1️⃣ Basic Muscle Information
✅ Persian Name: Deltoeid
✅ Latin Name: Deltoideus
✅ Common Name: Shoulder Muscle
✅ Location:
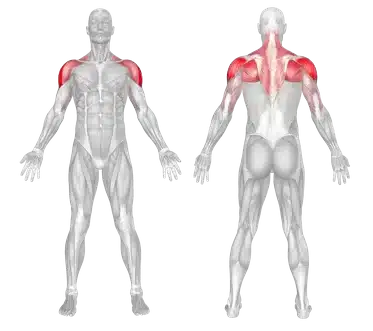
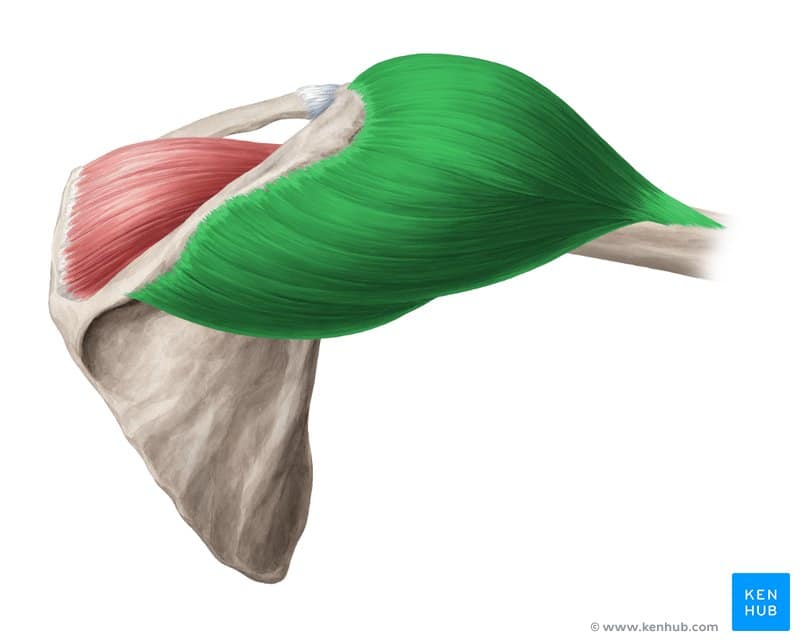
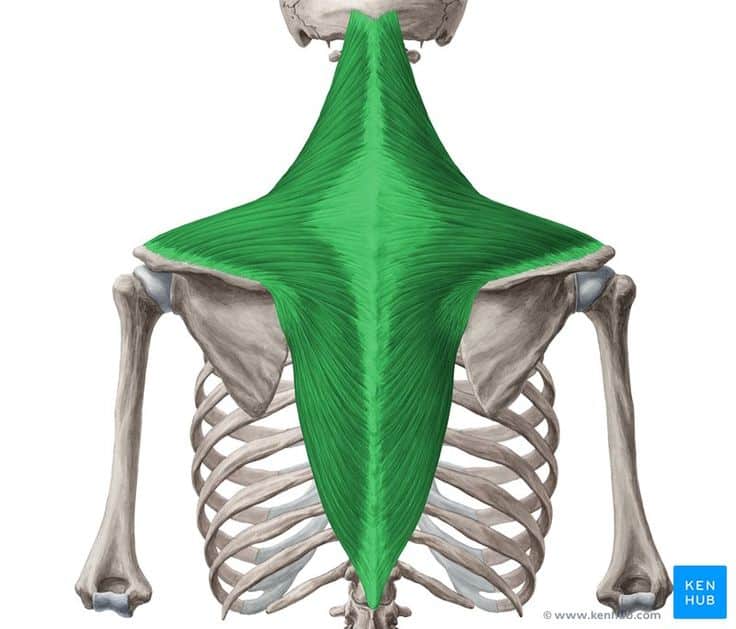
🟡 A superficial muscle located at the top of the upper arm, covering the shoulder joint.
🟡 It forms a cap-like structure over the shoulder joint.
🟡 It directly overlays the head of the humerus and originates from the clavicle, scapula, and the upper part of the arm.
