interesting Fact: This muscle is one of the key muscles responsible for precise and powerful thumb movements.
Extensor Pollicis Longus Muscle
Extensor Pollicis Longus Muscle
The extensor pollicis longus is one of the deep posterior muscles of the forearm. Its primary function is to extend the thumb’s interphalangeal (IP) joint and assist in thumb movements involved in gripping and object control. This muscle is highly active during activities that require thumb extension, rotation, and stabilization—such as writing, weightlifting, playing musical instruments, and racket sports. Weakness in this muscle can reduce thumb movement control and impair gripping ability. Below, we provide a detailed overview of this muscle following a standard checklist. ✅
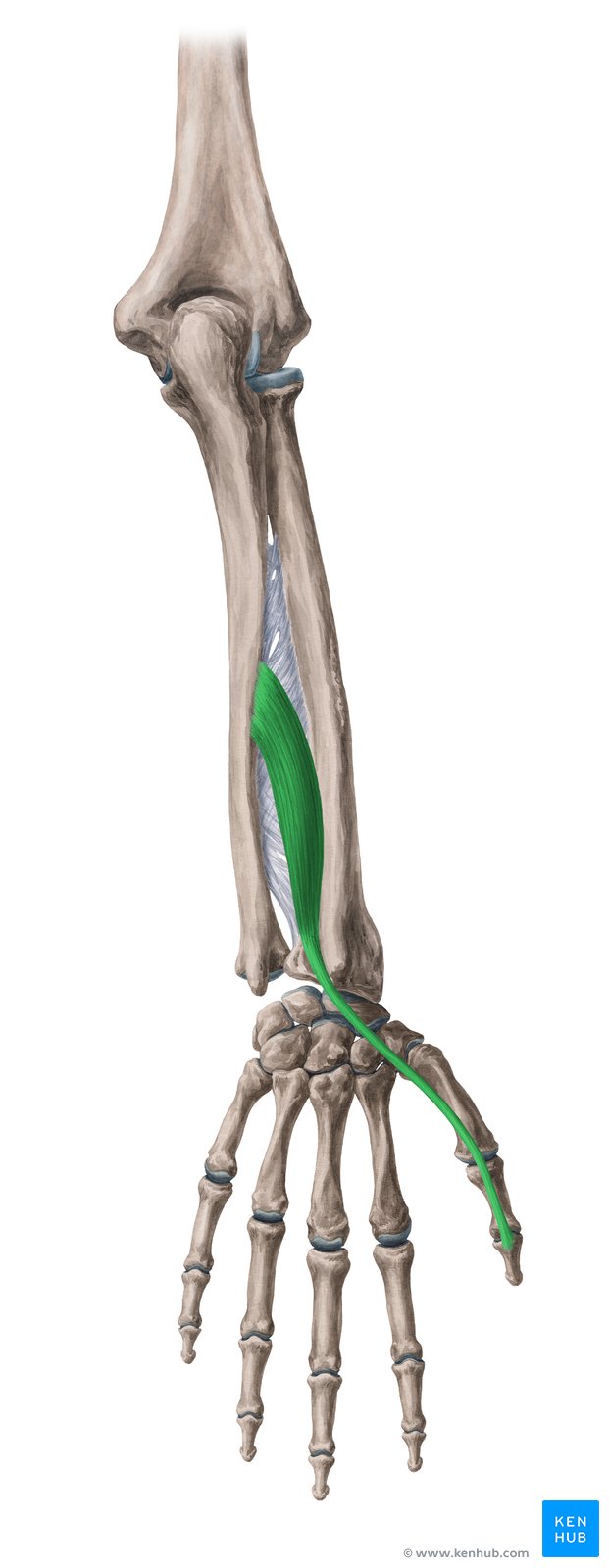
✅ Persian Name: Bazkondeh Boland-e Shast
✅ Latin Name: Extensor Pollicis Longus
✅ Common Name: Extensor Pollicis Longus
✅ Location:
🟡 Located in the deep posterior forearm, originating from the ulna and interosseous membrane, and attaching to the distal phalanx of the thumb.