2️⃣ Muscle Anatomy
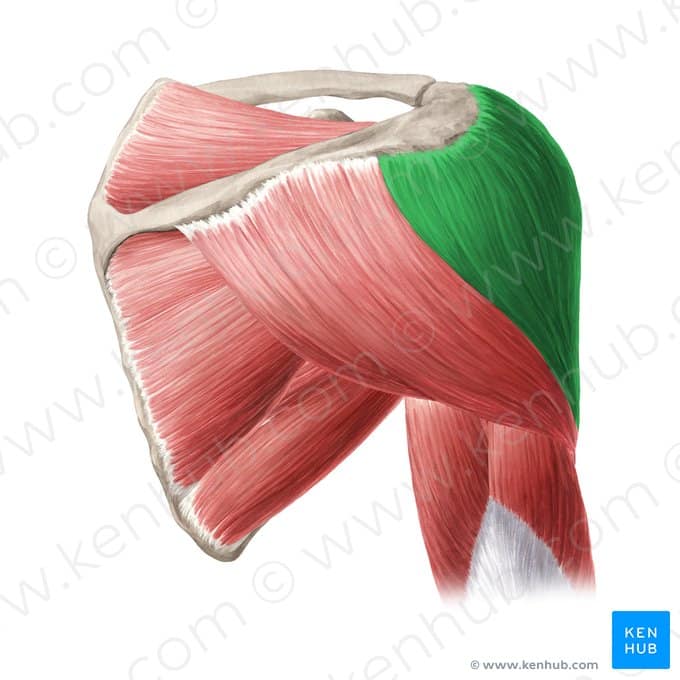
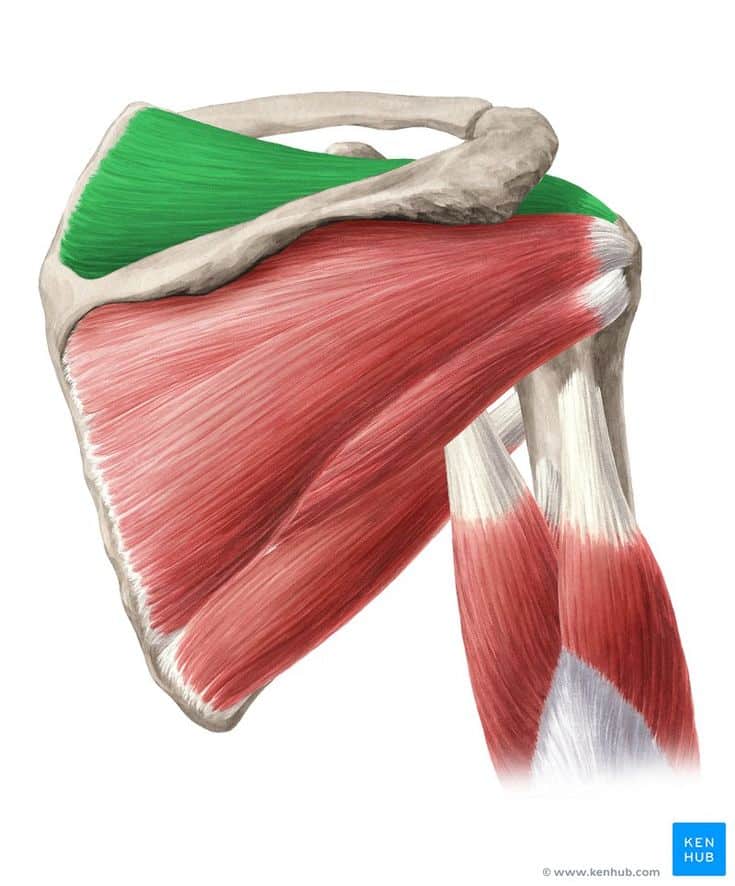
✅ 🔹 Origin
✔ Anterior part: from the outer surface of the clavicle
✔ Middle part: from the acromion, a portion of the scapula
✔ Posterior part: from the spine of the scapula
✅ 🔹 Insertion
✔ All parts of the deltoid muscle insert onto the deltoid tuberosity of the humerus.
✅ 🔹 Function
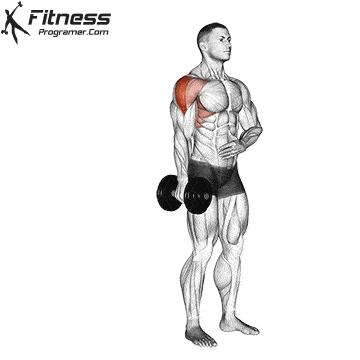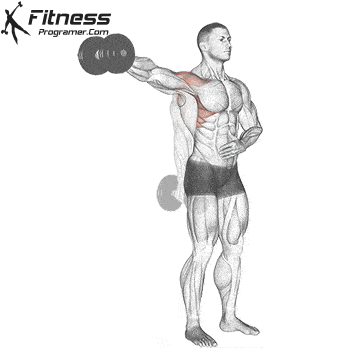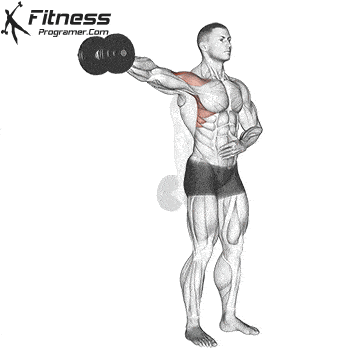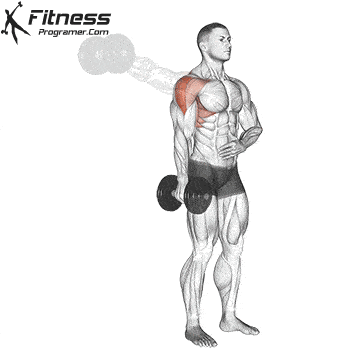
📌 The deltoid muscle is divided into three parts, each with a specific function:
1️⃣ Anterior Head
- ✔ Moving the arm forward (shoulder flexion)
- ✔ Internal rotation of the arm
- ✔ Assists in horizontal adduction of the arm (moving the arm forward across the body)
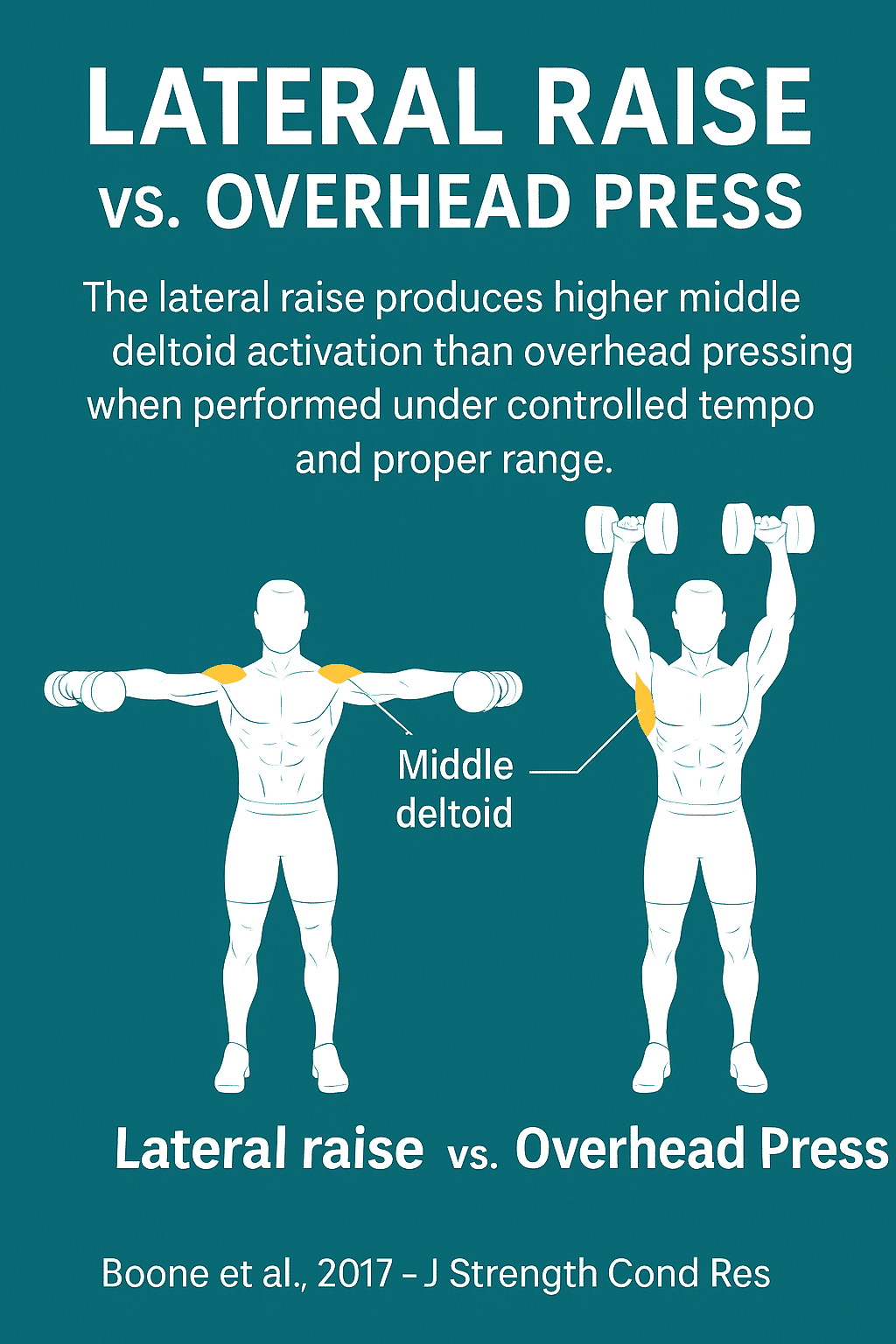
2️⃣ Middle Head
- ✔ Lifting the arm outward (shoulder abduction)
- ✔ Assists in stabilizing the shoulder during arm elevation
3️⃣ Posterior Head
- ✔ Moving the arm backward (shoulder extension)
- ✔ External rotation of the arm
- ✔ Assists in horizontal abduction of the arm (moving the arm backward across the body)
📌 Function Summary: The deltoid muscle plays a key role in all shoulder movements and is one of the primary muscles responsible for moving the arm in various directions.