🟡 Part of the deep posterior forearm muscle group.
🟡 Responsible for extending the thumb’s interphalangeal (IP) joint, assisting in thumb extension and stabilization.
✅ 🦾 Origin
✔ Posterior surface of the ulna
✔ Interosseous membrane of the forearm
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ Base of the distal phalanx of the thumb
✅ 📌 Function
✔ Extension of the thumb’s interphalangeal (IP) joint
✔ Assists in extending other thumb joints (MCP and CMC)
✔ Stabilizes the thumb during gripping, tool handling, and rotational hand movements
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Type
✔ A combination of slow-twitch fibers (Type I) for endurance and fast-twitch fibers (Type II) for quick, powerful movements.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Movement and Sports Performance
✔ Plays a crucial role in sports that require precise thumb control, such as tennis, badminton, weightlifting, basketball, and rock climbing.
✔ Essential for fine motor skills involving the hand, including writing, typing, playing musical instruments, and operating industrial tools.
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ Plays a vital role in grip strength, thumb movement control, and stabilizing hand motions.
✔ Weakness in this muscle can lead to reduced thumb endurance, a weaker grip, and less precision in rotational hand movements.
🧠 Innervation
✔ Posterior interosseous nerve (a branch of the radial nerve, C7, C8)
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Posterior interosseous artery
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Tennis and Badminton: Assists in controlling the racket during strokes.
✔ Weightlifting: Stabilizes the thumb while gripping heavy weights.
✔ Basketball and Volleyball: Enhances accuracy in catching and throwing the ball.
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Interaction with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Works closely with the extensor pollicis brevis and abductor pollicis longus muscles to stabilize thumb movements.
✔ Collaborates with the thumb flexor muscles to maintain balanced control during precise thumb motions.
✅ 💉 Vulnerabilities and Common Issues
✔ Tendon inflammation known as De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis, causing pain at the base of the thumb.
✔ Difficulty in thumb extension and reduced precision in rotational movements and gripping objects.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Key Exercises to Strengthen the Extensor Pollicis Longus Muscle
1️⃣ Thumb Extension with Resistance Band – boosts the strength of the thumb extensors.
2️⃣ Thumb Rotation with Dumbbell – enhances control over rotational thumb movements.
3️⃣ Grip Strength Training with a Stress Ball – improves thumb endurance and agility.
4️⃣ Pinch Grip Training – increases grip power and fine motor precision using the thumb tip.
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery Exercises
✔ Stretching the thumb and wrist backward to relieve tension and improve flexibility.
✔ Massaging the thumb and forearm to enhance blood flow and speed up recovery.
✅ 🔍 Fun Fact
✔ This muscle is the one that helps you extend your thumb when using your smartphone or playing video games!
✅ 💡 Practical Tip
✔ To prevent thumb pain and weakness, make sure to include strengthening and stretching exercises for this muscle in your training routine.
🔴 Name and Location:
A deep posterior forearm muscle that originates from the distal ulna and interosseous membrane, extending to the distal phalanx of the thumb.
🟠 Anatomy:
Originates from the distal ulna and the interosseous membrane of the forearm, inserting into the distal phalanx of the thumb.
🟡 Function:
Extends the thumb’s interphalangeal (IP) joint, stabilizes gripping motions, and controls precise thumb movements.
🟢 Physiology: Composed of both slow-twitch and fast-twitch muscle fibers to support endurance and precise control of thumb movements.
🔵 Innervation:
Posterior interosseous nerve (C7, C8).
🟣 Importance: Active in racket sports, weightlifting, rock climbing, writing, and typing.
🟤 Exercises: Thumb extension with resistance bands, rotational exercises, and grip training using stress balls.
⚫ Interesting Fact:
This muscle is highly active during smartphone use and video gaming.
Extensor Indicis Muscle
Extensor Indicis Muscle
The extensor indicis is a deep muscle located on the back of the forearm. Its primary function is to extend the joints of the index finger (the second finger) and assist with fine motor movements of the hand. This muscle enables you to move your index finger independently from the other fingers, which is essential for precise tasks such as typing, writing, playing musical instruments, and finely controlling tools. Weakness in this muscle can lead to reduced control over index finger movements and a weaker grip. Below, we provide a detailed overview of this muscle following a standardized checklist. ✅
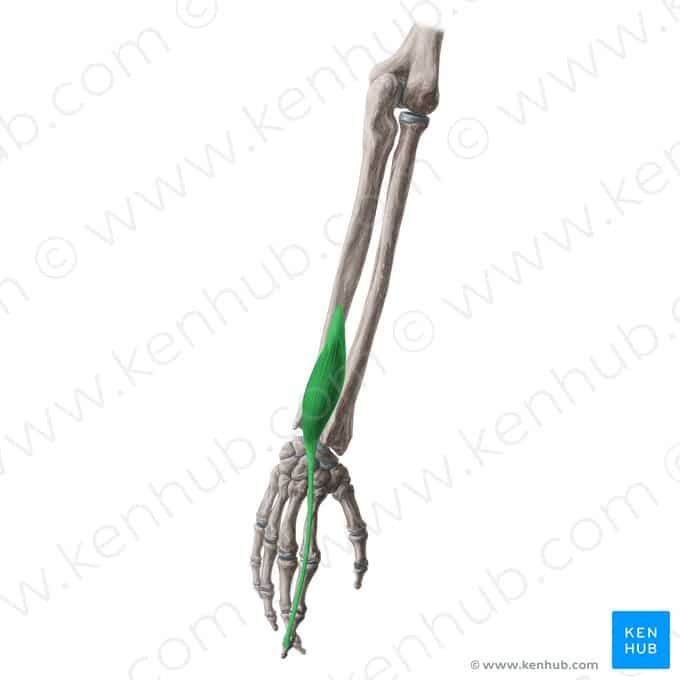
✅ Persian Name: Bāzkonandeh Eshāre
✅ Latin Name: Extensor Indicis
✅ Common Name: Extensor Indicis
✅ Location:
🟡 Located in the deep posterior compartment of the forearm, originating from the distal ulna and the interosseous membrane, and attaching to the index finger.
🟡 Part of the deep posterior forearm muscles group.
🟡 Responsible for extending the joints of the index finger and stabilizing its movements during daily activities.
✅ 🦾 Origin
✔ Posterior surface of the ulna
✔ Interosseous membrane of the forearm
✅ 🦿 Insertion
✔ Middle and distal phalanges of the index finger via the extensor expansion (Extensor Expansion of the Second Finger)
✅ 📌 Function
✔ Extends the joints of the index finger (Index Finger Extension)
✔ Assists in wrist extension and stabilizes finger movements
✔ Provides independent control of the index finger for precise tasks
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Type
✔ Contains a mix of slow-twitch fibers (Type I) for endurance and fast-twitch fibers (Type II) for quick and powerful movements.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Motor and Sports Performance
✔ Plays a key role in fine hand activities such as typing, painting, playing musical instruments, and using smartphones.
✔ Active in sports that require precise finger control, including basketball, volleyball, and rock climbing.
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Muscle Strength and Endurance
✔ Plays a crucial role in precise control of the index finger and enhances grip strength.
✔ Weakness in this muscle leads to reduced endurance of the index finger and diminished accuracy in fine hand movements.
🧠 Innervation
✔ Posterior interosseous nerve (a branch of the radial nerve, C7, C8)
🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Posterior interosseous artery
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Basketball and Volleyball: Assists in controlling and throwing the ball.
✔ Weightlifting and Gymnastics: Stabilizes the fingers while gripping bars or ropes.