3️⃣ Muscle Physiology
✅ 💪🏻 Muscle Fiber Types
✔ The deltoid muscle consists of a combination of fiber types. ✔ A combination of slow-twitch fibers (Type I) and fast-twitch fibers (Type II). ✔ It is composed of both fiber types.
✔ The anterior and posterior heads contain more fast-twitch fibers, which are suited for powerful and rapid movements.
✔ The middle head has a higher proportion of slow-twitch fibers, which help maintain muscular endurance during sustained activity.
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Plays a key role in all overhead movements, such as shoulder press and bench press.
✔ Crucial for sports like weightlifting, swimming, gymnastics, and wrestling.
✔ Considered one of the primary muscles involved in carrying heavy objects, throwing, and raising the arm.
✅ 🧗🏻♂️ Strength and Endurance
✔ The deltoid plays a vital role in maintaining shoulder joint stability, and its weakness can reduce control over shoulder movements.
✔ This muscle is well-suited for both strength and endurance activities and is heavily engaged in many professional sports.
4️⃣ Innervation and Blood Supply
✅ 🧠 Innervation
✔ Axillary Nerve (also known as the underarm nerve) – responsible for controlling deltoid muscle movements and providing sensation to the shoulder area.
✅ 🩸 Blood Supply
✔ Posterior Circumflex Humeral Artery
✔ Thoracoacromial Artery
5️⃣ Importance of the Muscle in the Body and Sports
✅ 🤼♂️ Role in Sports and Physical Activities
✔ Directly involved in all shoulder and arm movements.
✔ A key muscle for athletes in bodybuilding, weightlifting, swimming, boxing, and combat sports.
✔ Strengthening this muscle improves shoulder shape, prevents injuries, and boosts upper body strength.
✅ 🏌🏻♂️ Interaction with Other Muscles and Joints
✔ Works closely with the rotator cuff muscles, back muscles, and pectoralis major.
✔ Weakness in this muscle can lead to excessive strain on the shoulder and scapular joints, increasing the risk of injury.
✅ 💉 Vulnerability and Potential Issues
✔ One of the most injury-prone muscles in bodybuilding and strength sports due to its crucial role in heavy movements.
✔ Common injuries include tears, strains, tendon inflammation, and cramps—often caused by improper use of heavy weights.
6️⃣ Strengthening Exercises
✅ 🏋🏻♂️ Strength Training Exercises for the Deltoid Muscle
1️⃣ Dumbbell or Barbell Shoulder Press – Strengthens all parts of the deltoid
2️⃣ Lateral Raise – Targets the middle head of the deltoid
3️⃣ Bent-Over Reverse Fly – Strengthens the posterior head of the deltoid
4️⃣ Front Raise with Dumbbell or Barbell – Focuses on the anterior head
5️⃣ Arnold Press – Activates all heads of the deltoid simultaneously
✅ 🧘🏻♀️ Stretching and Recovery
✔ Forward and backward shoulder stretches
✔ Wall walks with the hand to improve flexibility
7️⃣ Scientific and Interesting Facts
✅ Fun Fact
✔ The deltoid muscle is actually one of the key muscles that shapes and enhances the appearance of the upper body.
✅ Practical Tip
✔ Overtraining the deltoid without strengthening the back and rotator cuff muscles can disrupt shoulder muscle balance.
📌 Muscle Summary
🔴 Name and Location: A superficial muscle that covers the shoulder joint and originates from the clavicle, scapula, and humerus.
🟠 Anatomy: Composed of three parts—anterior, middle, and posterior—each responsible for different shoulder movements.
🟡 Function:
✔ Anterior: Arm flexion and internal rotation
✔ Middle: Arm abduction and elevation
✔ Posterior: Arm extension and external rotation
🟢 Physiology: A combination of slow- and fast-twitch fibers, allowing for both endurance and explosive power movements.
🔵 Innervation: Axillary nerve, which controls the muscle’s movement and sensation in the shoulder area.
🟣 Importance: Active in all upper-body movements, bodybuilding, weightlifting, swimming, boxing, and combat sports.
🟤 Exercises: Shoulder press, lateral raise, front raise, bent-over raise, Arnold press.
⚫ Fun Fact: A key muscle for shoulder strength and aesthetics, yet one of the most injury-prone muscles during heavy training.

Comments