✔ Rock Climbing: Enhances finger endurance for gripping edges and uneven surfaces.
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Interaction with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Works in coordination with the extensor digitorum and extensor pollicis brevis muscles to stabilize finger movements.
✔ Collaborates with the flexor muscles of the index finger to maintain balanced control during finger motions.
✅ 💉 Vulnerabilities and Common Issues
✔ Extensor tendinitis of the index finger tendon, causing pain at the back of the hand and forearm.
✔ Weakness in extending the index finger, leading to reduced ability to control precise hand movements.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Key Exercises to Strengthen the Extensor Indicis Muscle
1️⃣ Index Finger Extension with Resistance Band – enhances the strength of the finger extensors.
2️⃣ Finger Press with Stress Ball – improves control and endurance of the index finger.
3️⃣ Finger Grip Training with Weight Plate – increases grip strength and precision in index finger movements.
4️⃣ Isolated Index Finger Movement Training – develops independent control of the index finger.
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery Exercises
✔ Stretching the index finger and wrist backward – helps reduce tension and improve flexibility.
✔ Massaging the index finger and forearm – promotes blood flow and speeds up recovery.
✅ 🔍 Interesting Fact
✔ This muscle is one of the key reasons humans can use their index finger independently for pointing, typing, and handling precise tools!
✅ 💡 Practical Tip
✔ To prevent weakness in the index finger, incorporate strengthening and stretching exercises for this muscle into your daily routine.
🔴 Name and Location:
A deep posterior forearm muscle that originates from the distal ulna and interosseous membrane, extending to the tendons of the index finger.
🟠 Anatomy:
Originates from the distal ulna and the interosseous membrane of the forearm, inserting into the middle and distal phalanges of the index finger.
🟡 Function:
Extends the joints of the index finger, stabilizes gripping motions, and controls precise finger movements.
🟢 Physiology:
Contains both slow-twitch and fast-twitch muscle fibers, providing endurance and precise control for index finger movements.
🔵 Innervation:
Posterior interosseous nerve (C7, C8).
🟣 Importance:
Active in activities like typing, writing, weightlifting, rock climbing, basketball, and volleyball.
🟤 Exercises:
Index finger extension with resistance bands, pressing exercises, and finger control drills.
⚫ Interesting Fact:
This muscle is the main reason humans can move their index finger independently.
Interesting and Practical Facts
1. The forearm is made up of 19 muscles!
📌 Contrary to what many people think, the forearm doesn’t just have a few muscles—in fact, it contains 19 different muscles that work together to enable precise and powerful movements of the wrist and fingers! 💪🔥
2. Grip strength depends more on the forearm than on the fingers!
📌 The forearm muscles play the primary role in grip strength, and if these muscles are weak, even strong fingers won’t be able to hold heavy objects. 🏋️♂️🖐
3. The forearm muscles never fully rest!
📌 Even when your hand is relaxed, the forearm muscles stay active to keep your fingers in their natural position! 😲🖖
4. The forearm’s flexor muscles are twice as strong as the extensor muscles!
📌 The muscles responsible for bending the wrist and fingers (like the flexor digitorum superficialis and profundus) are twice as strong as the extensor muscles such as the extensor digitorum! 💪🆚🛠
5. Strong forearms help prevent carpal tunnel syndrome!
📌 Strengthening the forearm muscles can reduce pressure on the median nerve and help prevent issues like numbness and pain in the fingers (Carpal Tunnel Syndrome)! ⚠️🖐
6. You have an extra muscle in your forearm that you might never even use!
📌 The palmaris longus muscle is absent in about 10 to 15 percent of people and is completely non-essential for some! This muscle is often used as a donor tendon in surgical grafts. 😲🦾
7. Forearm muscles get stronger mostly through isometric exercises!
📌 Exercises like static holds (holding weights without movement) or dead hangs (hanging from a pull-up bar) have the greatest impact on building forearm strength and endurance! 🏋️♂️💪
8. Forearm strength is one of the best indicators of overall body health!
📌 Research shows that people with stronger grip strength tend to live longer and have a lower risk of heart disease and stroke! ❤️🏋️
9. The forearm muscles are divided into two main groups: anterior (flexors) and posterior (extensors)!
📌 The anterior forearm muscles are responsible for flexing the wrist and fingers, while the posterior group handles their extension! These two groups have opposite but complementary functions. 🔄🖐
10. Weak forearm muscles can be a primary cause of tennis elbow!
📌 This injury, also known as lateral epicondylitis, occurs due to weakness in the wrist and finger extensor muscles. 🎾💢
11. Left-handed people usually have stronger forearms compared to right-handed individuals!
📌 Since the left hand is more involved in physical tasks and object control for left-handed individuals, their left forearm is usually stronger and more developed than their right! 🤚🏋️
12. People with stronger forearms generally have an advantage in physical confrontations!
📌 Research shows that individuals with stronger grip strength tend to have the upper hand in physical hand-to-hand confrontations! 💥🥊
13. Your fingers don’t have muscles! All finger movements are controlled by muscles in the forearm!
📌 Contrary to popular belief, your fingers have no muscles of their own — all their movements are controlled by long tendons connected to muscles in the forearm! 🤯🖖
14. Farmers usually have the strongest forearms!
📌 Due to working with heavy tools, digging, and carrying loads, farmers and manual laborers often develop the strongest forearms—even without formal workouts! 👨🌾💪
15. Strengthening your forearms helps improve your deadlift, squat, and pull-up form!
📌 Most people who struggle with these movements do so because of weak forearm muscles and an inability to hold the weight for long periods! 🏋️♂️⚡
16. Explosive movements intensely activate the forearm muscles!
📌 Exercises like sledgehammer swings and battle rope waves have a powerful effect on strengthening the forearm muscles! 🛠🔥
17. If you have strong forearms, your fingers will get tired less easily!
📌 Most finger fatigue actually comes from weak forearm muscles, not the fingers themselves! Strengthening your forearms can help your fingers last longer without tiring! 🖐💪
18. Stretching exercises can boost forearm muscle recovery speed by up to 30%!
📌 Forearm stretches can help prevent pain and stiffness, speeding up muscle recovery! ⚡🧘♂️
19. Some of the strongest forearms in the world belong to professional rock climbers!
📌 Rock climbing is one of the best sports for building grip strength and forearm endurance, as it requires supporting your entire body weight with your fingers and forearms! 🧗♂️💪
20. Simple exercises like hanging from a pull-up bar can make your forearms stronger!
📌 The dead hang exercise, which involves hanging from a pull-up bar, is one of the best ways to build grip strength and forearm endurance! 🏋️♂️🙌
Conclusion
Conclusion
📢 Forearm muscles aren’t just important for overall body strength—they’re essential for hand health, movement control, and better performance in various sports! Strengthening them improves daily function and helps prevent wrist and finger injuries. So, if you want strong, resilient hands, don’t skip your forearm workouts! 💪🔥

References
Resources
Anatomy and medical books :
Gray's Anatomy (one of the standard references in anatomy)
Netter's Atlas of Human Anatomy (a well-known illustrated atlas in anatomy)
Clinically Oriented Anatomy by Keith Moore
Medical databases :
PubMed (for scientific and research articles)
MedlinePlus (health and medical information)
WebMD (for practical and general health information)
Sports and training references :
Strength Training Anatomy by Frederic Delavier
Essentials of Strength Training and Conditioning by NSCA
Well-known articles and training programs by international coaches
Medical databases :
PubMed (for scientific and research articles)
MedlinePlus (health and medical information)
WebMD (for practical and general health information)
Specialized sports and health websites :
Images used:
(Kenhub) kenhub.com
Further Reading
Further reading
Pelank Life | Body Health Assessment
The Best Body Health Calculators Using Scientific Methods
Developed by Pelank Life ©